Biology DNA and RNA exam
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
DNA are macromolecules called ______. They are made up of smaller, monomer units called _____.
Nucleic acids, nucleotides
Structure of a nucleotide
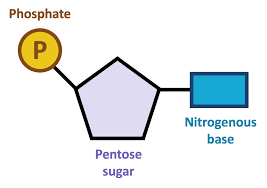
The structure and function of DNA
2 strands, double helix shape, deoxyribose sugar, adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine bases, made for storing genetic info copying info and gene expression.
The structure of RNA
1 strand, single strand shape, ribose sugar, adenine, uracil, cytosine or guanine bases, made for converting DNA’s genetic information into proteins
Where is genetic information in DNA carried?
Order of the bases
What are there always equal amounts of? (Chargaff’s rule)
A & T, C & G
If a sample of DNA has 20% T, what percentage of A, C, and G does it have?
20% A 30% C 30% G
What is the arrangement of two strands of DNA in opposite directions?
Antiparallel
Explain the experiment by Hershey and Chade that proved DNA was hereditary material
Tested what part of a bacteriophage virus carried genetic info of bacteria. Grew viruses using Phosphorus-32 or Sulfur-35, let viruses infect bacteria, nearly all p-32 was in the bacteria
What is replication?
Process of copying DNA
Each new DNA helix is made up of one original or _____ strand, and one new or _____ strand. DNA replication is said to be __________ because each new helix has a half of the original DNA.
Leading, lagging, semi-conservative
What is meant by complementary base pairing?
If you know the order of one, you know the order of the other
What is the advantage of complementary base pairing in replication?
Makes duplication simple, copying is more accurate
First step of replication
Original DNA molecule unzips between the nitrogen bases and the strands separate.
Second step of replication
The enzyme DNA polymerase bonds the two new nucleotides together.
Third step of replication
The new DNA is proofread for any errors
When RNA is formed alongside DNA, the _____ in RNA bonds with adenine in the DNA strand.
Uracil
The ____ on the RNA strand will bond with the thymine in the DNA
adenine
First step of transcription
The enzyme RNA polymerase attaches to the promotor, which indicates where replication should start. DNA nucleotides separate.
Second step of transcription
RNA polymerase joins the RNA nucleotides together to form RNA
Third step of transcription
RNA polymerase comes to a termination sequence. The new RNA leaves the nucleus, the DNA bonds together again.
DNA → RNA → Protein
Any changes in the _____ can cause changes in the final ______
DNA, protein
The “Central dogma” is called such because all life on Earth shares the same five nucleotide bases:
Adenine, cytosine, thymine, uracil, and guanine
mRNA structure and function
Single stranded complementary copy of DNA’s instructions to make a protein. Each 3 bases are a codon a code that specifies a specific amino acid.
rRNA structure and function
2 RNA subunits and some proteins. The RNA strands fold to form a ball-like structure. Attaches to a strand of mRNA and directs the production of the new proteins.
tRNA structure and function
folded into a t-shape, carrying amino acid on the end, has a 3-case anticodon. Carries amino acids into correct position by temporarily bonding it’s anticodon to the mRNA codon.
mRNA is a sequence of 3 base words, or ____. There is a total of ___ possible codons, and only ___ types of amino acids.There are also start and ___ codons.
Codons, 64, 20, stop
First step of translation
The ribosome attaches to a strand of mRNA at the start codon.
Second step of translation
The tRNA’s 3 base anticodons temporarily bonds with the 3 base codons on the mRNA, bringing the correct amino acid with it to form the proper sequence of the protein.
Third step of translation
Another tRNA moves in and brings in another amino acid. The ribosome makes a bond between the amino acids, beginning the formation of a protein.
Fourth step of translation
The first amino acid is always Methianine, which is coded for by the start codon AUG.
Fifth step of translation
When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, the translation stops. The ribosome detaches from the mRNA. The mRNA may be read by ribosomes over and over until the cell has enough protein.
What is a mutation?
A permanent change in the DNA nucleotide sequence.
What are some types of mutagens?
UV radiation, X-rays, tobacco
If a change in the nucleotide changes the codons, then one or more ______ in the protein chain will be different
Amino acids
These mutations are a change in 1 nucleotide base.
Point
Frameshift mutations are caused by _____ or ______. Causes a shift in which 3 bases are read as a codon.
Insertion, deletion
These mutations are changes in bases that do not alter the amino acid sequence. These occur because amino acids may be coded by several codons.
Silent
DNA structure