BIOL 1306 Cheek Exam 3 Vocabulary
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Free energy
The energy of a system that can be converted into work. The amount of this energy that is available can be measured only by how it changes in a reaction. AKA Gibbs Free Energy
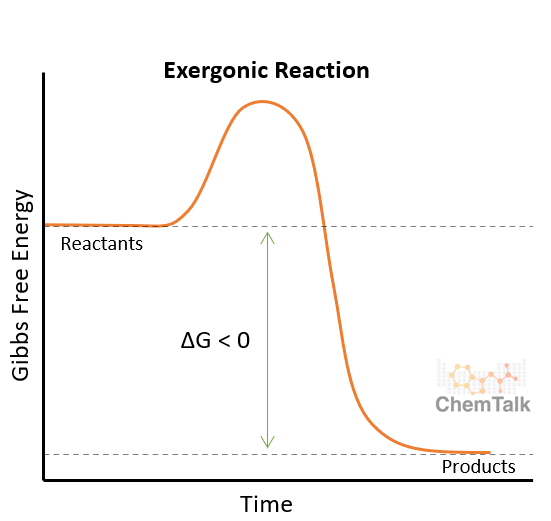
Exergonic
Referring to a chemical reaction that has a change in Gibbs free energy less than zero (ΔG) (NEGATIVE CHANGE IN GIBBS)
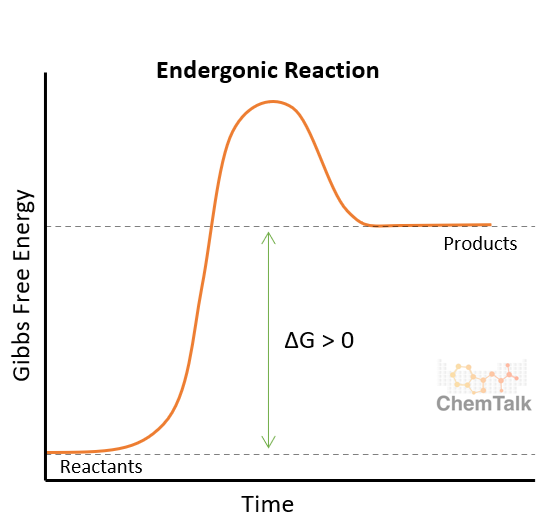
Endergonic
Referring to a chemical reaction that has a change in Gibbs free energy more than zero (ΔG) (POSITIVE CHANGE IN GIBBS)
Catabolism
Any set of chemical reactions that breaks down large, complex molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process.
Anabolism
Any set of chemical reactions that synthesizes large molecules from smaller ones. Generally requires an input of energy.
Activation Energy
The amount of kinetic energy required to initiate a chemical reaction; specifically, the energy required to reach the transition state.
Active Site
The location in an enzyme molecule where substrates (reactant molecules) bind and react.
Substrate
A reactant that interacts with a catalyst, such as an enzyme or ribozyme, in a chemical reaction.
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Enzymes are this.
Enzyme Activity
the number of substrate molecules that are converted into product molecules in a definite time. Certain factors can affect this like temperature, pH, etc.
Competitive Inhibitor
Inhibition of an enzyme’s ability to catalyze a chemical reaction via a non-reactant molecule that competes with the substrate(s) for access to the active site.
Allosteric Inhibitor
Inhibition of an enzyme’s (or other protein’s) activity by binding of a different molecule at a site distinct from the active site. Binding often results in a change in the shape of the active site that prevents the substrate from binding.
Interphase
The portion of the cell cycle between one Mitotic phase and the next. Includes G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase.
G1-Phase of Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle that constitutes the first part of interphase, before DNA synthesis (S phase). cell prepares to divide by growing in size, synthesizing proteins, and producing the enzymes and nucleotides needed for DNA replication
S-Phase Of Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle during which DNA is synthesized for the replication of chromosomes.
G-2 Phase of Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle between synthesis of DNA (S phase) and mitosis (M phase); the last part of interphase. cells enhance the lipid synthesis required for membrane formation and ensure that everything is ready to initiate the mitotic process.
Mitosis
In eukaryotic cells, the process of nuclear division that results in two daughter nuclei that have chromosomes and genes identical to the parent nucleus. Subsequent cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm) yields two daughter cells.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm to form two daughter cells. In eukaryotic cells, typically occurs immediately after division of the nucleus by mitosis or meiosis. Not included in mitosis but included in Mitotic Phase. Cytoplasm is separated.
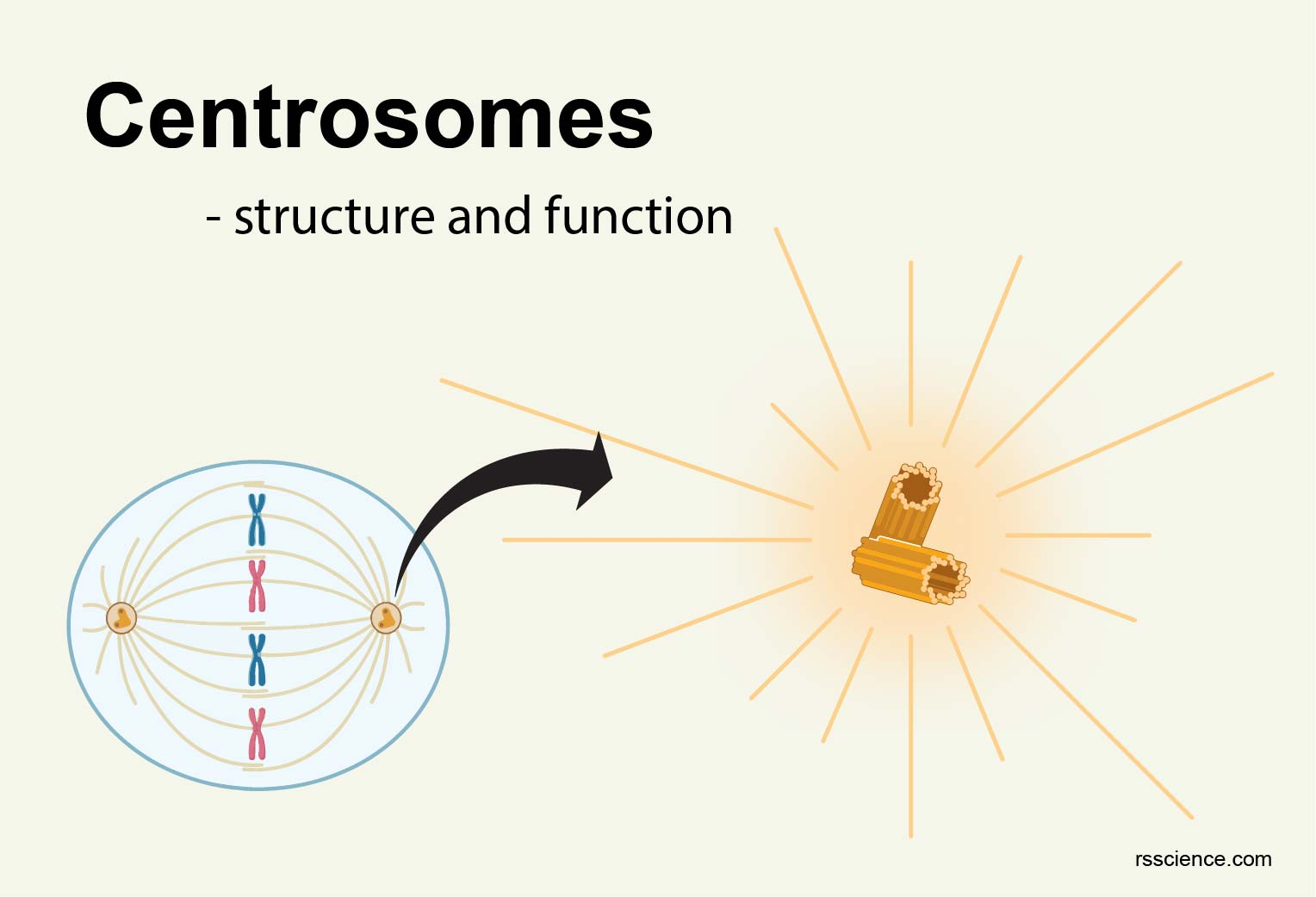
Centrosome
A structure that serves as a microtubule-organizing center for the cell’s cytoskeleton and for the spindle apparatus during cell division. Includes centrioles in animal cells and certain plants and fungi.
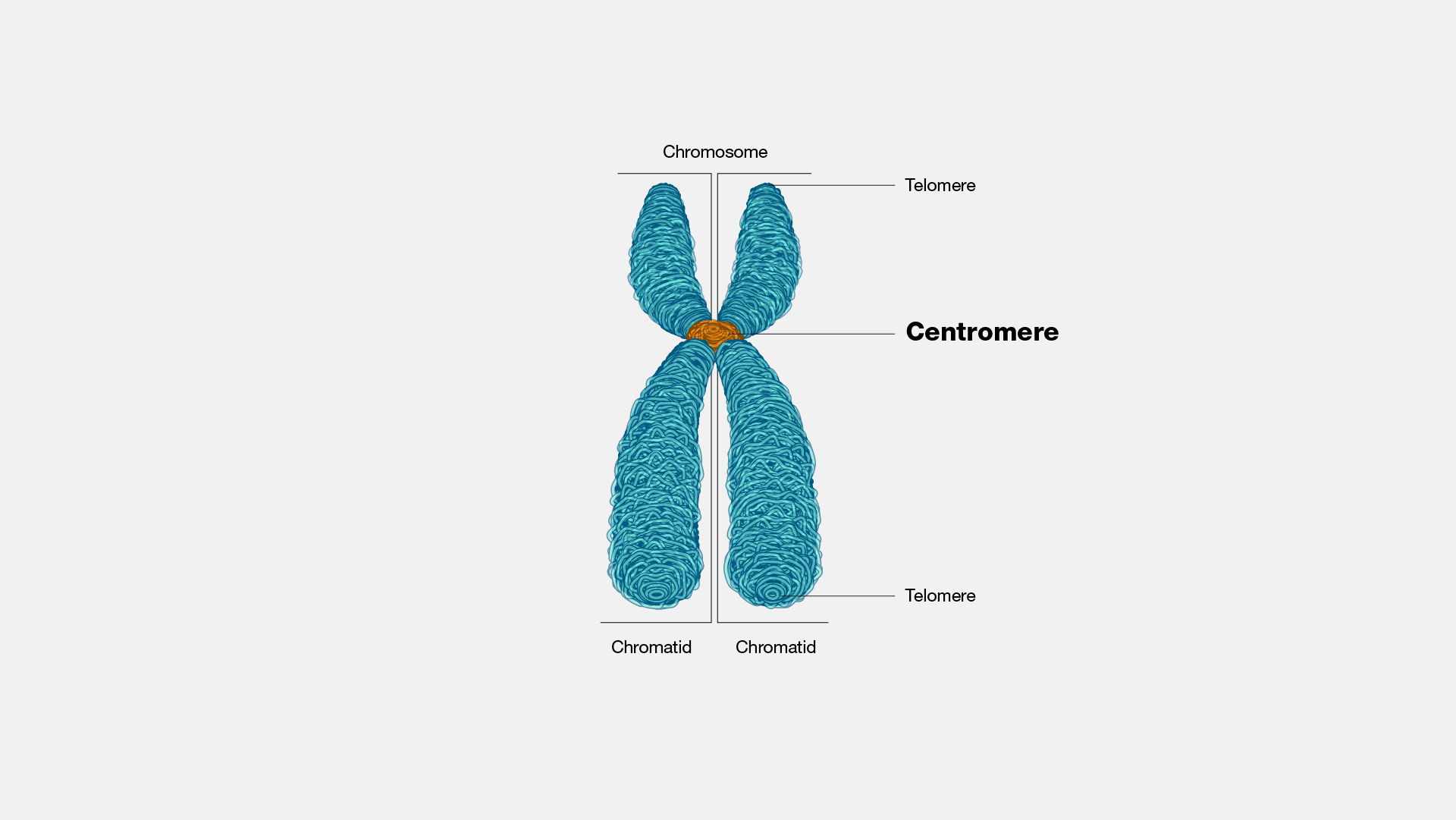
Centromere
The region of a replicated chromosome where the two sister chromatids are joined most tightly and the kinetochore is formed during M phase.
Chromosome
Gene-carrying structure consisting of a single long molecule of double-stranded DNA and associated proteins (e.g., histones). Most prokaryotic cells contain a single circular chromosome; eukaryotic cells contain multiple noncircular (linear) chromosomes located in the nucleus.
Chromatid
One of the two identical double-stranded DNAs that are connected at the centromere and compose a replicated chromosome.
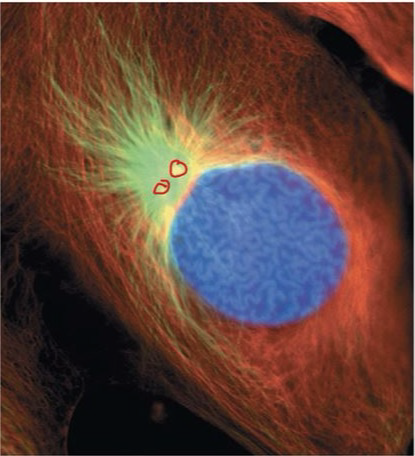
Prophase
The first stage in mitosis or meiosis, during which nucleoli disappear, chromosomes coil tightly, spindle forms, centrosomes begin to move away from each other
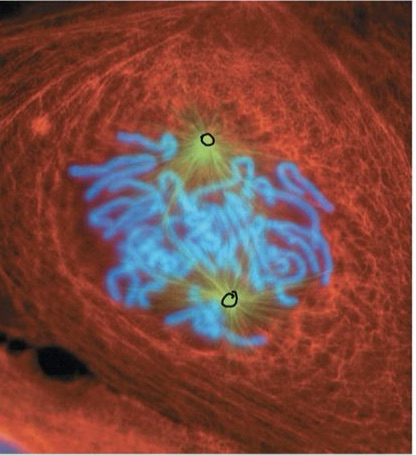
Prometaphase
A stage in mitosis during which the nuclear envelope breaks down and centrosomes are at opposite poles, microtubules attach to kinetochores on the chromosomes.
Spindle Fiber
protein structures that come from centrosomes that pull apart the genetic material in a cell when the cell divides.
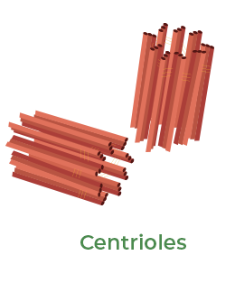
Centriole
One of two small cylindrical structures contained within the centrosome near the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell (found in animals but not in most plants). MAKES UP THE CENTROSOME.
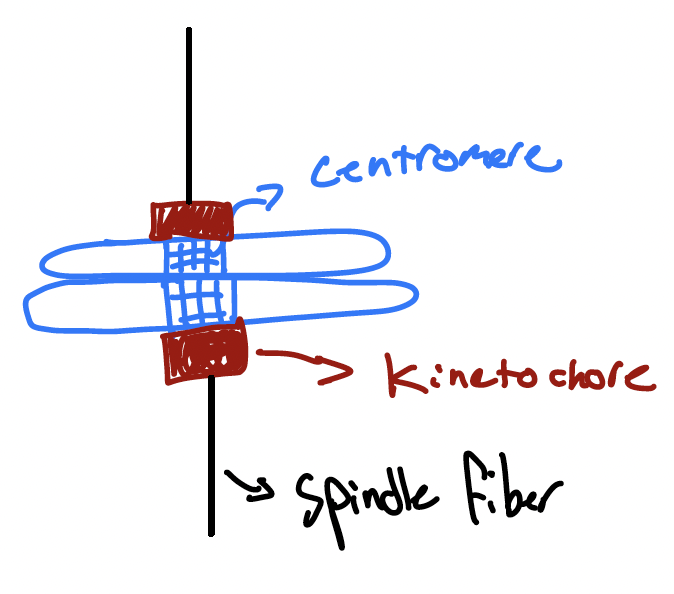
Kinetochore
A protein complex that forms on a chromosome during M phase. Forms at the centromere and serves as a site for microtubule attachment. Contains motor proteins and microtubule-binding proteins that are involved in chromosome segregation during M phase.
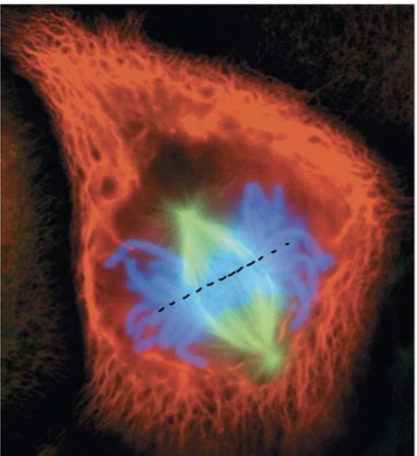
Metaphase
A stage in mitosis during which chromosomes line up across the middle of the spindle. Kinetochore of each chromatid is attached to microtubule from opposite pole, centrosomes are at opposite poles.
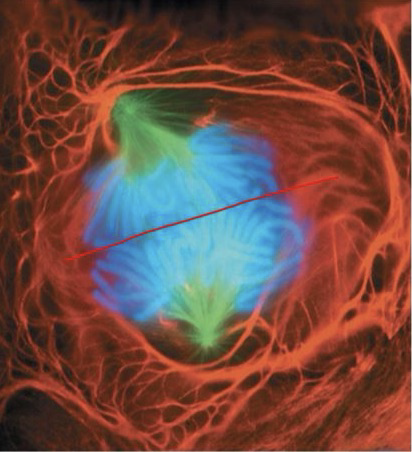
Anaphase
The stage in mitosis or meiosis during which chromosomes are moved to opposite poles of the spindle apparatus. Sister chromatids separate, kinetochore microtubules shorten, daughter chromosomes move towards opposite poles.
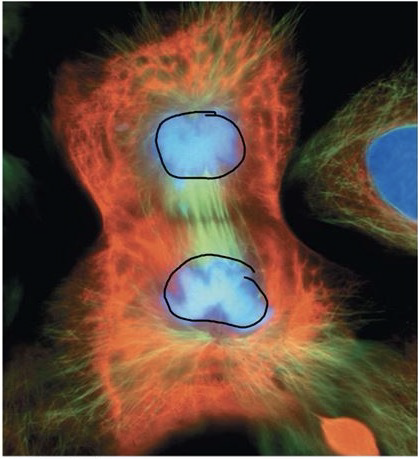
Telophase
The final stage in mitosis or meiosis, during which daughter chromosomes have moved to opposite poles and new nuclear envelopes begin to form around each set of chromosomes. Chromosomes de-condense, nucleoli re-appear, spindle microtubules depolymerize.
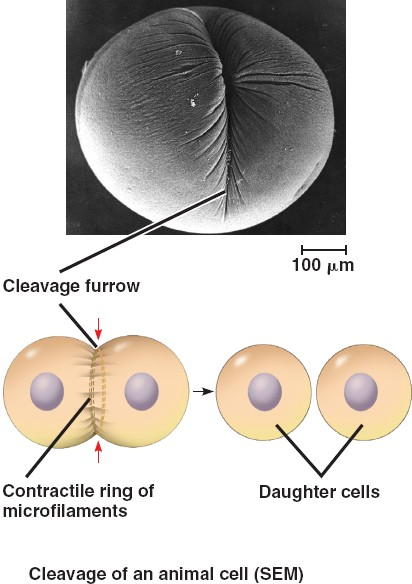
Cleavage Furrow
An indentation in the cell surface that occurs as the plasma membrane is pulled inward during cytokinesis in animal cells. The furrow deepens until the membrane fuses, dividing the cytoplasm into two daughter cells.
Adaptation
Any heritable trait that increases the fitness of an individual with that trait, compared with individuals without that trait, in a particular environment.
Acclimatization
A change in an individual’s phenotype that occurs in response to a change in natural environmental conditions.

Conformer
A creature that has internal physiological conditions that vary with environmental conditions. Doesn’t spend energy to regulate the variable, limits the range of thermal habitats in which the animal can survive.
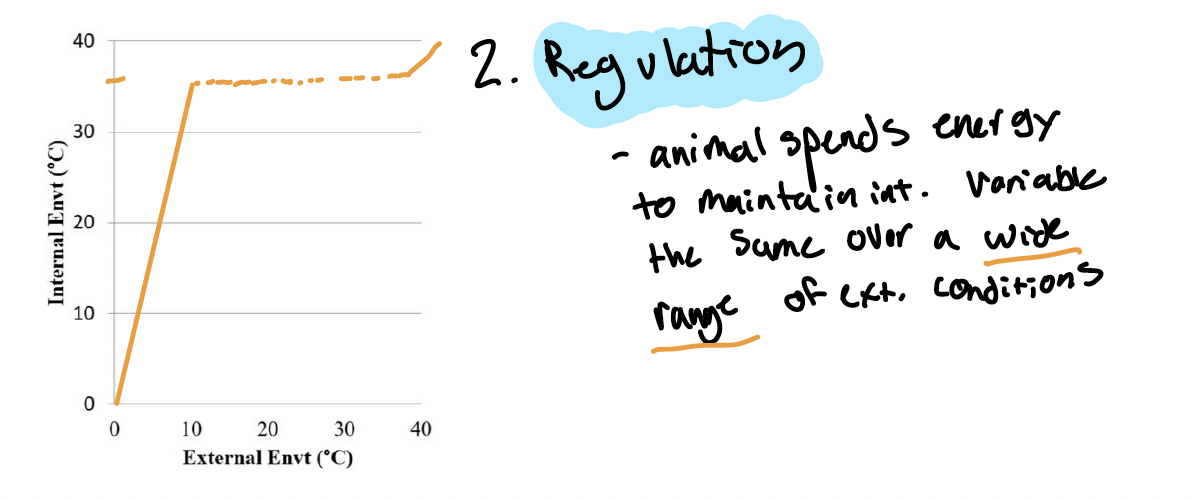
Regulator
A creature that actively maintains homeostasis of internal physiological conditions. Spends energy to maintain the internal variable the same over a wide range of external conditions.
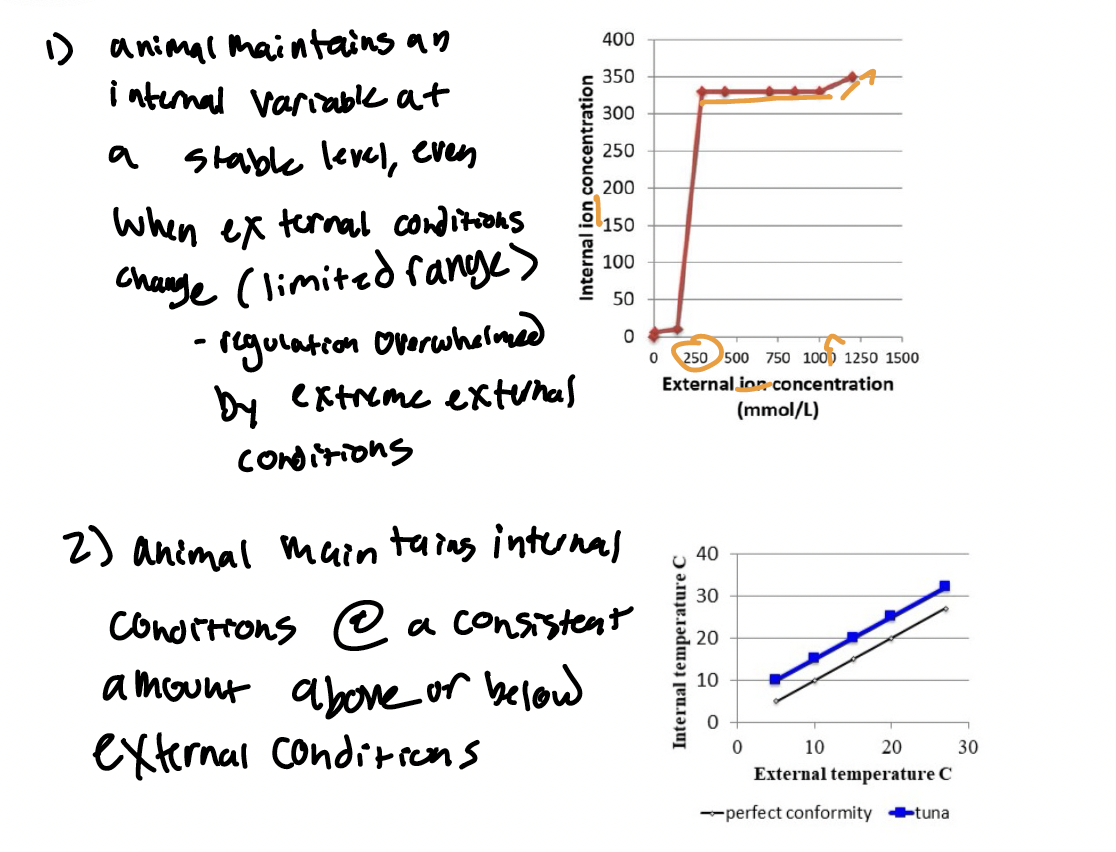
Partial Regulation (Two Types)
Type 1 - Animal Maintains an internal variable at a stable level, even when external conditions change (limited range)
Type 2 - Animal maintains internal conditions at a CONSISTENT amount above or below external conditions
Homeostasis
The array of relatively stable chemical and physical conditions in an organism’s cells, tissues, and organs. May be achieved by passively matching the conditions of a stable external environment (conformational homeostasis) or by active physiological processes (regulatory homeostasis) triggered by variations in the external or internal environment.
Insulin
A peptide hormone produced by the pancreas in response to high levels of glucose (or amino acids) in the blood. Enables cells to absorb glucose and coordinates synthesis of fats, proteins, and glycogen.
Glucagon
A peptide hormone produced by the pancreas in response to low blood glucose levels. Raises the blood glucose level by triggering breakdown of glycogen and stimulating gluconeogenesis (after fasting 24 hours).
Ectotherm
An animal that gains most of its body heat from external sources as opposed to metabolic processes. (Cold-Blooded)
Endotherm
An animal that gains most of its body heat from internal metabolic processes. (Warm-Blooded)
Convection
Transfer of heat by movement of large volumes of a gas or liquid.
Conduction
Direct transfer of heat between two objects that are in physical contact
Radiation
Transfer of heat between two bodies that are not in direct physical contact.
Evaporation
The energy-absorbing phase change from a liquid state to a gaseous state. Many organisms evaporate water as a means of heat loss.
Osmolarity
The concentration of dissolved solutes in a solution, measured in osmoles per liter.
Hypoosmotic
a solution has a lower osmotic pressure or a lower concentration of solutes than another solution
Hyperosmotic
a solution has a higher osmotic pressure or a greater concentration of solutes than another solution
Isosmotic
having the same osmotic pressure or solute concentration.
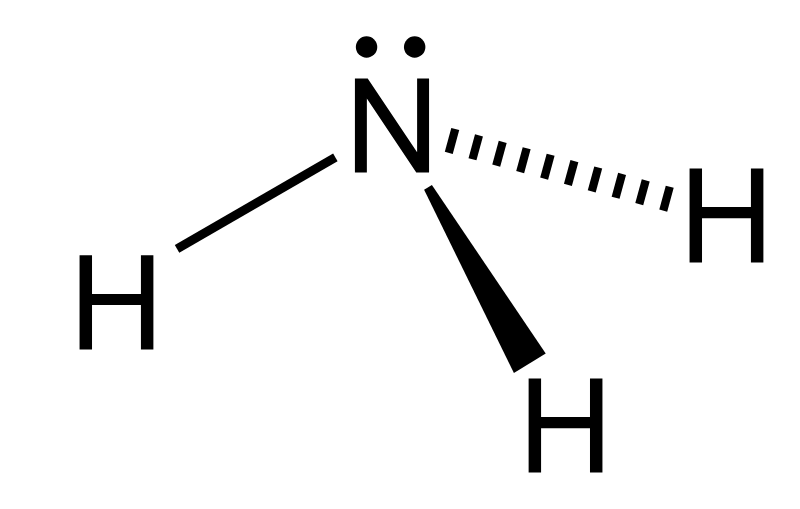
Ammonia
A small molecule, produced by the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids, that is very toxic to cells. It is a strong base that gains a proton to form the ammonium ion. The major nitrogenous waste of bony fishes and aquatic invertebrates.
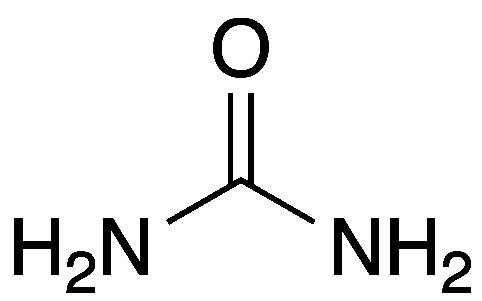
Urea
The major nitrogenous waste of mammals, adult amphibians, and cartilaginous fishes.
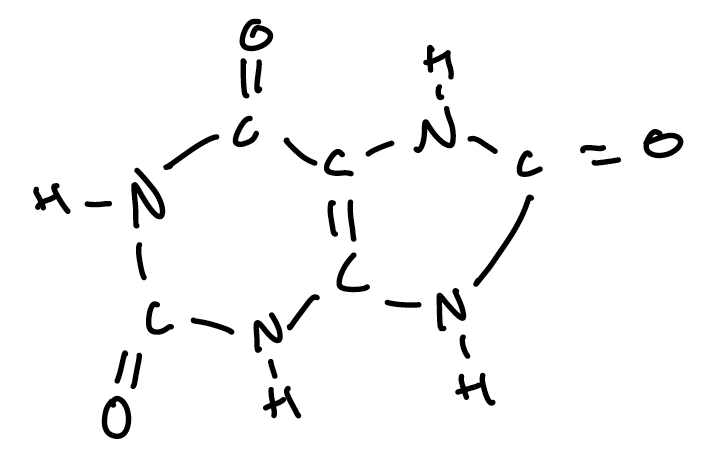
Uric Acid
The major nitrogenous waste of birds, other reptiles, and most terrestrial arthropods.
Hemolymph
The circulatory fluid of animals with open circulatory systems (e.g., insects), in which the fluid is not confined to blood vessels.
Interstitial Fluid
In animals with a closed circulatory system, extracellular fluid that is not enclosed in blood vessels or lymphatic vessels.
Erythrocyte
Red Blood Cell
Leukocyte
White Blood Cell