E1 Ortho- Fx, Casting, Splinting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is the hard layer of bone?
Cortex
What is the softer inner layer of bone?
Cancellous bone
What is the inner lining of the cancellous bone?
Endosteum
What is the thick layer of bone that covers cortex and contains vessels, nerve endings, cells for fracture repair?
Periosteum
What part of the bone provides bony growth?
Physis
What part of the bone that consists of spongy cancellous bone, where fractures most commonly occur?
Metaphysis
What is the thick cortical bone that provides structure?
Diaphysis
What is the most distal end of a long bone?
Epiphysis
How many views should you order on an Xray?
2 views, 90 degrees to each other (AP & lateral)
*can add 3rd (oblique)
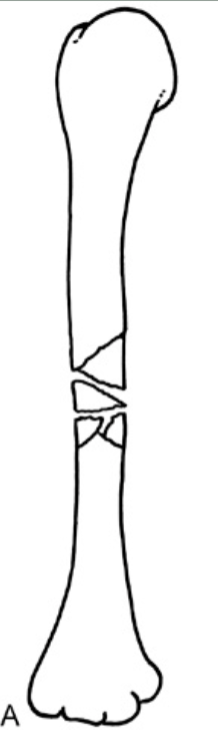
Which fracture?
comminuted
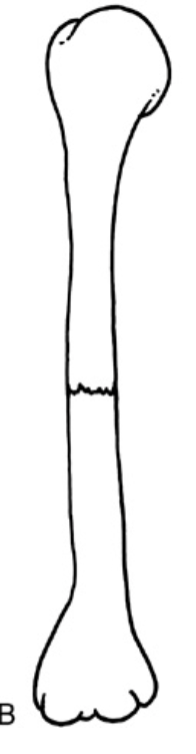
Which fracture?
transverse, undisplaced
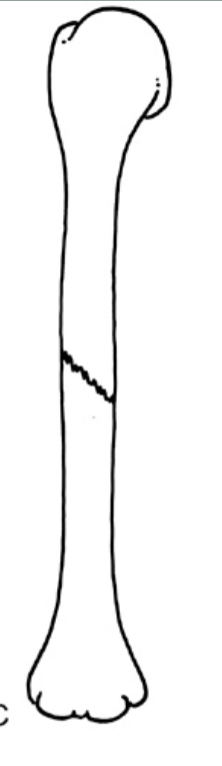
Which fracture?
oblique, undisplaced
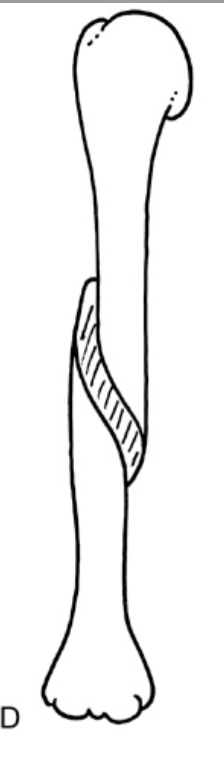
Which fracture?
spiral
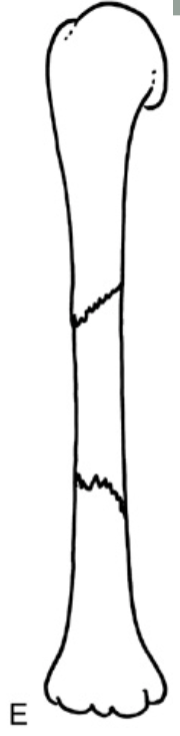
Which fracture?
segmental
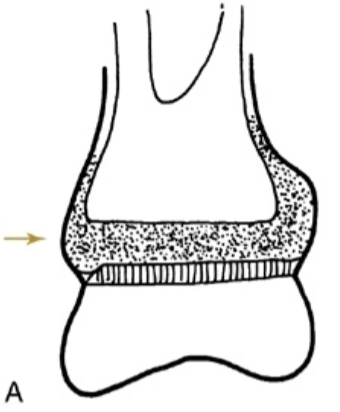
What type of Salter Harris fracture is the following:
Fx through the Physis plate
Type I
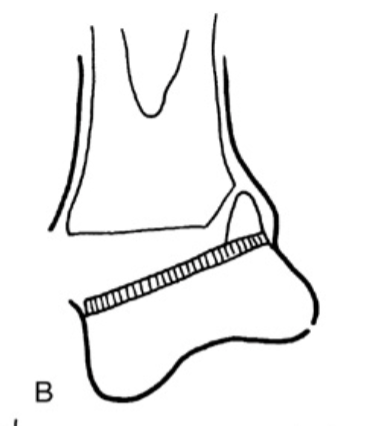
What type of Salter Harris fracture is the following:
fx of Physis plate w/ Metaphysis fragment
*MC
Type II
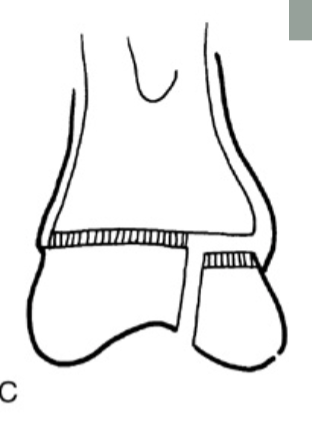
What type of Salter Harris fracture is the following:
Fx through Physis w/ Epiphysis fragment
Type III
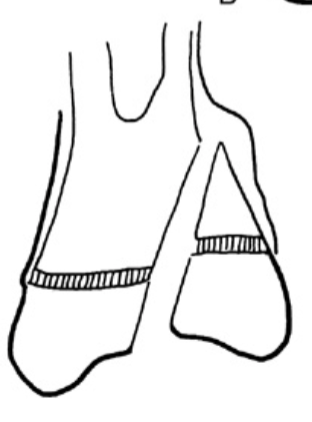
What type of Salter Harris fracture is the following:
Fx through distal Metaphysis, Physis & Epiphysis
Type IV
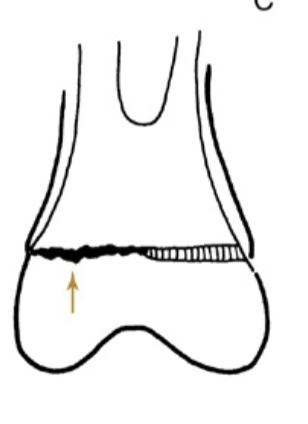
What type of Salter Harris fracture is the following:
Crush or impaction of the Physis plate
Type V
What fractures are MC missed?
scaphoid, talar neck, radial head, tibial plateau
Which nerve injury is associated with/ closed fx, dislocation, or blunt trauma?
Contusion (neuropraxic) & crush (axonotmesis)
What type of nerve injury is associated with/ open fx?
Transection (neurotmesis)
If a patient has a wrist drop, this would indicate injury to what nerve? What fracture could be related?
Radial nerve injury- Spiral fracture of humerus
If a patient has a foot drop, this would indicate injury to what nerve? What fracture could be related?
Peroneal nerve injury- Tibial plateau fracture
How long does it take for a Type1 nerve injury to recover?
2-3 months, except knee
How long does it take for a Type 2 nerve injury to recover?
1-2 cm per month (95% recover by 6 mo, may take 12 months)
What fx MUST go to an orthopedic surgeon?
any open fx, displaced intraarticular fx, all femur fx, fx of both bones in lower leg
What factors delay bone healing?
smoking, elderly, DM, malnutrition
What is the benefit of a closed reduction?
less risk of infxn
How is an epiphyseal fx fixed in a closed reduction?
distal fx “pushed” back into place
How is a transverse fx fixed during a closed reduction?
reduced by simple traction
How is an oblique “toggle” type fx fixed during a closed reduction?
more complex manipulation
What age range should a rotational deformity be completely corrected at?
should ALWAYS be fully corrected
When should angular deformities be completely corrected in adults?
always
When do angular deformities in children not need correction?
when they are close to a joint & in the same plane of motion (will correct itself)
What is the advantage of a plaster cast?
easier to apply; warmer the water the faster it sets
What is the advantage of a fiberglass cast?
lighter weight, waterproof is an option
What are signs a pt is developing compartment syndrome?
paresthesia, sensory loss, tenseness, pain on stretching the muscle in that compartment
What are complications to watch for after casting a pt?
compartment syndrome, Volkmann’s ischemic contracture, tissue necrosis
How long does PT typically last?
4-6 weeks
How long does a fx take to heal?
6-12 weeks
Guidelines for splinting/casting an arm:
should not extend beyond the distal palmar
MCP should be able to flex
pt should be able to fan their fingers
elbow casts should = 90 degrees
Guidelines when splinting/casting a leg:
foot/ankle at 90 degrees
always extend under metatarsals heads
toes MUST be exposed
50% overlap each turn → do a figure 8
What are the most common fractures seen with child abuse?
Long bone fracture: Shaft (eg. humerus)
What fxs might suggest child abuse?
long bone fx -especially displaced, rib fx, vertebral body compression fx, multiple different fxs at other sites/stages of healing
What are S&S of senior abuse?
hand fxs, unset broken bones, repeat fall injuries