AP World 1.2 Developments in Dar al-Islam
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Muhammad
The founder of Islam who died in 632.

House of Wisdom
A center of learning in Baghdad at which scholars traveled from far away to study.
Mamluks
Enslaved Turks that eventually seized control of the Egyptian government.
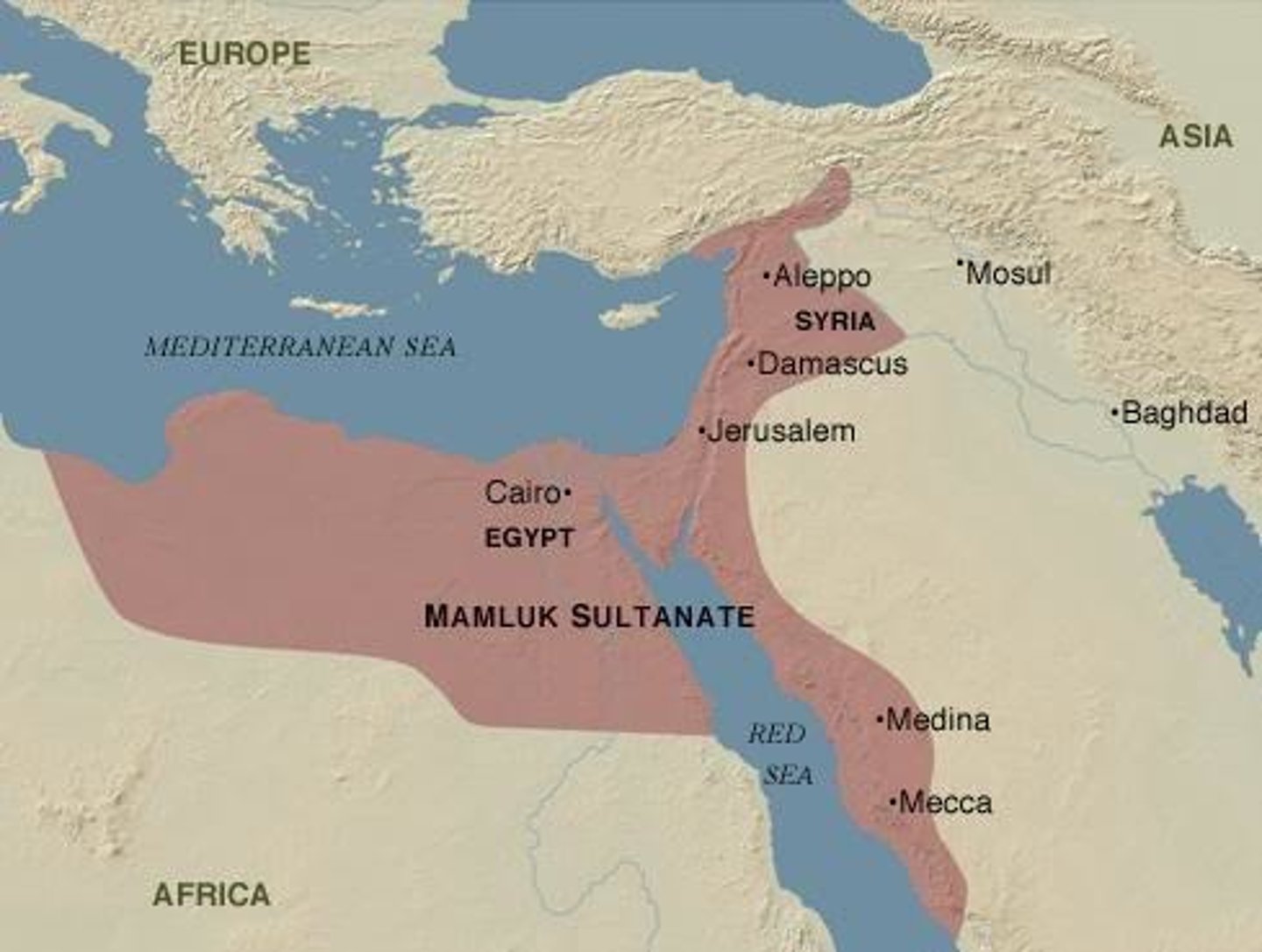
Mamluk Sultanate
A political unit in Egypt established by Mamluks that lasted from 1250-1517.
Seljuk Turks
Central Asian Muslims who conquered parts of the Middle East.
Crusaders
European Christian soldiers who fought the Seljuk Turks to reopen access to holy sites in and around Jerusalem.

Mongols
Central Asian people who conquered the Abbasid Empire in 1258 and ended Seljuk rule.

Baghdad
The capital of the Abbasid Empire.
Shariah
The Islamic code of law.
Caliph
The political and religious leader in a Muslim government.
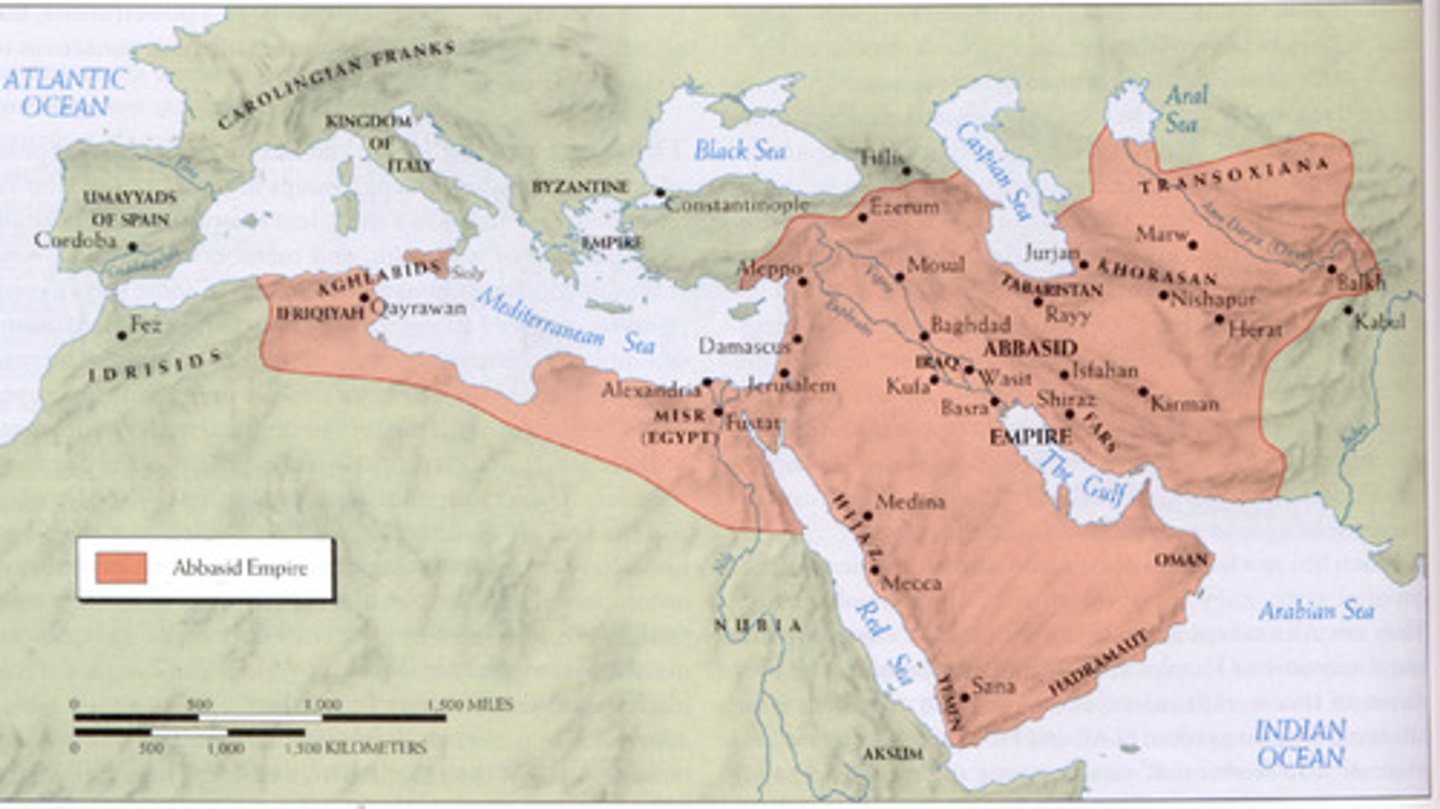
Abbasid Caliphate
The Islamic dynasty with the most influential rulers under which Islam experienced a golden age.
How did Islamic states form a cultural region even though they were fragmented politically?
Trade spread goods and ideas, the common use of shariah created similar legal systems, and intellectual innovations were shared at universities.
How did Islamic scholars carry on the work of earlier scholars?
They translated Greek books into Arabic, studied math from India, and used Chinese paper-making techniques.
Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
An Islamic scholar who studied medicine, astronomy, logic, ethics, philosophy, and trigonometry. He oversaw the building of an observatory.

Ibn Khaldun
An Islamic scholar who founded historiography and sociology.

A'ishah al-Ba'uniyyah
A female Muslim (Sufi) writer and poet. She wrote poetry honoring Muhammad and describing her spiritual journey as a Sufi. Her writings reflect a contrast between Muslims, who focused on intellectual pursuits, and Sufis, who emphasized introspection to grasp truths they believed could not be understood through learning.
Sufis
A Muslim group that emphasized introspection and played an important role in spreading Islam.

Did Muslims own slaves?
Yes, but they did not enslave other Muslims or monotheists.
How did Muhammad raise the status of Muslim women?
He treated his wives kindly, insisted that dowries were paid to women, and forbade infanticide. His wife was also educated and owned a business.
What was the status of women in Islam?
Women could remarry, inherit property, initiate divorce, use birth control, and testify in court. However, their testimony was worth only half that of a man's and they wore hijabs to cover their faces in public.
What was the significance of the Battle of Tours in 732?
It marked the limit of rapid Islamic expansion to Western Europe when the Islamic military was defeated by Frankish forces.
Dhows
Ships with long, thin hulls that were good for carrying goods.

How did Muslims, Christians, and Jews interact in Córdoba?
They interacted peacefully and often influenced each other's studies. For example, Ibn Rushd's commentaries on Aristotle influenced a Jewish philosopher, Maimonides.
al-Andalus
The Islamic state in Spain.
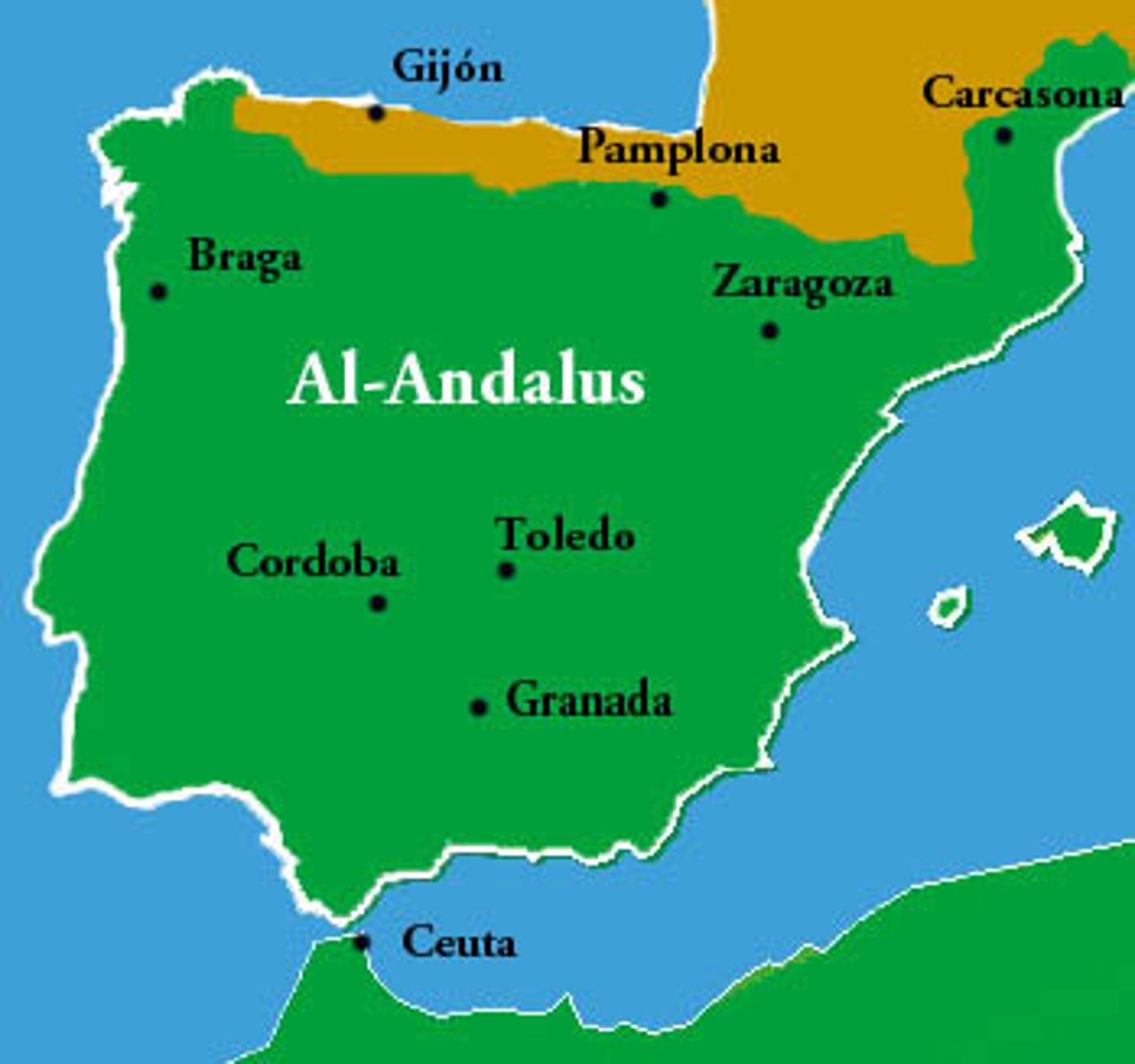
What was the importance of the discoveries made in Córdoba?
The knowledge discovered there laid the groundwork for the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution.
Sultan
The Seljuk leader.