L3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Book keeping
=accounting system where every financial transaction is recorded in at least two accounts:
1- Debit
2-Credit
Principles
1-every transaction has two entries
2-debits=credits
3-based on the accounting equation
4-debit & credit rules by account type
5-every transaction tells a story
6-balance accumulates over time
7-trial balance confirms accuracy
1-every transaction has two entries
one debit & one credit
2-Debits = credits
must match on each side to keep the books balanced
3-Based on the Accounting equation
Assets = Equity + Liabilities
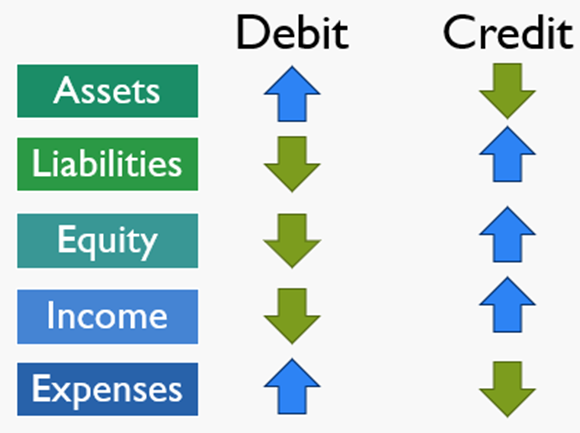
4-Debit & Credit rules by account type
DEAD CLIC
Debit: Expenses, Assets, Drawings
Credit: Liabilities, Income, Capital
5-Every transaction tells a story
What accounts effected, increase/decrease, debited/credited
6-Balances accumulate over time
Real accounts= assets, liabilities, equity accounts (balances carry forward) Nominal accounts= income, expense accounts (close to equity at year-end)
7-The trial balance confirms accuracy
if debits & credits recorded accurately, sum of both sides will agree
elements of financial statements & bookkeeping
Assets = Liabilities + Income – Expenses
A = L + OE
A = L + SC + RE + (I-E) – D
Key
Sc= shared capital
RE= retained earnings beginning
I= income
E= expenses
D= dividends paid
The Quadrant
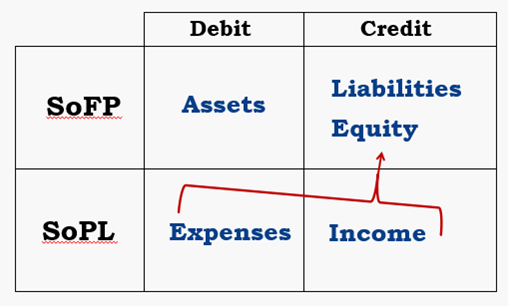
every transaction must have opposite and equal impacts
Accounting ledger
=book/collection of accounts to record financial transactions
set outs include: leger account, t account
ledger account
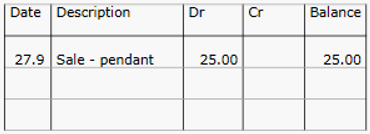
example of setout

T account

example of setout
-simpler version of a ledger account