BIO 189 - LAB 5 Light Microscopy and Cell Structure
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
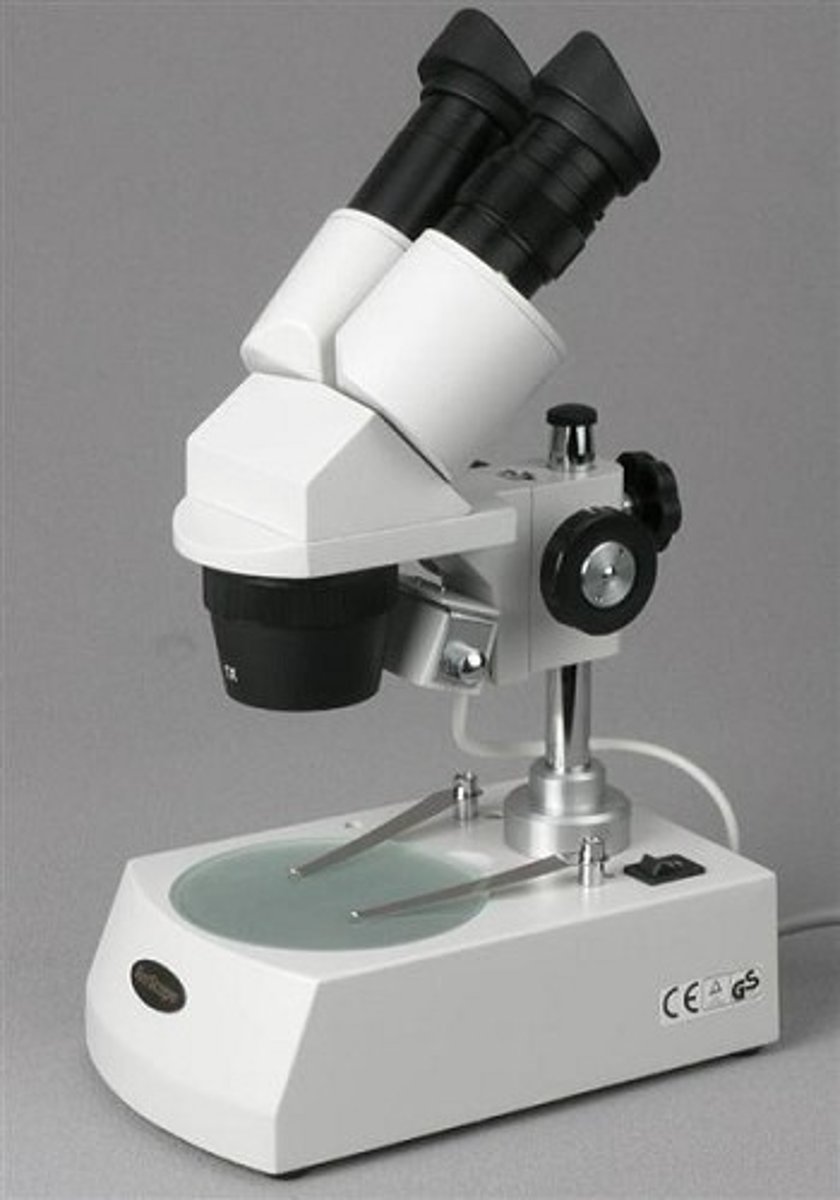
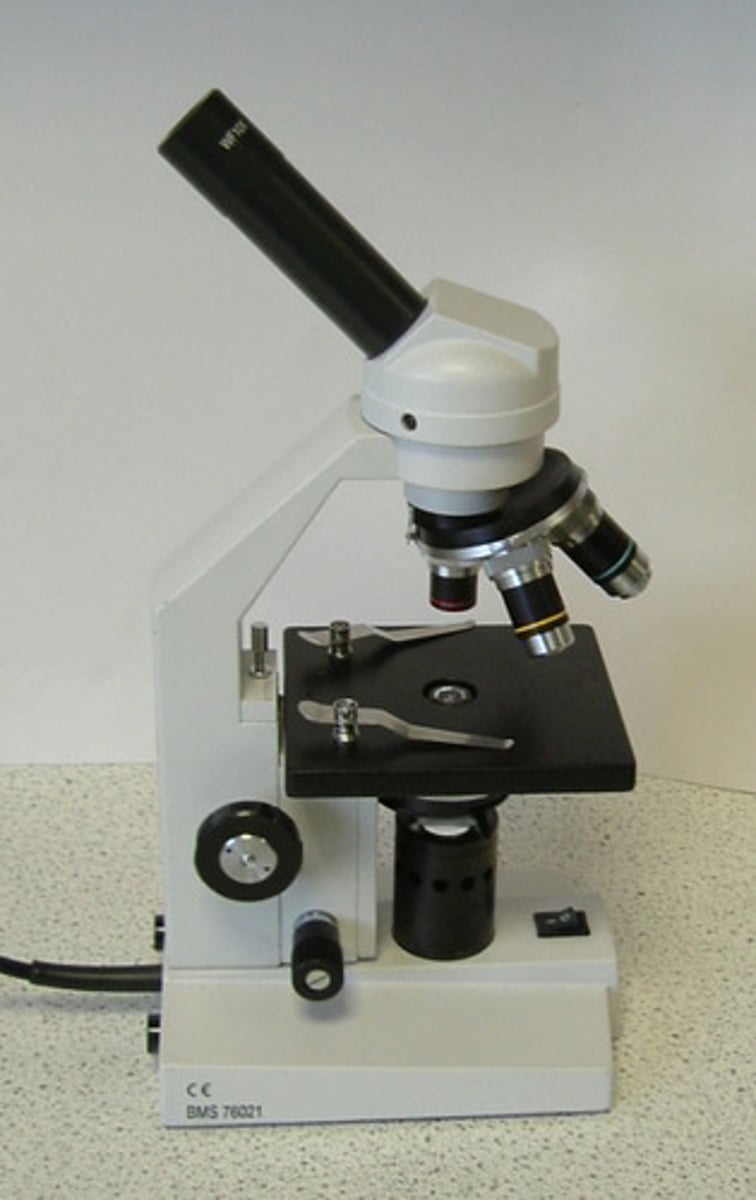
Compound Light Microscope
is used in this lab. It magnify the image of the specimen using light and lenses.

Parfocal
means that once an object is in focus using the scanning lens; it will remain in coarse focus when lenses are change to higher power.

Ocular Lenses
Lenses to look through to view the specimen.
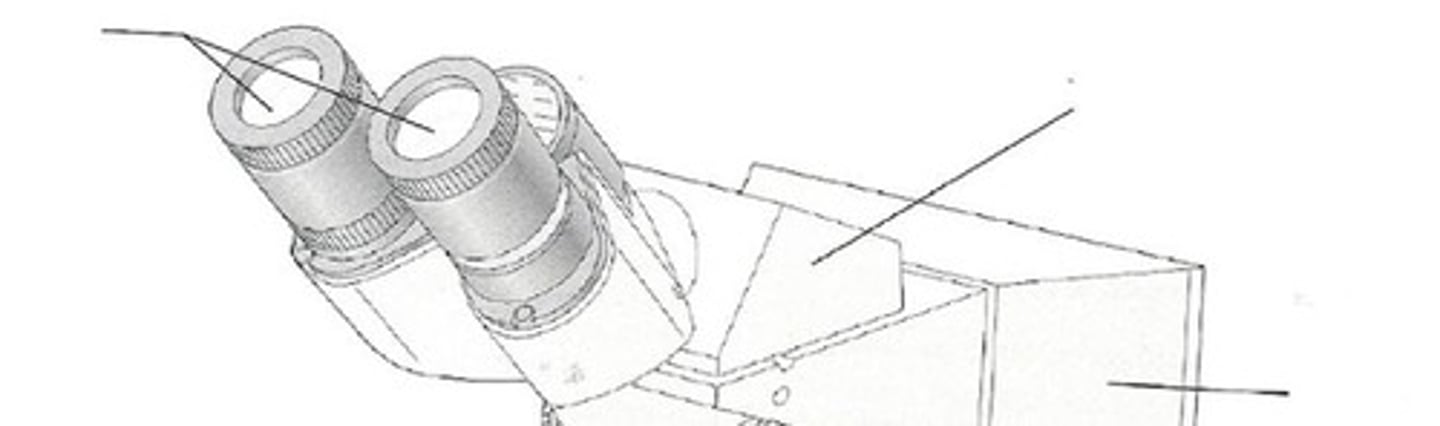
Head
upper part of microscope containing oculars and rotating nose piece.
Arm
narrow, vertical part connecting the head and base.
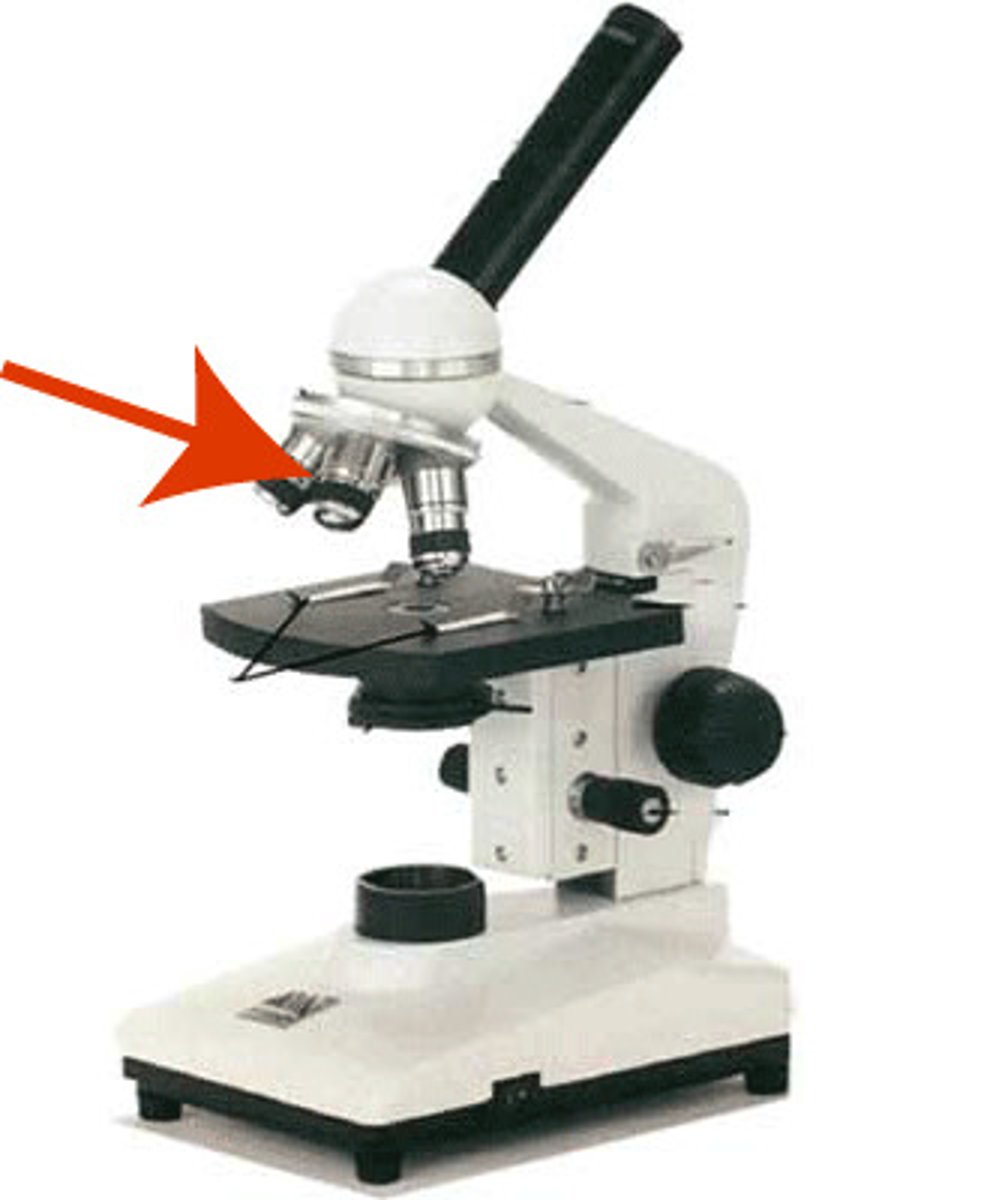
Rotating Nose Piece
revolving device located below the ocular lenses. It serve as an attachment for the objecting lenses.
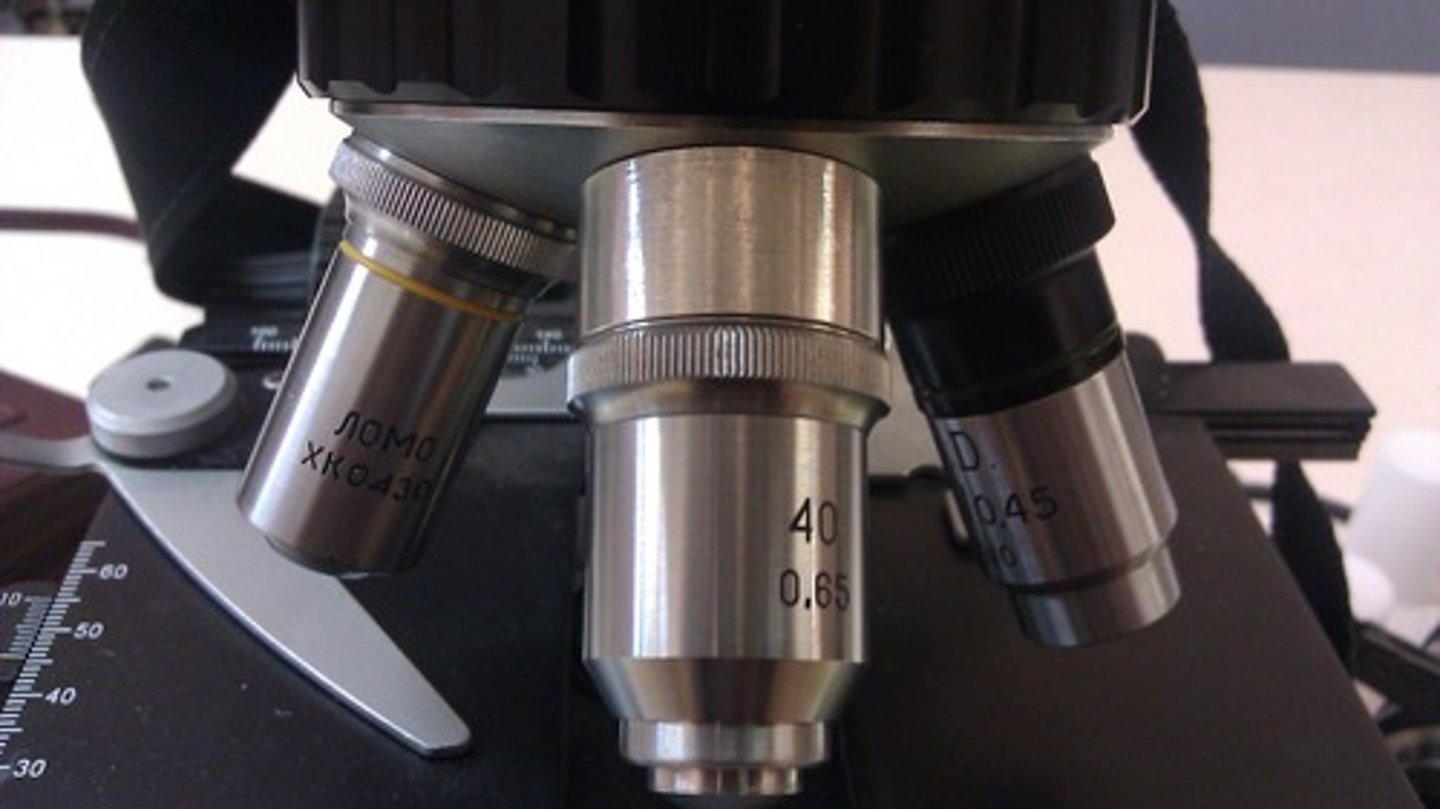
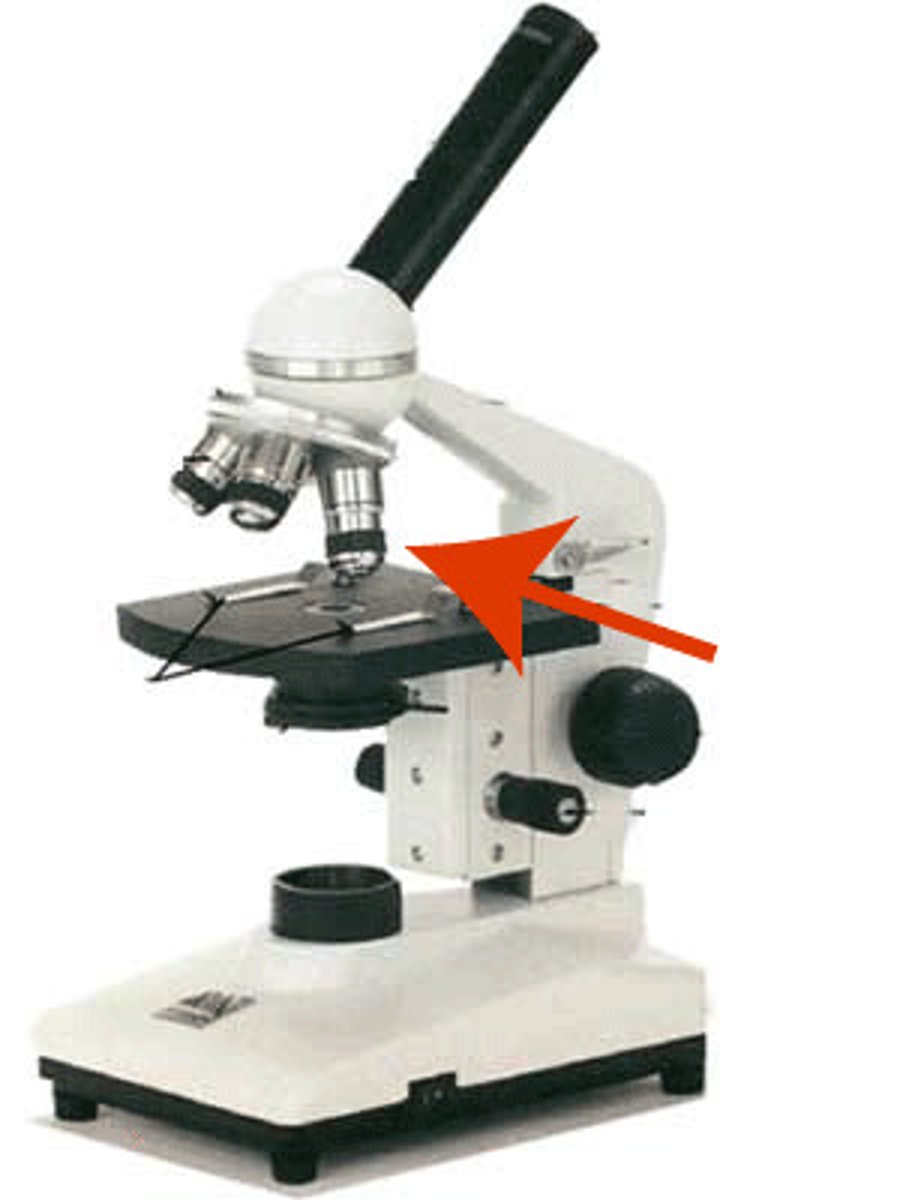
Scanning Lens
magnification 4x. The shortest of the objective lenses, used to scan the whole slide.
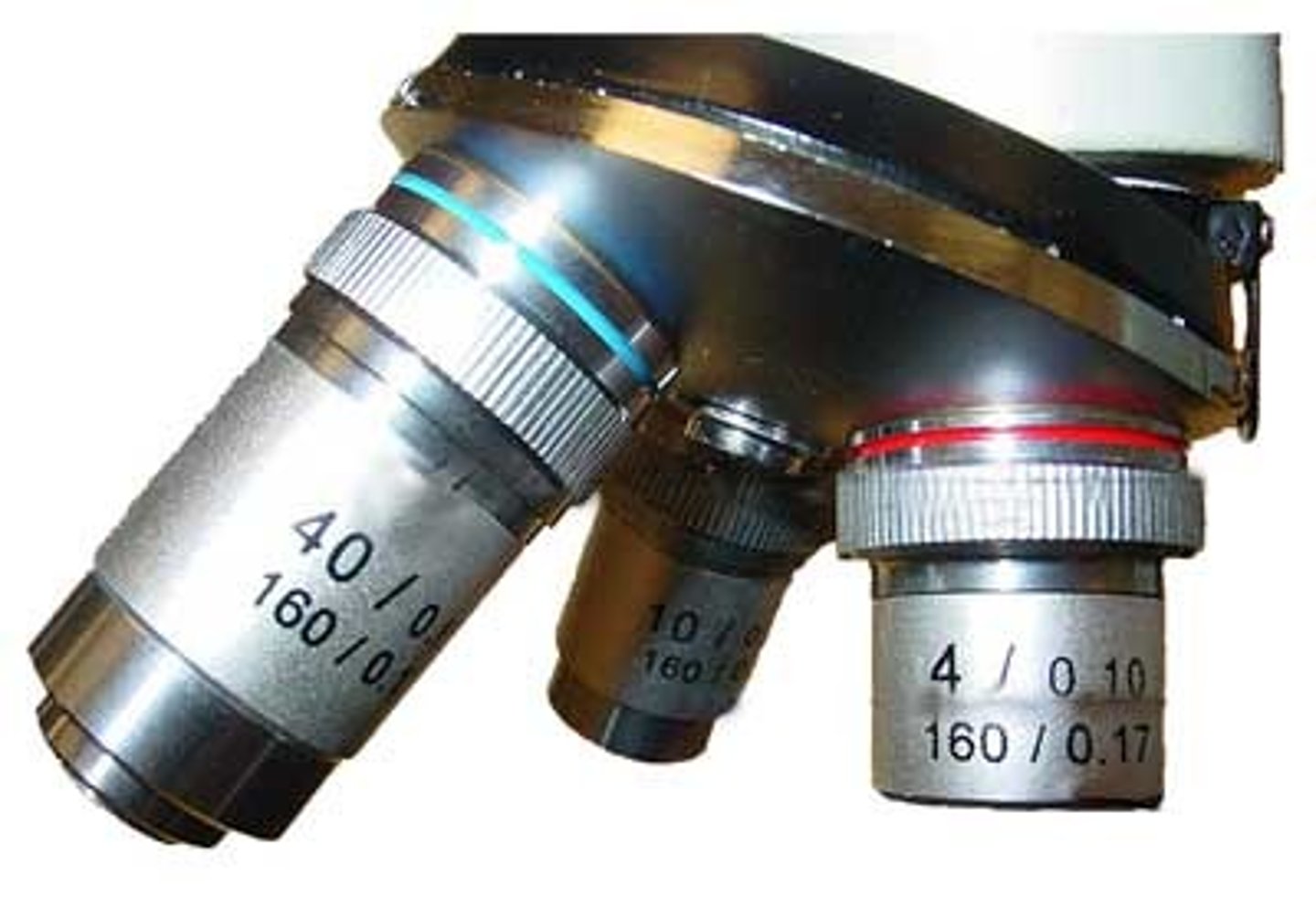

Low Power Lens
magnification 10x. Longer than the scanning objective lens and is used to view objects in greater detail.

High Power Lens
magnification 40x. Used to view and object to even greater detail.
Oil Immersion Lens
magnification 100x. Used in conjunction with immersion oil to view objects with the greatest magnification.
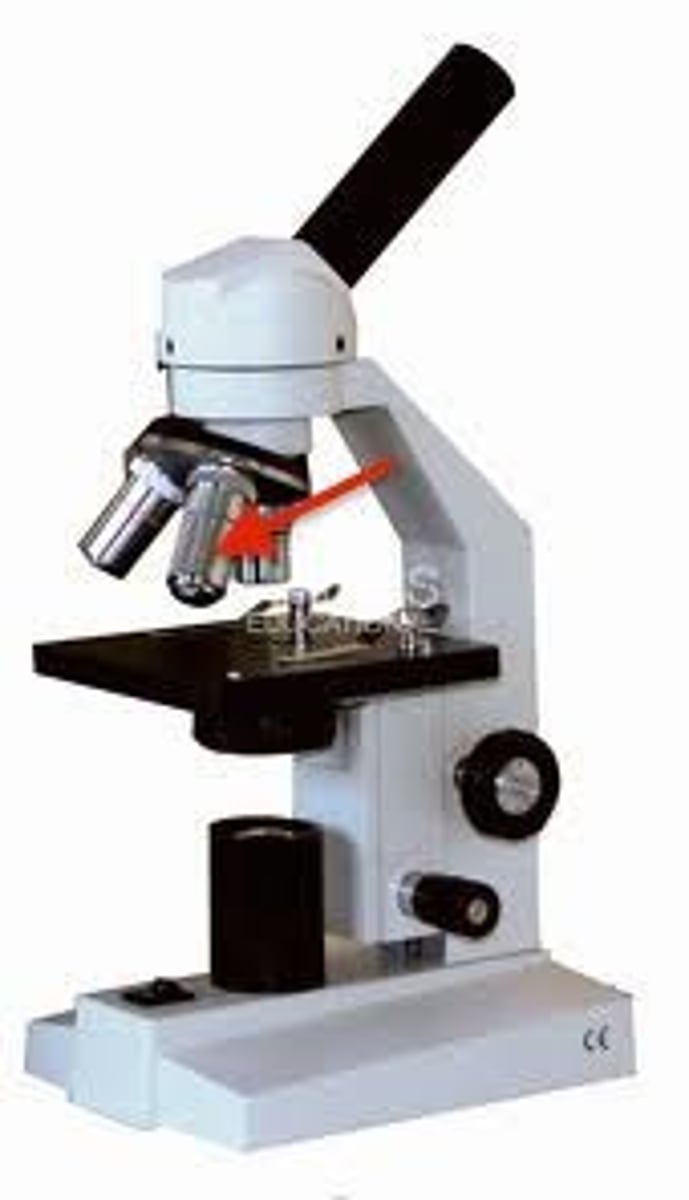

Mechanical Stage/Stage Clip
keeps the specimen slide stationary while viewing.
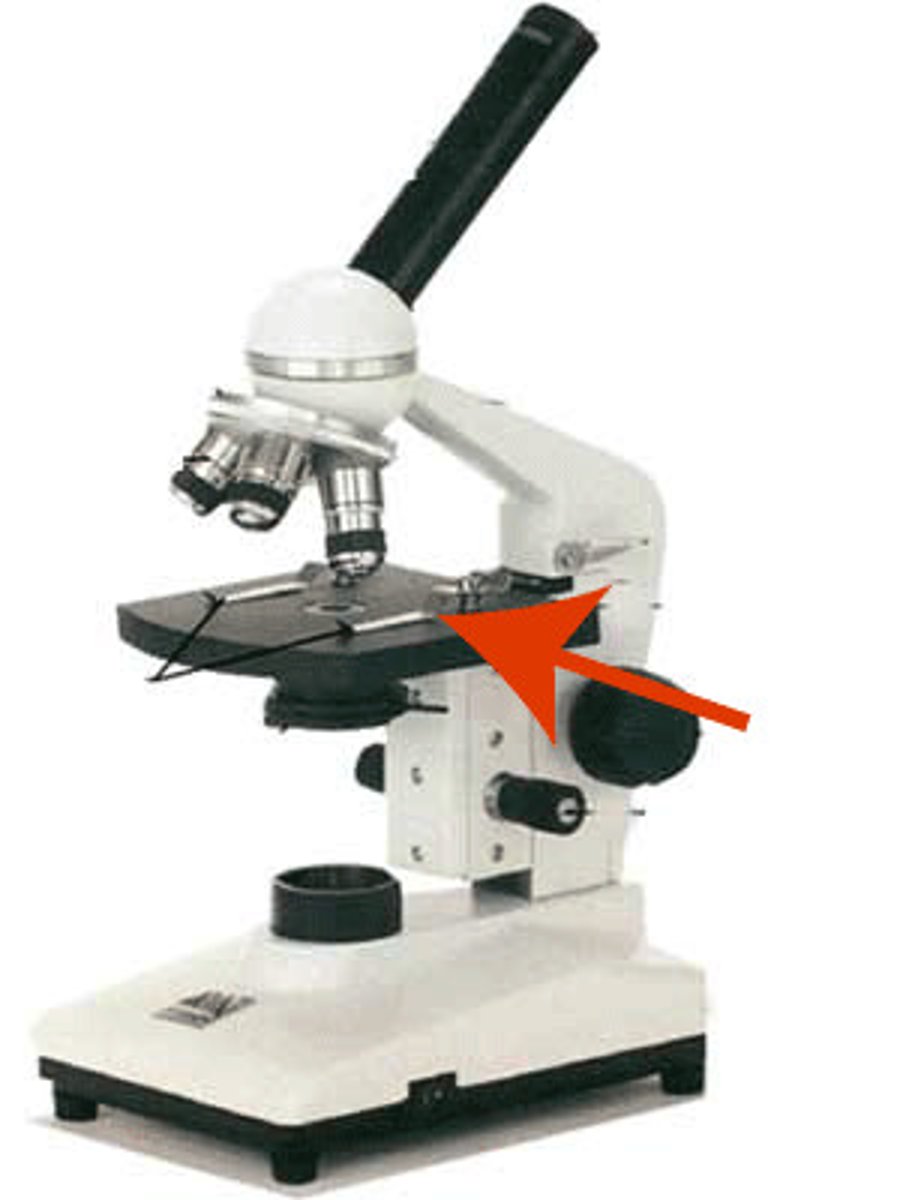
Mechanical Stage/Stage Clip Control
two knobs that allow the movement of the specimen of the specimen slide on the stage while viewing.
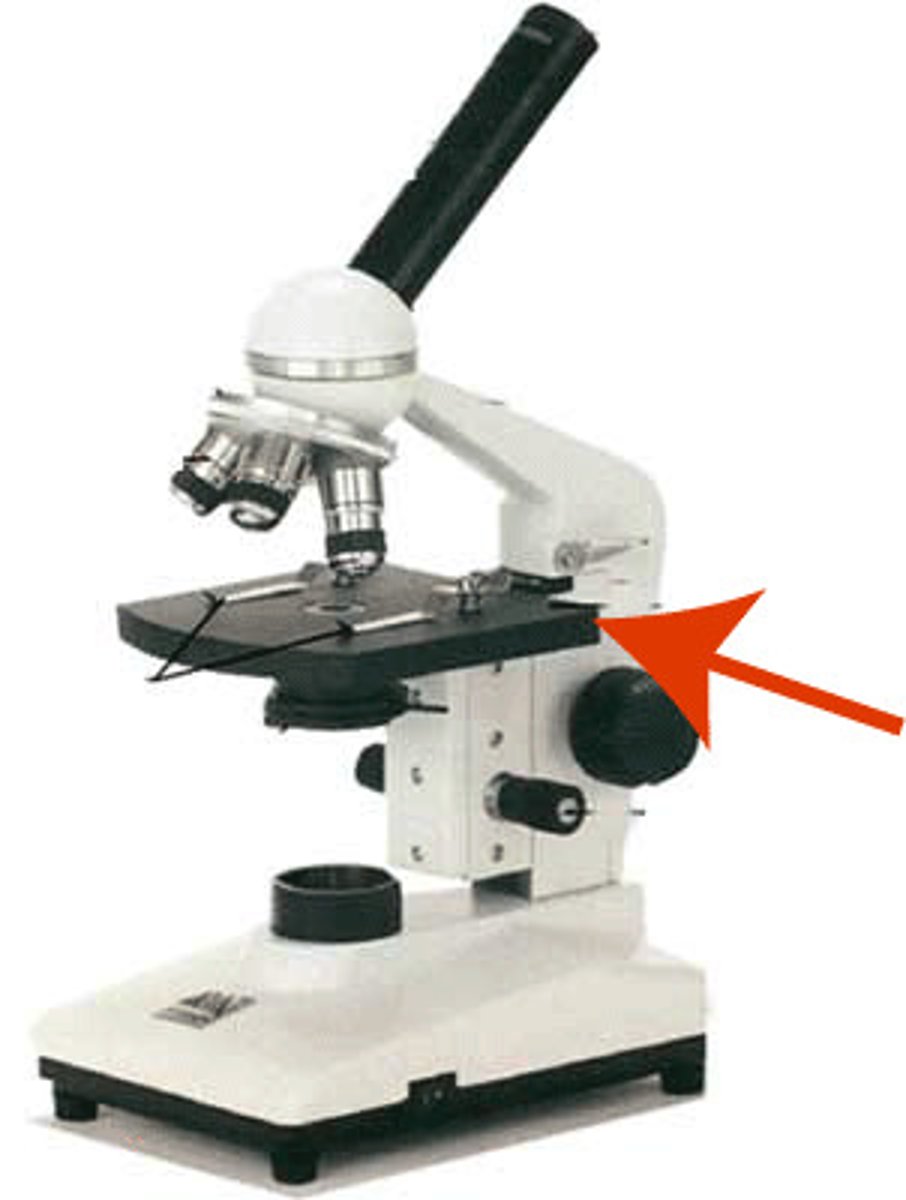
Stage
the flat platform connected to the arm and beneath the objective lenses, upon which the specimen slide is place.
Condenser
a lens located just below the stage that concentrates the light on the specimen.
Condenser Control
knob allowing the viewer to control the position of the condenser.
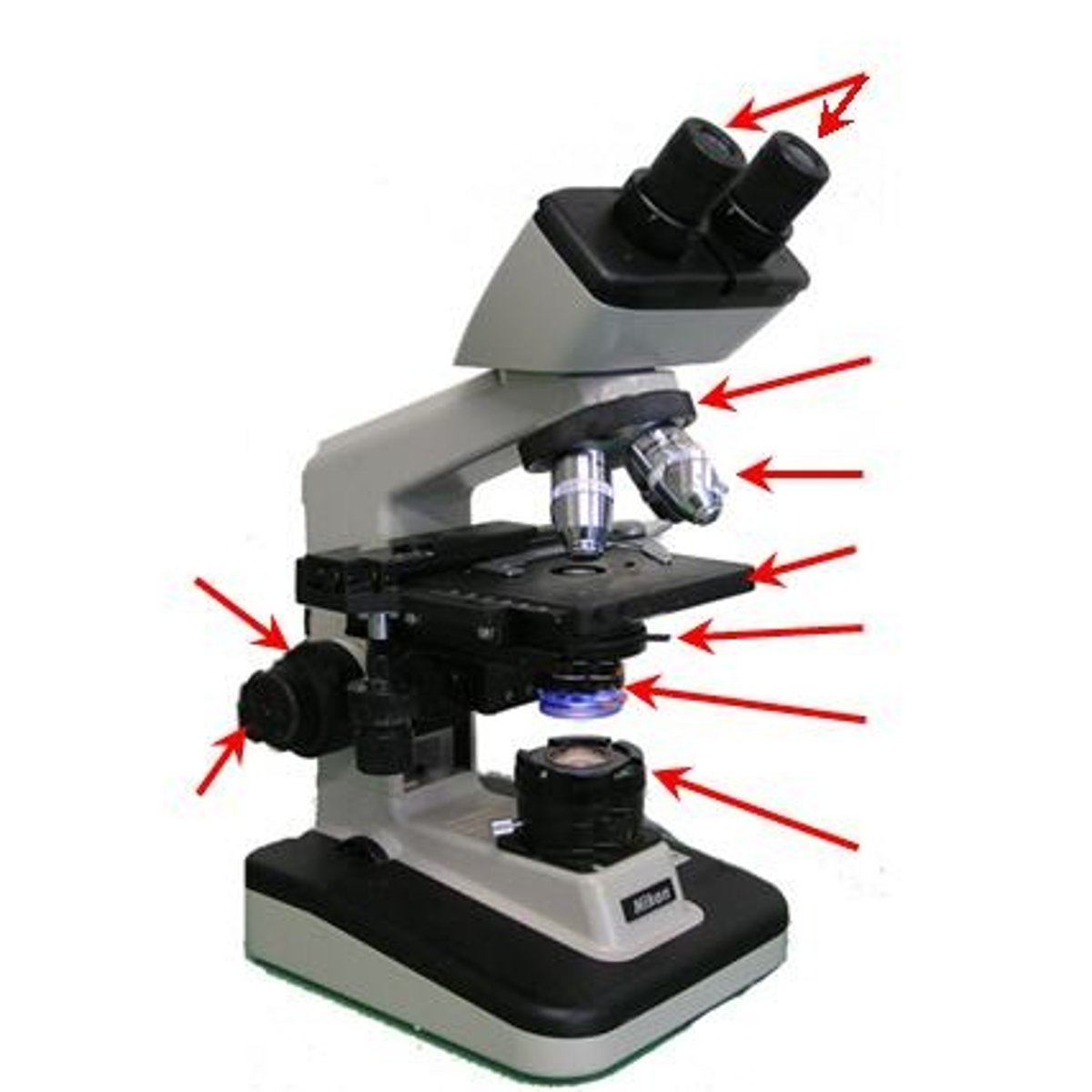
Iris Diaphragm
lever located beneath the condenser, it opens and closes the iris diaphragm regulating the light passing through the condenser.
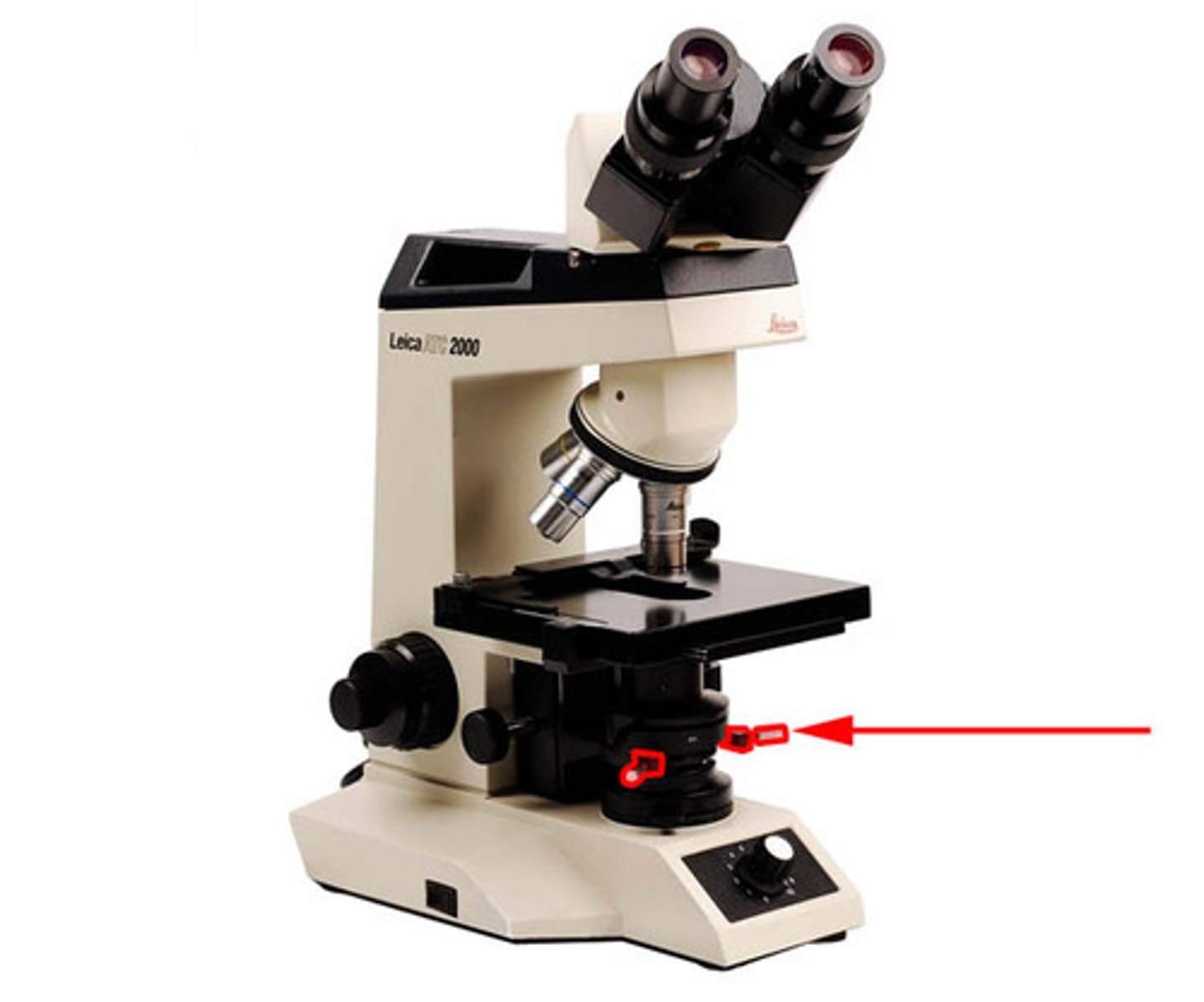
Coarse Adjustment Knob
two knobs on either side of the microscope at the base of the arm. Usually the largest knobs on the arm.
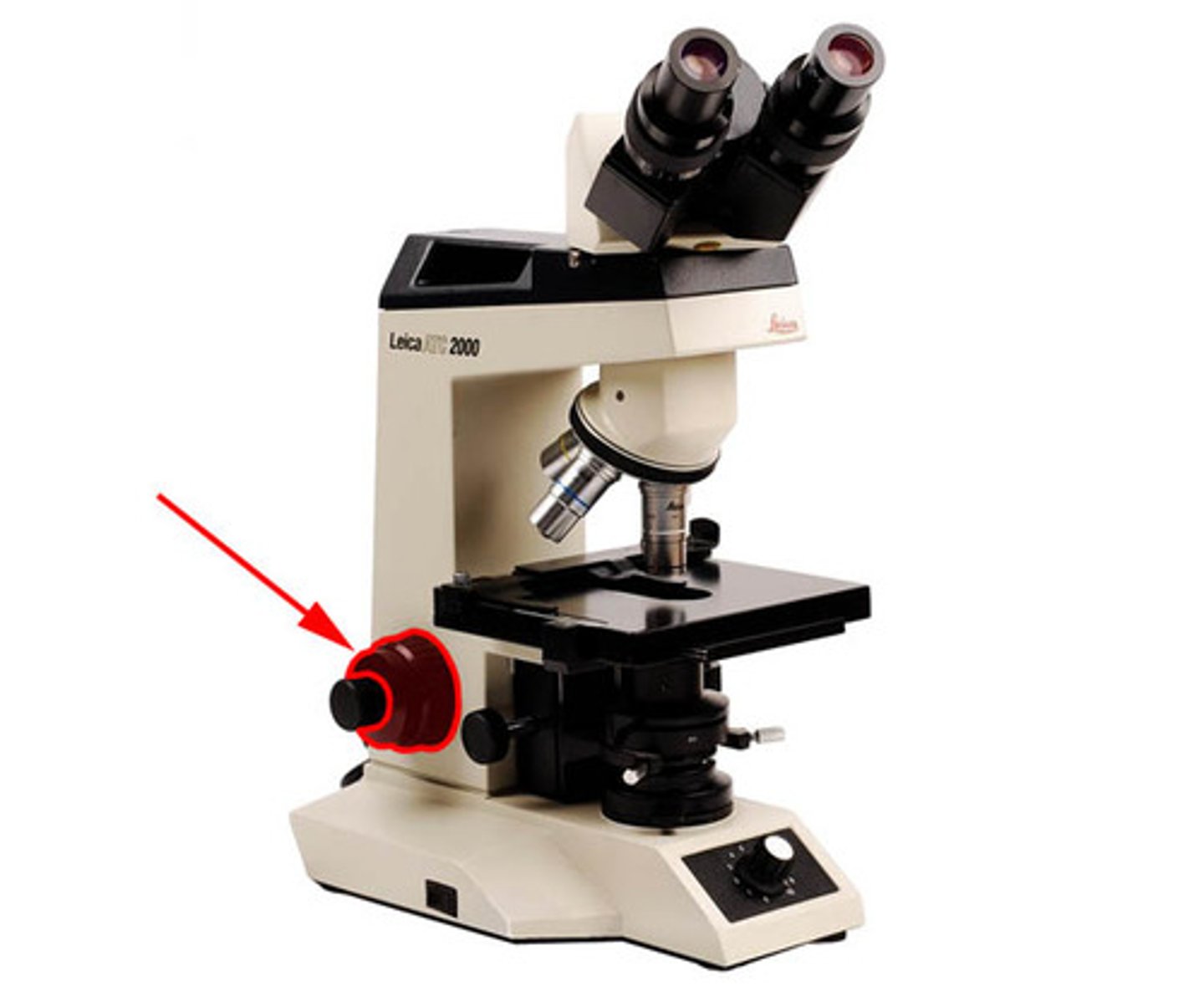
Fine Adjustment Knob
two knobs usually located in the center of each coarse adjustment knob. Used for precision focusing, since they raise or lower stage in very low increments.Safe to use with the high power (40x) and oil immersion (100x) lenses.
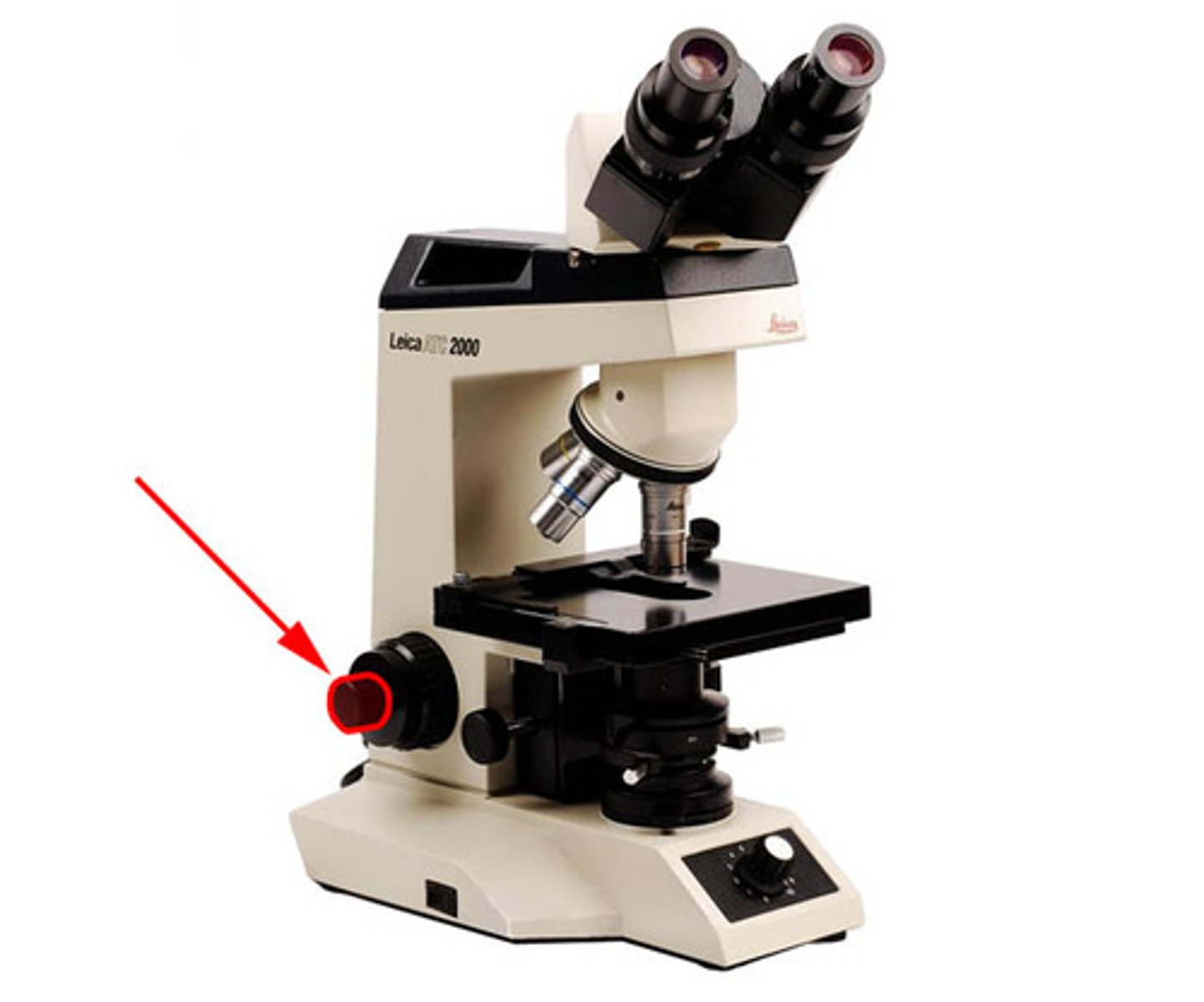
Substage Light
a light within the base providing the light source for illumination of the specimen. The power switch is usually at the side or front of the microscope turns it off and on.
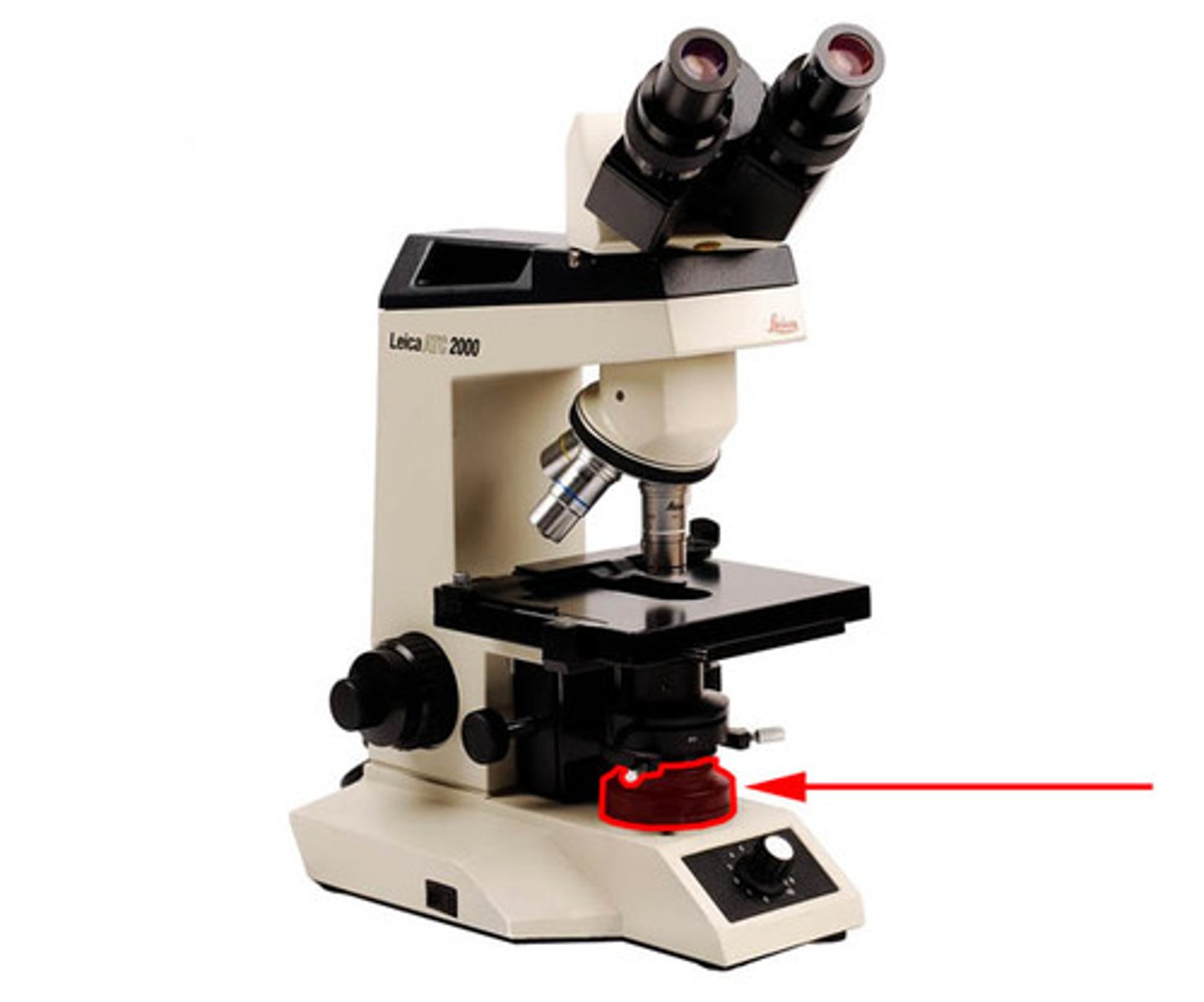
Rheostat
dial that adjusts the light intensity allowed through the condenser on to the specimen.
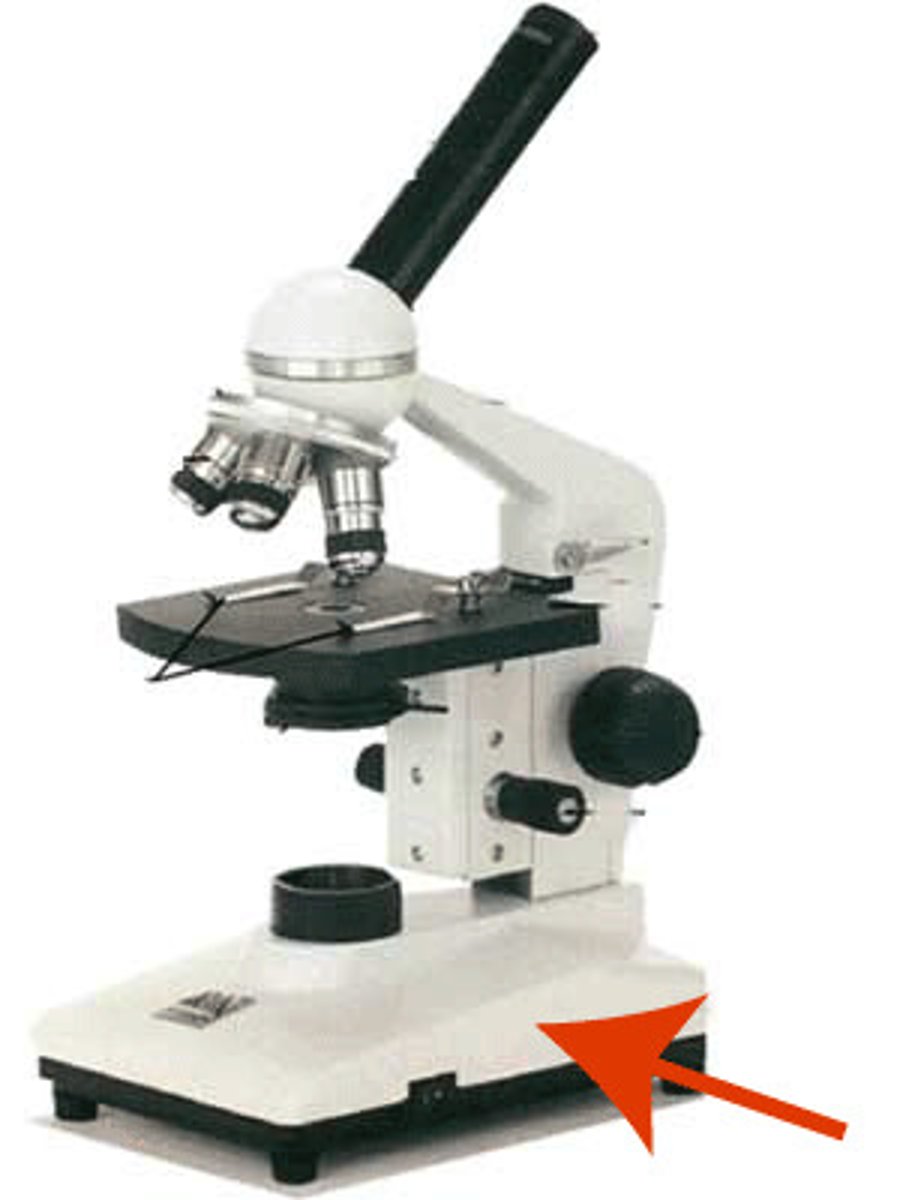
Base
supportive flat surface of the microscope that rests on the table.

Field of View
total amount of specimen that is visible, will decrease anytime an object is magnified.
Refraction
when a ray of light travels through the glass slide and comes into contact with air and it bends.

Depth of Field
vertical distance that remains in focus at a time.
Cells
come in different shapes, sizes and are designed to perform specific functions.
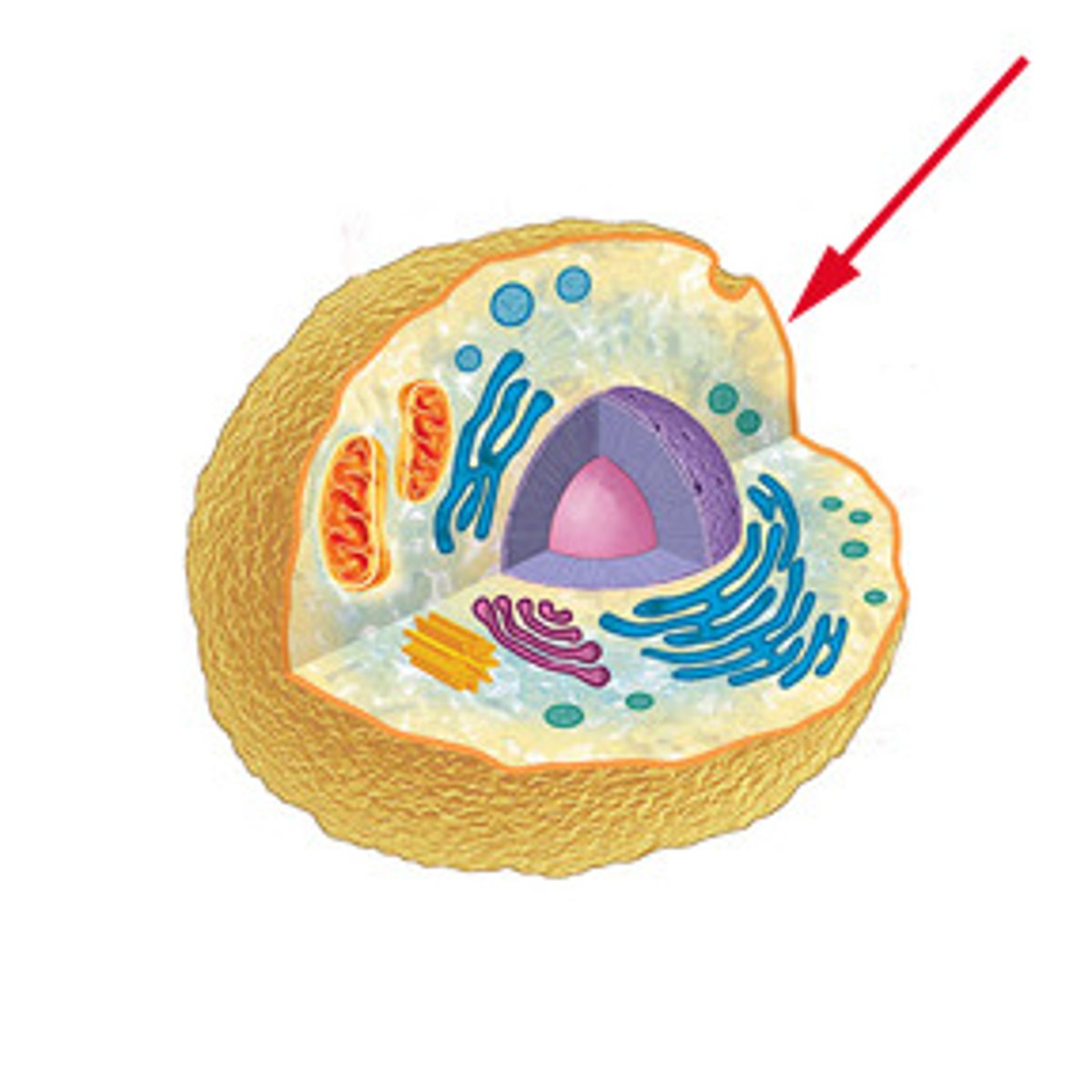
Plasma Membrane
outer boundary of the cell.
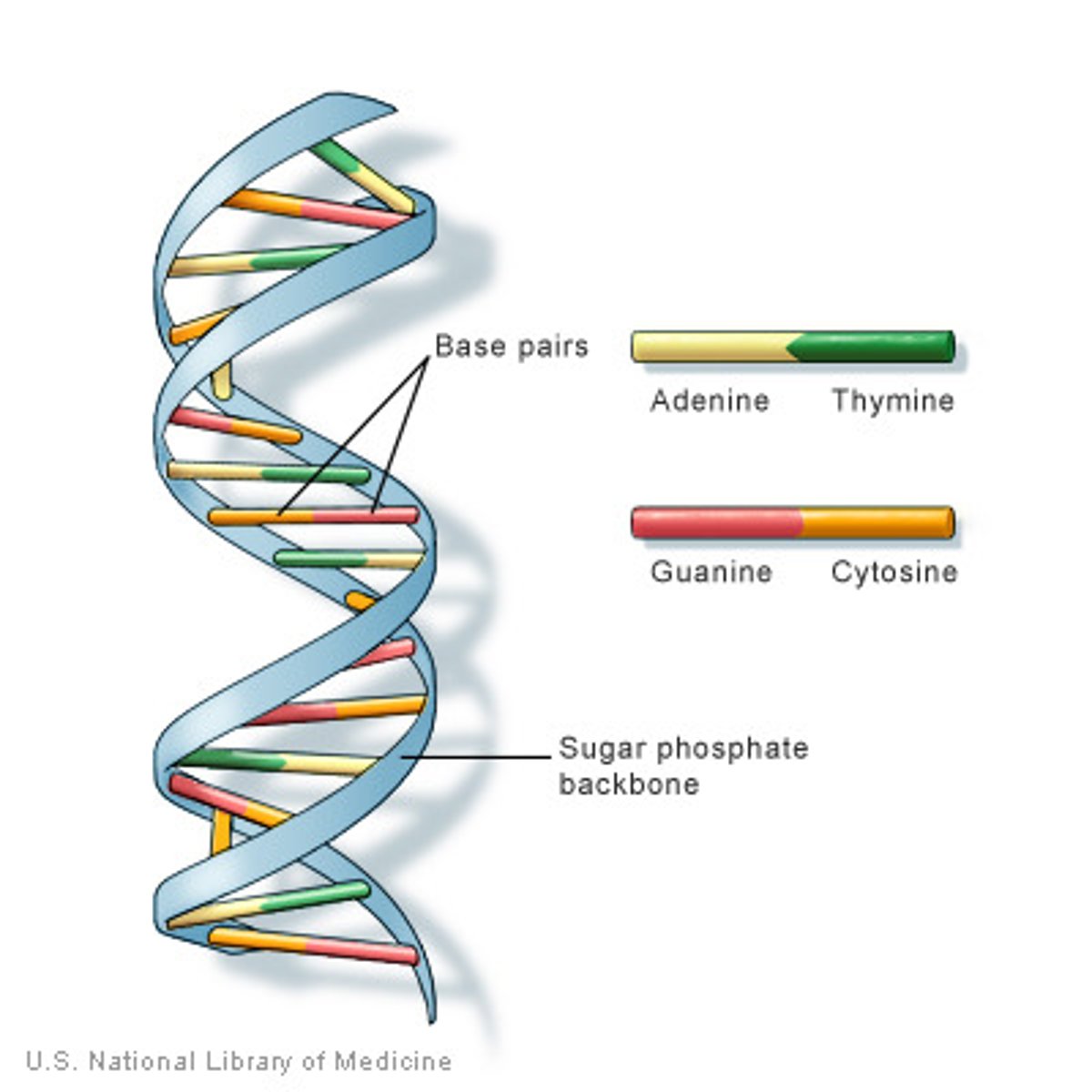
DNA
all cells store genetic information in the form of
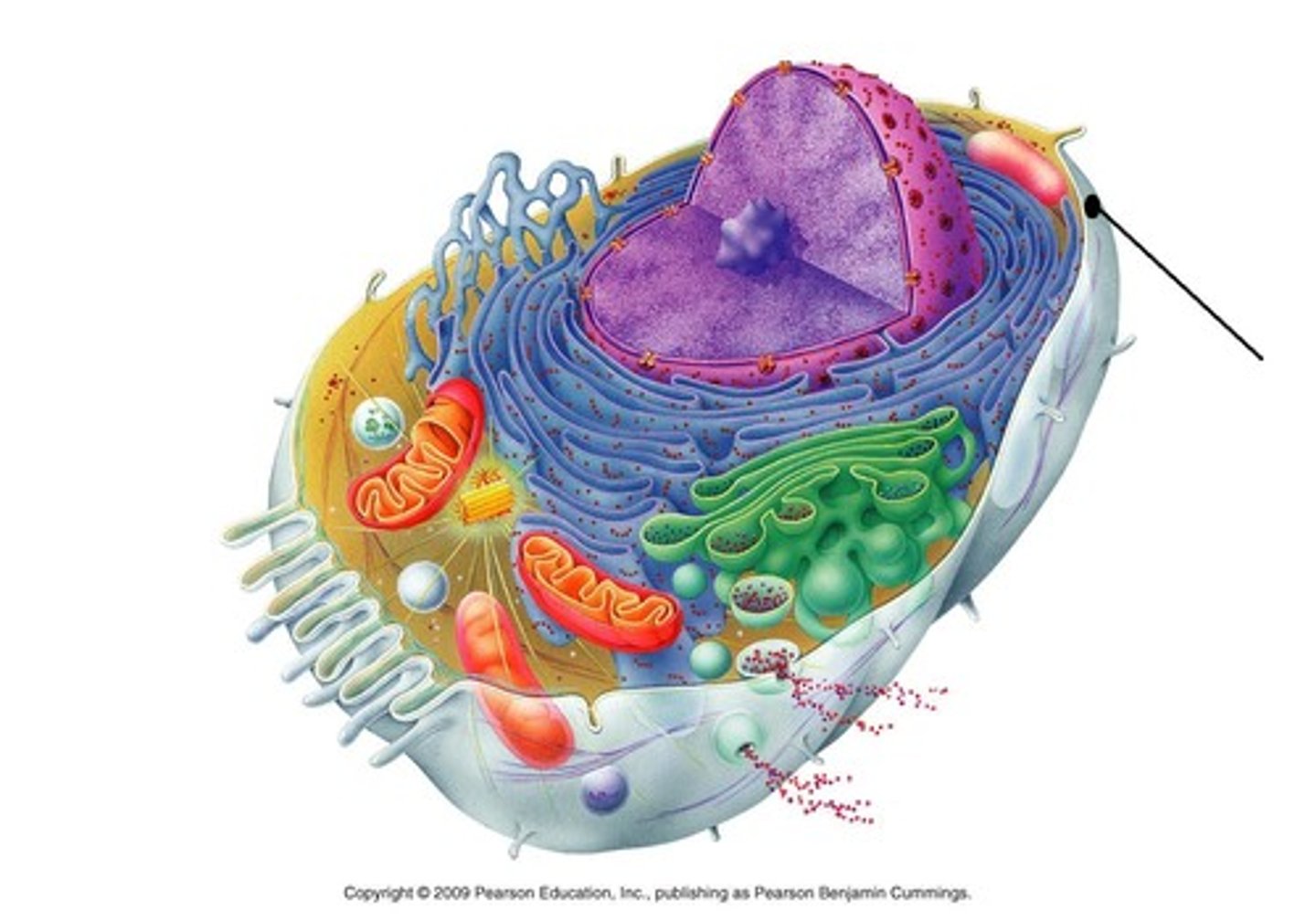
Cytoplasm
everything inside the plasma membrane that is not DNA or nucleus.
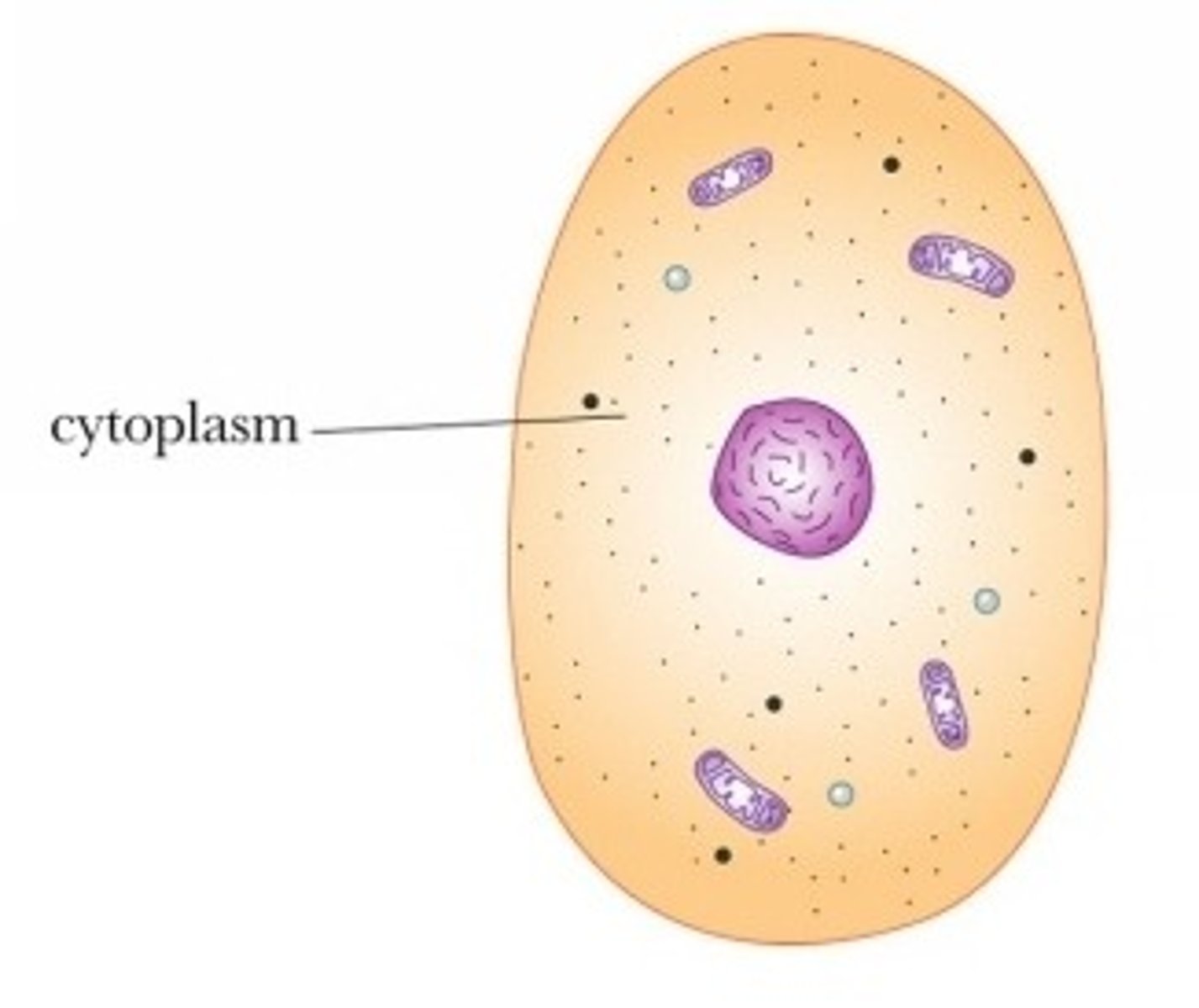
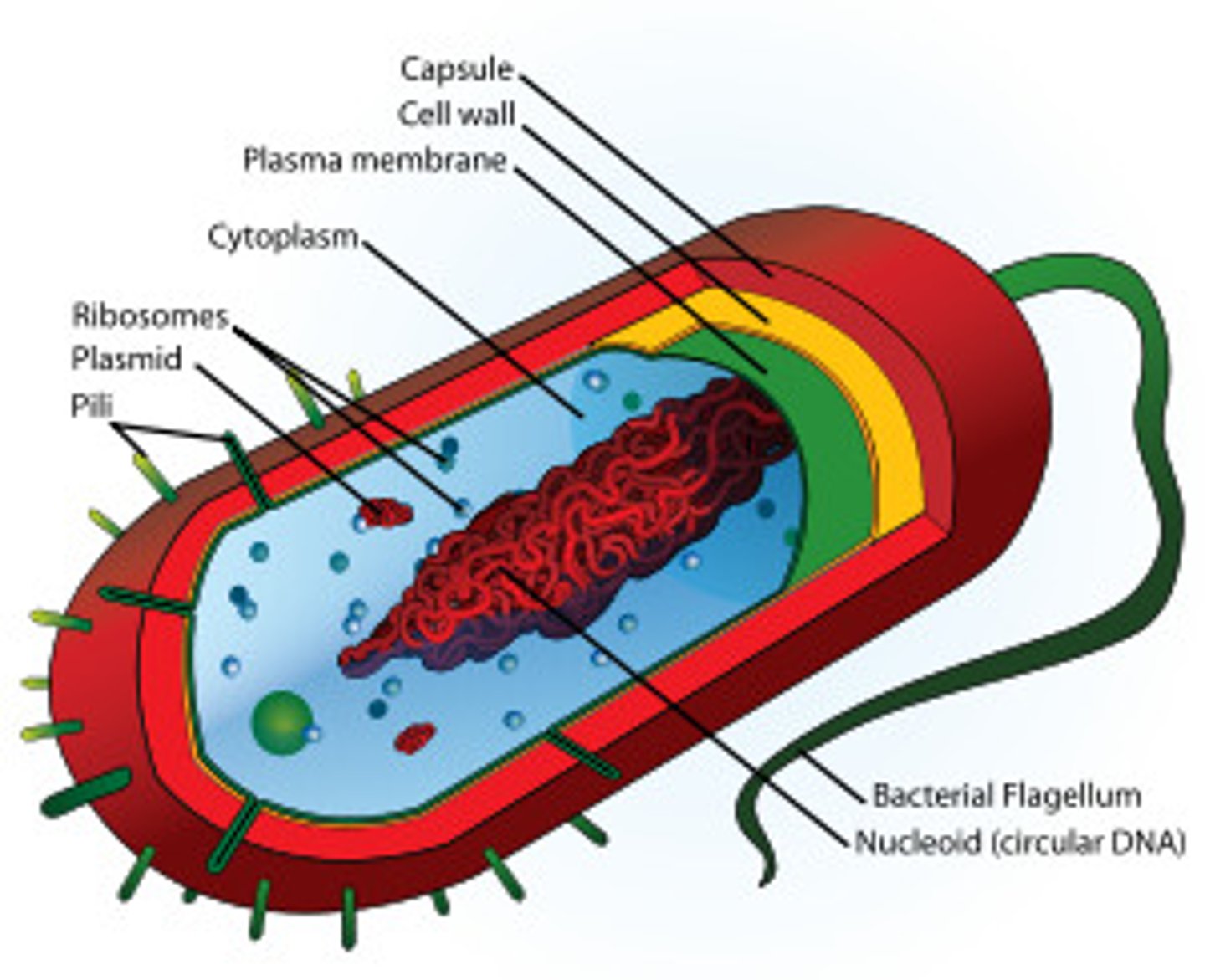
Prokaryotes
their DNA is found in the cytoplasm and not within a nucleus and they do not have any other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotes
they contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplast. They also house their DNA within the nucleus.

Kingdoms Eubacteria and Archae
both have unicellular prokaryotic organisms known as bacteria.
Kingdom Protista, Plantae, Animalia, Fungi
contain both unicellular and multicellular eukaryotic organism.
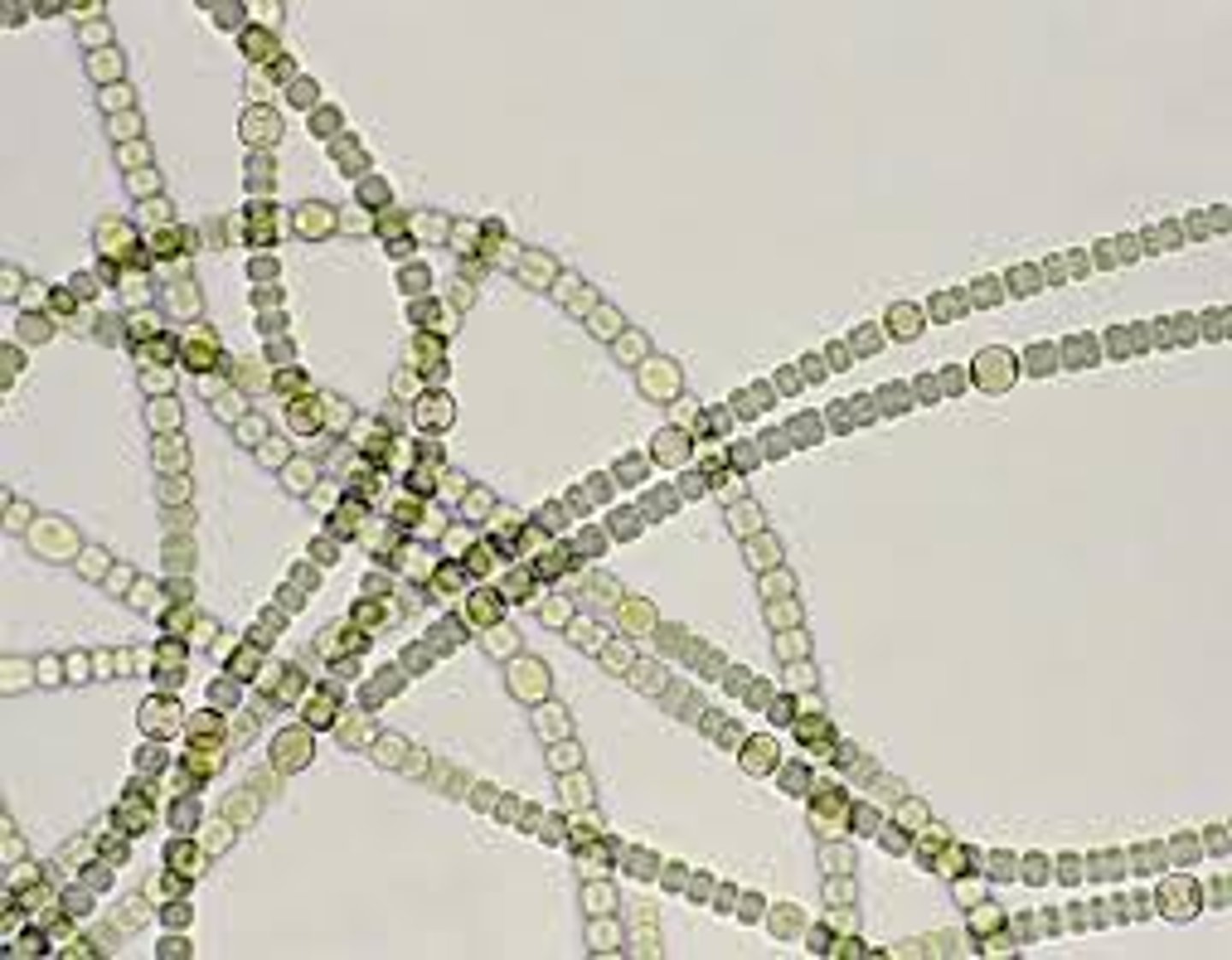
Cyanobacteria
organism is a colony of prokaryotic cells that can photosynthesize.
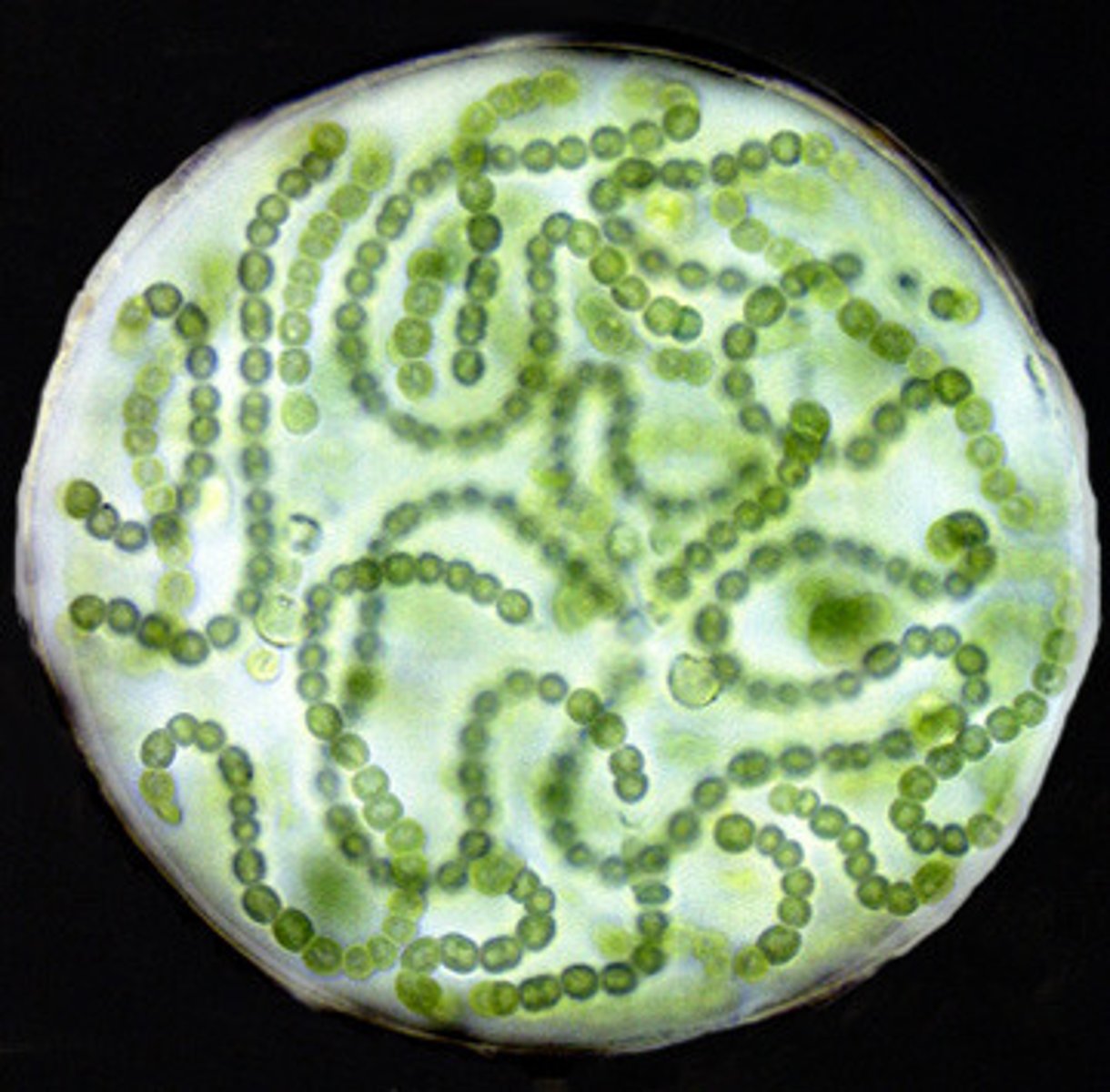
Anabaena
lab test for kingdom eubacteria and kingdom archaebacteria

Pond Water with living protist
lab test for kingdom protista
Mushroom
lab test for kingdom fungi
Red Onion and elodea
lab test for kingdom plantae
Cheek Cell
lab test for kingdom animalia
Dissecting Microscope
Type of microscope used to observe larger specimens such as insects, leaves, and rock minerals.