Glycogen Synthesis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Glycogen degradation yields ________, while glycogen synthesis requires ________
glucose 1-phosphate, UDP glucose
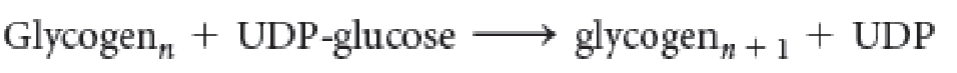
Is this net reaction showing glycogen synthesis or degradation?
Synthesis
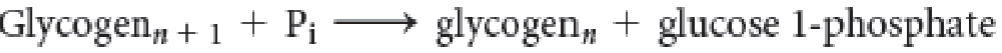
Is this reaction showing glycogen synthesis or degradation?
Degradation
What is the glucose donor in glycogen synthesis?
UDP-glucose (Uridine-diphosphate glucose)
How is UDP glucose made?
Glucose 1-phosphate and UTP, catalyzed by UDP glucose pyrophosphorylase
How is glucose attached to glycogen from UDP glucose?
Glycogen synthase catalyzes the attachment of glucose to glycogen from UDP glucose
Which enzyme synthesizes the oligosaccharide primer needed for glycogen synthesis? How large is the primer usually?
Glycogenin, 10-20 glucose units
How are a-1,6 linkages formed in glycogen synthesis?
Branching enzyme breaks the a-1,4 linkage of a block of glucose residues and synthesizes the linkage
How does branching affect the properties of glycogen?
Branching increases solubility and allows for quicker degradation and synthesis
Glycogen synthesis is _______ (stimulated/inhibited) by epinephrine and glucagon.
Inhibited
Protein kinase A _________ (stimulates/inhibits) glycogen breakdown and __________ glycogen synthesis (stimulates/inhibits)
stimulates, inhibits
Glycogen synthase kinase _______ (stimulates/inhibits) glycogen synthase
inhibits
Phosphorylation _______ (stimulates/inhibits) glycogen synthesis
inhibits
What is the role of PP1 (Protein phosphate 1) in glycogen metabolism?
It switches metabolism from degradation to synthesis by dephosphorylating glycogen synthase b, thereby activating it and also inhibits glycogen degradation
In glycogen synthesis, the more active a form is ________ (phosphorylated/dephosphorylated)
dephosphorylated
How does insulin affect glycogen synthesis?
Stimulates it by inactivating glycogen synthase kinase
How do glucagon, epinephrine, and insulin regulate glycogen metabolism?
Glucagon and epinephrine stimulate glycogen degradation and inhibit glycogen synthesis, insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis and inhibits glycogen degradation
Which hormone is associated with a starved/fasting state?(insulin, epinephrine, or glucagon?)
Glucagon
Which hormone is associated with a fed state?(insulin, epinephrine, or glucagon?)
Insulin
Type 1 vs type 2 diabetes
Type 1 - the body cannot properly produce insulin, present before the age of 20 due to autoimmune destruction of insulin producing cells
Type 2- the body becomes resistant to insulin, often occurring after the age of 40
How does type 1 diabetes cause damage?
The body is constantly in a fasting state due to excess glucagon, which shifts fuel source from carbs to fats and produces ketone bodies which are harmful to the body, as well as a high amount of blood glucose due to the liver releasing too much glucose in response to fasting
von Gierke disease
Causes massive enlargement of liver and hypoglycemia due to lack of glucose 6-phosphatase in the liver or a genetic defect of the glucose 6-phosphate transporter
Cori disease
Lack of debranching enzyme causes abnormal liver structure, abnormal muscle glycogen levels, and higher glycogen amounts, as well as slight hypoglycemia
McArdle disease
Defective muscle glycogen phosphorylase, leading to painful cramps when exercising