NEURO EX IN PT Part 4
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sensory testing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
How to document sensory testing
O> Neurological sensory testing> 100% sensation intact as to light touch, pain, & temperature on (R) UE
flow in sensory testing
Perform superficial → deep → combined cortical
how to test for superficial sensations
Light touch
Pin prick
Deep pressure
*if there is a mistake use percentage → if percentage is used → should be bilateral stimulation
10 = sobrang nararamdaman
0 = wala na nararamdaman at all
*can use 0-10 or 0-100%
How to test the deep sensations?
Proprioception (position sense)
First to test (easier)
“Taas, baba, labas, loob”
ask when extremity is positioned – POSITION FIRST
Deep sensation in distal extremities (not sa trunk!)
Sasabihin niyo po sir, ito po yung taas, baba, loob, labas. Pikit po sir. Posisyon ko lang po muna, ano pong posisyon to sir?
OR poposition ko po muna, gayahin niyo po
Kinesthesia (movement sense)
“Pataas, pababa, paloob, palabas
ask while moving the extremity – same as proprioception but WHILE MOVING
Habang ginagalaw ko po yung daliri niyo, ito po yung pataas baba etc. ito po…
OR sabayan niyo po habang ginagalaw ko (yung good side yung gumagaya)
Vibration
Put on any bony prominence (at least 3 bony prominence)
At least 5 trials
Most important sensory test when pt has stroke or brain problem
Combined cortical
Where should you test for combined cortical sensation?
Only on hand
What are the tests for combined cortical sensations?
2-POINT DISCRIMINATION
STEREOGNOSIS
GRAPHESTHESIA
BAROGNOSIS
TACTILE LOCALIZATION
DOUBLE SIMULTANEOUS STIMULATION
TEXTURE RECOGNITION
Starts from wide to narrow and ends at the last 2 points where patient can discriminate the 2 points.
2-POINT DISCRIMINATION
What is measured in 2 point discrimination?
SHORTEST 2 POINTS! NOT 1 POINT!
Once the patient senses one-point, move the points 1 point wider
Then measure the shortest 2 points
If the patient has INTACT___, other combined cortical sensations are also normal
2-point discrimination and stereognosis
Introduce the object first. Let them feel it with eyes open, even just do it on affected side
STEREOGNOSIS
What Brodmann’s area is affected if there is (-) stereognosis?
BA 5, 7 — Somatosensory area
Trace letter/number on patient’s palm (or any body part) and ask them to identify what was written
GRAPHESTHESIA
Distinguish weights
Use the same shape and size of objects. Object must only differ in weight
Better to use bottled water for pracs
Pakiramdaman niyo po tong bottle, and ito. Sa right or left, alin po mas mabigat?
BAROGNOSIS
Normal values for 2 point discrimination:
Fingertips:
Dorsum of hand:
Palms:
Normal values for 2 point discrimination:
Fingertips: 3-5 mm
Dorsum of hand: 20-30 mm
Palms: 8-15 mm
how to test for tactile localization
Introduce (paper clip) to unaffected side → say that u will do it to the affected side, then using their unaffected hand they will point where they felt the sensation → you measure the distance to where they pointed from where you actually pricked
With patient’s eye closed, place a dot on any part of their skin and ask them to point where the dot is placed
Measure distance of the dot PT inputted from where the pt identified to have felt the sensation
Remember where you put the sensation
Can have 2 trials → compare the hand and the forearm
Tactile Localization > 0 cm
Using your right hand, pakituro po kung nasan yung sensation… ok pikit po kayo
Do NOT use ballpen to mark (bc they will see)
Remember to speak loudly with stroke patients (applicable in general not only here)
how to test for double simultaneous simulation
Introduce first to unaffected → apply two sensations simultaneously on both sides → ask ilan sensation naffeel → ask ano sensation → ask saan side na ffeel (R/L/both) → ask ano body part
Same body part bilaterally
1 distal 1 proximal bilaterally
1 distal 1 proximal unilaterally
Ask pt to verbally identify, c their eyes closed, where they felt the sensation
Same body part, R/L | diff body part, R/L | one side, proximal/distal
Area doesn't really matter, as long as you apply two of the same sensation simultaneously
There will be absence of sensation of the distal extremities in DSS. while simultaneously applying proximal sensation during double simultaneous stimulation
EXTINCTION PHENOMENON
how to test for texture recognition
Use silk and wool/sandpaper; introduce them first -> close eyes
Ask pt to answer either silk/wool or smooth/rough
Not the same as babinski; here toes will flex
Scratch parallel to the ball of the foot
Use brush; if none use tip of reflex hammer
PLANTAR SCRATCH
[reflex testing]
Upper Abdominal Reflex
T8 - T10
[reflex testing]
Lower Abdominal Reflex
T10 - T12
[reflex testing]
Plantar Scratch
L2 - S1
[reflex testing]
Anal Reflex
S2 - S4
[reflex testing]
Biceps, Brachialis Reflex
C5 - C6
[reflex testing]
Brachioradialis Reflex
C5 - C6
C6 - C7
[reflex testing]
Triceps Reflex
C6 - C7
C7 - C8
[reflex testing]
Patellar Reflex
L2-L4
[reflex testing]
Ankle (Achilles) Reflex
S1
How to document reflex testing?
O> Neurological Examination> Reflex testing> Superficial> (+/-) finding
O> Neurological Examination> Reflex testing>DTR> Hyperreflexia on R patellar tendon (or on R quads — can be tendon or muscle)
> absent abdominal reflex
> DTR > hyperreflexia on R patellar tendon (or R quads)
> gr 3 reflex on R quads
Should be oppressed at a certain age
Normal in children
For survival
PRIMITIVE REFLEXES
Should exist when you get old
Normal reflex in adults
absence indicates possible impairment
PHYSIOLOGIC REFLEXES
What are the 3 physiologic reflexes?
REP
RIGHTING
EQUILIBRIUM
PROTECTIVE EXTENSION
are defined as 'automatic reactions that enable a person to assume the normal standing position and maintain stability when changing positions'
RIGHTING REFLEX
Important for balancing
EQUILIBRIUM REFLEX
Pt has the tendency to extend hand when you are about to fall
PROTECTIVE EXTENSION REFLEX
What are the associated reactions?
RAIMISTE’S
STERLING’S
MARIE-FOX
SOQUE
HOMOLATERAL SYNKINESIS
pt has stroke manifestations on the R. If PT will resist hip abduction of the unaffected side (L), then there will be an associated hip abduction on the affected side ®
RAIMISTE’S PHENOMENON
pt has stroke manifestations on the R. If PT will resist shoulder abduction on the unaffected side (L), then there will be an associated abduction on the affected side ®
STERLING’S PHENOMENON
Passively flexing the toes on the affected side, it will elicit massive flexion of the entire lower extremity on the ipsilateral side
MARIE-FOX PHENOMENON
Passively flexing the shoulder of the affected side will elicit extension of the fingers ipsilaterally
SOQUE’S PHENOMENON
Passively flexing the UE will elicit flexion of the LE of the same side
HOMOLATERAL SYNKINESIS
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Stroking of lateral aspect of sole of foot towards big toe
BABINSKI
Extension of big toes and fanning of four small toes
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Stroking of lateral side of foot beneath lateral malleolus → going distal
CHADDOCK
Extension of big toes and fanning of four small toes
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Stroking of anteromedial surface of tibia distally
OPPENHEIM
Extension of big toes and fanning of four small toes
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Squeezing of calf muscles firmly
GORDON
Extension of big toes and fanning of four small toes
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Percussion of tibialis anterior muscle
PIOTROWSKI
Dorsiflexion and supination of foot
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Passive flexion of one lower limb
BRUDZINKSI
Flexion of opposite lower limb
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Tapping of index, middle, or ring finger (distal phalanx)
HOFFMAN
Flexion of the distal phalanx of thumb
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Tapping of plantar surface of toes
ROSSOLIMO
Plantarflexion of toes
[give the positive response and the name of reflex]
Pinching of Achilles tendon in middle third
SCHAEFER
Flexion of foot and toes
FLEXION SYNERGY OF UE
scapular retraction
elevation
hyperextension
shoulder abduction, ER
elbow flexion*
forearm supination
wrist and finger flexion
What is the strongest component of the flexion synergy of UE?
elbow flexion
EXTENSION SYNERGY OF UE
scapular protraction
shoulder adduction, IR
elbow extension
forearm pronation*
wrist and finger flexion
FLEXION SYNERGY OF LE
hip flexion*, abduction, ER
knee flexion
ankle dorsiflexion, inversion
toe dorsiflexion
What is the strongest component of the extensor synergy of the UE?
forearm pronation
What is the strongest component of the flexor synergy of the LE?
hip flexion
What is the strongest component of the extensor synergy of the LE?
hip adduction
EXTENSION SYNERGY OF LE
hip extension, adduction*, IR
knee extension
ankle plantarflexion, inversion
toe PF
where do you document limb synergy?
O> OI> (+) UE Flexion synergy
spasticity assessment table
O> Palpation> Gr 1 spasticity on R hamstrings
O> spasticity > grade 1 on R biceps
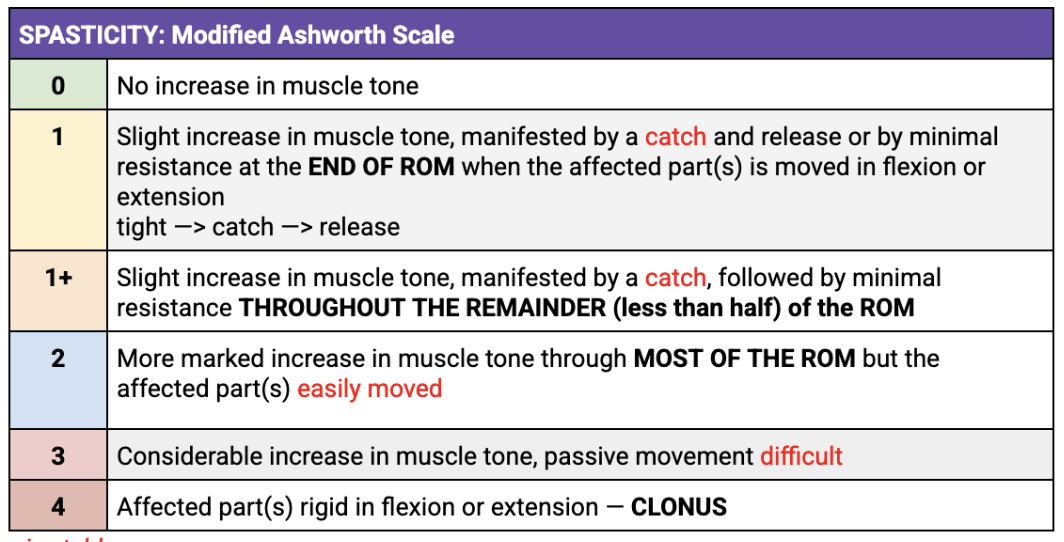
rigidity 2 types
Slow movement
BOTH COGWHEEL & LEADPIPE SLOW VELOCITY
cogwheel: matigas, mawawala tigas, matigas, mawala, so on
leadpipe: throughout matigas
End range slow movement
TIGHTNESS
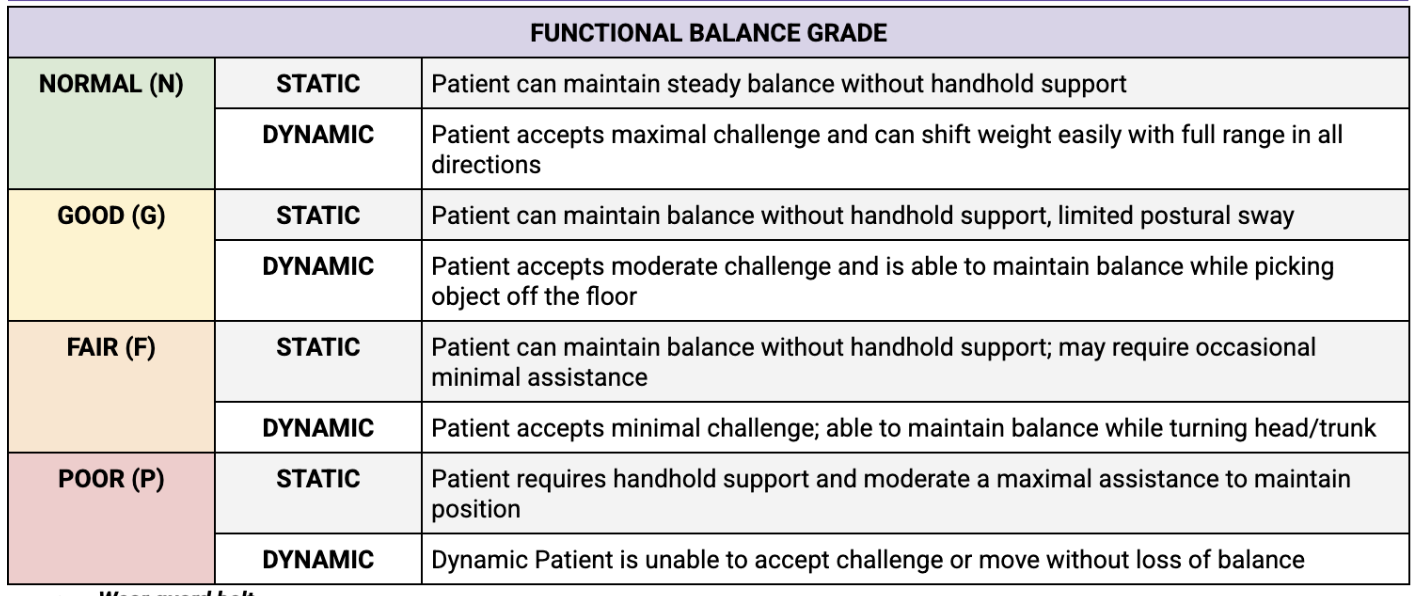
balance assessment
types of assistance
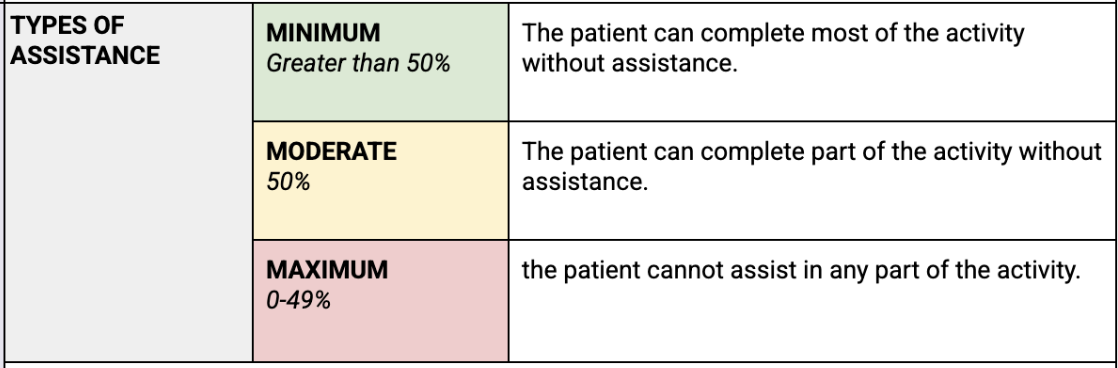
minimum change of pt in order for them to do ADLs (more important for the pt)
Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID)
minimum grade/number change NOT because of measurement error
Minimal Detectable Change (MDC)
A score of __ in the StrokEDGE Scoring Matrix means the tool has good to excellent psychometric properties and clinical utility.
3 or 4
Based on the article table 3
If __ u CAN use it
__ DO NOT use the test
Based on the article table 3
3 is written – if ur pt is acute na 3 then u dan use 5 times sit to stand
If 3 or 4 u CAN use it
1-2 DO NOT use the test
Ex. isang 3, isang 1 → DO NOT USE STILL