bruh howd i forgot to make flashcards for this
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
receptive aphasia
damage to Wernickes area
uable to understand sensory input
expressive aphasia
damage to Broca’s area
unable to understand complicated sentences, diffuculy speaking or writing
global aphasia
receptive and expressive
beta rhythm
alert
alpha rhythm
relax with eyes closed
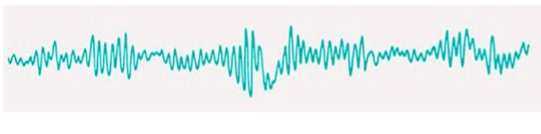
what properties of wave changes when we get sleepy in EEG
waves become lower fequency and larger amplitude
2 phases of sleep
NREM (non-rapid eye movement) N1, N2, N3
REM (rapid eye movement)
Stage N1
NREM: theta waves appear in alpha pattern (light sleep)

Stage N2
NREM
theta waves, sleep spindles, K complexes
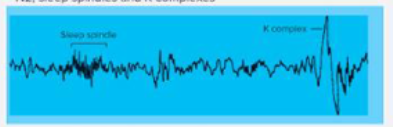
Stage N3
NREM (slow wave or deep sleep)
delta waves

how does sleep start
progresson of N1 to N2
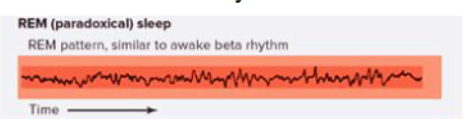
paradoxical sleep
in REM because it is hard to wake up
but the EEG avtivity similar to alert/awake (beta)
what happens in REM
paradoxical sleep and dreaming
T or F: each episode of REM gets longer per sleep
true
cycle of sleep
N1, N2, N3, N2, REM, N2
what does sleep deprivation do
impair immune
causes cognitive and memory deficits
leads to psychosis and death
2 types of emotion
internal attitude toward environment (happy/sad)
external responses (emotional behaviour)
primary motivated behaviour
directly related to homeostasis
secondary motivated behaviour
pleasure or addictive behaviours
reward and punishment are ____ from motivation
inseparable
mesolimbic and mesocortical dopamine paths
part of reticular activating system involving motivation, reward and punishment
how do mesolimbic and mesocortical dopamine pathways work
begin in midbrain and release dopamine to areas that process information
forebrain structures in emotional response
cerebral cortex
modulate, direct, interpret, and inhibit emotional behaviours
limbic areas in emotional responses
inner emotions
amygdala
lateral hypothalamus in emotionla responses
aggressive and defensive behaviours including rage