Chapter Four: Epithelial Tissue
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Epithelium
A sheet of cells that cover a body surface or lines a body cavity
Covering and Lining Epithelium
Covers the outer and inner surfaces of most body organs
Glandular Epithelium
Forms most of the body glands
Functions of Epithelia
Protection of the underlying tissues, secretion, absorption, diffusion, filtration, sensory reception
Cellularity
Epithelia are composed almost entirely of cells. They are separated by a minimal amount of extracellular material, mainly projections of their integral membrane proteins into the narrow spaces between the cells
Specialized Cell Junctions
Adjacent epithelial cells are directly joined at many points
Polarity
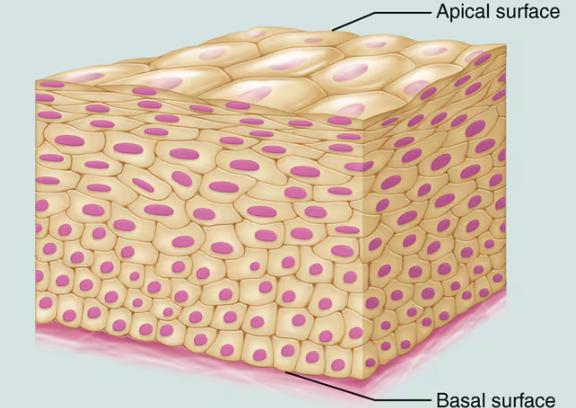
All epithelia have a free apical surface and an attached basal surface
Apical Surface
Abuts the open space of a cavity, tubule, gland, or hollow organ
Basal Surface
Lies on a thin supporting sheet (basal lamina) which is part of the basement membrane
Support by Connective Tissue
All epithelial sheets in the body are supported by an underlying layer of this tissue
Avascular but Innervated
Epithelial cells lack blood vessels and receive nutrients from capillaries in the underlying connective tissue. Nerve endings do penetrate epithelial sheets.
Regeneration
Epithelial tissue has a high capacity of this due to some exposure to friction and the surface cells rub off
Simple and Stratified
Describes the number of cell layers in an epithelium
Simple Epithelia
Contain a single layer of cells, which each cell attached to the basement membrane
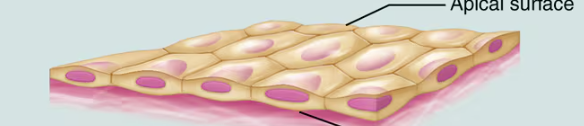
Stratified Epithelia
Contain more than one layer of cells. The cells on the basal surface are attached to the basement membrane; those on the apical surface border an open surface. Cell shape of this type is named according to the shape of the cells in the apical layer
Squamous, Cuboidal, or Columnar
Describes cell shape and refers to the appearance of the cells in section
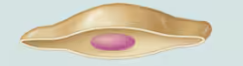
Squamous Cells
Flat cells with flat, disc-shaped nuclei
Cuboidal Cells
Cube-shaped cells with spherical, centrally located nuclei

Columnar Cells
Taller than they are wide, like columns. The nuclei are located near the basal surface and are commonly oval in shape, elongated from top to bottom

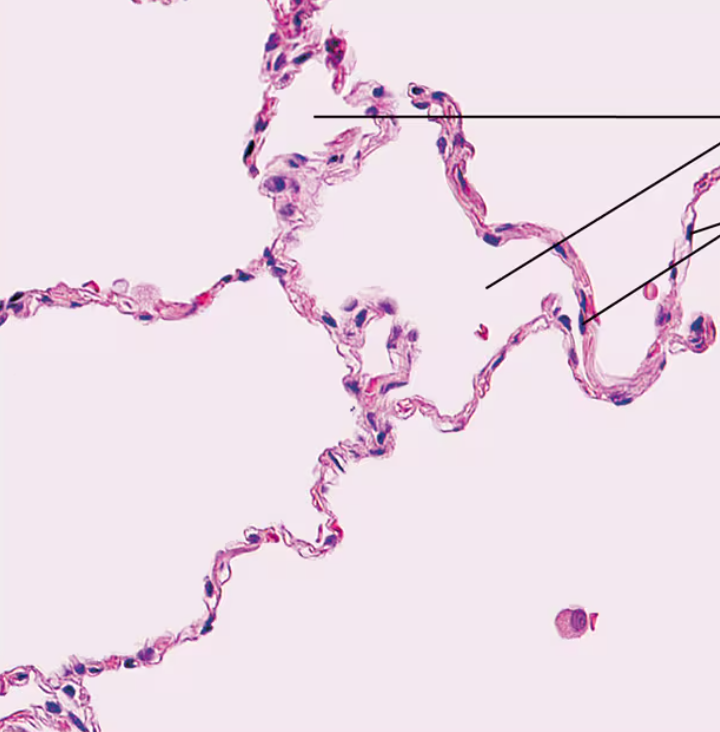
Simple Squamous Epithelium Description
Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm
Simple Squamous Epithelium Function
Allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae (lining of ventral body cavity)
Simple Squamous Epithelium Location
Kidney glomeruli; air sacs of lungs; lining of heart; blood vessels; and lymphatic vessels; serosae
Simple Squamous Epithelium Photomicrograph
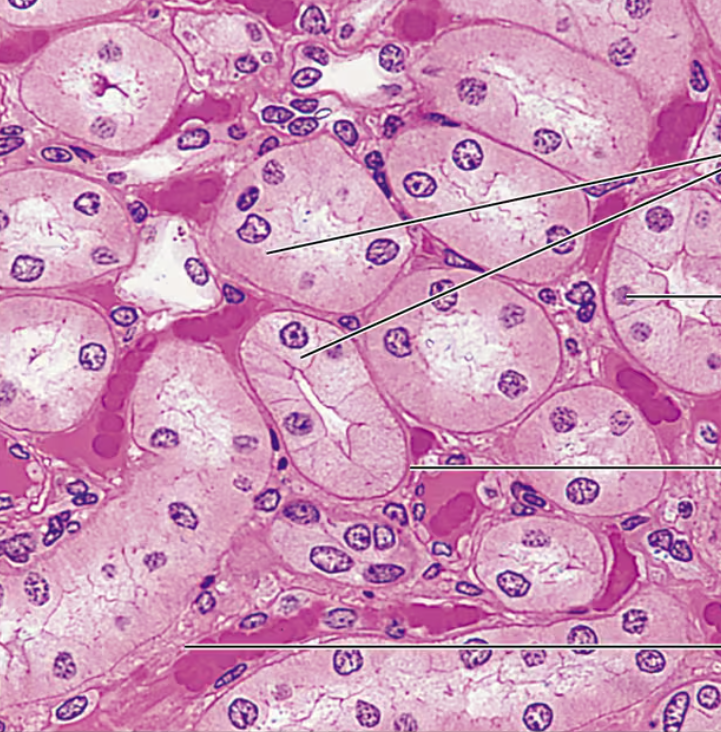
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Description
Single layer of cube like cells with large, spherical central nuclei
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Function
Secretion and absorption
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Location
Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Photomicrograph
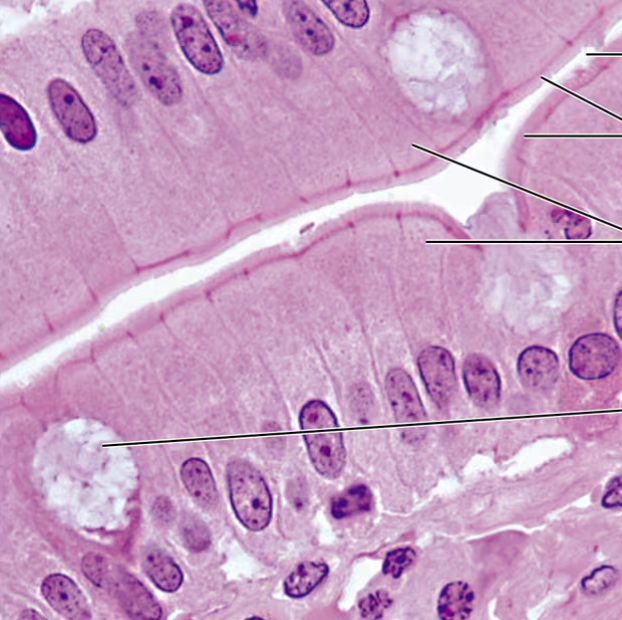
Simple Columnar Epithelium Description
Single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; many cells bear microvilli, some bear cilia; layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands (goblet cells)
Simple Columnar Epithelium Function
Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliary action
Simple Columnar Epithelium Location
Nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to rectum), gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
Simple Columnar Epithelium Photomicrograph
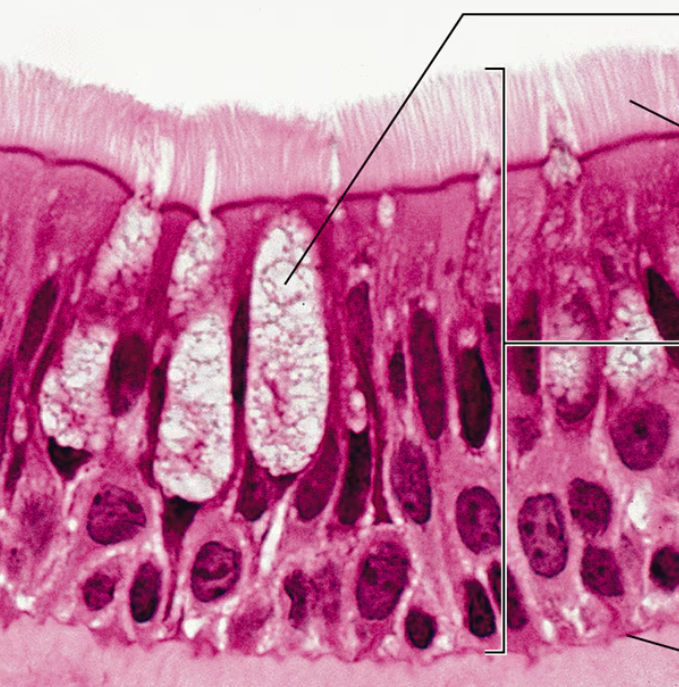
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Description
Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface; nuclei seen at different levels; may contain mucus-secreting cells and bear cilia
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Function
Secrete substances, particularly mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Location
Ciliated variety lines the trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract; no ciliated type in males’ sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Photomicrograph
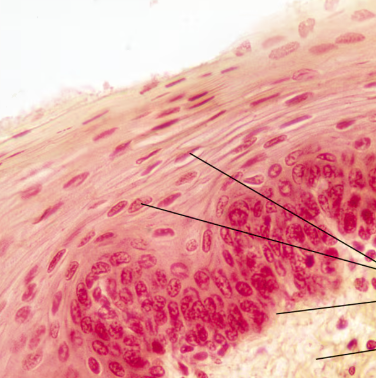
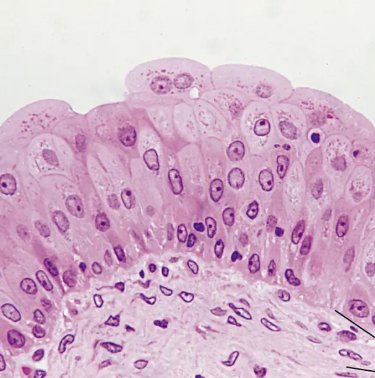
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Description
Thick epithelium composed of several cell layers; basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active; surface cells are squamous; in the keratinized type, the surface cells are full of keratin and dead; basal cells are active in mitosis and produce the cells of the more superficial layers
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Function
Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Location
Nonkeratinized type forms the moist linings of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina; keratinized variety forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Photomicrograph
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Description
Generally two layers of cube like cells
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Function
Protection
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Location
Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Photomicrograph
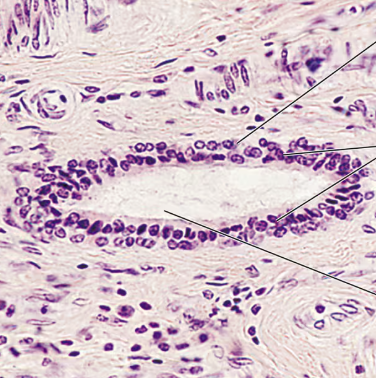
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Description
Several cell layers; basal cells usually cuboidal; superficial cells elongated and columnar
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Function
Protection and Secretion
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Location
Small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Photomicrograph
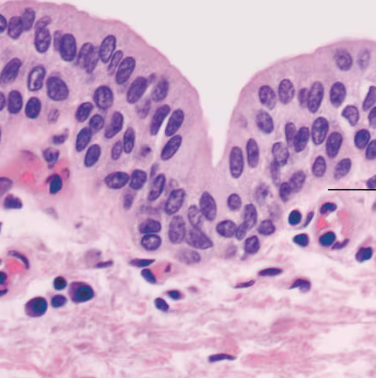
Transitional Epithelium Description
Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal or columnar; surface cells doomed shaped or squamous-like, depending on degree of organ stretch
Transitional Epithelium Function
Stretches readily, permits stored urine to distend urinary organ
Transitional Epithelium Location
Lines the uterus, bladder, and part of the urethra
Transitional Epithelium Photomicrograph
Glands
A structure whose cells are specialized for secretion. They secrete aqueous (water-based) fluids that usually contain proteins
Secretion
The process whereby gland cells obtain needed substances from the blood and transform them chemically into a product that is then discharged from the cell
Endocrine Glands
Lack ducts and are often referred to as ductless glands. They secrete directly into the tissue fluid that surrounds them. They produce hormones which they release into the extracellular space
Hormones
Messenger molecules that are released by endocrine glands and travel in the blood to regulate specific body functions. They enter capillaries and travel through the bloodstream to specific target organs, which are far removed from the endocrine gland that produces them.
Exocrine Glands
Numerous and many of their products are familiar ones. They secrete their products onto body surfaces (skin) or into body cavities. Multicellular glands have ducts that carry product to the epithelial surfaces. Any activity Is local and is a diverse group. Includes sweat glands, oil glands, salivary glands, the liver, pancreas, mammary glands, etc.
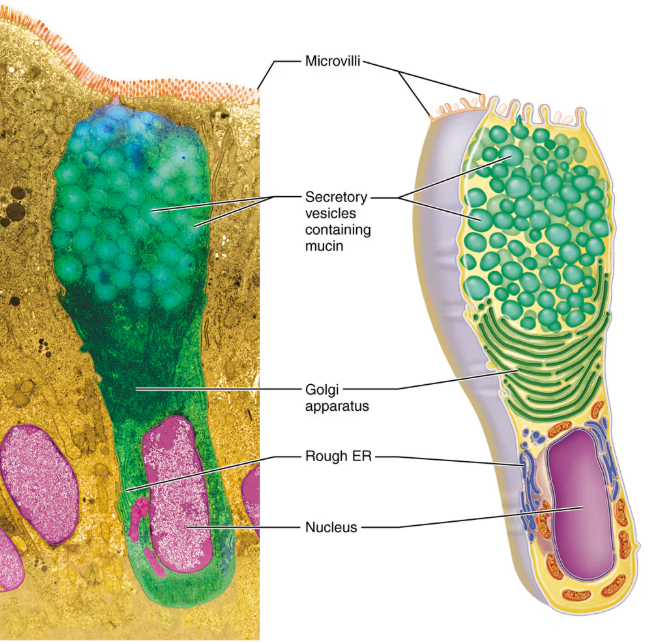
Goblet Cell
The only major one-celled exocrine gland. They are scattered within the epithelial lining of the intestines and respiratory tubes. They produce mucin and mucus.
Globet Cell Diagram
Multicellular Exocrine Glands
Have two basic parts consisting of an epitehlium-walled duct and a secretory unit consisting of the secretory epithelium
Simple Tubular Gland
Duct does not branch and secretory structure is tubular in nature
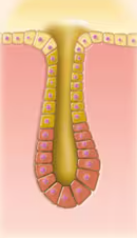
Simple Branched Tubular
Duct does not branch and secretory structure is tubular in nature
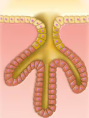
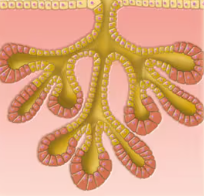
Compound Tubular
Duct branches and tubular secretory structure
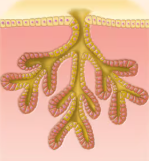
Simple Alveolar
Duct does not branch and alveolar secretory strucure
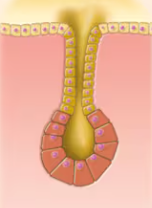
Simple Branched Alveolar
Duct does not branch and alveolar secretory structure
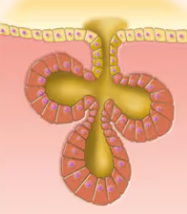
Compound Alveolar
Duct branches and alveolar secretory structure
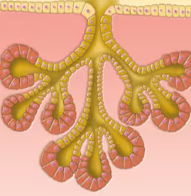
Compound Tubuloalveolar
Duct branches and both tubular and alveolar secretory structures
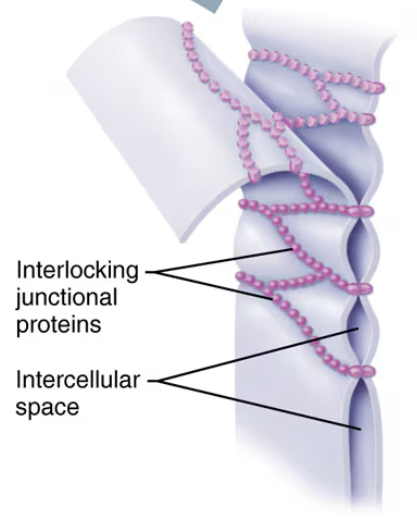
Factors that act to bind epithelial cells to one another
Adhesion proteins in the plasma membranes of the adjacent cells link together in the narrow extracellular space
The wavy contours of the membranes of adjacent cells join in a tongue-and-groove fashion
Special Cell Junctions
Cell Junctions
Crucial structures that bind epithelial cells together, ensuring the integrity and function of tissues. Has three main types.
Tight Junction
Impermeable junctions prevent molecules from passing through the intercellular space
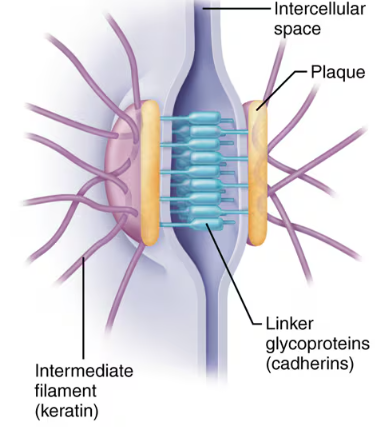
Desmosomes
Also known as anchoring junctions. Bind adjacent cells together and help form an internal tension-reducing network of fibers. Linker glycoproteins (cadherins) just out from each cell membrane and interdigitize like a zipper so that if one cell gets pulled, it won’t easily detach.
Gap Junctions
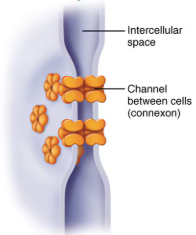
Communicating junctions allow ions and small molecules to pass from one cell to the next for intercellular communication
Basal Lamina Structure
At the border between the epithelium and the connective tissue. It is a thin, noncellular sheet consisted of proteins secreted by the epithelial cells
Basal Lamina Function
Acts as a selective filter determining which molecules from capillaries in the underlying connective tissue are allowed to enter the epithelium. Acts as scaffolding along which regenerating epithelial cells can migrate
Basal Membrane
Made up of reticular fibers directly deep to the bassal lamina and the basal lamina itself
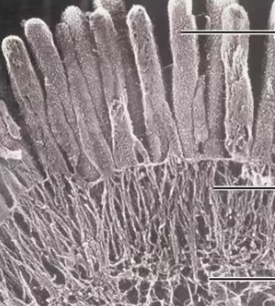
Microvilli
Fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane of apical epithelial cells. Contain a core of actin filaments that extend into the network of actin microfilaments of the cytoskeleton which stiffen the extensions. Maximize the surface area on the surface of the cell
Cilia
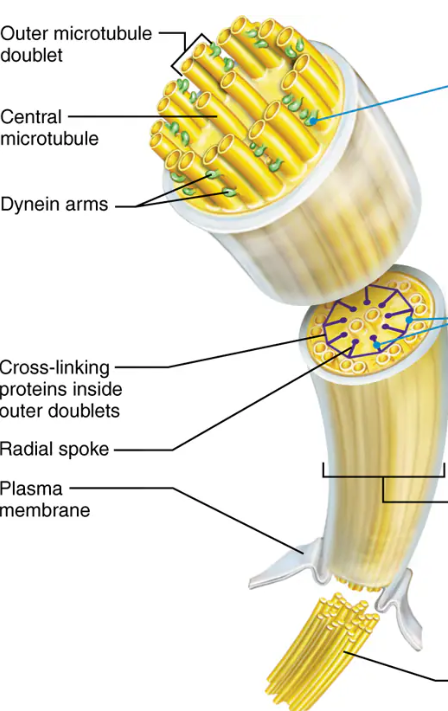
Whiplike, highly motile extensions of the apical surface membranes of certain epithelial cells. Each one contains a core of microtubules held together by cross-linking and radical proteins. Movement is generated when adjacent doublets grip one another with side arms made of dynein and the arms start to oscillate
Basal Body
Centriole at the base of each cilium