NE101 Lec 11: Neuroanatomy I
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Explains brain regions, ventricles, and nervous system organization.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
3 types of tissue
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
oligodendrocytes
glial cells in the CNS
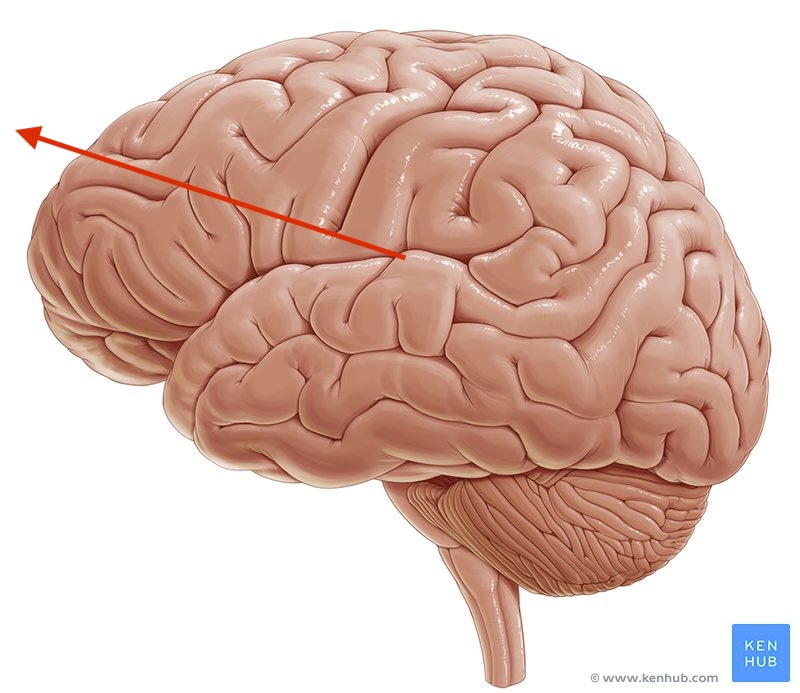
what direction is this?
rostral
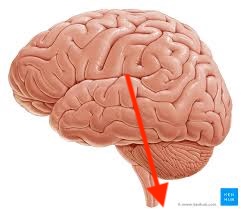
what direction is this?
caudal
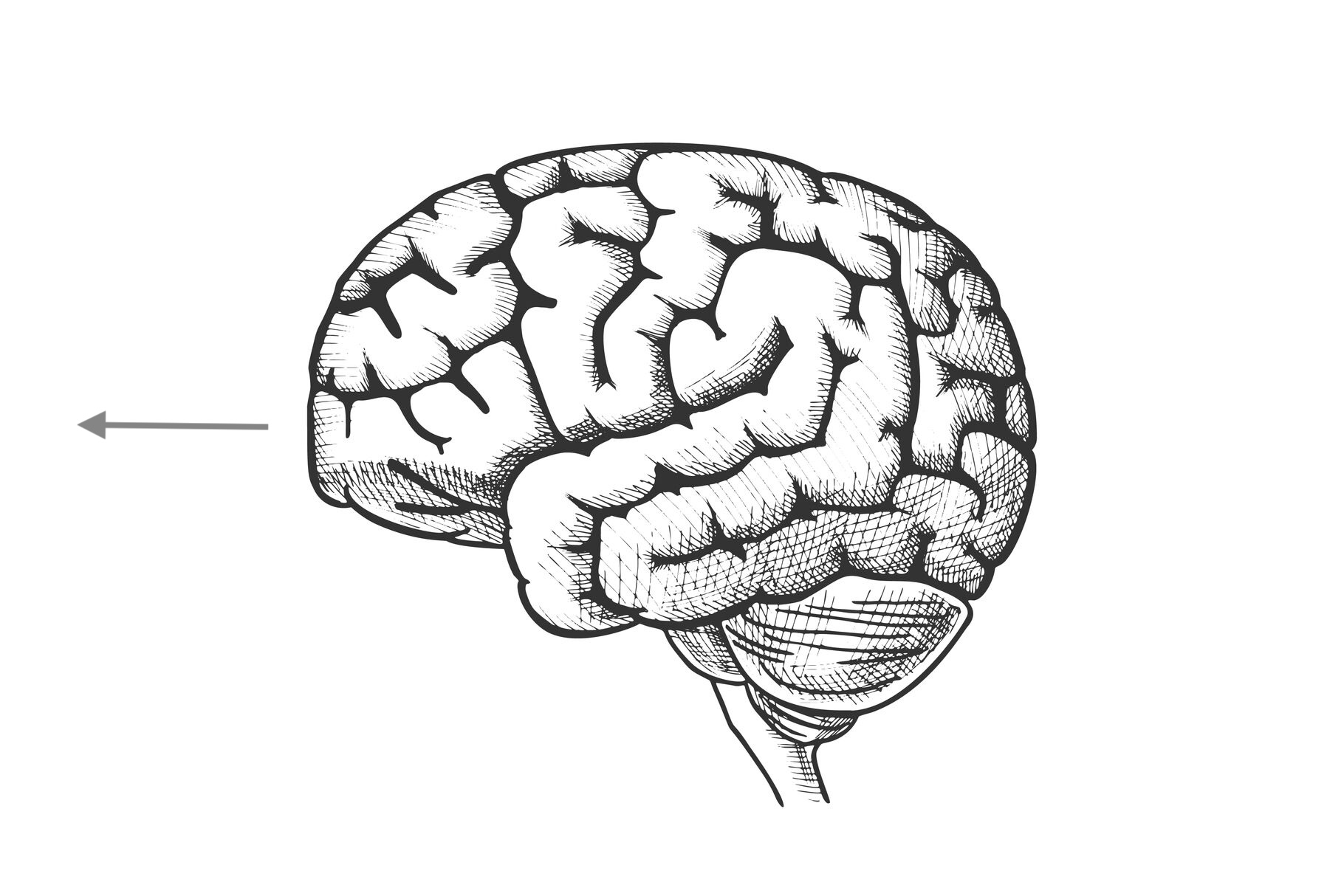
what direction is this?
anterior
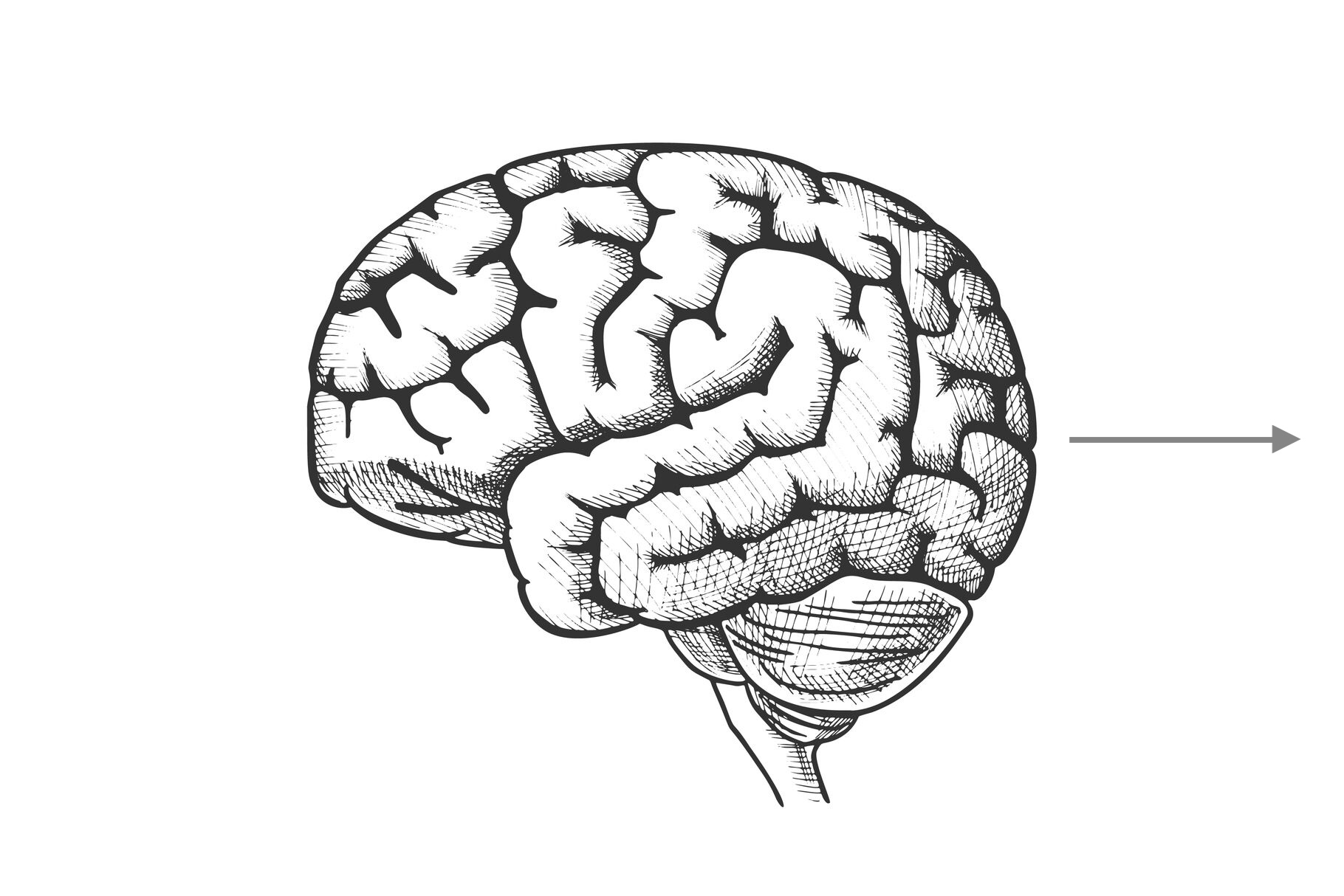
what direction is this?
posterior
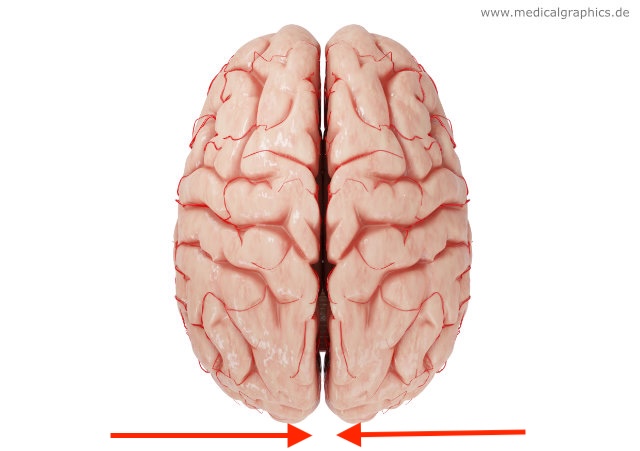
what direction is this?
medial
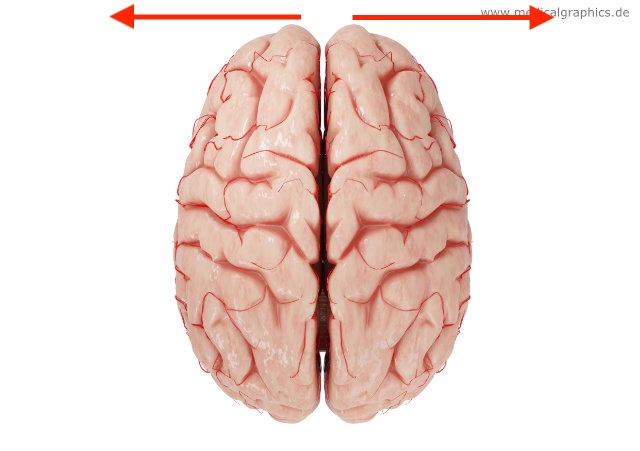
what direction is this?
lateral
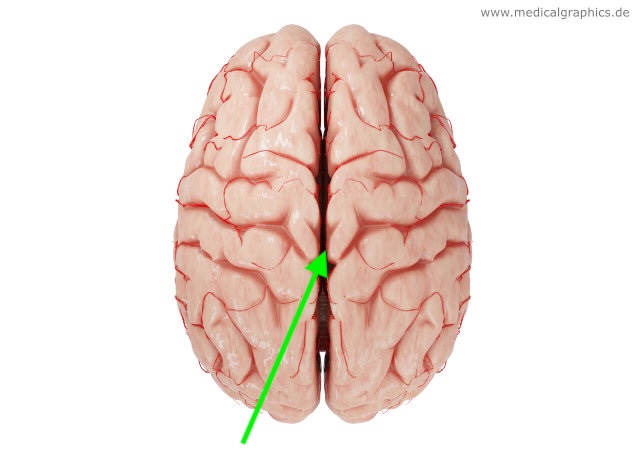
what part of the brain is this?
midline
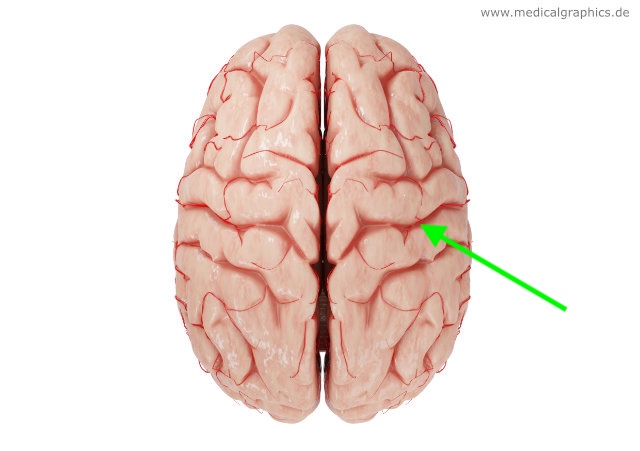
what hemisphere is this?
right
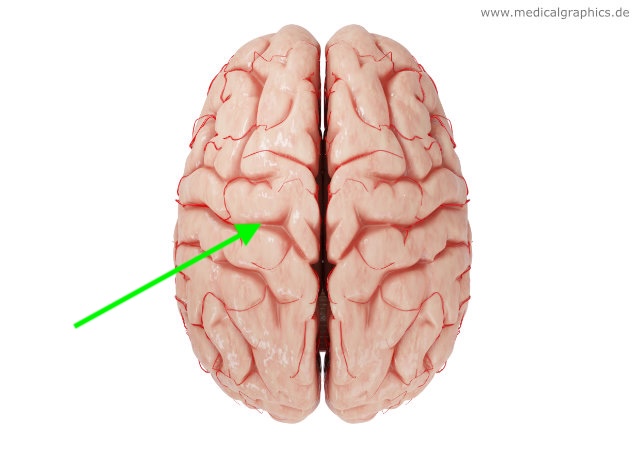
what hemisphere is this?
left hemisphere
what plane is this?
coronal
what plane is this?
sagittal
light matter
Axons
inner parts of the cortex
traveling towards the cortex and away to the sub cortex, traveling through the axon bundles
axon tractography
Visualize axon travel in white matter
Diagnose conditions that cause miswiring of axons
grey matter
cell bodies
Outer parts of the cortex
nissl stain
Stains brain nuclei purple
nuclei (in this contex)
collection of cell bodies
gyri
bumps and big folds
sulci
grooves
fissure
big grooves
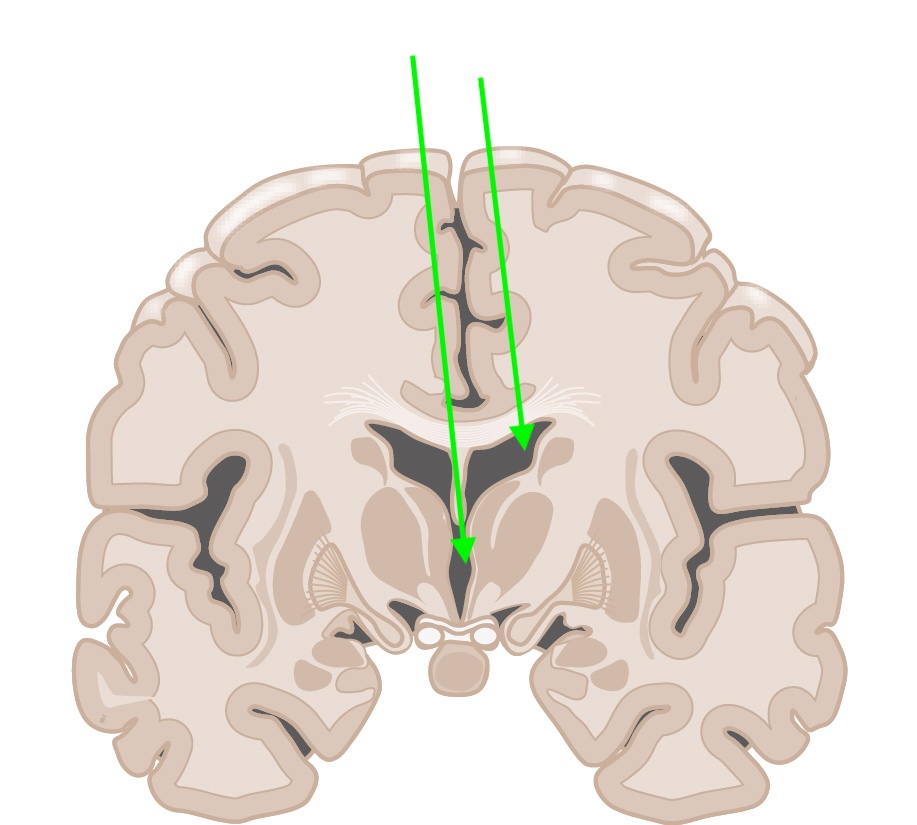
what are these?
ventricles
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
removes metabolic waste and maintains composition of extracellular fluid
Flows through waves in sleep
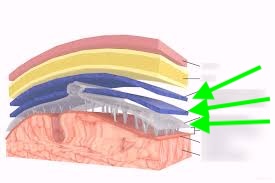
what are these?
meninges
meninges
Layers between skin, bone, and brain
Protect the brain from physical trauma
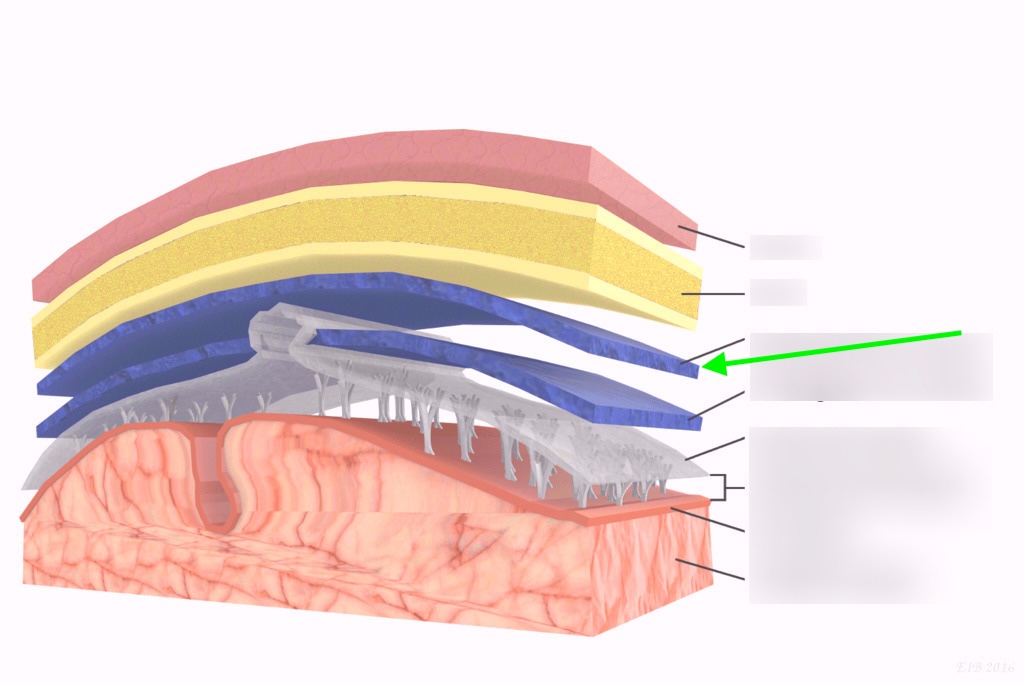
what layer is this?
dura mater
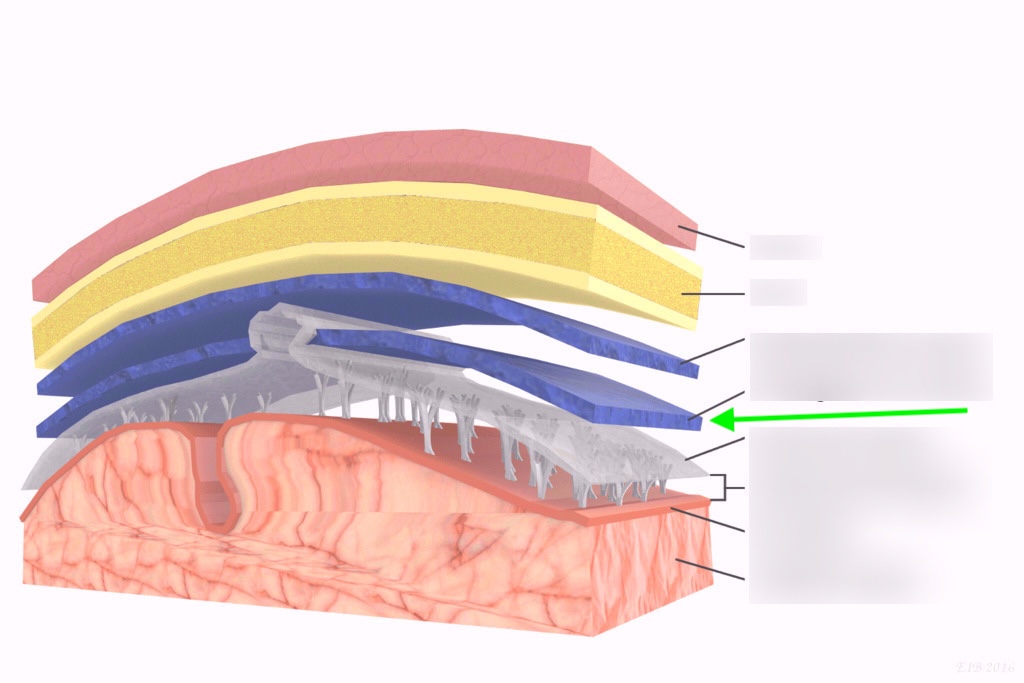
what layer is this?
arachnoid
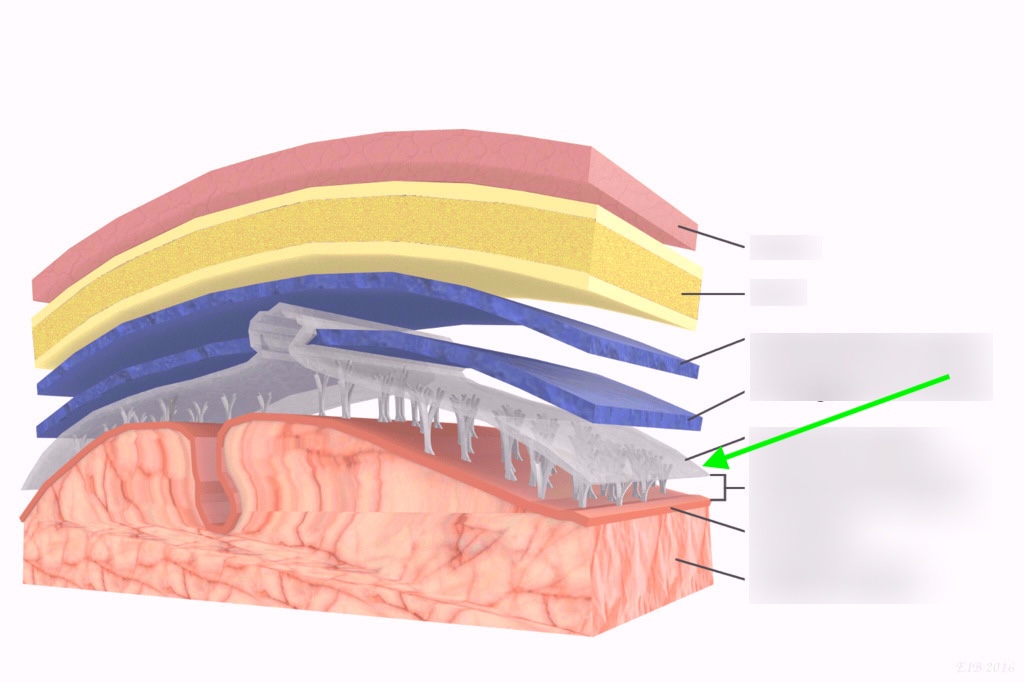
what layer is this?
pia mater
central nervous system covers the ___
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system covers ____
all nervous tissue outside of the spinal cord and brain
parasympathetic nervous system
calming, stimulates digestive function
sympathetic nervous system
fight/flight response, inhibits digestion, elevating HR
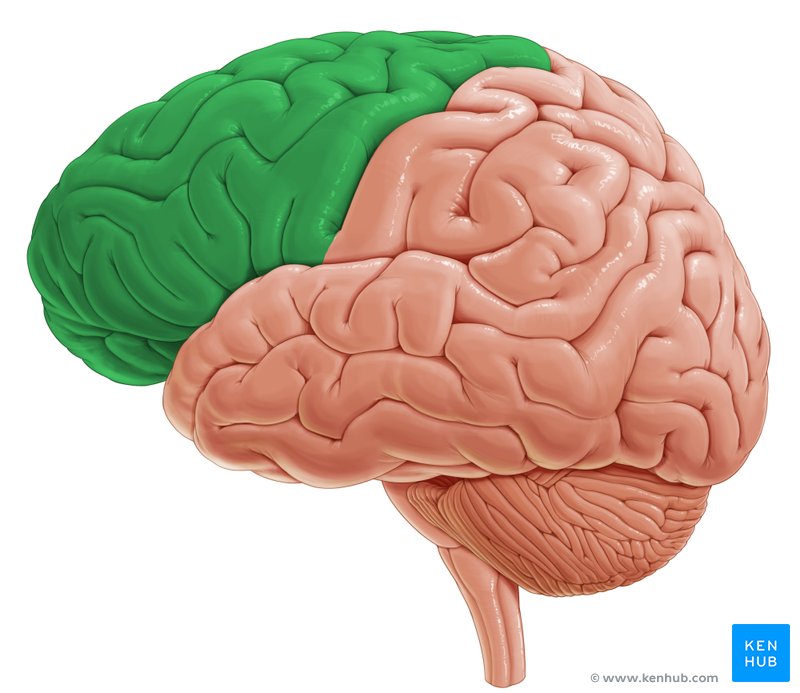
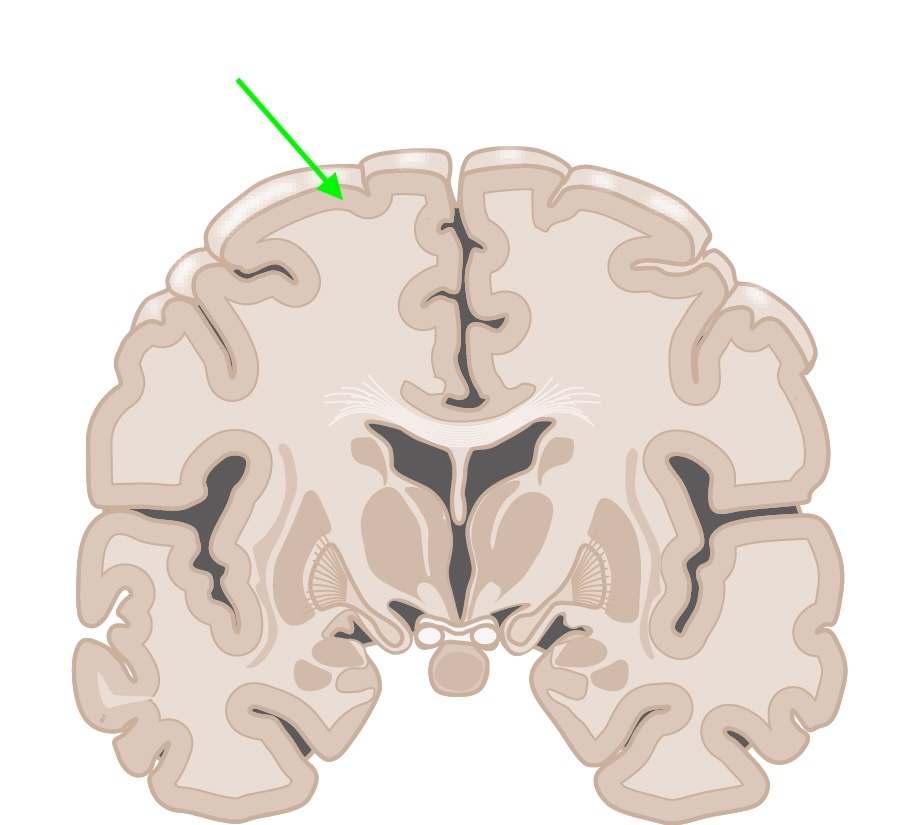
what brain area is this?
frontal lobe

what brain area is this?
precentral gyrus
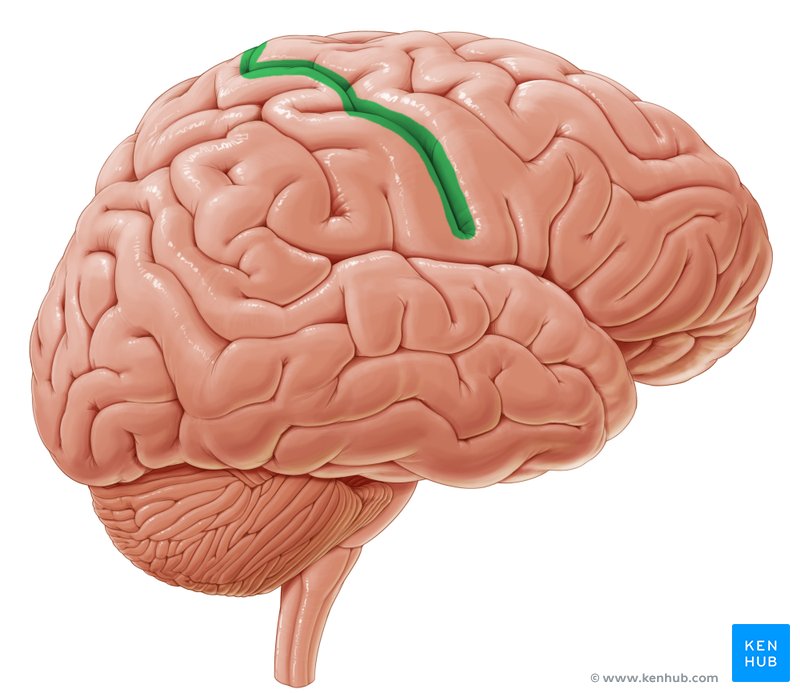
what brain area is this?
central sulcus
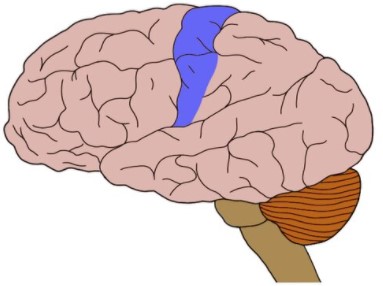
what brain area is this?
primary somatosensory cortex

what brain area is this?
post central gyrus
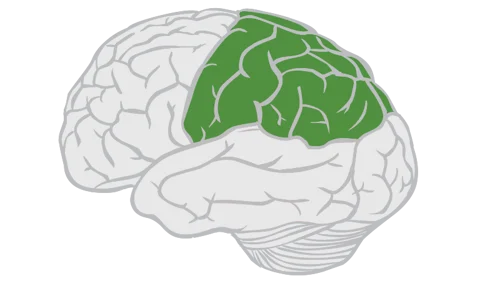
what brain area is this?
parietal lobe
parietal lobe function
integrating sensory and motor functions
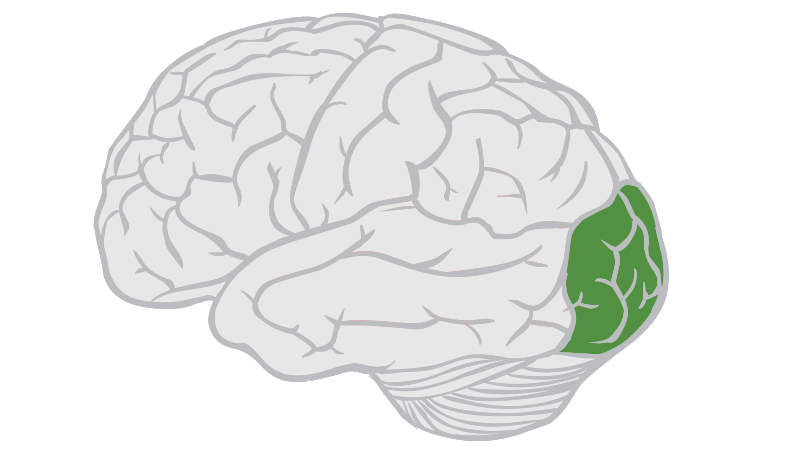
what brain area is this?
occipital lobe
occipital lobe function
vision
wernicke’s area function
language and comprehension
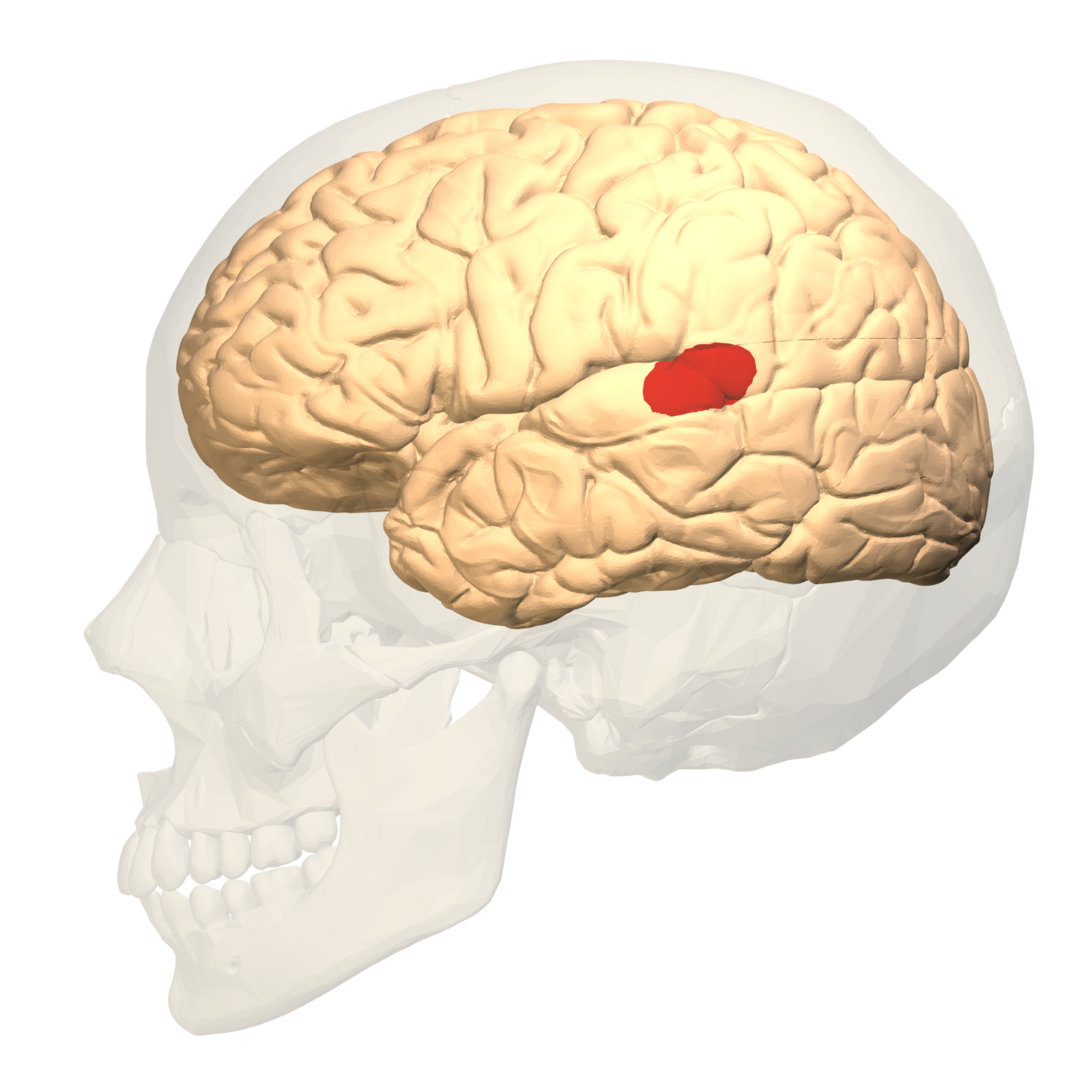
what brain area is this?
wernicke’s area
cerebellum function
motor functions, coordination, and learning
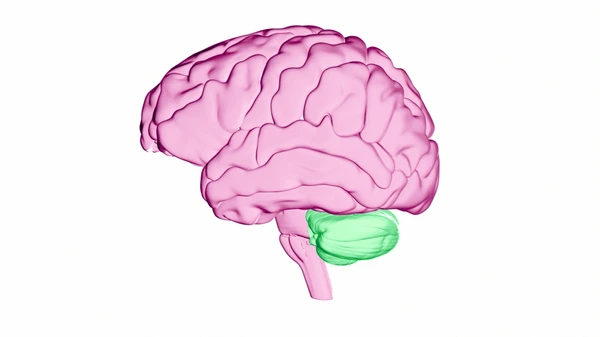
what brain area is this?
cerebellum
primary auditory cortex function
hearing
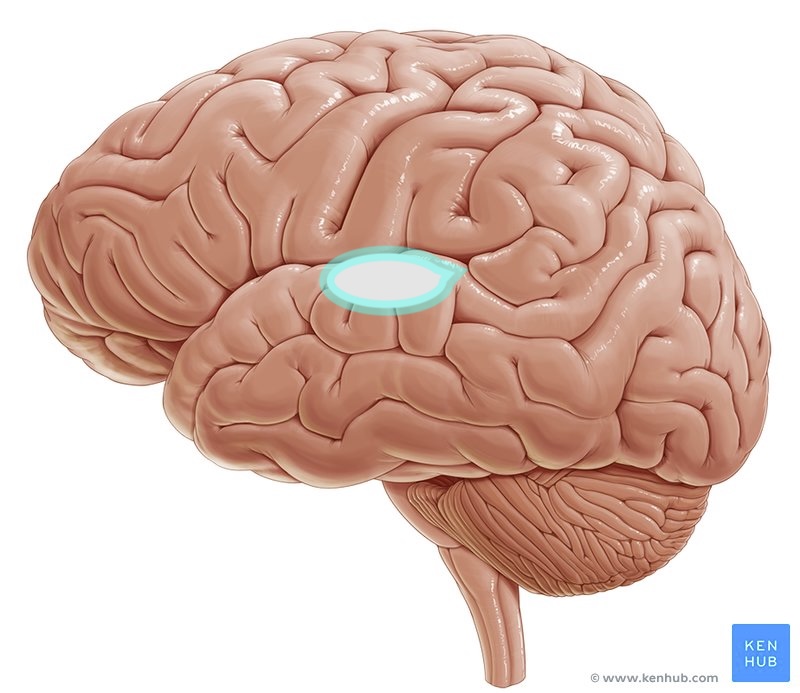
what brain area is this?
primary auditory cortex
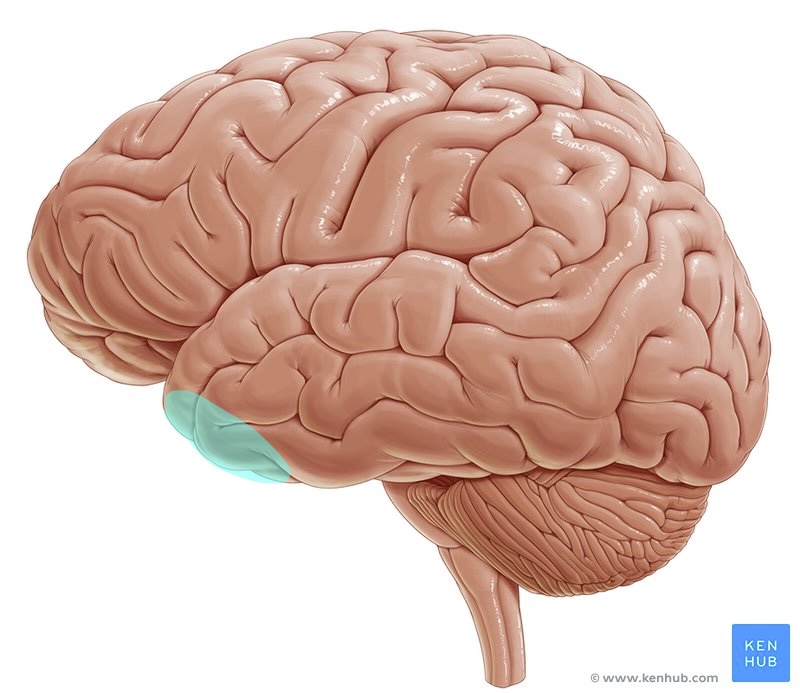
what brain area is this?
limbic association cortex
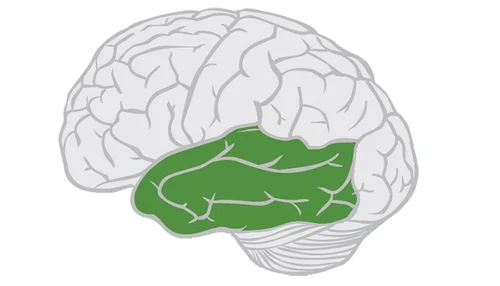
what brain area is this?
temporal lobe
olfactory cortex function
smell
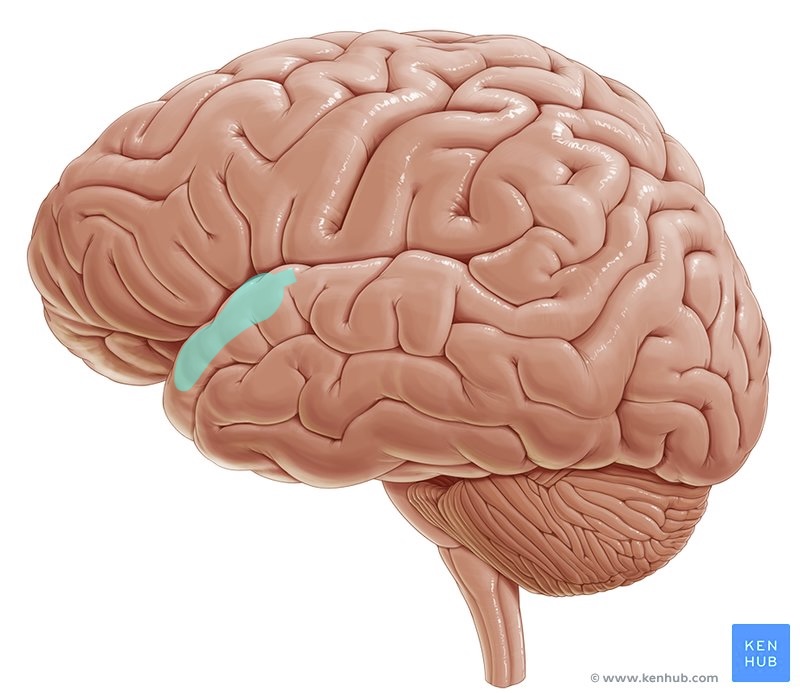
what brain area is this?
olfactory cortex
broca’s area function
speech
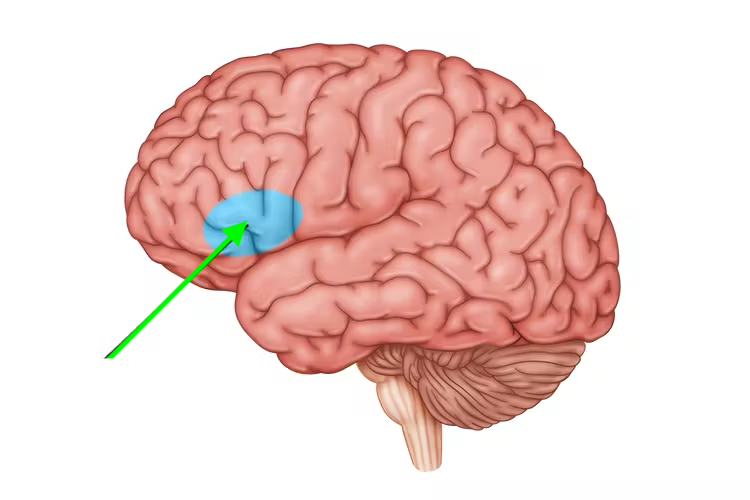
what brain area is this?
broca’s area
prefrontal cortex function
executive functioning
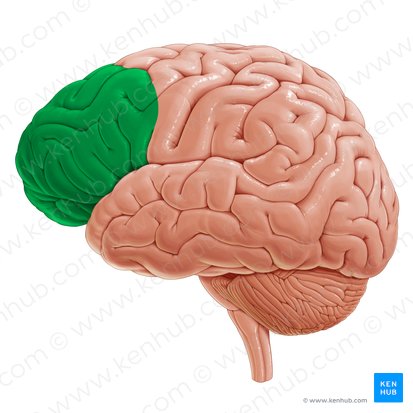
what brain area is this?
prefrontal cortex
corpus callosum function
fiber tract that connects the 2 hemispheres of the brain, made up of bundles of axons
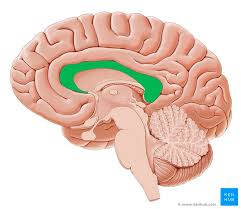
what brain area is this?
corpus callosum
hypothalamus function
regulates autonomic functions: BP, pupil dilation, arousal, hunger, thirst
responsible for hormone production and release
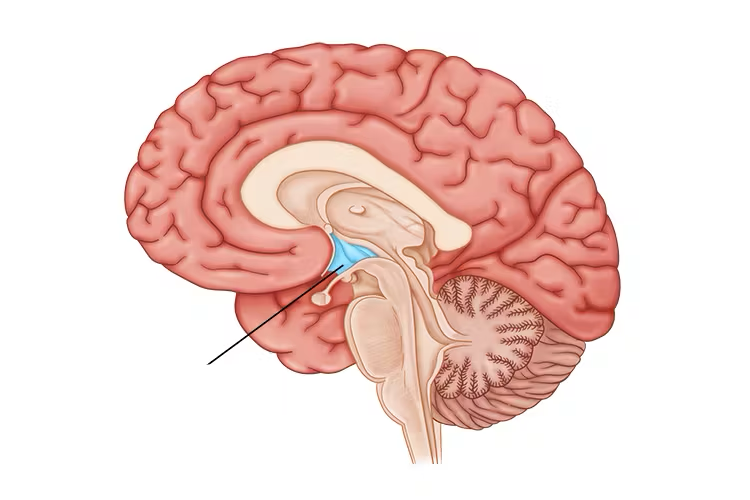
what brain area is this?
hypothalamus
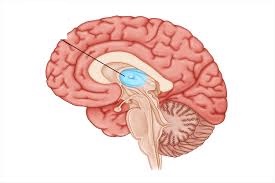
what brain area is this?
thalamus
thalamus function
Routes, combines, and processes signals from all across the CC and subcortical structures (hub)
Performs computations
what brain area is this?
spinal cord
spinal cord function
Transmits and receives signals from the PNS
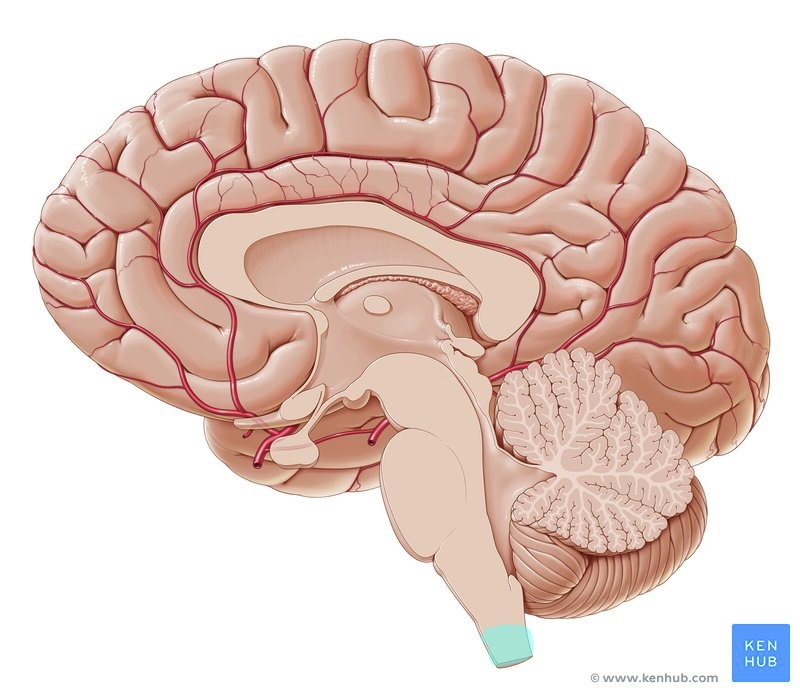
what brain area is this?
midbrain
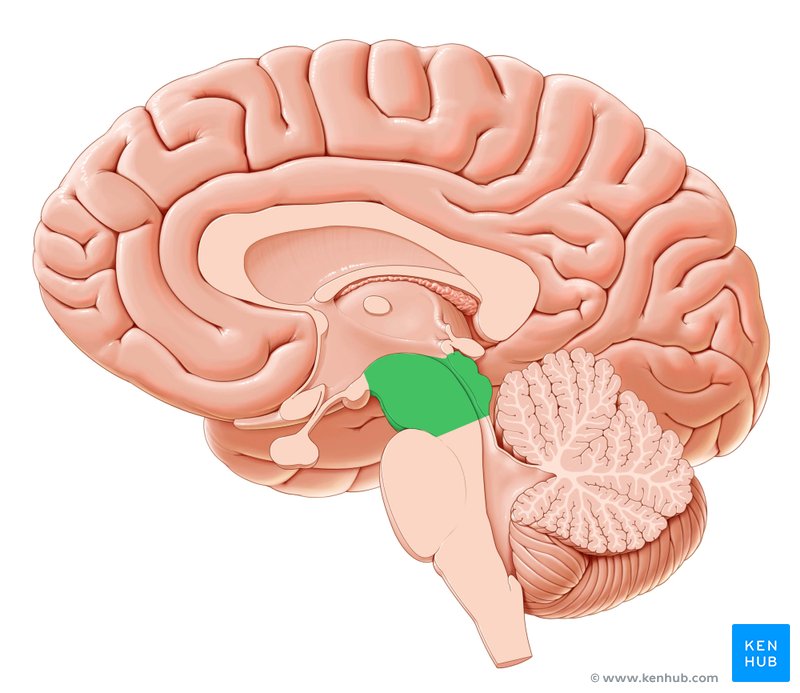
what brain area is this?
pons
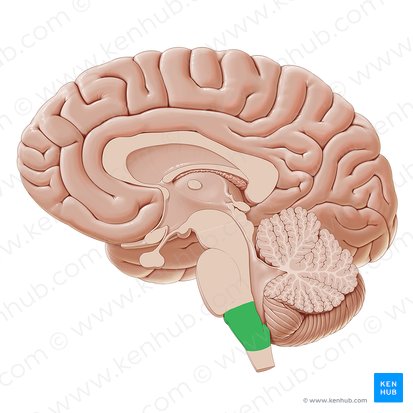
what brain area is this?
medulla
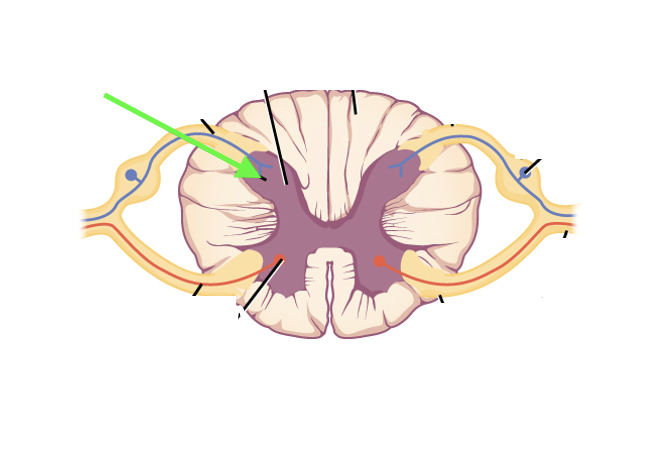
what spinal cord area is this?
dorsal horn
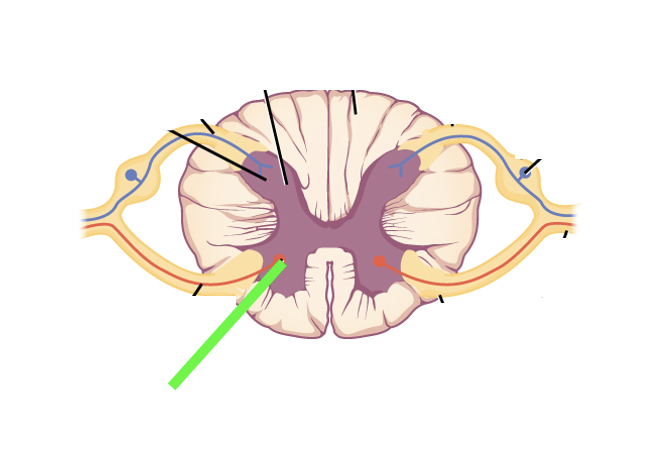
what spinal cord area is this?
ventral horn
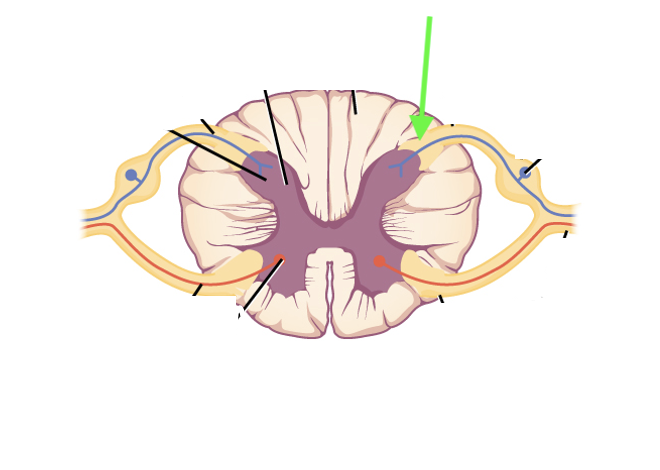
what spinal cord area is this?
dorsal root
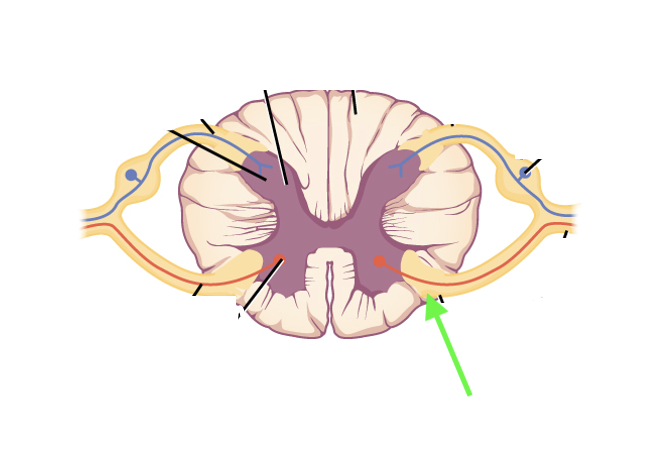
what spinal cord area is this?
ventral root
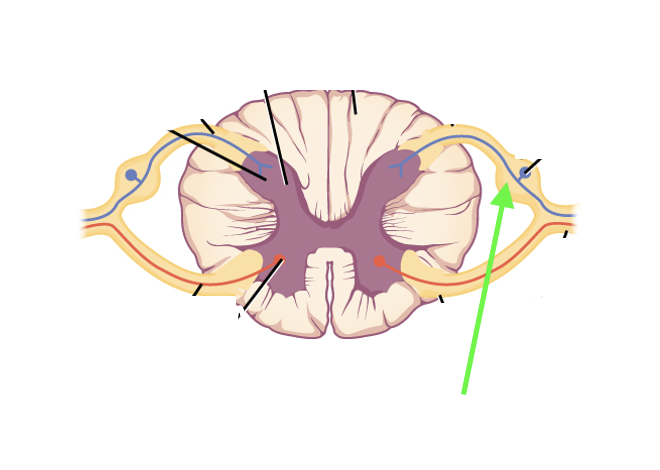
what spinal cord area is this?
dorsal root ganglion
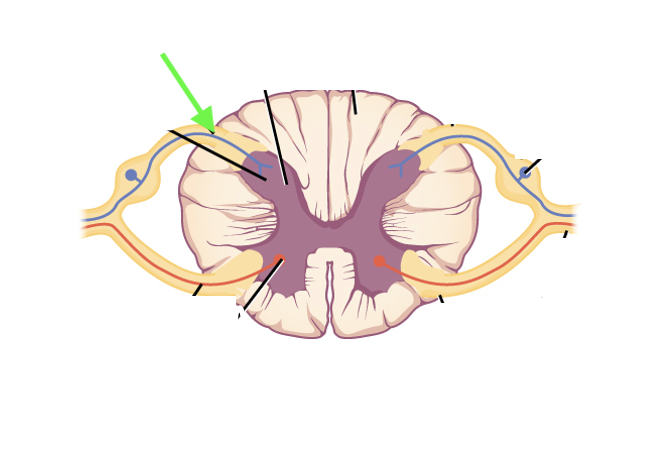
what spinal cord area is this?
sensory neuron
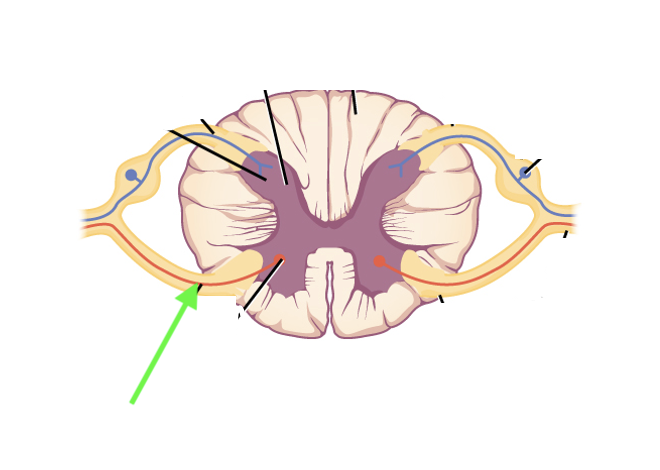
what spinal cord area is this?
motor neuron
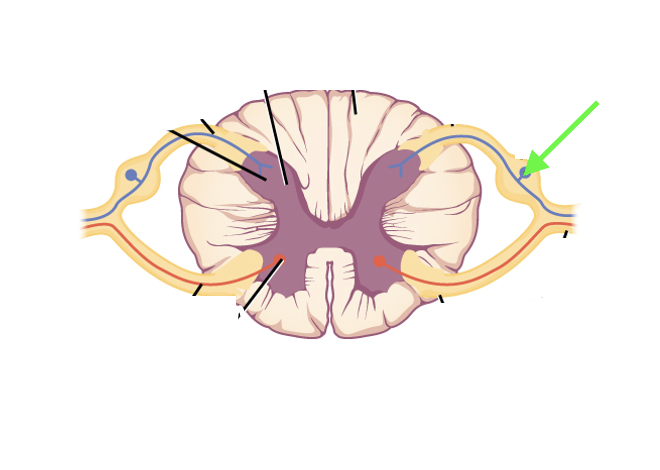
what spinal cord area is this?
sensory neuron soma
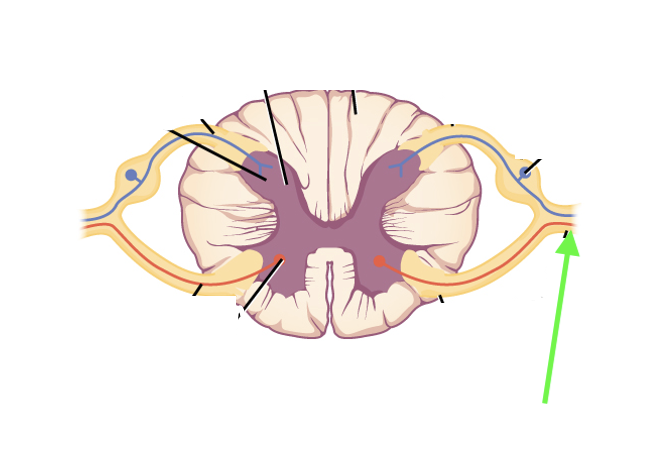
what spinal cord area is this?
spinal nerve
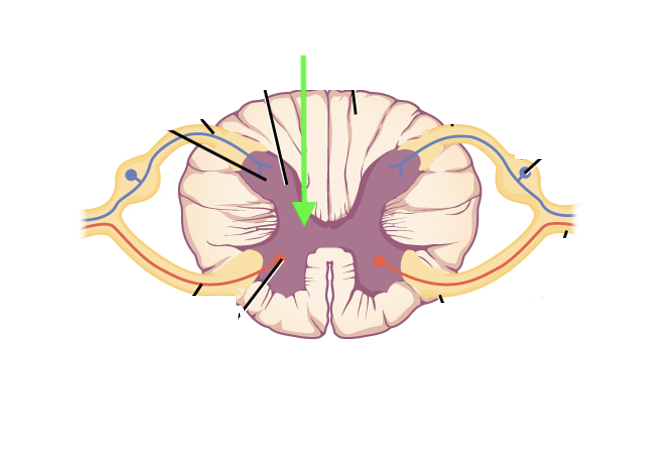
what spinal cord area is this?
gray matter
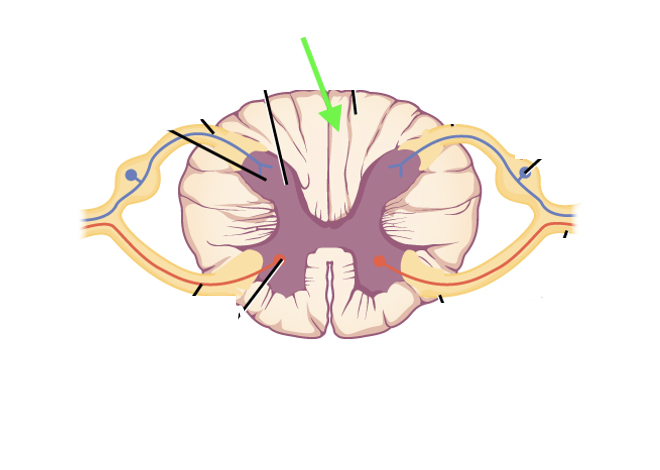
what spinal cord area is this?
white matter
contralateral
opposite side
ipsilateral
same side
spinal cord levels
cervical, thoratic, lumbar, sacral
cervical
head, neck, hands
thoratic
Abdominal muscles, chest muscles
lumbar
Leg muscles
sacral
Bowel, bladder, balance
MRI is ________ and safe under most conditions.
noninvasive
The resolution of an MRI is approximately
1 mm
One voxel (3D pixel) in MRI contains ________ to ________ neurons.
hundreds, thousands
MRI allows us to see general brain structures but cannot show ________ potentials or specific ________ types.
action, cell
Neuroradiology is used to locate precise ________ for neurosurgical implants.
coordinates
White matter consists primarily of ________.
axons
White matter is found in the ________ parts of the cortex.
inner
Grey matter consists primarily of ________.
cell bodies
Axon tractography can diagnose conditions that cause ________ of axons.
miswiring
Axon tractography is used to visualize ________ travel in white matter.
axon
Humans have the highest degree of ________ in the cerebral cortex.
folding
The ventricles circulate ________ fluid.
cerebrospinal
CSF removes ________ waste and maintains extracellular composition.
metabolic
The ________ plexus produces CSF.
choroid
Axons in the periphery enter the spinal cord through the ________ nerve and ________ root.
spinal, dorsal
Axons controlling muscles exit the spinal cord through the ________ root.
ventral