Concept 7.1: Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins
1/11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
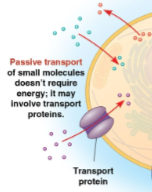
Passive transport
The transport of small molecules from areas of high to low concentration that does not require energy
May require transport proteins in a cell membrane
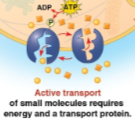
Active transport
The transport of small molecules from areas of low to high concentration that does require energy and a transport protein
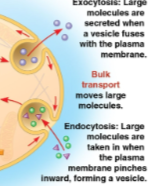
Bulk transport
The transport of large molecules as a form of active transport that utilizes exo- or endocytosis
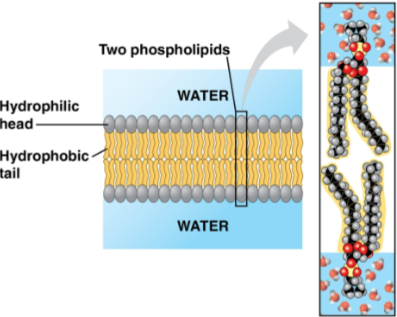
Membrane
Cellular substance comprised of phospholipids and proteins with some carbohydrates
Hydrophobilc phospholipid tails remain on the inside of the bilayer
Hydrophilic heads remain on the outside of the bilayer toward the cytosol and extracellular fluid
Amphiphile
A molecule that contains hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, such as phospholipids
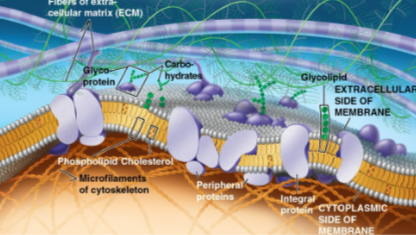
Fluid mosaic model
A model of the membrane as a mosaic of protein molecules bobbing in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
Proteins typically form groups that carry out common functions
Most lipids and some proteins can move sideways within the membrane
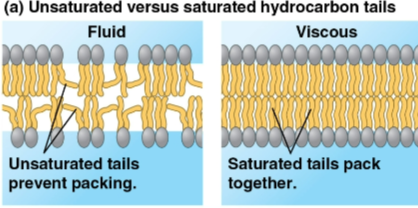
Membrane solidification
Occurs as temperatures cool around a membrane depending on the types of lipids present
More unsaturated fatty acids have higher fluidity than saturated fatty acids
Lowers membrane function through higher packing of molecules — but too fluid membranes do not support protein function
Addressed by some animal behaviors such as hibernation or migration
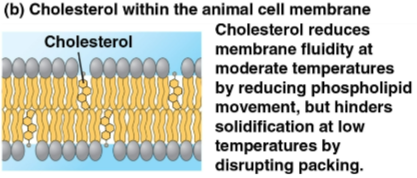
Cholesterol
Membrane component in animal cells that can affect membrane fluidity
Warmer temperatures lead to restriained movement
Cooler temperatures prevent tight packing
Lipid composition
Depends on the environmental conditions of an organism
Extremely cold environments are more conducive to higher unsaturated fats in the membrane
Seasonal changes can occur such as in winter wheat’s increased levels to prevent solidification
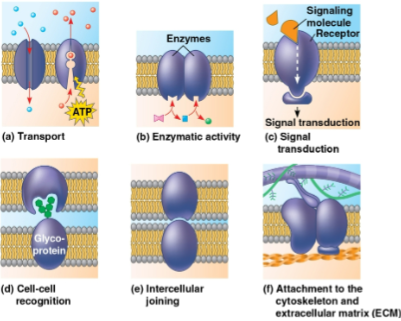
Membrane proteins
Proteins held in place via the cytoskeleton or materials outside the cell that function in:
Transport
Enzymatic activity
Signal transduction
Cell-cell recognition
Intercellular joining
Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
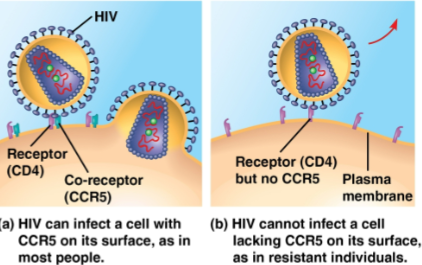
HIV
A disease that enters immune cells by binding to a cell-surface protein and co-receptor
Individuals without the receptor are immune, so drugs are in development to mask the receptor and block entrance in nonimmune individuals
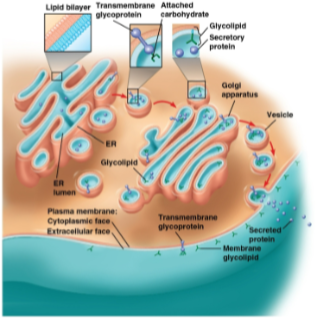
Cell identification
Performed through the binding of molecules on the surface of the membrane; these molecules include glycolipids and glycoproteins for identification markers