Lecture #15: Protein Anabolism
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
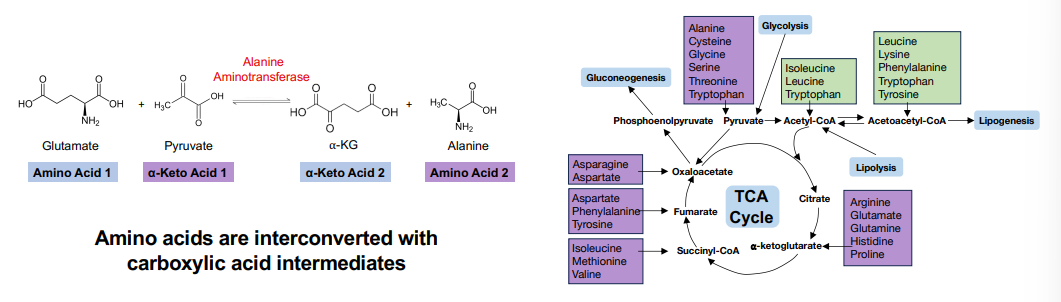
Amino acids are _____ with many of the metabolites in core energy metabolites (pyruvate and TCA pathways)
interchangeable
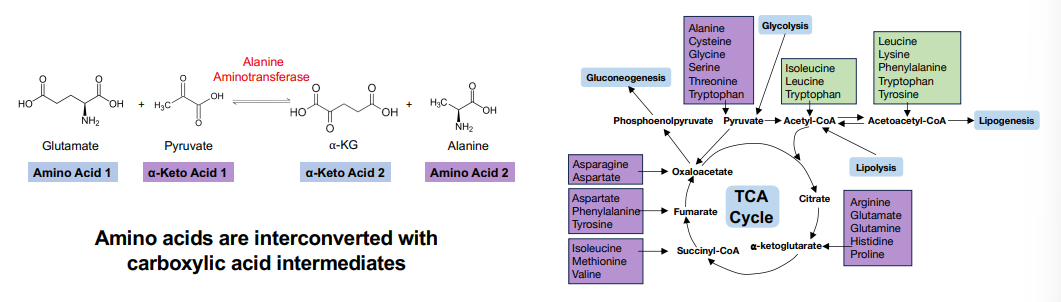
What are amino acids interconverted to?
Carboxylic acid intermediates

Which macromolecules contain nitrogen?
Protein
Nucleic acids
Nitrogen catabolism
(mostly amino acids) is energy-intensive
Nitrogen anabolism
Revolves around the transfer of amino and methyl groups

Essential amino acids (NOT synthesized at sufficient amounts in the body)
Histidine
Phenylalanine
Isoleucine
Threonine
Leucine
Tryptophan
Lysine
Valine
Methionine

Non-essential (Synthesized at sufficient amounts in the body)
Alanine
Glutamine
Arginine
Glycine
Asparagine
Proline
Aspartate
Serine
Cysteine
Tyrosine
Glutamate
Can the body make essential amino acids?
No essential amino acids need to be consumed through diets (synthesized by microbes and plants)
Who synthesizes essential amino acids?
Microbes
Plants
Do all animals have the same essential amino acids?
No, they are based on the organism, life stage, and health condition.
Ex.
Arginine may be conditionally essential for rapid growth
Taurine is essential for cats
Tyrosine and cysteine are essential if phenylalanine and methionine are deficient respectively (they are precursors)
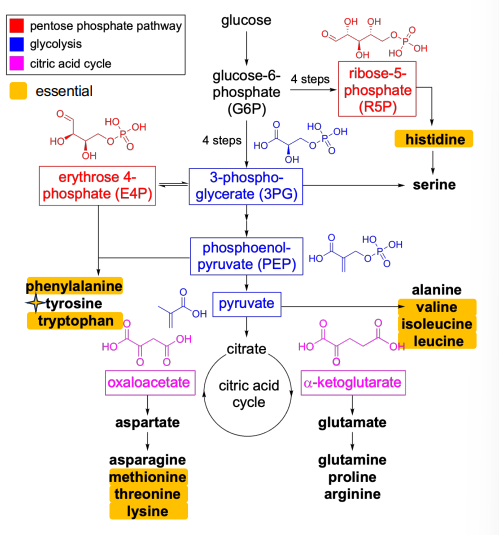
How are amino acids categorized?
Categorized by families based on their structures
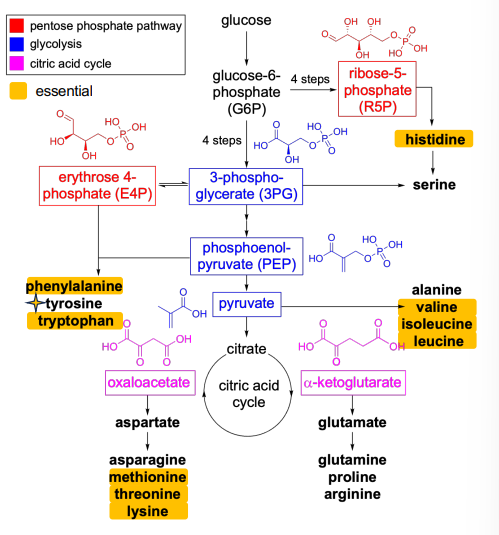
Glycolysis (amino acids)
3-Phosphoglycerate (Serine)
Pyruvate (Alanine)
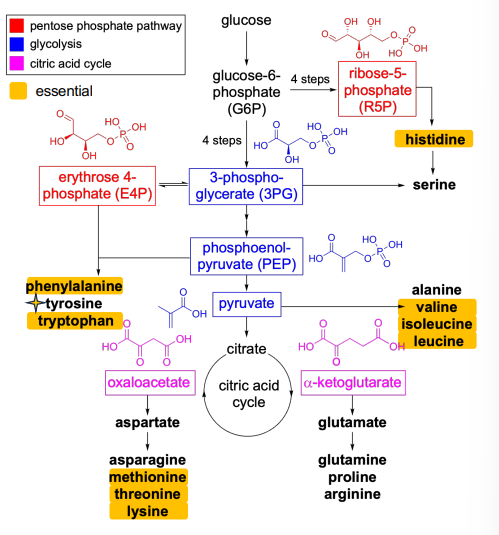
Tricarboxylic acid cycle TCA (amino acids)
Alpha-Ketoglutarate (Glutamate)
Oxaloacetate (Aspartate)
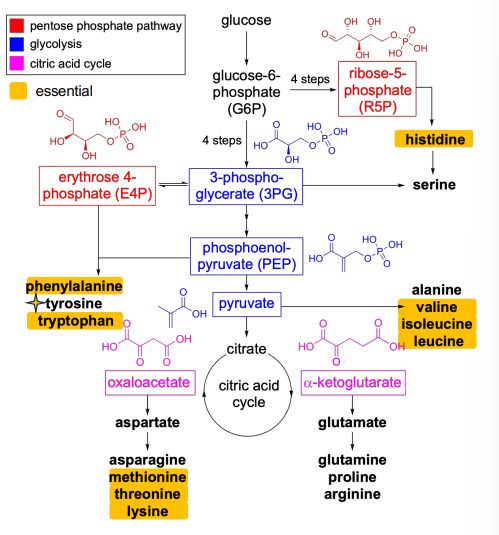
Pentose phosphate pathway
Most mammals cannot synthesize tyrosine and histidine from PPP intermediates
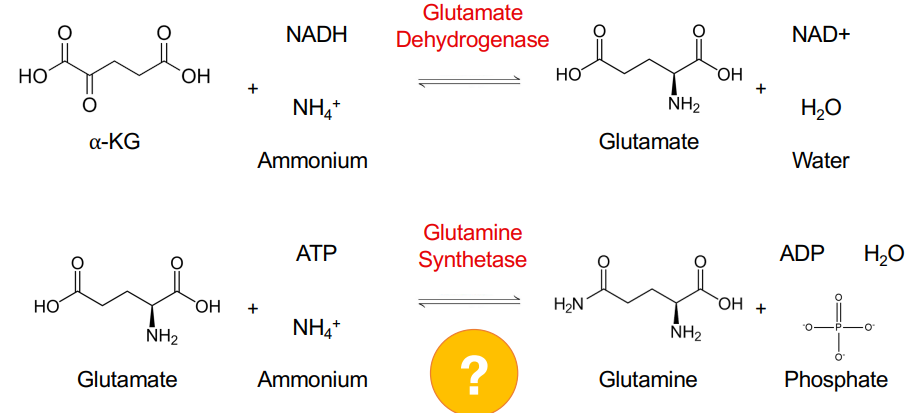
What is glutamate and glutamine synthesized from?
Ammonium assimilation and transamination rxns
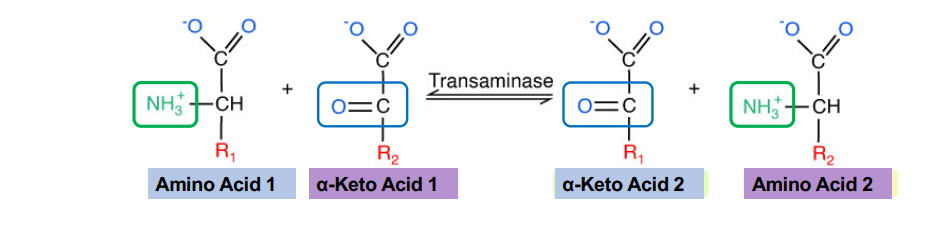
What is essential to amino acid synthesis?
Transamination
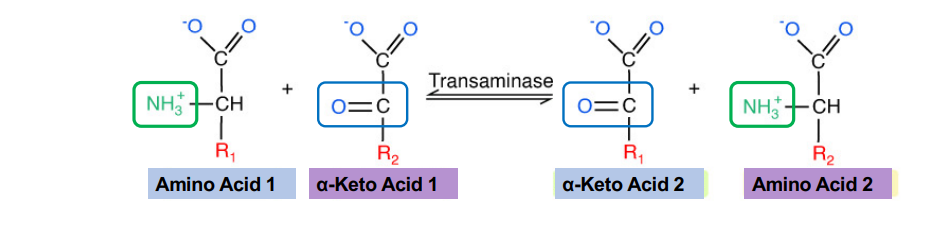
Transamination
Occurs both in cytosol and mitochondria
Enzyme names: Transaminase (glutamate or glutamine)
Reaction type: transfers an amino group onto a molecule that does not already have one
This is how non-essential amino acids receive their amino group! ***Does not require ATP***

Where does transamination take place?
Both in cytosol and mitochondria
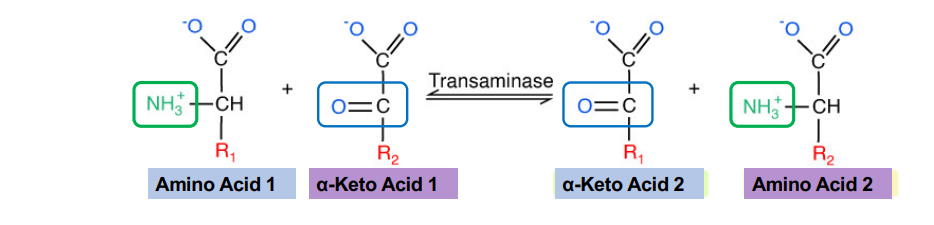
What are the enzyme names for transamination?
Transaminase (glutamate or glutamine)
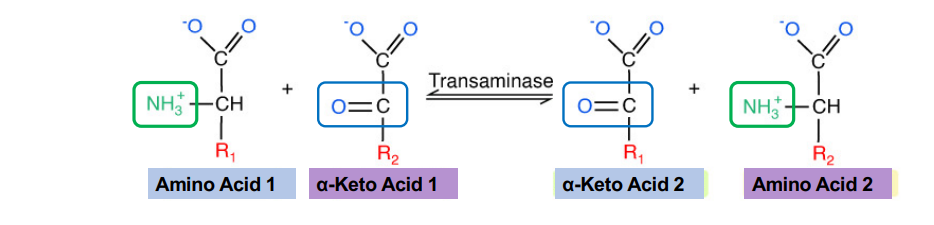
What is the reaction type in transamination?
Transfers an amino group onto a molecule that doesn’t already have one
This is how non-essential amino acids receive their amino group! ***Does not require ATP***
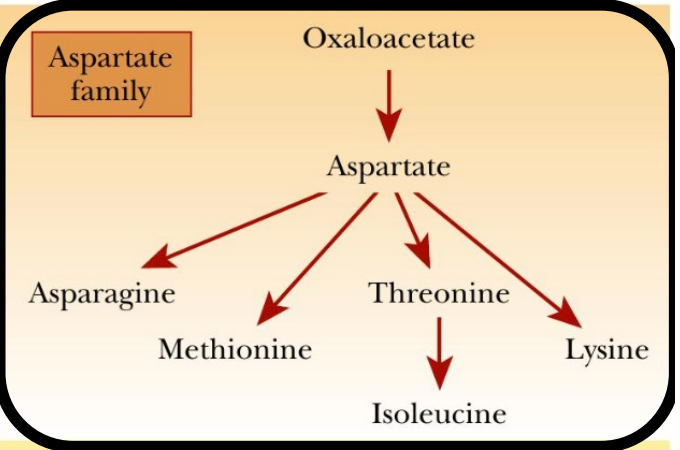
What is a precursor to many amino acids?
Aspartate
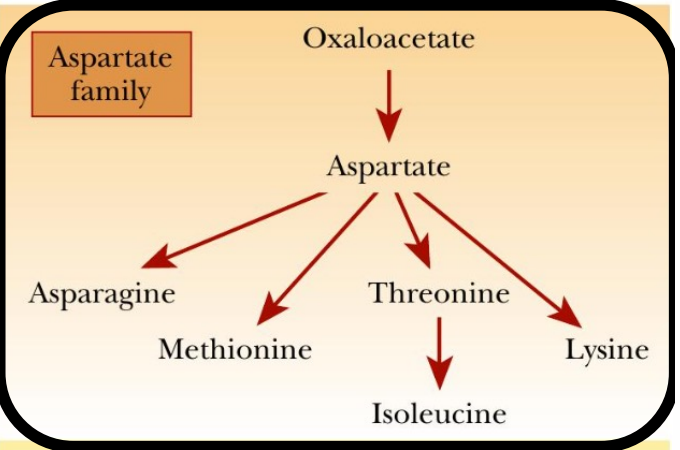
AST
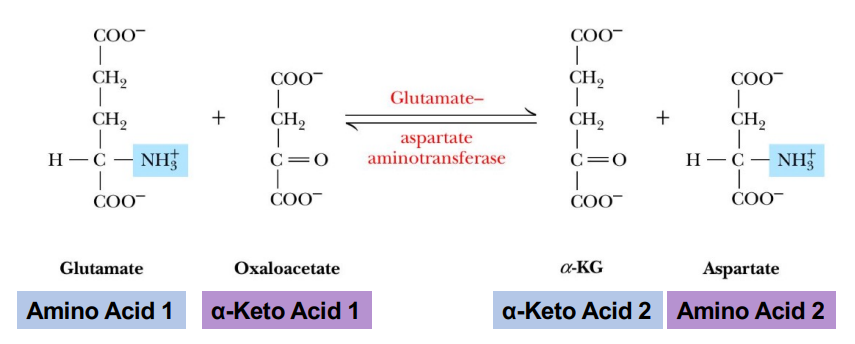
Transamination Aspartate synthesis
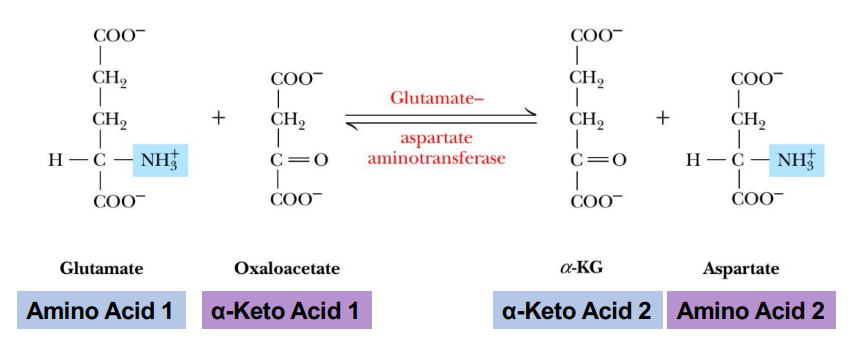
Transamination Aspartate synthesis (AST)
Amino group from glutamate is transaminated to oxaloacetate
Forms aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate
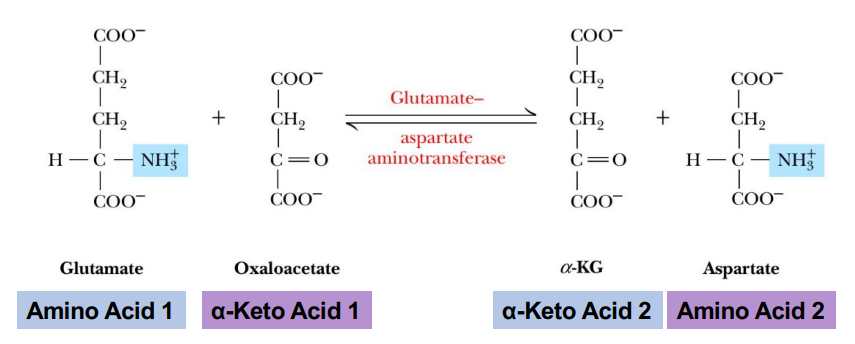
What happens to the amino group in transamination aspartate synthesis (AST)?
The amino group from glutamate is transmitted to oxaloacetate to form aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate
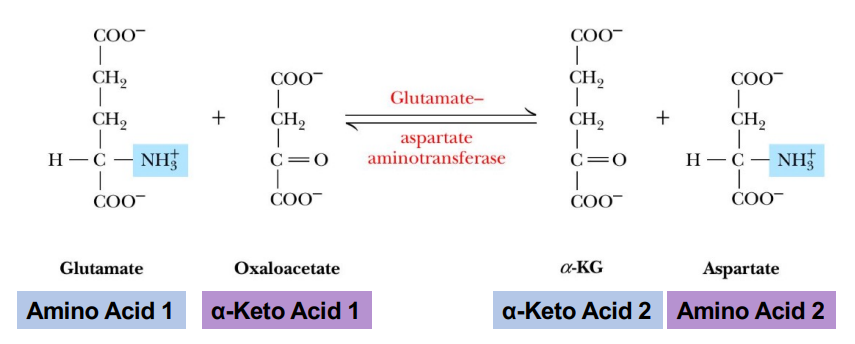
What forms when the amino group from glutamate is transaminated to oxaloacetate?
Aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate
ALT
Alanine synthesis transamination
The amino group from glutamate is transaminated to what in AST (Aspartate synthesis transamination)
Oxaloacetate
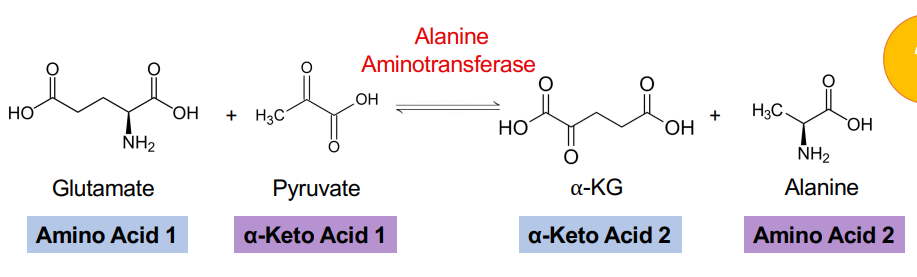
Alanine synthesis transamination (ALT)
Amino group from glutamate is transaminated to pyruvate
Forms alanine and alpha-ketoglutarate ***AST and ALT used as a clinical marker for hepatic damage***
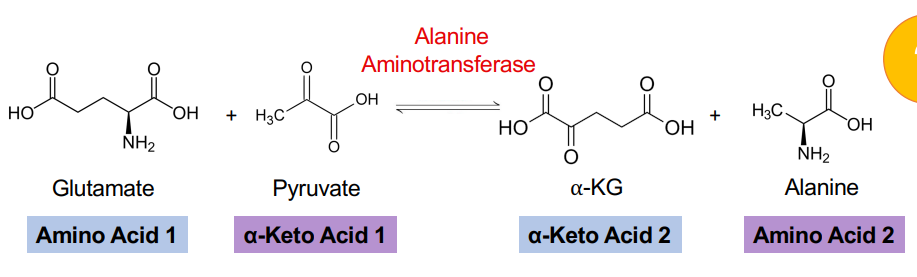
What is transaminated from the amino group from glutamate in Alanine synthesis transamination (ALT)
Pyruvate
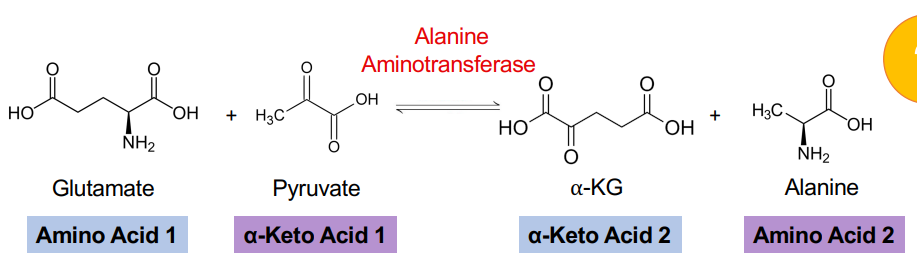
What is fromed in ALT?
Alanine
Alpha-ketoglutarate
What is a clinical marker for hepatic damage?
AST and ALT
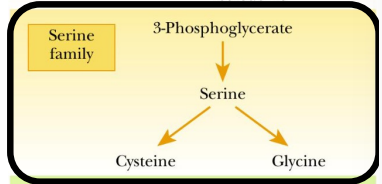
What is serine synthesized from?
3-phosphoglycerate

What are the requirements for serine synthesis?
Dehydrogenation
Transamination
Dephosphorylation
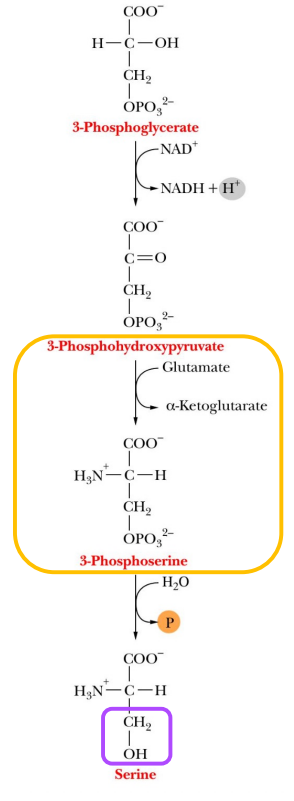
Serine converts to?
Glycine via serine hydroxymethyltransferase
Cysteine via multiple steps that transfer sulfur group from methionine…
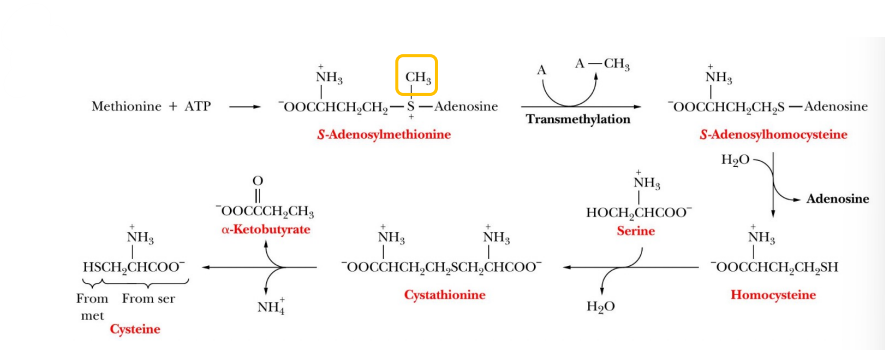
What works together to transfer methyl groups?
Serine
Methionine
Cysteine
Methionine
Essential amino acid for vital transmethylation (CH4 transfer)
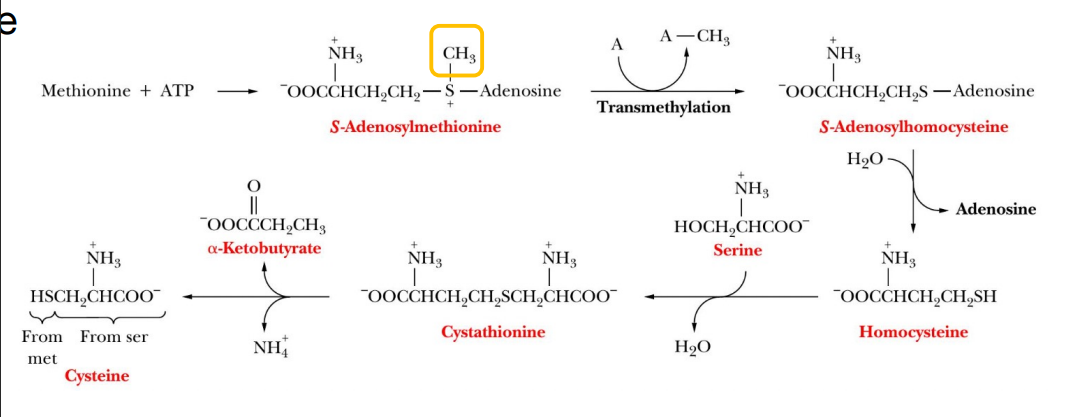
Cysteine synthesis
Activation via ATP to form S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)
Methyl group is donated to another metabolite “A” (methylation)
Hydrolysis yields homocysteine
Condensation of serine yields cystathionine
Hydrolysis yields Cysteine
How does the body gain access to essential amino acids?
Through diet
How does the body gain access to non-essential amino acids?
Synthesizing them from other molecules, primarily intermediates from the glycolytic citric acid pathways.
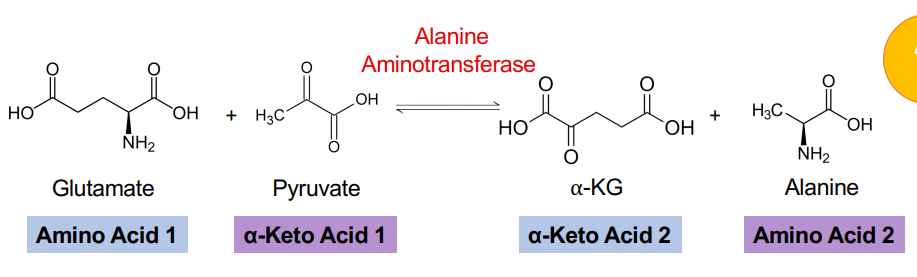
What is the precursor (carbon skeleton) for alanine?
Pyruvate
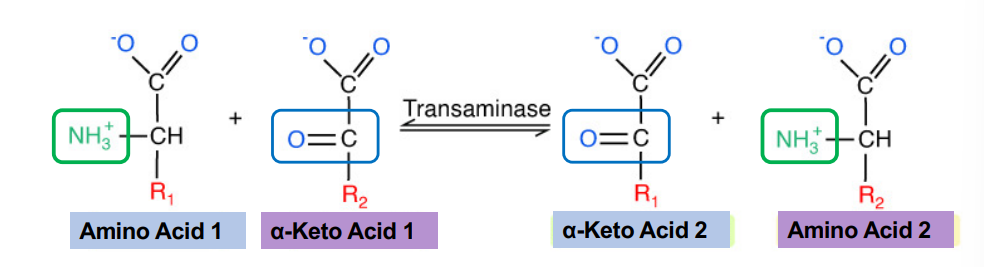
What is the precursor (carbon skeleton) for glutamate?
Alpha-Ketoglutarate
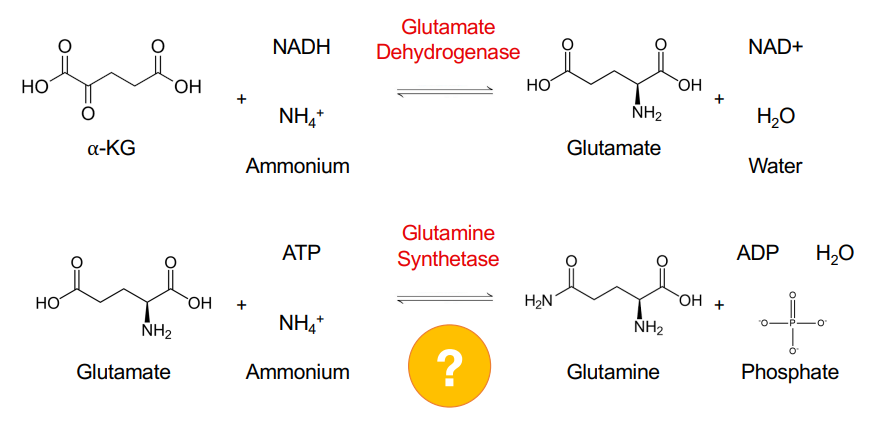
Which amino acids are formed via ammonia assimilation?
Glutamate and glutamine
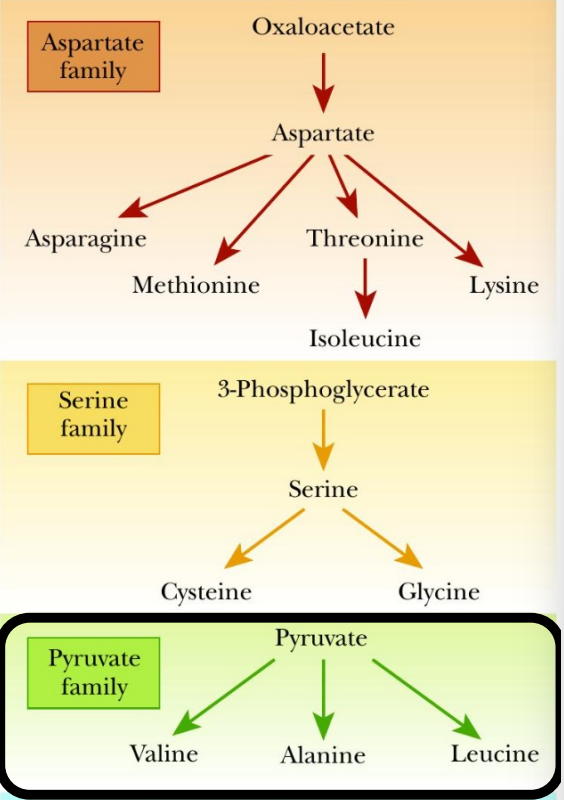
Which amino acids are formed via transamination?
AST: (aspartate family) asparagine, methionine, isoleucine, lysine
ALT: (pyruvate family) valine, alanine, leucine