Lab Mid Term
1/245
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
246 Terms
How to stand in an anatomical position?
standing straight, feet slightly apart, head and toes pointed forward, arms at the sides, and palm facing forward
Superior/Inferior
above/below
Anterior/Posterior
front/back
Ventral/Dorsal
belly side/backside
Medial/Lateral
toward midline/away from midline
Proximal/DIstal
closer to trunk or attachment/farther from trunk or point of attachment
Cephalic(Cranial)/Caudal
toward the head/toward the tail
Superficial/Deep
toward the body surface/away from the body surface
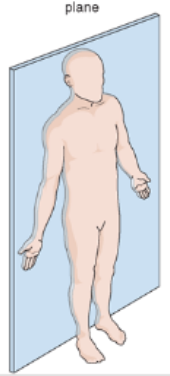
What Body Plane is this?
Frontal Plane
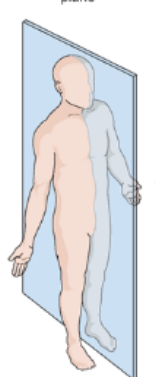
What body plane is this?
Sagittal Plane
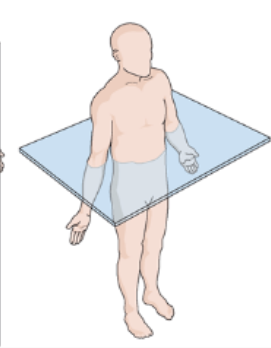
What body plane is this?
Transverse Plane
Dorsal Body Cavity subdivisions
cranial cavity and vertebral (spinal) cavity
Organs found in cranial cavity
skull - encases the brain
Organs found in the vertebral(spinal) cavity
vertebral column and encloses the spinal cord
Ventral Body Cavity subdivisions
Thoracic Cavity and Abdominopelvic Cavity
Organs found in the thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs (protected by the ribs)
Organs found in the abdominopelvic cavity
reproductive system, stomach, intestines
Two areas found in the abdominopelvic cavity and the organs
abdominal cavity (stomach, intestines, liver, etc.) and pelvic cavity (reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum)
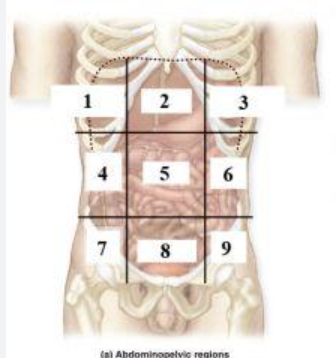
What is 1?
right hypochondriac region
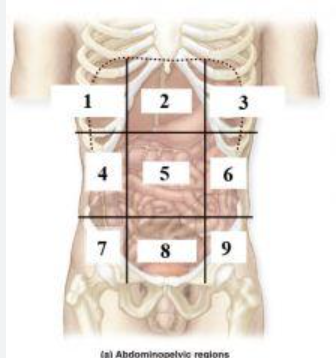
What is 2?
Epigastric region
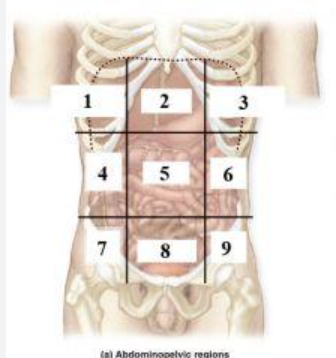
What is 3?
left hypochondriac region
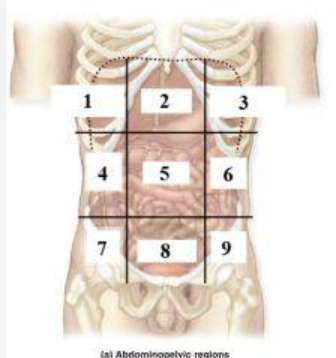
What is 4?
right lumbar region
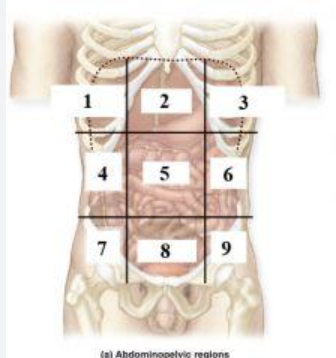
What is 5?
Umbilical regioin
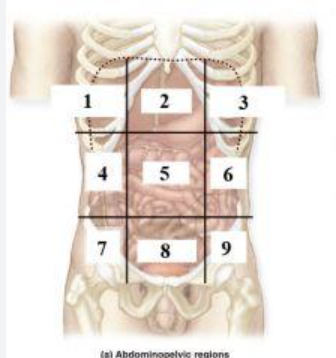
What is 6?
Left lumbar region
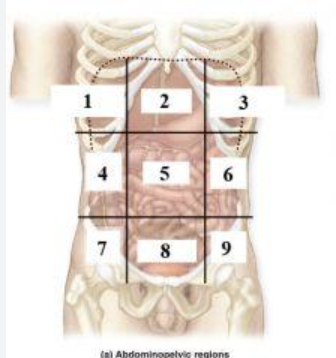
What is 7?
right inguinal (iliac) region
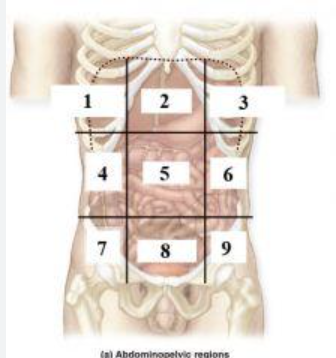
What is 8?
Hypogastric region
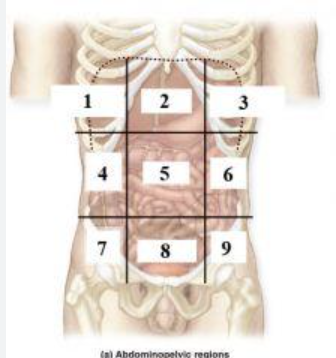
What is 9?
Left inguinal (iliac) region
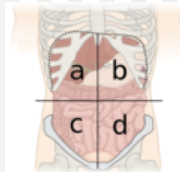
What is A?
right upper quadrant
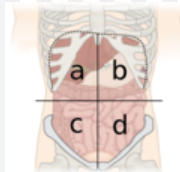
What is B?
left upper quadrant
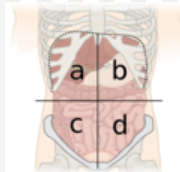
What is C?
right lower quadrant
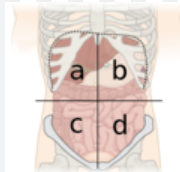
What is D?
left lower quadrant
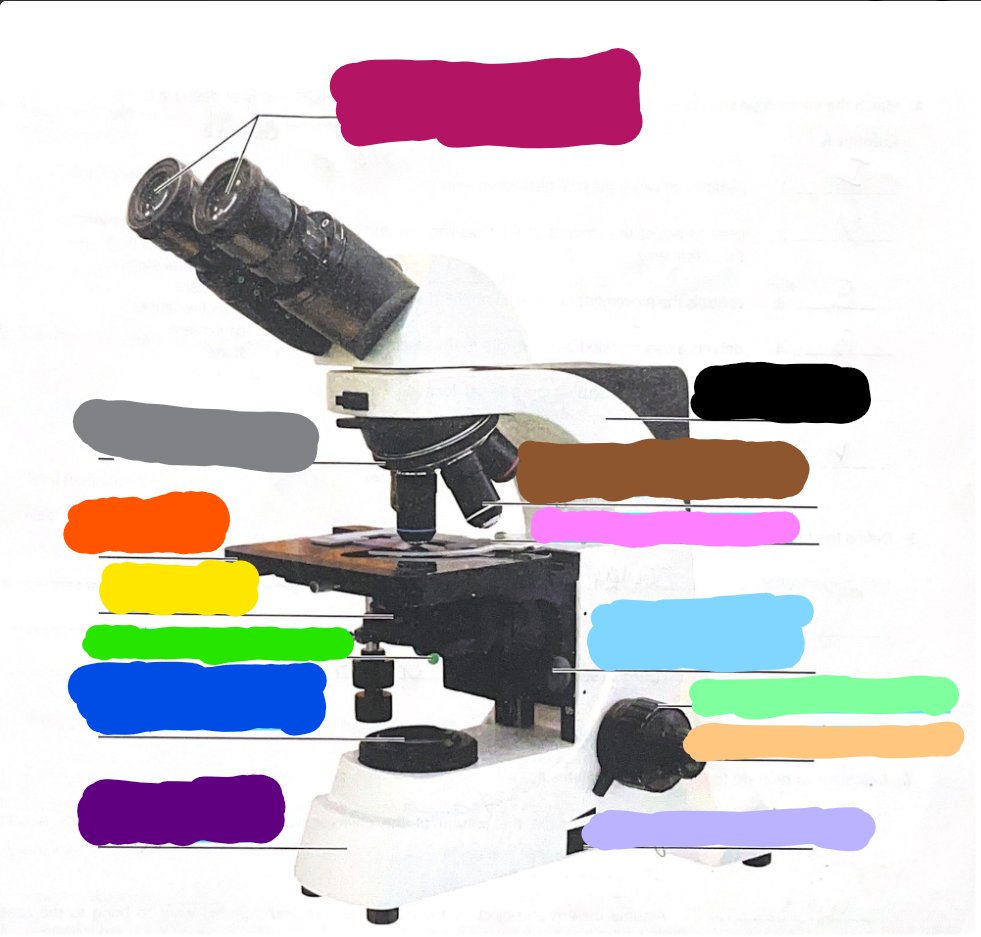

Dark Purple
Base
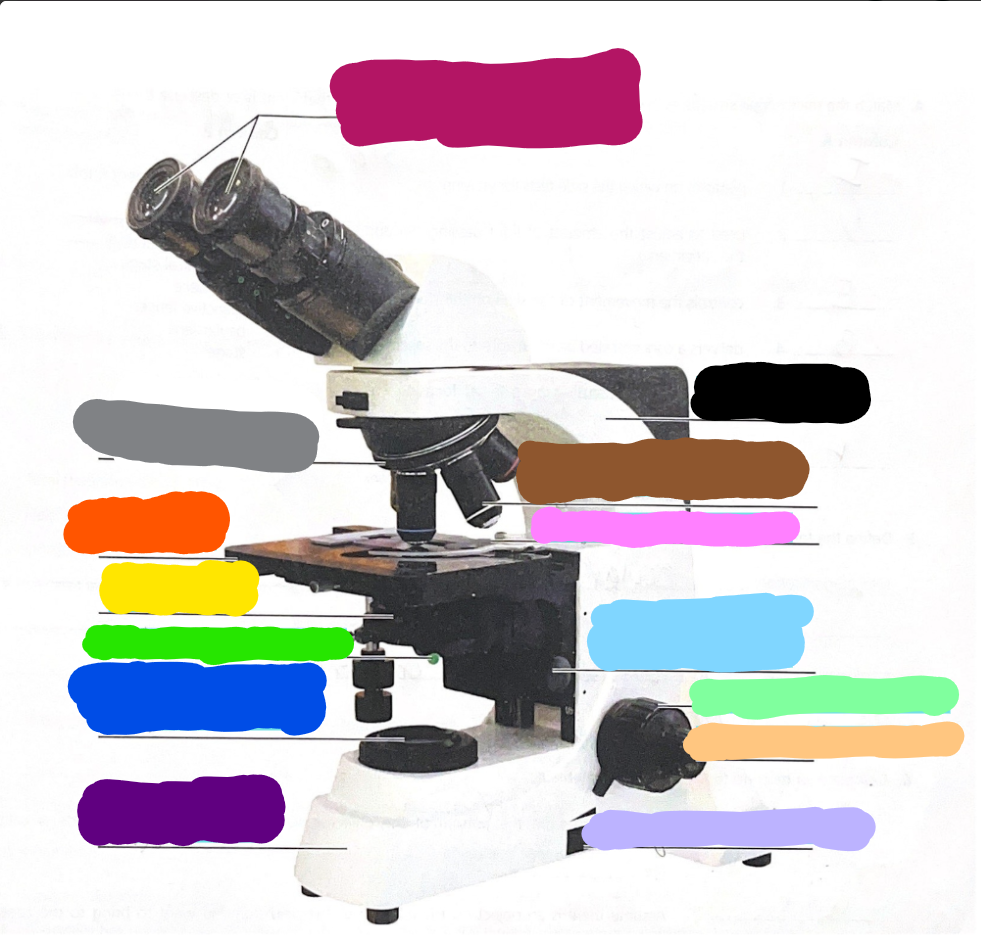

Dark Blue
substage light
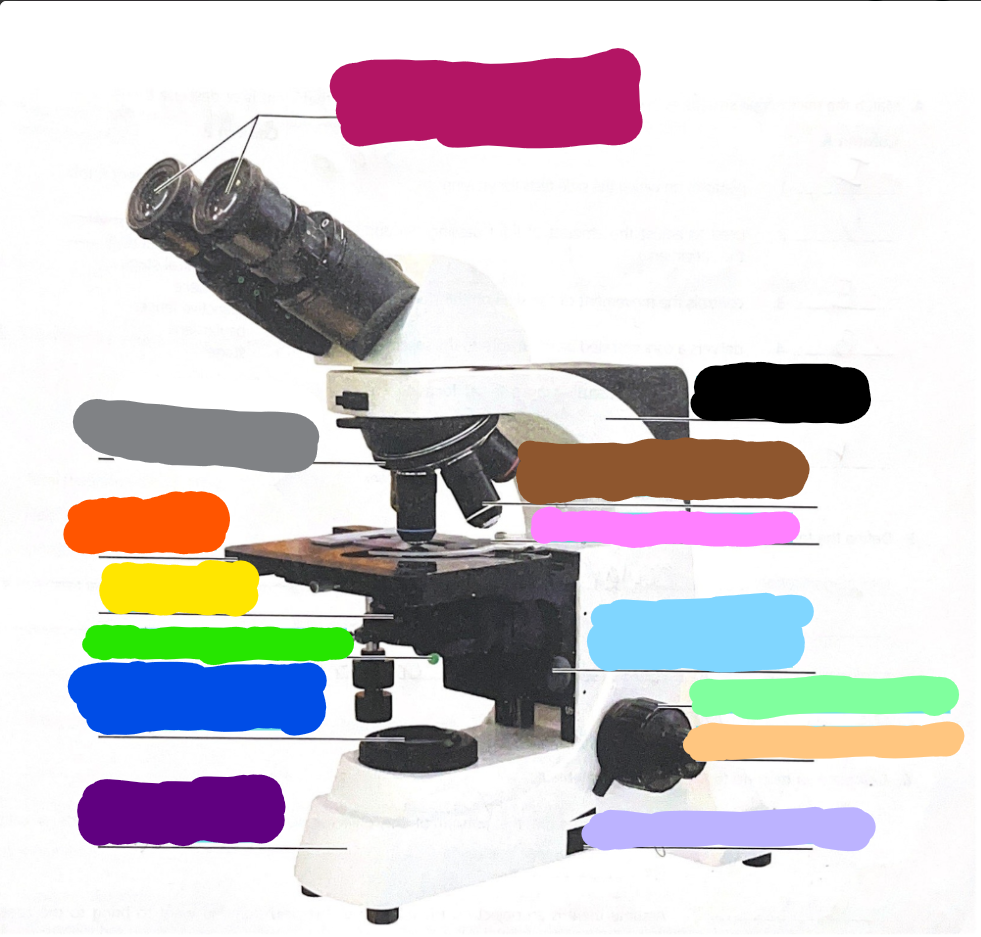

Dark Green/What it does?
Iris Diaphragm lever - used to adjust the amount of light passing through the specimen
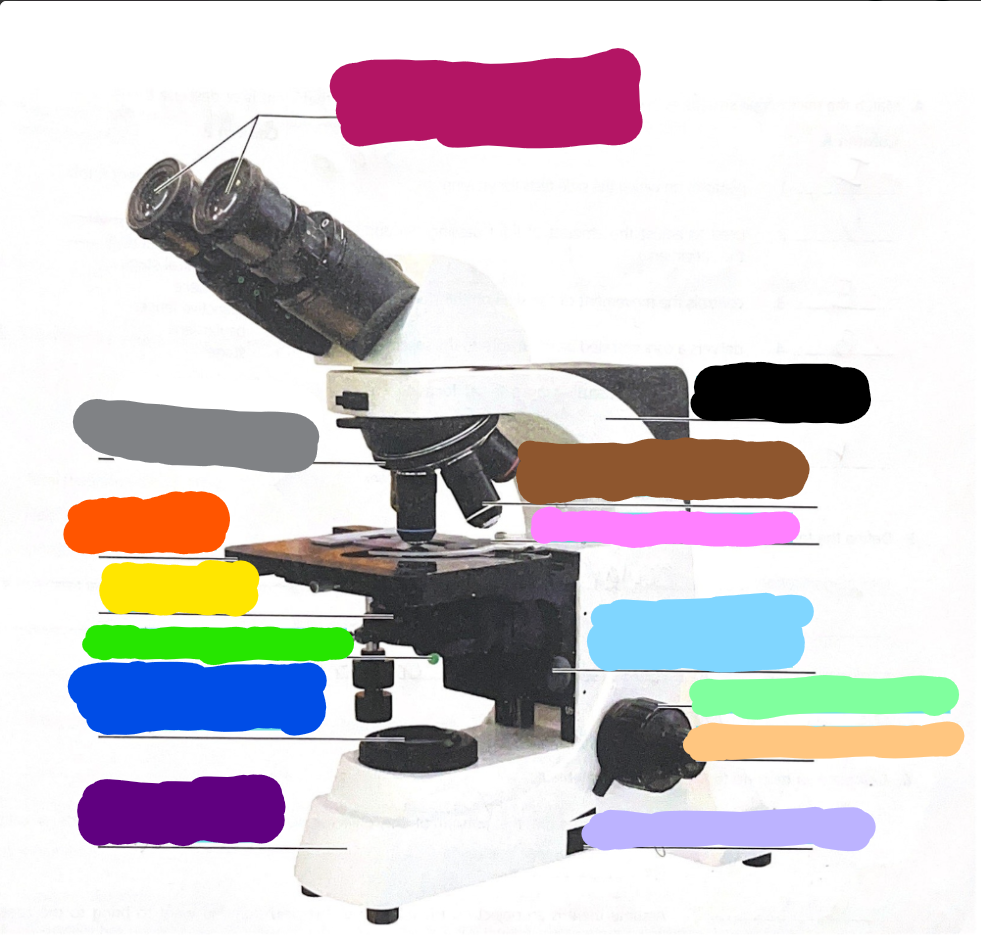

Yellow/What it does?
condenser- delivers a concentrated beam of light to the specimen
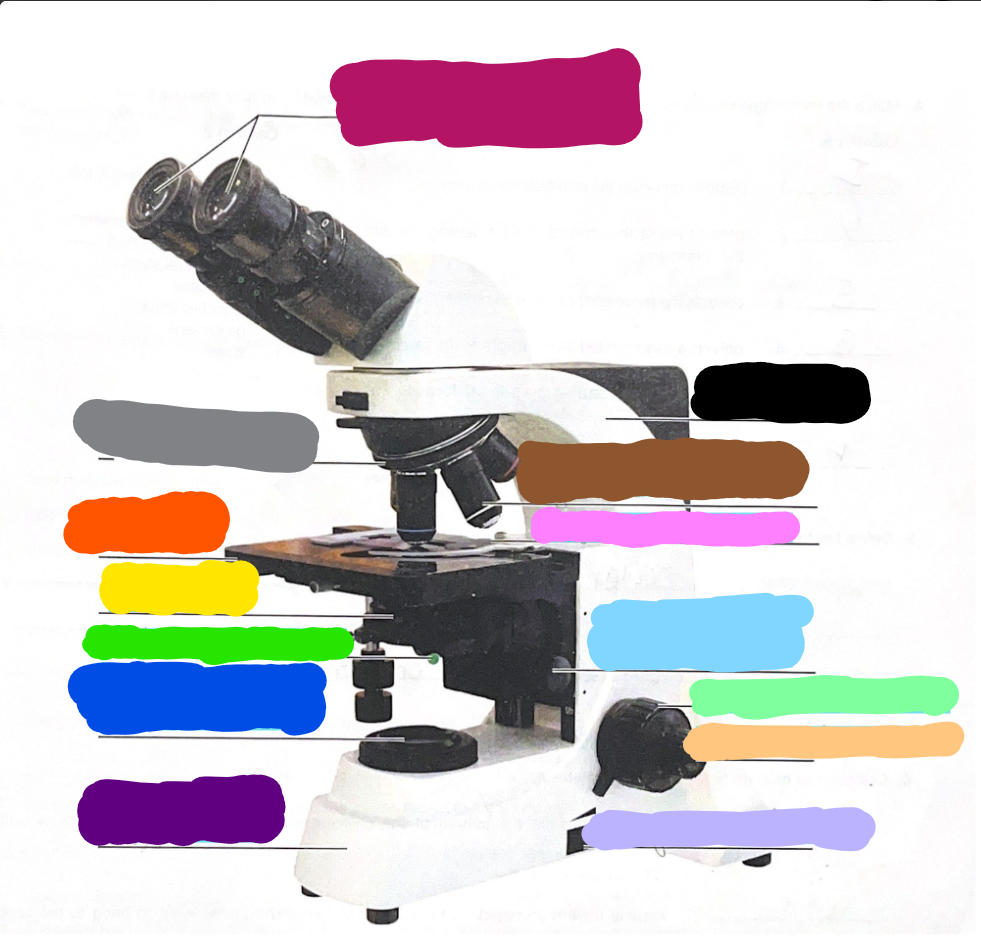

Dark Orange/what it does?
stage - platform at which the slide rests for viewing
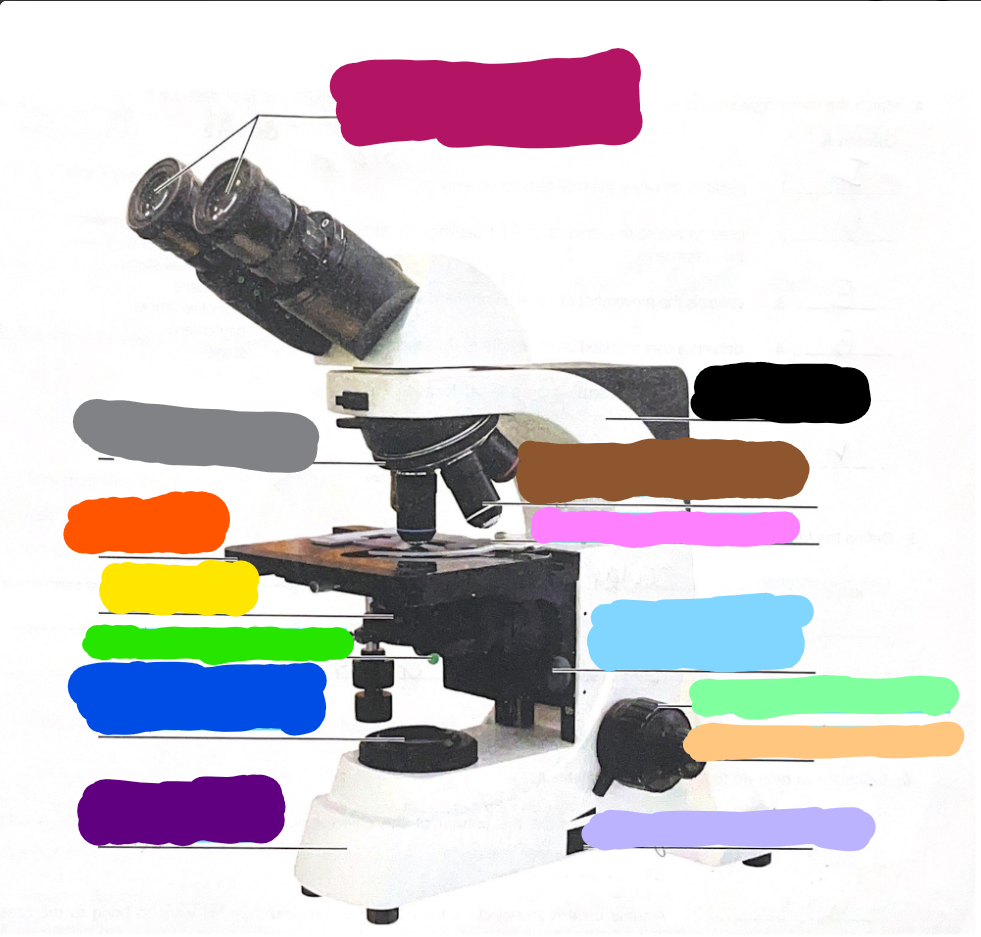

Grey/what it does?
Rotating nosepiece - carries the objective lenses; rotates so that the different objective lenses can be brought into position over the specimen
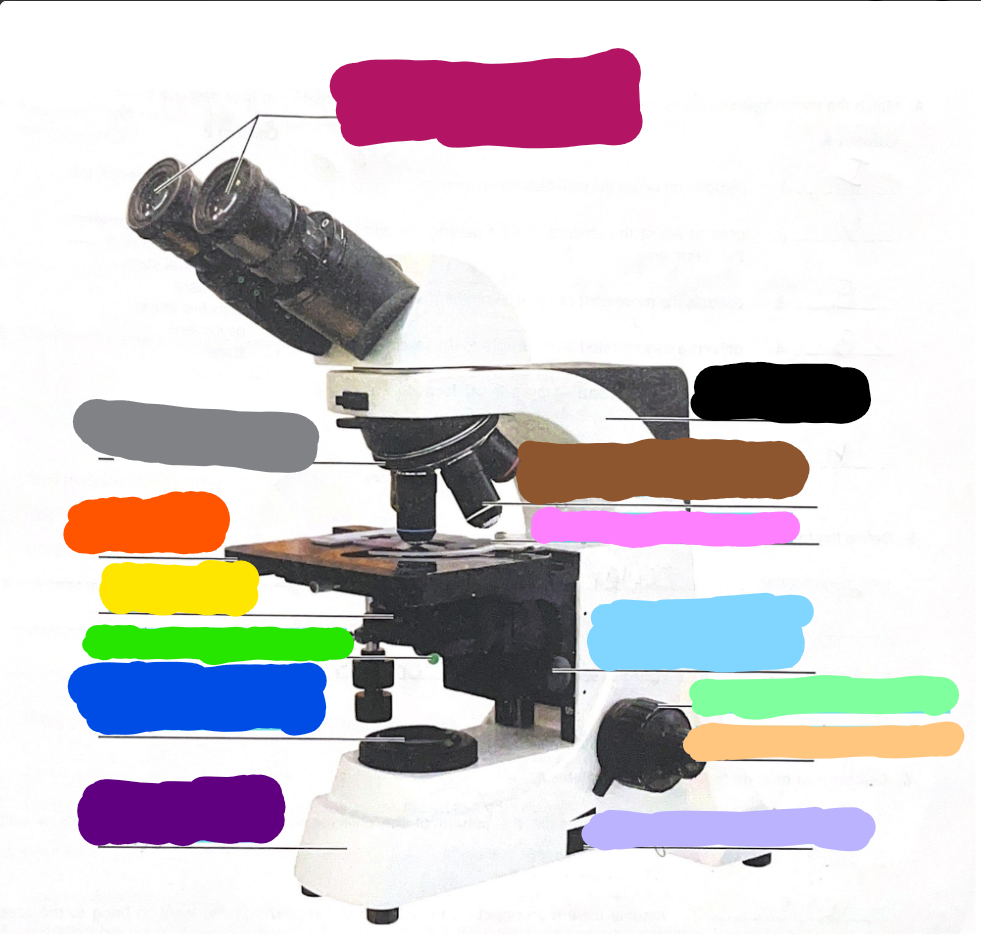

Magenta
Ocular Lense
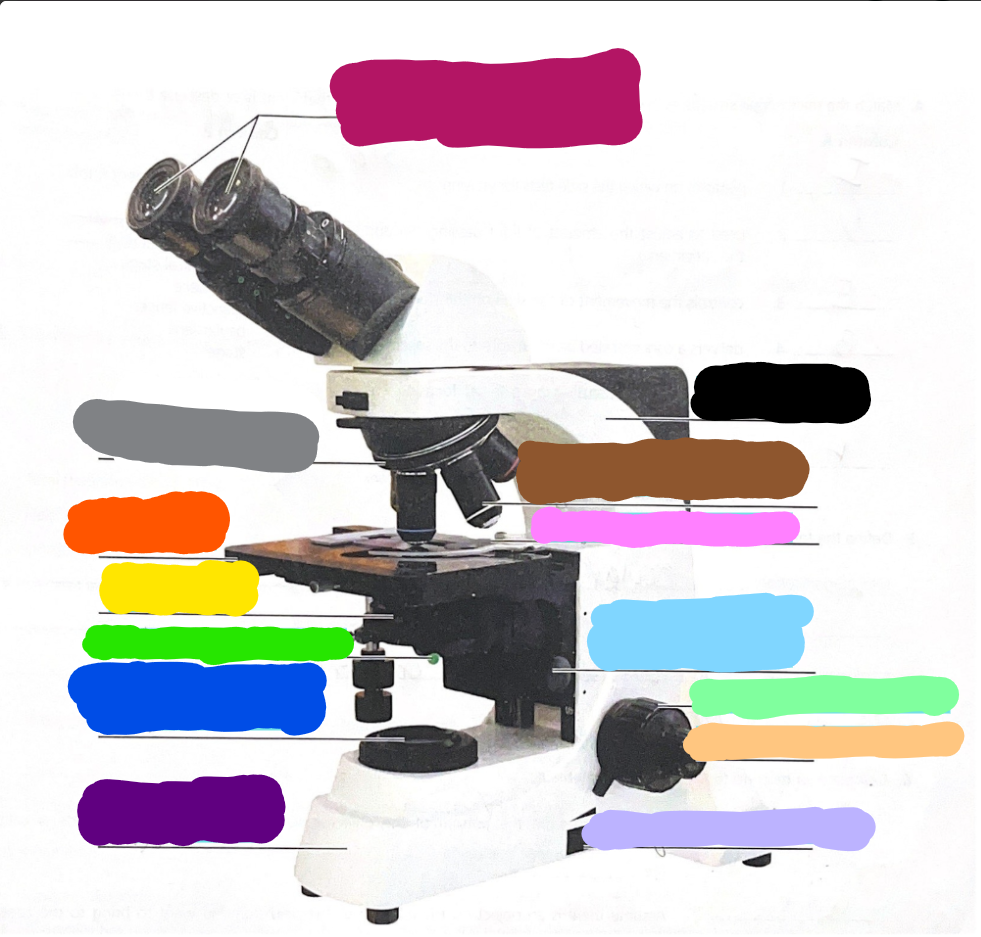

Black
Arm
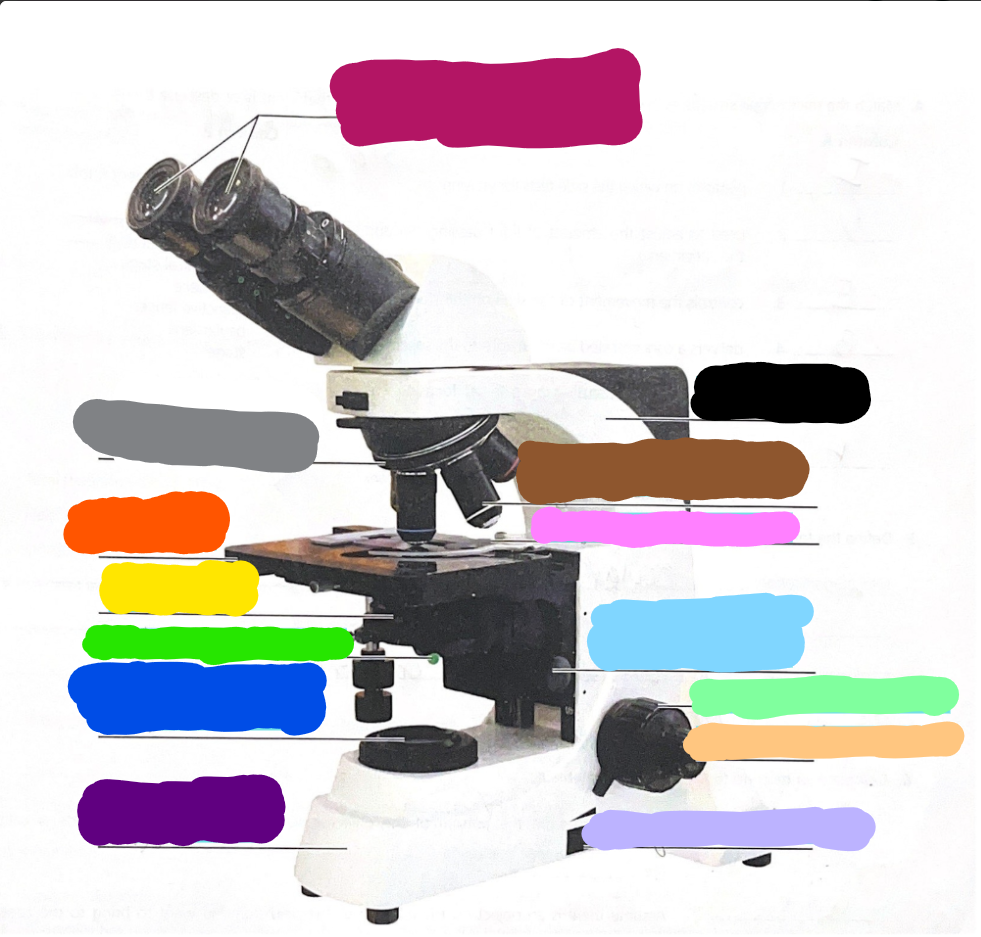

Brown
objective lense
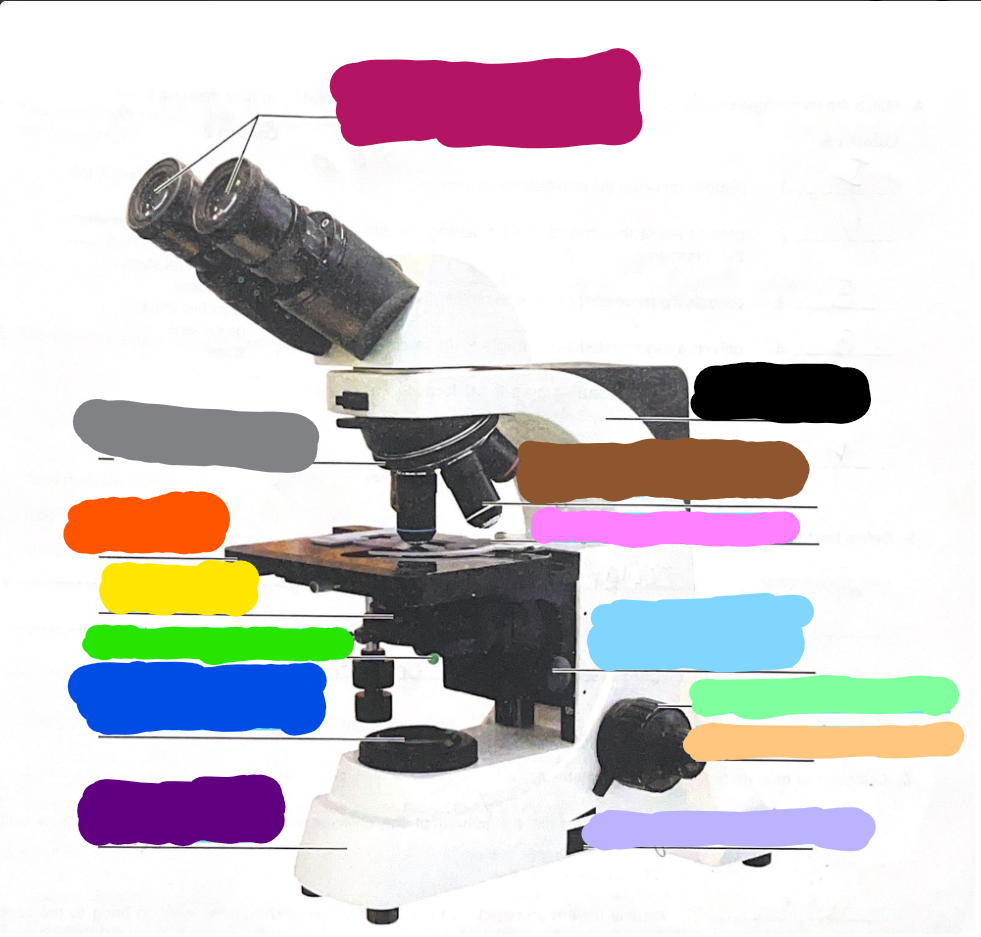

Pink/what it does?
Mechanical Stage/Stage clips - controls the movement of the slide on the stage
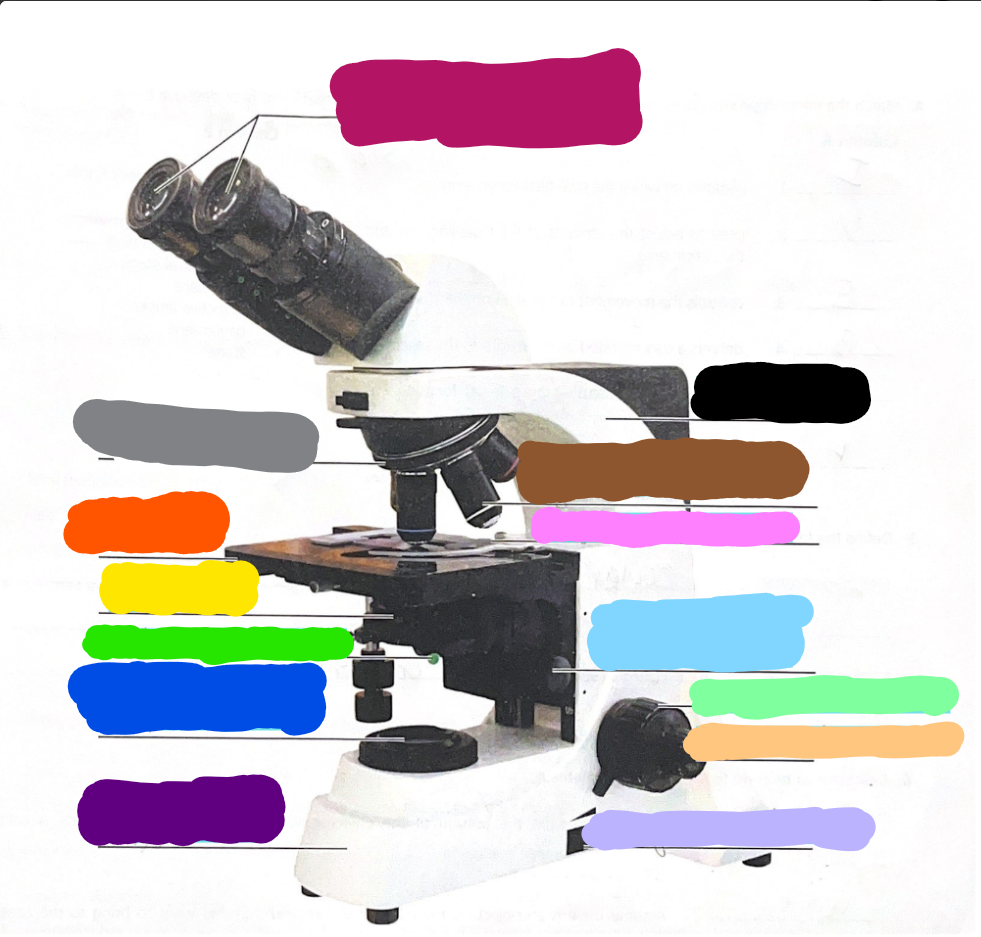

Light Blue
Condensor Knob
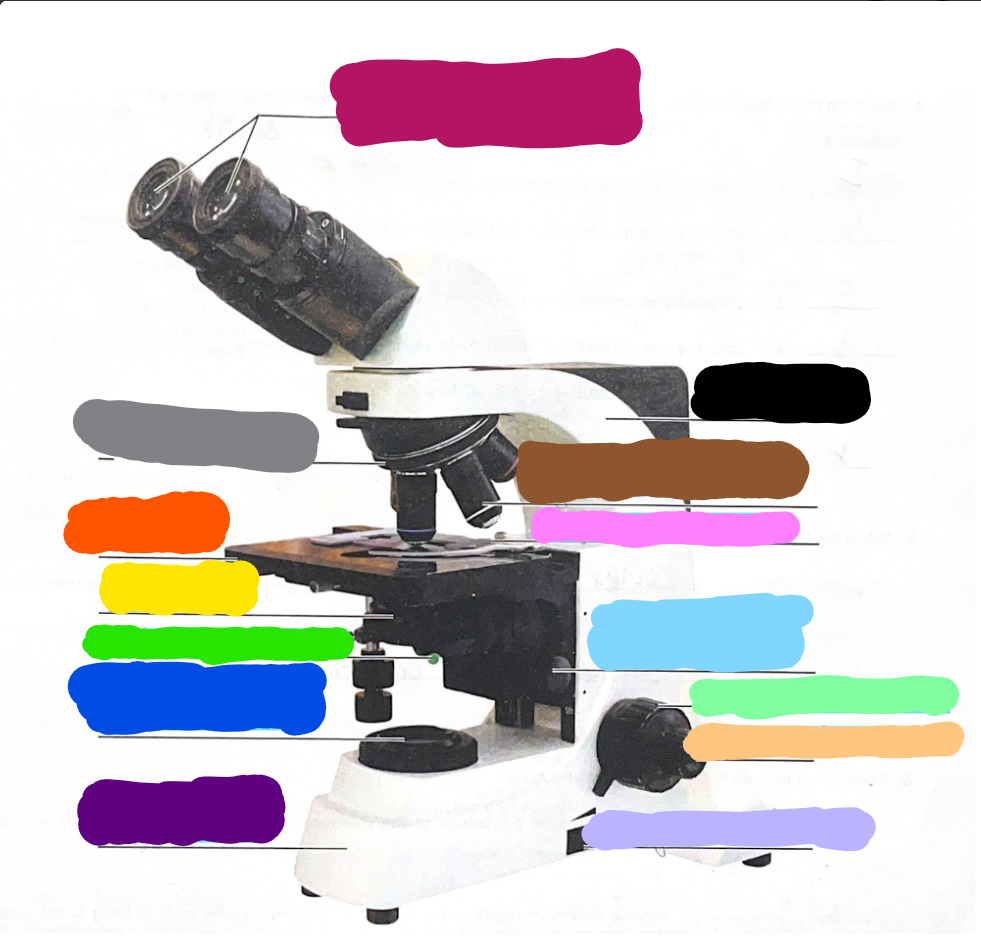

Light Green
Coarse Adjustment Knob
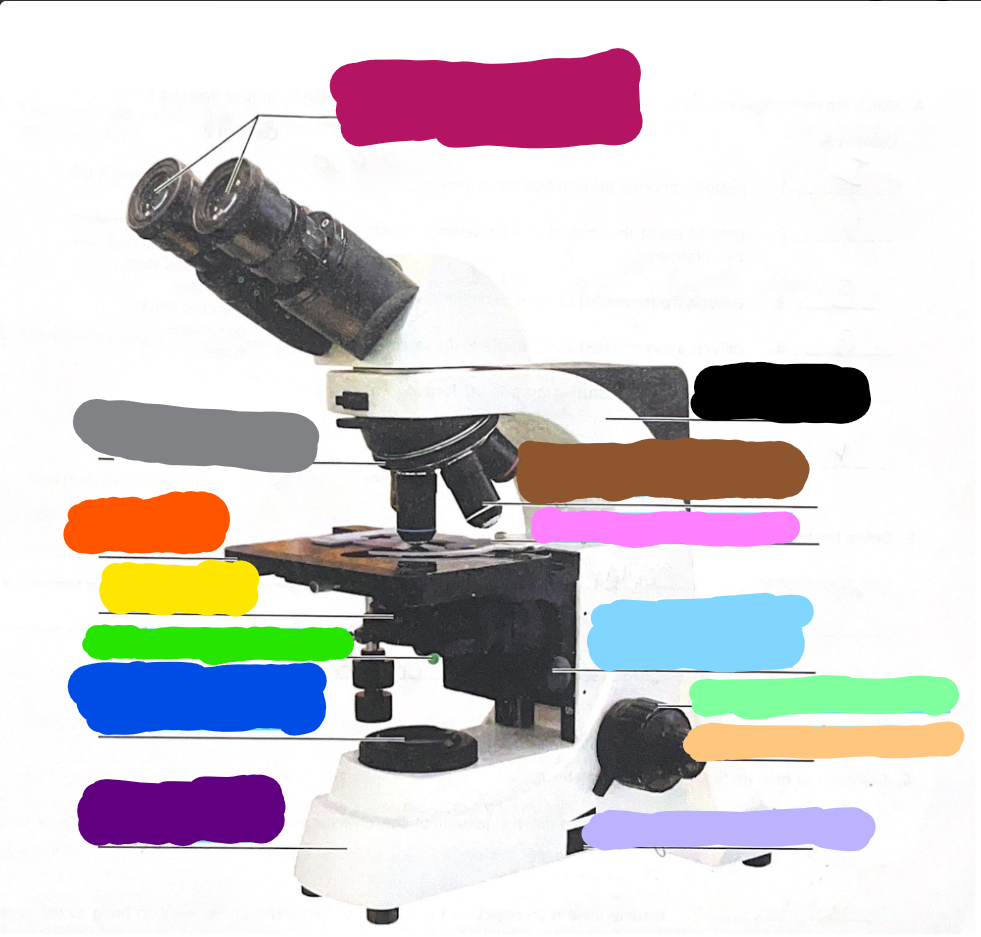

Light Orange/what it does?
Fine adjustment knob - used for precise focusing one initial focusing has been done
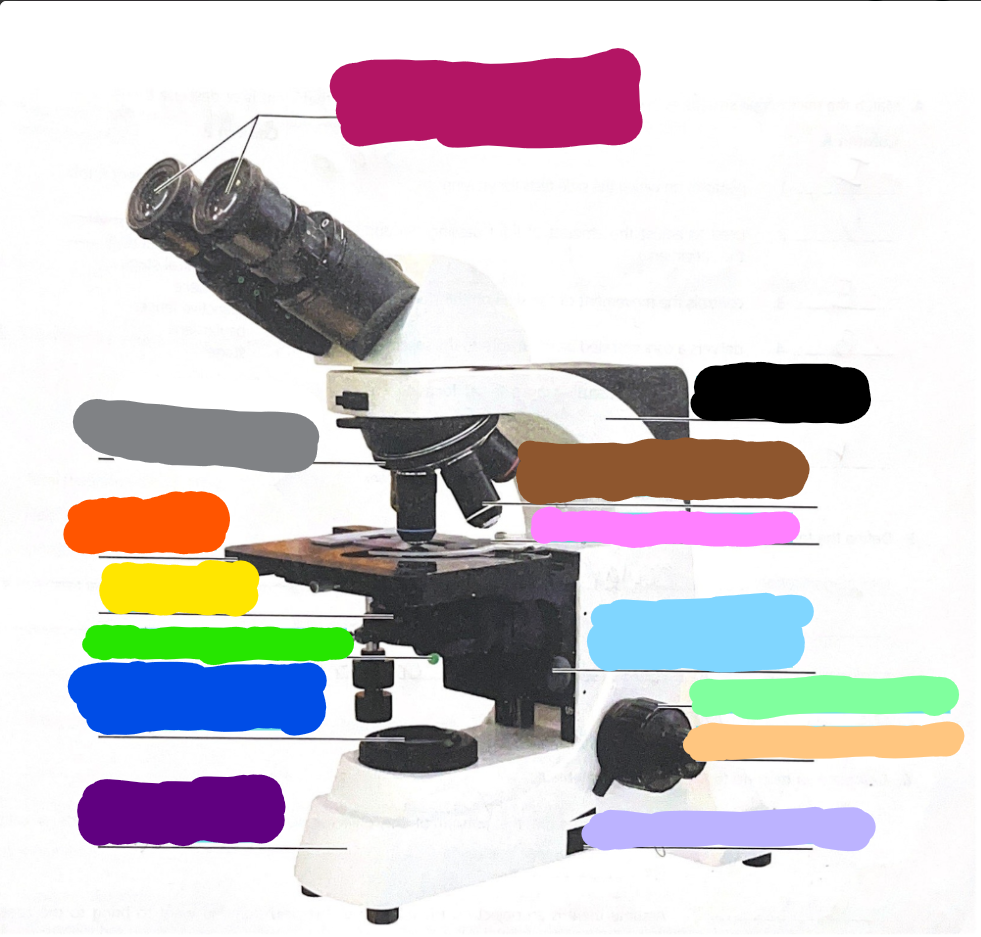

Light Purple
light control
Working distance
distance from the bottom of the objective lens to the surface of the slide
What direction would you move a slide if you want to bring an object on the left side of the field to the center?
left
Field
area of the slide seen when looking through the microscope
Why should the light be dimmed when looking at living (nearly transparent) cells?
to increase contrast
Parfocal
needing to use only fine adjustment to focus the specimen at the higher power
Ocular lens magnification
10x magnification
Objective lens; names and magnification
scanning lens - 4x
low power - 10x
high power - 40x
oil immersion - 100x
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
Smooth ER
site of lipid synthesis
Mitochondrion
main site of ATP synthesis
Rough ER
has ribosomes
involved with protein producing and transporting
Nucleus
encloses the chromatin
Golgi Apparatus
packages proteins for transportation
Lysosome
sac of digestive enzymes
Centriole
forms basal bodies and helps direct mitotic spindle formation
Cytoskeleton
internal cellular network of rodlike structures
Inclusion
glycogen granules and ingested foreign materials
Plasma membrane
forms the external boundary of the cell
Nucleolus
packaging site of ribosomes
Mitosis Cell divison in order
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis
Interphase
cell check point
Prophase
chromatin coils and condenses, forming chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
Metaphase
chromosomes line up in the center of the cell, chromosomes attach to spindle fibers
Anaphase
the chromosomes are v-shaped
Telophase
the nuclear envelope re-forms, chromosomes stop moving toward the poles. separation starts
Cytokinesis
two identical daughter cells
Four primary tissue types
epithelium, connective, muscle, nervous
Epithelium
lines body cavities and covers the body’s external surface
cells may absorb, secrete, and filter
forms endocrine and exocrine glands
Connective Tissue
anchors, packages, and supports body organs
derived from mesenchyme
consists of cells within an extracellular matrix
most widespread tissue in the body
Muscle tissue
pumps blood, flushes urine out of the body, allows one to swing a bat
transmits electrical signals
major function is to contract
Nervous Tissue
transmits electrical signal
most involved in regulating and controlling body functions
forms nerves and the brain
classified based on the shape and arrangement of the cells
Six main functions of epithelial cells
Protection
Absorption
Filtrating
Excretion
Secretion
Sensory Reception
Four Main Types of Connective Tissue
Connective Proper (loose & dense), cartilage, bones, and blood
Example of Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar, adipose, and reticular
Example of Dense Connective Tissue
dense regular, irregular, and elastic
Function of Blood
transports repiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and more
Types of Muscle Tissue
Smooth, Skeleton, and Cardiac
Function of Nervous Tissue
communicates w/other neurons, transmits electrical signals from receptors to effectors
Epidermis is
the superficial layer of the skin
Epidermis is composed of
epithelium underlying connective tissue
Deeper region of tissue is
dermis
composed of connective tissue
Most numerous cell of the epidermis is
Keratinocytes
Two primary layers of the dermis
papillary dermis
reticular dermis
Papillary Dermis
composed of areolar connective tissue, responsible for fingerprints, most superficial region
Reticular Dermis
composed of dense irregular connective tissue, deep layer of dermis
Four cell types of the epidermis
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes
Dendritic Cells
Tactile epithelial cells
Keratinocytes
most abundant, product keratin (provides durability and protection)
Melanocytes
spidery black cells that produce melanin
Dendritic Cells
ingest foreign substances
Tactile Epithelial Cells
form sensitive touch receptors
Layers of Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulsom
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
Stratum Corneum
most superficial layer of translucent cells in thick skin containing 20-30 layers of dead keratinocytes, these layers continuously come off
Stratum Lucidum
(only present in thick skin) two layers of a thin band of dead cells
Stratum Granulosum
layer named for the numerous lamellar granules present and secretes a glycolipid that prevents water loss
contains keratohyalin granules (from keratin in above layers)
Stratum Spinosum
contains cells w/weblike bundles of intermediate filaments