chemistry/ organic compounds
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
type of bond
low/high melting pt in organic compounds?
covalent bond
low melting, boiling pt
can undergo combustion
what is a hydrocarbon
an organic compound consisting only of hydrogen and carbon atoms without any functional groups.
what reduces and what increases the oxidation number?
H reduces (-1)
every heteroatom (N,O,S…) increases
C leaves it unaltered
what kind of bond do the molecules in alkanes form (or any single bond)?
o (sigma) bond
what kind of arrangment do sp3 orbitals have?
tetrahedral
what kind of p atomic orbitals form pi molecular orbitals to form double (sp2) or triple (sp) bonds?
non-hybridized p atomic orbitals
why do organic compounds enter reactions?
single bonds are saturated double and triple bonds are unsaturated so the goal is to have as many single bonds to obtain the most saturated compounds.
what defines the properties of the organic molecule and adds reacticity?
functional groups
HYRDOCARBONS DONT MIX WITH WATER
just dont forget!! they are also composed of apolar bonds and they can be linear, branched or cyclic
why is the 3D structure of molecules important?
because it modulates their chemical properties and determines their biological function
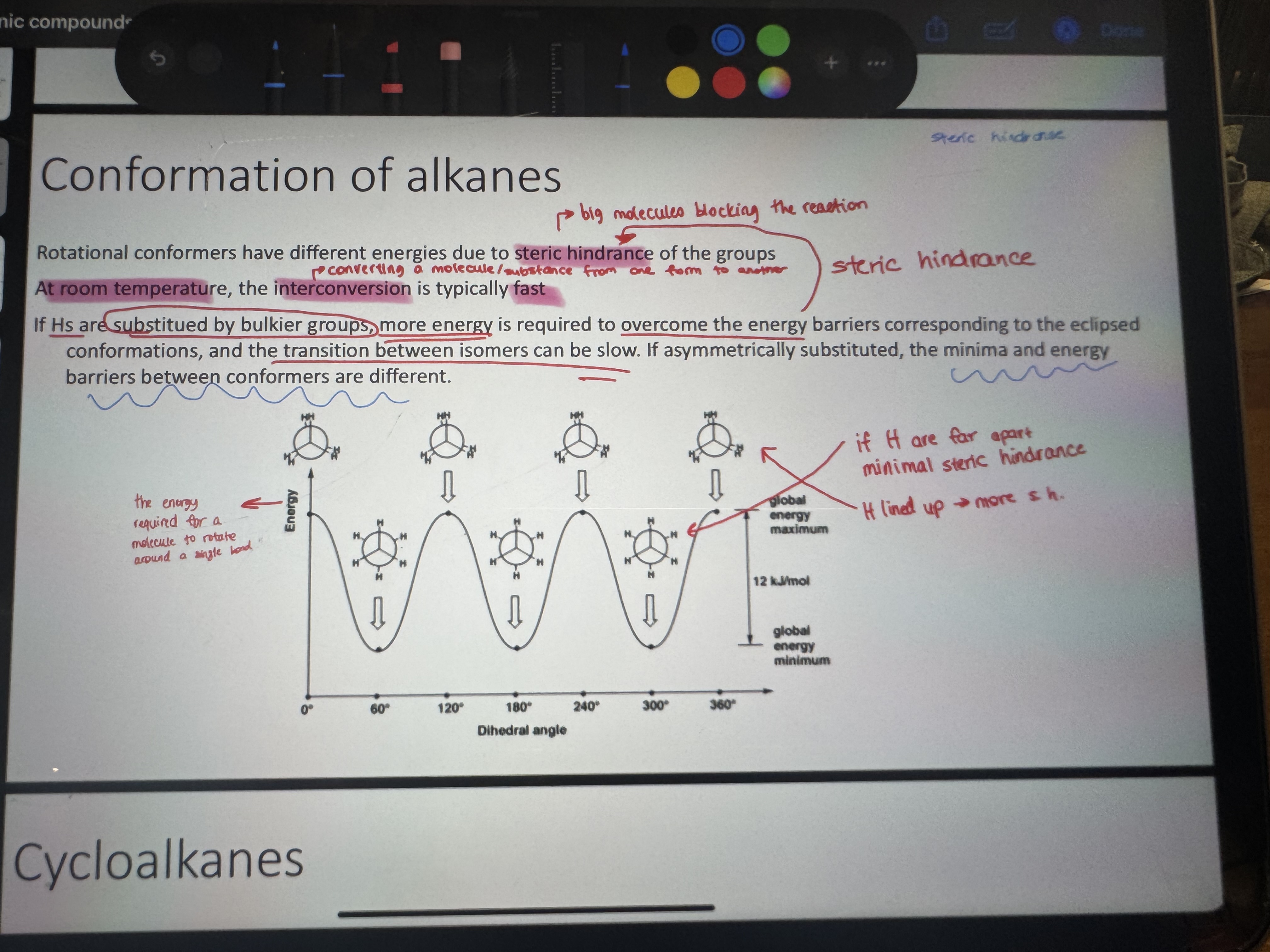
what is conformation
the shapes that molecules can adopt due to rotation about bonds (different conformation different properties)
what is a conformational isomer
same molecule different arrangment of the ch3 groups
what is steric hindrance
bic molecules blocking the reaction
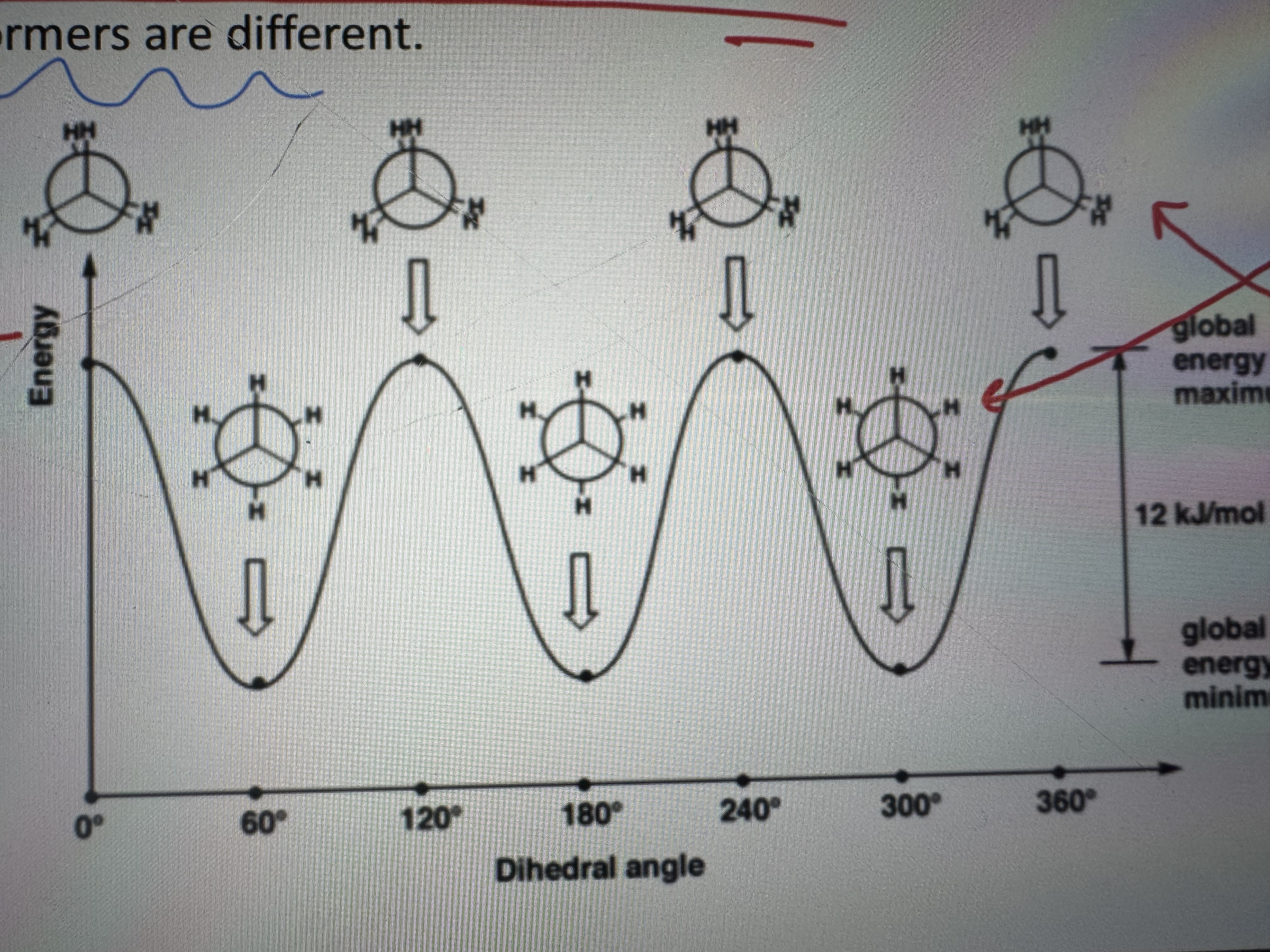
explain this
why does cyclohexane not have a planar structure?
-the sp3 interactions prevent it
-to obtain a planar structure the angles need to be 120 degrees which is much greater than the angle between hybrid orbitals
the required distortion would lead to a very high energy and thys unstable molecule
what is the chair conformation
four atoms on a plane one above and one below
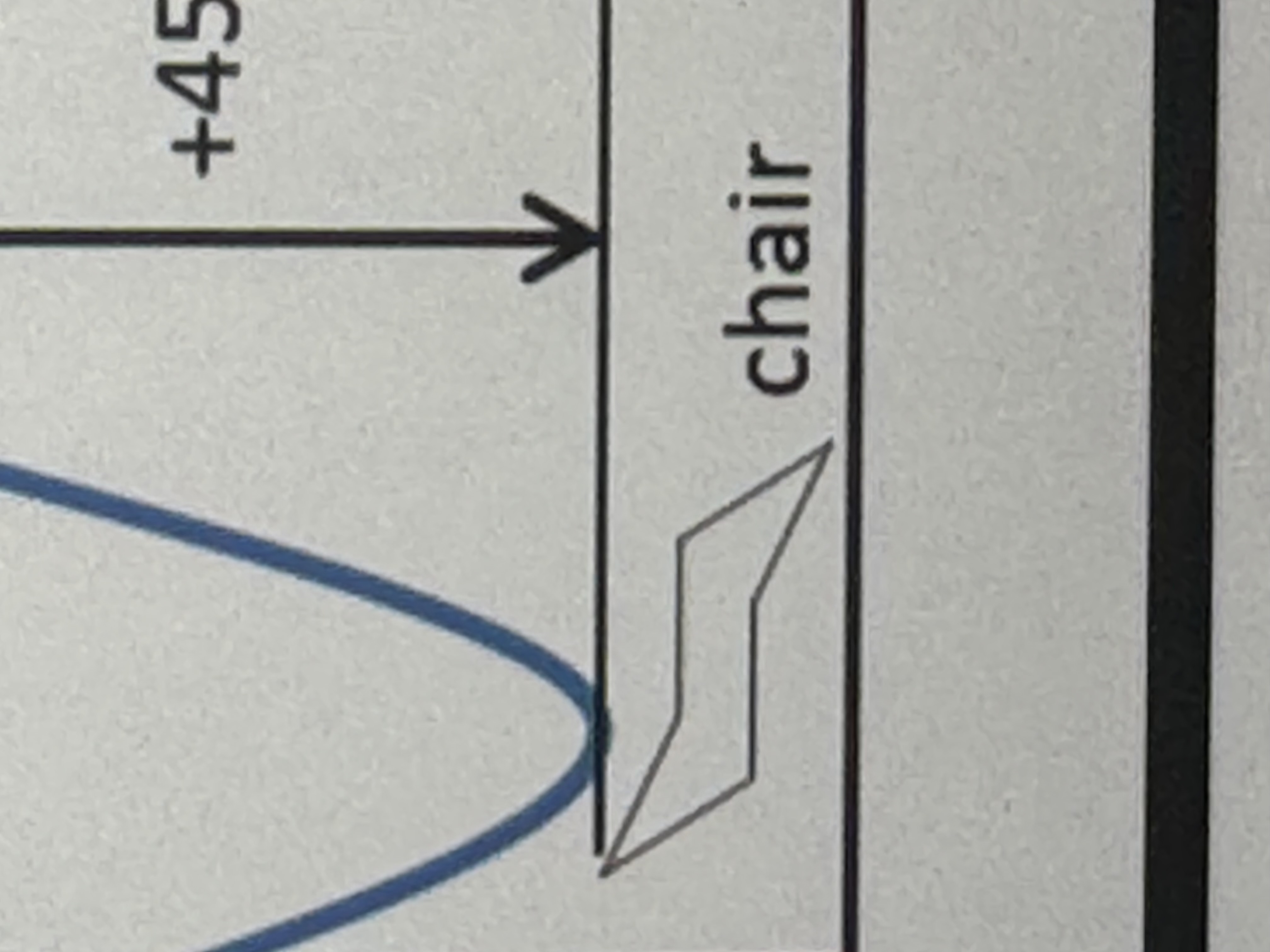
what are the orientations of a cyclic structure
axial (higher energy) or equatorial (lower energy) (both are chair cyclohexane forms)
which cylic structure is preferred
equatorial bc it has lower energy
what is the way to convert one cylic structure to another called?
chair flip
what can we replace a hydrogen in an alkane with?
a halogen or an alkyl chain
to create a structural isomer how many carbon atoms is the alkane supposed to have (minimum)
4+
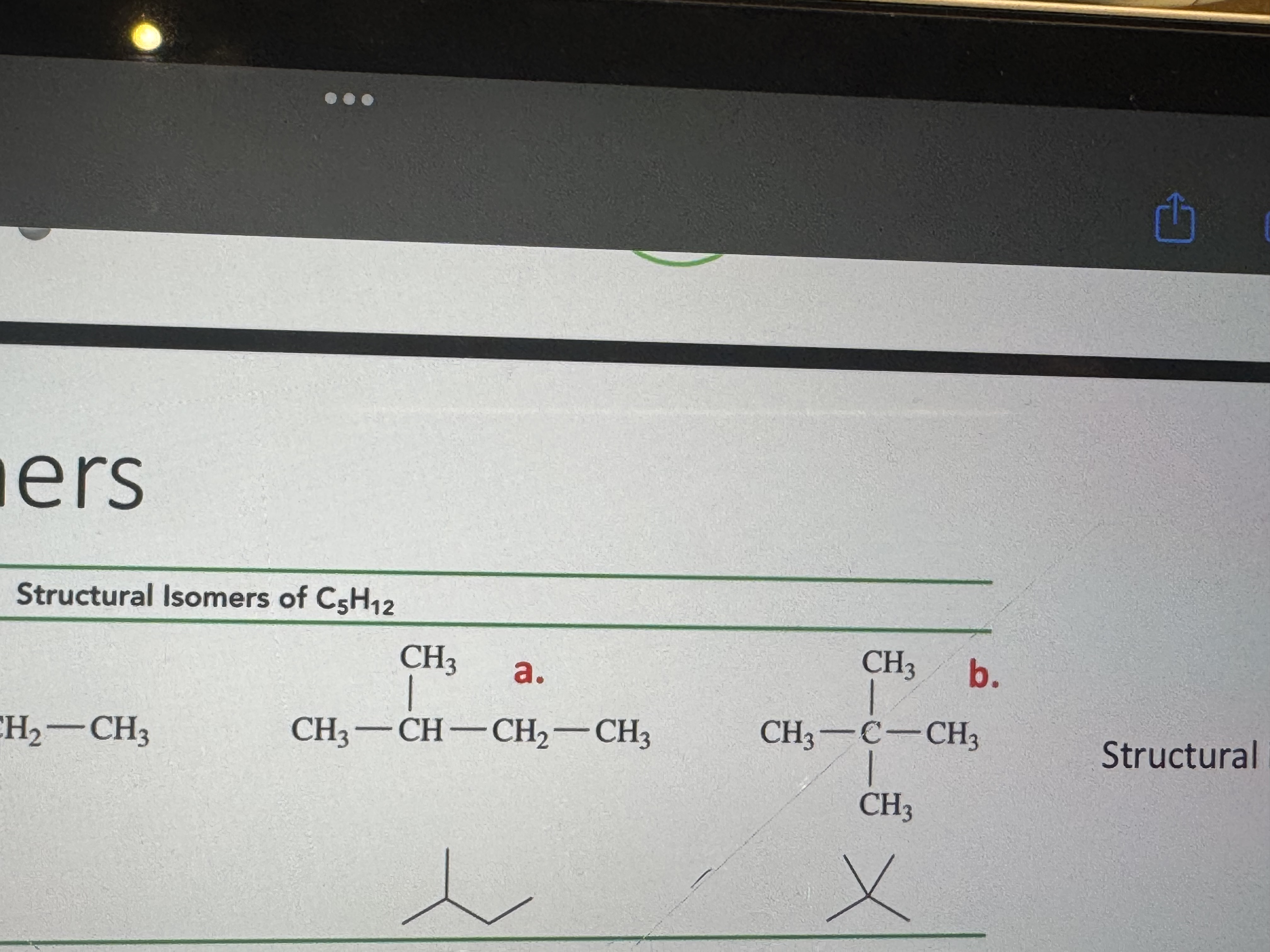
name these isomers
isopentane and neopentane
do an organic compound and it’s isomer have different chemical properties?
yes
which alkanes are used as heatinf fuels
methanes and butanes
which alkanes are volatile liquids, fuels