Pelvis and Upper Extremity anatomy
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
function of pelvis
provide structural support for the body and enclose male/female reproductive and digestive and urinary organs
pelvis is a
support mechanism for the body
bony pelvis formed by
sacrum, coccyx, 2 hip bones/innominate bones,
innominate bones
2 bones that form sides of pelvis
innominate bones consist of
ilium, ischium, pubis
fusion points of innominate bones
posteriorly to the lateral portion of sacrum (SI joints)
anterior at medial portion of pubis (pubic symphysis)
SI joints
fusion point of innominate bones posteriorly to lateral portion of sacrum
Pubic symphysis
fusion point of innominate bones (pubic portion) anterior at the medial portion of pubis
ilium and what it consists of
largest, most superior portion that consists of body and large wing called ala
iliac crest
superior ridge of ala
iliac spines
superior and inferior iliac spines on anterior and superior surfaces formed by ala
what creates upper portion of acetabulum
body of ilium
acetabulum
deep fossa that articulates with head of femur
what forms lower anterior portion of acetabulum
pubis
pubis consists of
a body and superior and inferior pubic rami
superior pubic ramus does what
projects inferiorly and medially from acetabulum to midline of body
inferior pubic ramus does what
projects inferiorly and laterally from the body to join ischium at the ischiopubic ramus
ischiopubic ramus
ischium and inferior pubic ramus combined
ischium composed of
body and 2 rami
ischium location
most inferior portion of hip bones
body of ramus forms
lower posterior portion of acetabulum
obturator foramen
union of pubic rami and ischium enclosed by obturator muscles
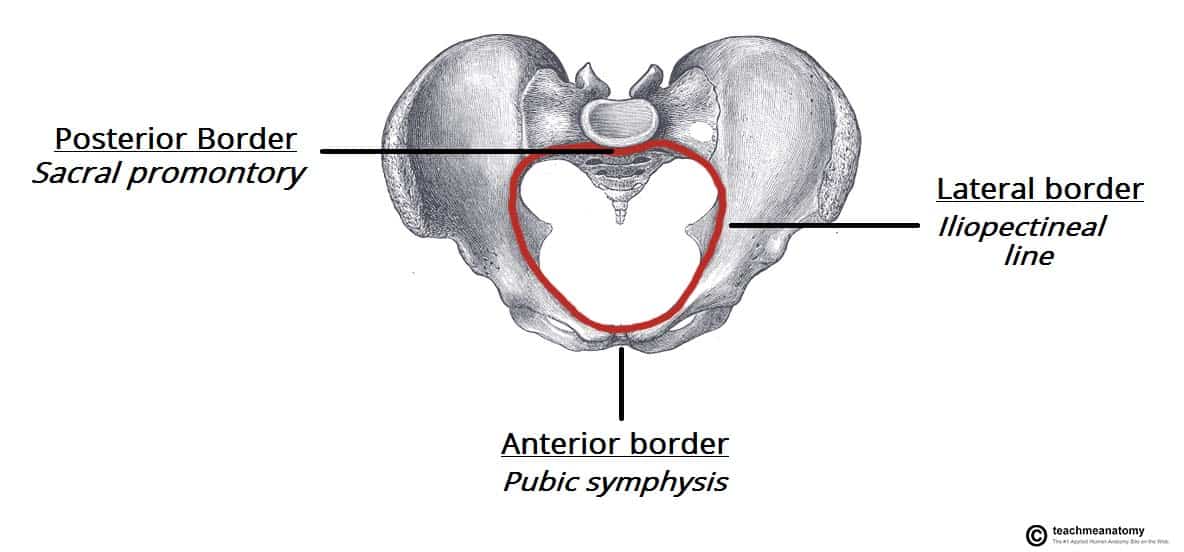
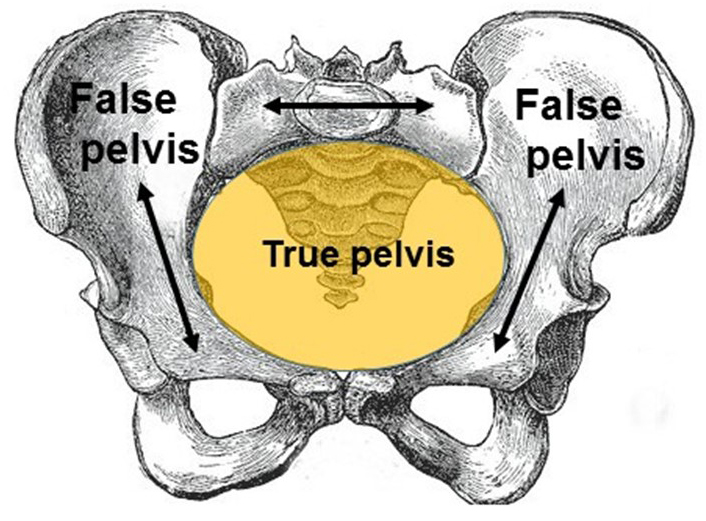
pelvis divided into
false or greater pelvis and true or lesser pelvis by an oblique plane that extends from the upper anterior margin of the sacrum to the upper margin of the pubic symphysis
pelvic brim
separates true and false pelvis
false pelvis
region above pelvic brim
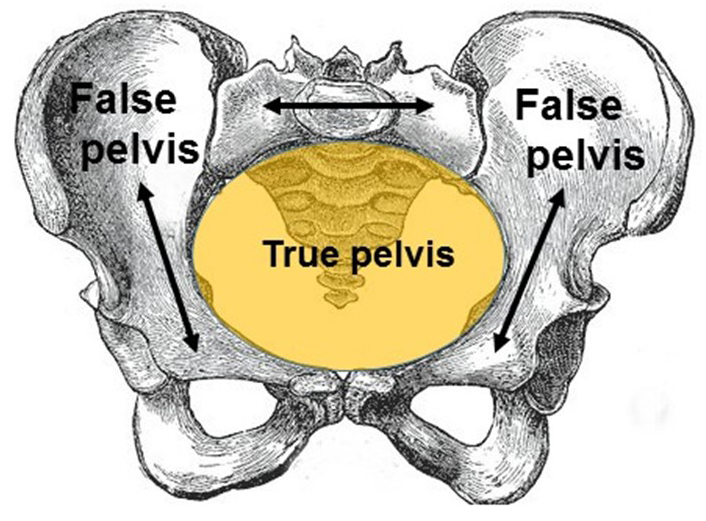
true pelvis
region below pelvic brim
muscle groups of pelvic girdle
gluteal and lateral thigh muscles
gluteal muscle region location
located posteriorly to pelvic girdle at proximal end of femur
gluteal muscle functions
muscles in this region move the lower limb at the hip joint
muscle groups of gluteal region
superficial abductors/extenders
deep lateral rotators
superficial abductors and extenders functions
large muscles that abduct and extend femur
superficial abductors and extenders include
gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, and tensor fascia lata
deep lateral rotators function
group of smaller muscles that mainly act to laterally rotate femur
deep lateral rotators include
quadratus femoris, piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator internus
gluteus maximus
largest of gluteal muscles, most superficial and produces shape of butt
gluteus maximus functions
main extensor of thigh and assists with lateral rotation
gluteus medius
fan-shaped and lies between gluteus maximus and minimus that is similar in shape and function to gluteus minimus
glutues medius functions
abducts and medially rotates lower limb
gluteus minimus
deepest and smallest of superficial gluteal muscles similar in shape and function to gluteus medius
gluteus minimus functions
abducts and medially rotates lower limb
tensor fascia lata location
small superficial muscle which lies towards the anterior edge of the iliac crest
tensor fascia lata functions
assists gluteus medius and minimus in abduction and medial rotation of the lower limb
plays supportive role in gait cycle
piriformis location
key landmark in gluteal region and most superior of deep muscles
what is most superior of deep lateral rotator muscles
piriformis
piriformis function
lateral rotation and abduction
obturator internus forms
lateral walls of pelvic cavity
obturator internus functions
lateral rotation and abduction
gemelli superior and inferior
two narrow and triangular muscles separated by obturator internus tendon
gemelli superior and inferior function
abduction and lateral rotation
quadratus femoris
flat, square-shaped muscle most inferior of deep gluteal muscles
quadratus femoris location
below gemelli and obturator internus
quadratus femoris function
lateral rotation
bladder location
pyramid shaped muscular organ that rests on pelvic floor posterior to pubic symphysis
bladder functions
temporary reservoir for storage of bladder
adult bladder urge to pee after
200-250 mL
bladder can hold
750 mL
superior body of bladder
covered by the peritoneum allowing loops of ileum and sigmoid colon to rest on it
posterior aspect of bladder
fundus or base of bladder
where is bladder base related to in female vs male
anterior wall of vagina
rectum
apex of bladder faces what
pubic symphysis
neck of bladder
inferior portion of bladder that is continuous with urethra
bladder neck contains
internal and urethral sphincters to provide for voluntary control over release of urine from bladder
trigone
triangular area formed by 3 openings in floor of bladder
2 - ureters
1 - urethra
rectum extends where
terminal part of large intestine extending from S3-S4 to the tip of the coccyx
rectum size
15cm
rectum shape and becomes what
follows anteroposterior curve of sacrum and coccyx and ends by turning inferiorly and anteriorly to become anal canal which ends at anus
uterus located where
pear shaped muscular organ located in pelvic cavity between bladder and rectum
uterus subdivided into
body and cervix
body of uterus
largest division comprising the upper 2/3 of the uterus
consists of a fundus superiorly where the uterine tubes enter the uterus
where do uterine tubes enter uterus
fundus
cervix
directed inferiorly and posteriorly into upper end of vagina or vaginal vault
wall of uterus
endometrium
myometrium
perimetrium
endometrium
inner glandular tissue lining inner wall and responds to cyclic ovarian hormone changes
myometrium
middle, muscular layer, and thickest component of uterine wall
perimetrium
outer layer consisting of serous membrane that covers fundus and posterior surface of uterus
ovaries
paired, small, almond shaped on either side of uterus
where do ovaries lie and held by
depression on lateral walls of pelvis held in place by ovarian and suspensory ligaments
ovarian ligaments
attach to inferior aspect of ovaries to the lateral surface of the uterus and uterine tubes
suspensory ligaments
attaches the superior aspect of ovaries to the lateral sides of the pelvic wall
suspensory ligaments contain
ovarian vessels
uterine tubes size
8-20cm long
uterine tubes extend
laterally from the body of the uterus to peritoneum near ovaries
uterine tubes form and are supported by
infundibulum and supported by broad ligament
infundibulum has
has numerous 1-2cm fingerlike projections called fimbriae which spread loosely over the surface of the ovaries
principle structures of of male reproductive system
testis, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, seminal vesicle, prostate gland, bulbourethral gland
what male structure is not located in pelvic cavity
testes
prostate gland
extraperitoneal fibromusclular structure is largest accessory gland of male reproductive system
largest accessory gland of male reproductive system
prostate gland
function of prostate
secretes thin, slightly alkaline fluid that forms a portion of seminal fluid
prostate where
located inferior to bladder and surrounds the prostatic urethra which courses through the anterior portion of the gland
base of prostate located
adjacent to neck of bladder
apex of prostate
in contact with perirenal membrane
appendicular skeleton and its #
126 bones involved in locomotion and manipulation of objects in the environment
appendicular skeleton groups
bones located within limbs
girdle bones that attach limbs to axial skeleton
axial skeleton forms
bones that form skull, laryngeal skeleton, vertebral column, thoracic cage
axial skeleton functions
provide support and protection for brain, spinal cord, organs in ventral body cavity
provides surface for attachment of muscles, directs respiratory movements and stabilizes portions of appendicular skeleton
skull, #
bones support structures of face and protect brain
22 bones in two categories (facial and cranial)
cranial bones
8 bones that form cranial cavity and encloses the brain and attachment site for muscles of the head and neck
1 frontal, 2 parietal, 2 temporal, 1 occipital, 1 sphenoid, 1 ethmoid
facial bones
14 bones that provide cavities for sense organs (eyes, mouth, nose)
protect entrances to digestive and respiratory tracts
attachment points for facial muscles
1 mandible, 2 maxilla, 2 zygomatic, 2 palatine, 1 vomer, 2 lacrimal, 2 inferior nasal conchae
laryngeal skeleton starts at
EAM