Radiology quiz 1 (slide content)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
For a right/left lateral view of the thorax, where do you measure with the calipers
caudal border of the scapula
For a right/left lateral view of the thorax where do you put the beam center
caudal border of the scapula, between the 5th-6th ribs, or point of strongest heartbeat
For a right/left lateral view of the thorax what is the cranial boundary
Thoracic inlet
For a right/left lateral view of the thorax what is the caudal boundary
L1 (1-2cm past the last rib to include all of the ribcage)
For a right/left lateral view of the thorax when do you take exposure at
peak of inspiration
What do you do with the limbs when position for lateral thorax view
front limbs- pull front limbs cranially, keep them symmetric
hind limbs- pull hind limbs caudally, keep symmetric
What do you do with the head and what do you do to the sternum to maintain a parallel position
head- gently extend sternum- foam wedge under sternum to maintain parallel position
What are some signs you have perfect positioning/symmetry lateral thorax
-rib heads superimposed
-intervertebral foramina same size
-transverse processes superimposed
-front limbs are pulled forward and not interfering with the visualization of anatomy
For VD and DV thorax view where do you measure with the calipers
caudal border of scapula
For VD and DV thorax view where do you position the beam center
midline at caudal border of scapula, between 5th—6th ribs
For VD and DV thorax view where is the cranial boundary
Thoracic inlet
For VD and DV thorax view where is the caudal boundary
L1, 1-2 cm past the last rib to include all of ribcage
For VD and DV thorax view when do you take exposure at
peak inspiration
what are signs of perfect positioning/symmetry for VD or DV thorax
-sternum/spine superimposed
-spinous processes centered over vertebral bodies
-two sides of ribcage equal in distance
When should you avoid VD
if the animal is in respiratory distress
What is DV view of the thorax better than VD
DV view- better visualization of heart
What is VD view of the thorax better than DV
better visualization of lung tissue, ventral pulmonary fields, caudal vena cava, mediastinum
when positioning for DV thorax what should you do with hind and front limbs
hind limbs- tucked under each hip and visible on each side
Front limbs- extended slightly, one on each side of the patient’s neck, symmetric
when positioning for DV thorax what should you do with the head
rest on table top (if possible)
What does VHS stand for and what do we use it for
Veterbral heart score
Help to diagnose cardiomegaly
To determine VHS what view do you need
lateral thoracic
How to get VHS
-measure the height and width of the heart(height- carinia to apex)(width- widest area, perpendicular to)
-Transfer measurements to vertebra, starting at cranial edge of T4
-count the number of vertebrae that fall within the distance measured for height and width
-add the 2 measurements together=VHS
Where should I avoid putting my label and why
over the lead blocker- it won’t be visible on the radiograph
What needs to be included on the label
-Name/address of veterinary facility
-patient ID/name
-date
-View/area of anatomy being imaged (ex- R. lateral ABD)
-Initials of radiographer
-species ,sex, breed, age
When doing a lateral view how to determine if we use R or L label
labeled by side that is down on the table
What does the dosimeter monitor (body part)
radiation to thyroid glands and lens of eyes- two areas susceptible to radiation damage
what way should we store the lead gloves and why
upright to allow drying
how should we hang aprons and why
avoid folding- to avoid cracking lead
what is the purpose of a technique chart
provide a consistent method of choosing proper exposure factors (kVp, mAs) to create consistent diagnostic radiographs
every individual x-ray machine in diffrent locations need there own______
unique technique chart
if it is the same x-ray machine but in 2 direct clinics do we still need a new technique chart
yes
what are some factors that affect technique charts
-input voltage
-calibration
-speed of screens (part of x-ray cassette)
-age of screens
-film speed(slow medium fast)
-beam filtration
-temperature/time of processing
-grid type
What are the types of technique charts
-extremity and skull(canine/feline), no grid(table top)
-Abdomen(canine/feline), with grid(film tray)
-Thorax(canine/feline), with grid
-pelvis and spine(canine/feline) with grid
-Avian and exotics, no grid
-Equine limb
When do we use a grid(film tray)
when the body parts measure greater than 10cm
How is a technique chart made
three test radiographs of each region (3 of each area) to visualization all tissue density(use different mAs for each test radiograph)
use the best radiograph
-mAs/kVp utilized to create the best test radiograph used as a basis to formulate the remainder of our new technique chart
How to estimate kVp
Sante’s Rule (2x measurement in cm)+40
mAs will _________ for all measurements of 10 cm or less
stay the same
mAs will ________ for all measurements greater than 10 cm
stay the same
mAs for measurements greater than 10 cm is ___________
twice that as for measurements 10cm of less
Where do you have to x-ray 3 times to create new technique chart
-thorax
-extremity
-spine
-exotics
-equine limb
what are 3 goals of quality assurance
-ensure every radiograph is as diagnostic as possible
-minimize retakes
-limit radiation exposure of patients and personnel
who performs most QC (quality assurance)
technicians/technologists
where all do we preform QA tests
-x-ray machine
-dark room
-image receptors
what do we do with the QA results and why
we must track them because is allows the identification of trends in test results and problems can be corrected early on
How do we do QA of SID
measure to make sure it is 40inches from the x-ray tube to table top and film tray positions
How to do the light field size QA
collimate 8×10 and measure to see if it is 8×10
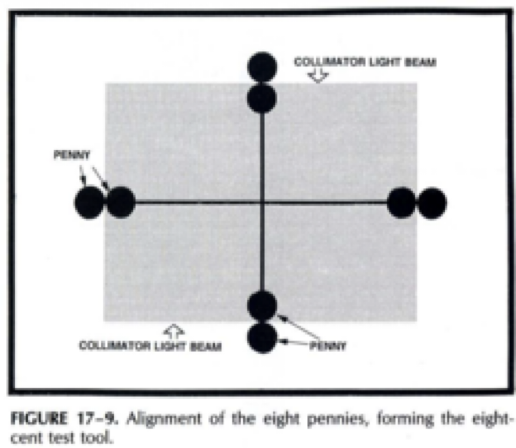
what is the light feild/X-ray field alignment QA
the 9 penny test
we do it to see if the X-ray is aligned with the light field
What do we see if there a problem with protective gear check (QA)
a crack in any lead PPE
What types of QA do we do
Protective gear check
9 penny test
light field size
SID marks
All radiographs are recorded where
-animal use log
-radiography animal use list(on wall)
-Radiograph log
How does the central ray location differ between cats and dogs for views of the abdomen
dog- caudal aspect of 13th rib
cat-2-3 fingers below 13th rib
How to appropriately position an animal for a view of abdomen VD
-front limbs pulled cranially, symmetrically
-hind limbs pulled caudally, symmetrically
-head/neck gently extended
-ensure patient is level- not tipping to one side
How to appropriately position an animal for a view of abdomen right lateral view
should ensure the limbs aren’t bent and blocking the view while having the same boundaries
for right later abdomen where do i measure
caudal aspect of 13th rib (thickest part)
for right later abdomen what is the cranial boundary
1 inch cranial to xiphoid
for right later abdomen what is the caudal boundary
greater trochanter of femur
for right later abdomen where is beam center on cats and dogs
cats- 2-3 finger widths below 13th rib
dogs- caudal aspect of 13th rib at level of umbilicus
for a VD view of the abdomen where is the site to measure
caudal aspect of 13th rib at level of umbilicus
for a VD view of the abdomen, what is the cranial boundary
1 inch cranial to xiphoid
for a VD view of the abdomen what is the caudal boundary
greater trochanter to femur including coxofemoral joint
for a VD view of the abdomen where is central ray on cats and dogs
cat- midline, 2-3, fingers below 13th rib
dog-midline at the caudal aspect of 13th rib at the level of the umbilicus