Pediatric Radiology
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What should you try to do with the child before entering the room?
Talk and try to make friends with the child
The success of pediatric radiology is dependent on what two things?
techs attitude and approach to the child
techs preparation in the room
What is the pre-exam preparation for pediatrics?
immobilization and shielding devices
cassettes and film markers
specific positioning routine
role of team radiographers
patient preparation
True or false: children do not reach a sense of understanding at a specific predictable age
True
By what age can children generally be talked through a diagnostic study without aid from parent or immobilization?
2-3
What are the steps you should take after bringing the parent and child into the x-ray room?
introduce yourself to both the pt and the parent as the tech who will be doing the exam
find out what info has been shared with them by the physician
explain what you will be doing and what you will require from the pt (including immobilization)
What are the three roles the parent can have?
parent is in the room has an observer/comforter
parent is a participant who assists in immobilization
parent is asked to wait in the waiting room
If the parent is participating in immobilization, what all should you explain to them?
Explain exactly what you need them to do, a lot of the time the parent won’t hold the child tightly for fear of hurting them, so explain the probability of repeats if not done properly
How can you protect your child when imaging them?
always have supervision of a young child
don't leave the room unless caretaker or another tech are in the room with them
use immobilization devices only when necessary
What is the term used to describe a child who might be a victim of abuse?
Battered child syndrome (older), non accidental trauma (used today)
What is the techs role when it comes to reporting child abuse?
not their job to make a judgement as to whether or not NAT has occurred, just report the facts
techs should know what their responsibilities are concerning this in the state they are working in
What should you look for when there is suspected abuse?
child may tell a different story than caretaker
numerous bruises, cigarette burns
parent not willing to leave child (especially teenager)
several fractures seen on radiographs
rib fx
corner fxs or bucket fx on limbs
fx’s that don’t align with the story
child tries to hid injuries
child fearful of adults or overly compliant
child extremely violent or says inappropriate comments
Who should you report any suspected abuse to?
Radiologist or physician
What are the radiographs typically ordered if suspect abuse case?
lateral and AP skull
complete AP and lateral spine
AP humerus, forearm, wrist, and hand
AP pelvis
AP femur and tib/fib, feet
AP and lateral ribs
What could your facility want when imaging for suspected abuse?
Leave collimation open to catch incidental findings
How must you act towards your patients parents if there is a suspected abuse case?
remain calm and give the parent the same courtesy as any other parent
remain nonjudgmental (the abuser may not be the person who brought the child in)
What are the six types of abuse?
neglect
physical
sexual
psychological
medical
other
What ages are included in pediatric pts?
Infants through the age of 12-14
If you are imaging an older child, they are treated more like adults except when it comes to what?
Gonadal shielding and reduced exposure factors according to their size
What type of technique should you always use when imaging pediatrics?
Short exposure times and as high of mA as allowable for an optimal image
Why do you want short exposure times and as high of mA as allowable for peds?
To minimize motion
What are the two main types of immobilization devices?
tan-em-board (papoose/brat board)
pigg-o-stat
What are some other common immobilization devices used?
tape
sheets or towels (mummifying)
sandbags
sponges
compression bands
stockinettes
ace bandages
When can you not use a pigg-o-stat?
When the child cannot hold their head up on their own
How can you reduce patient motion in peds?
good communication
immobilization
short exposure time
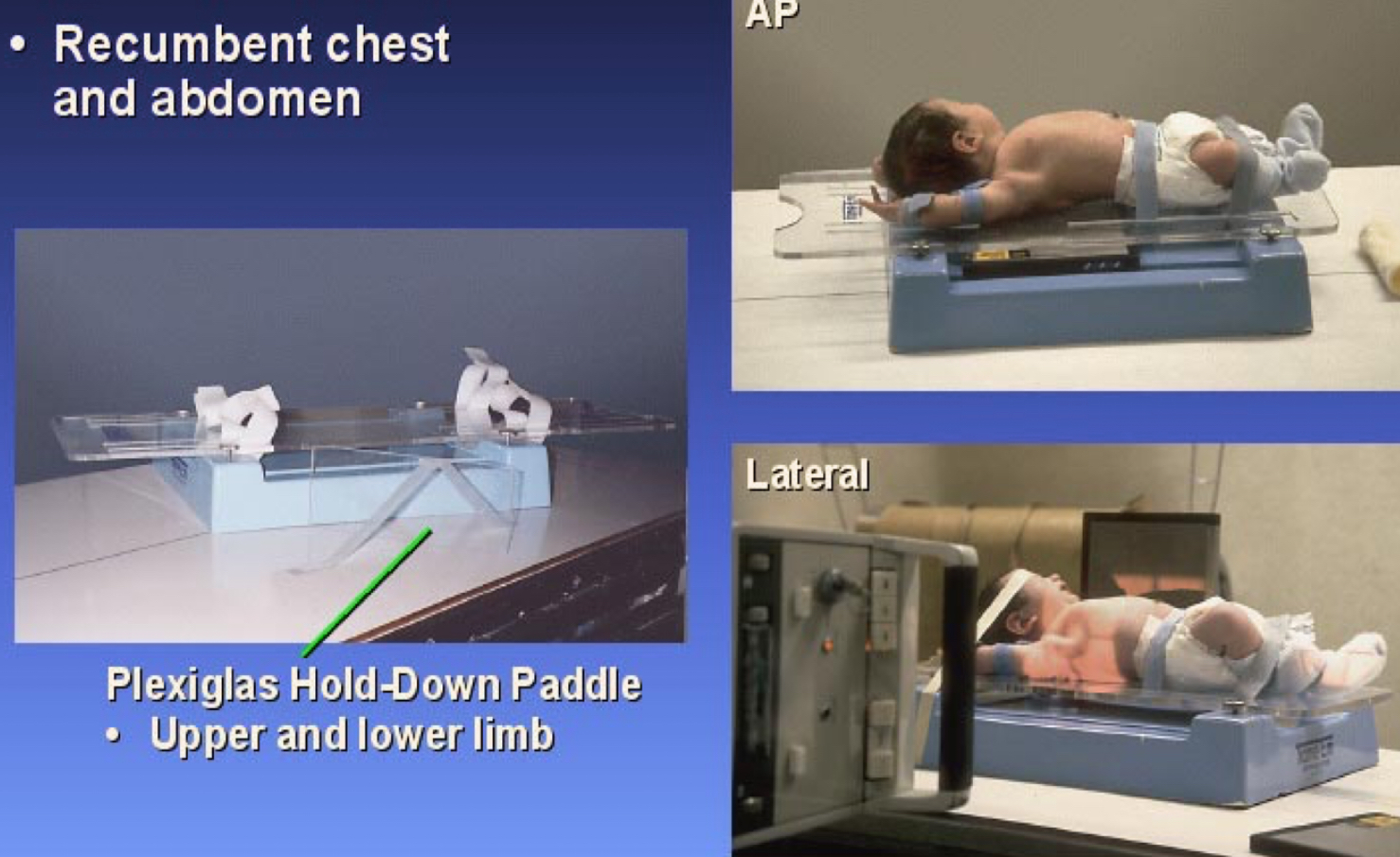
What type of immobilization device is this?
Tam-em-board
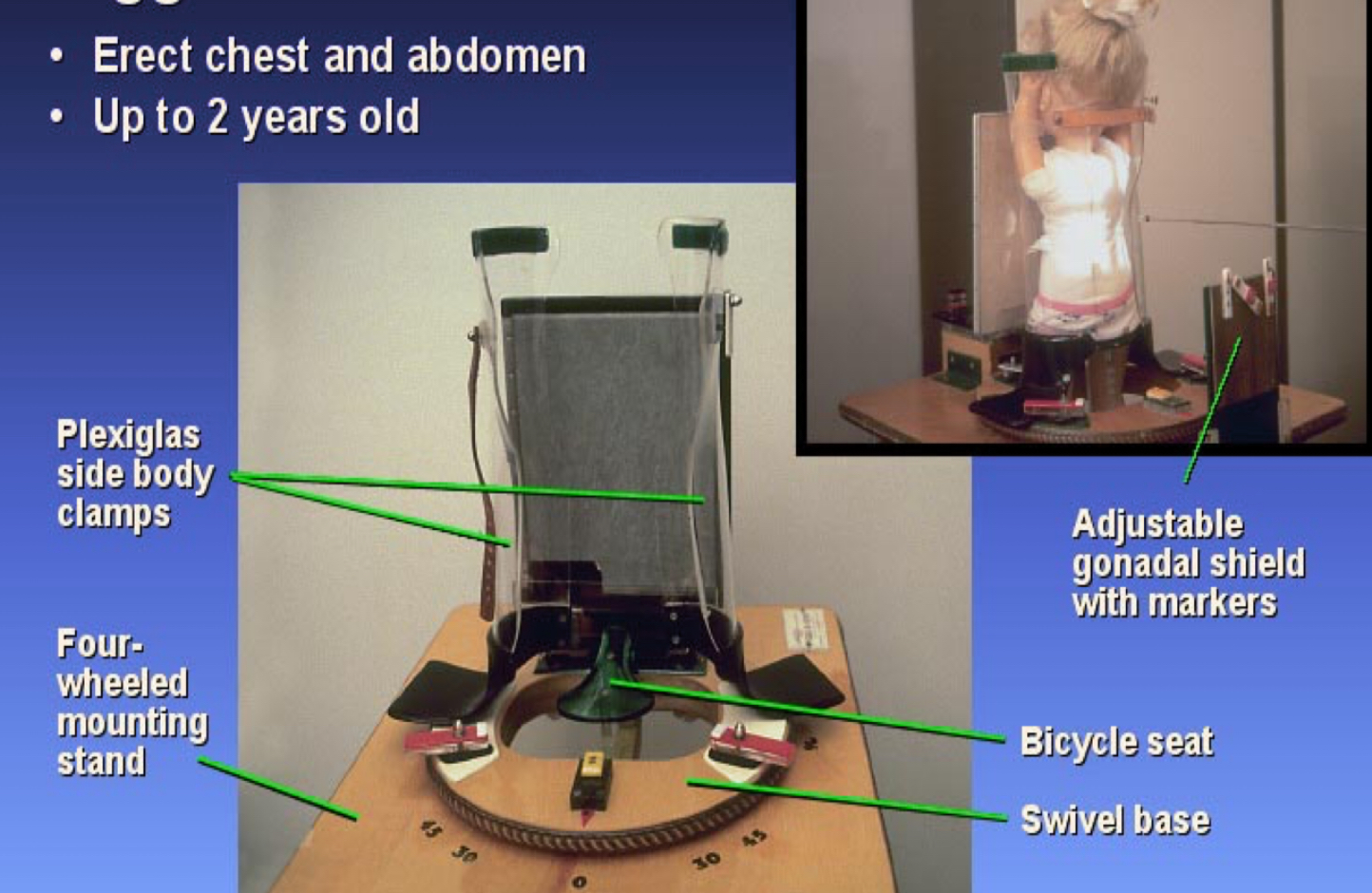
What type of immobilization device is this?
Pigg-o-stat
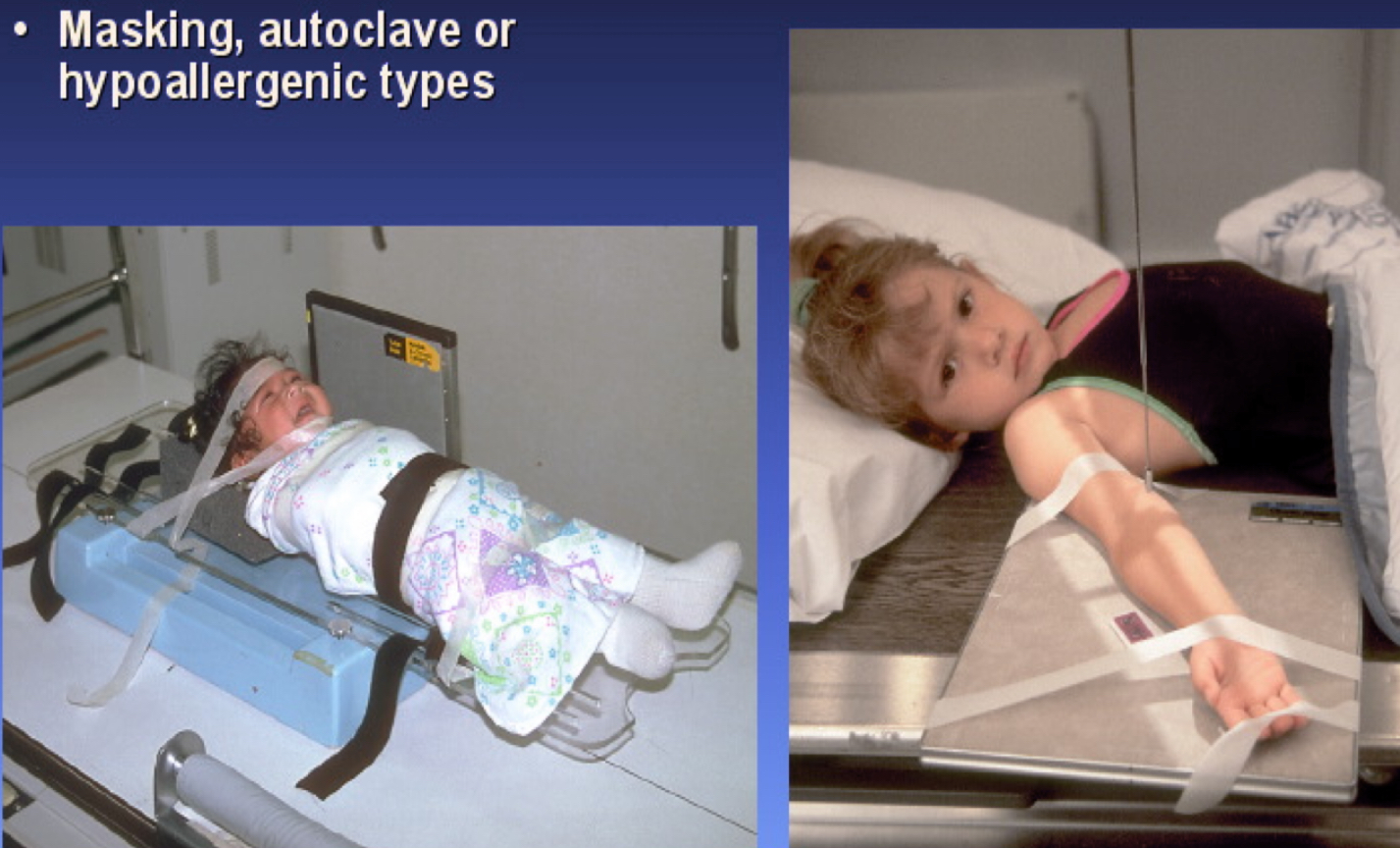
What type of immobilization device is this?
Tape
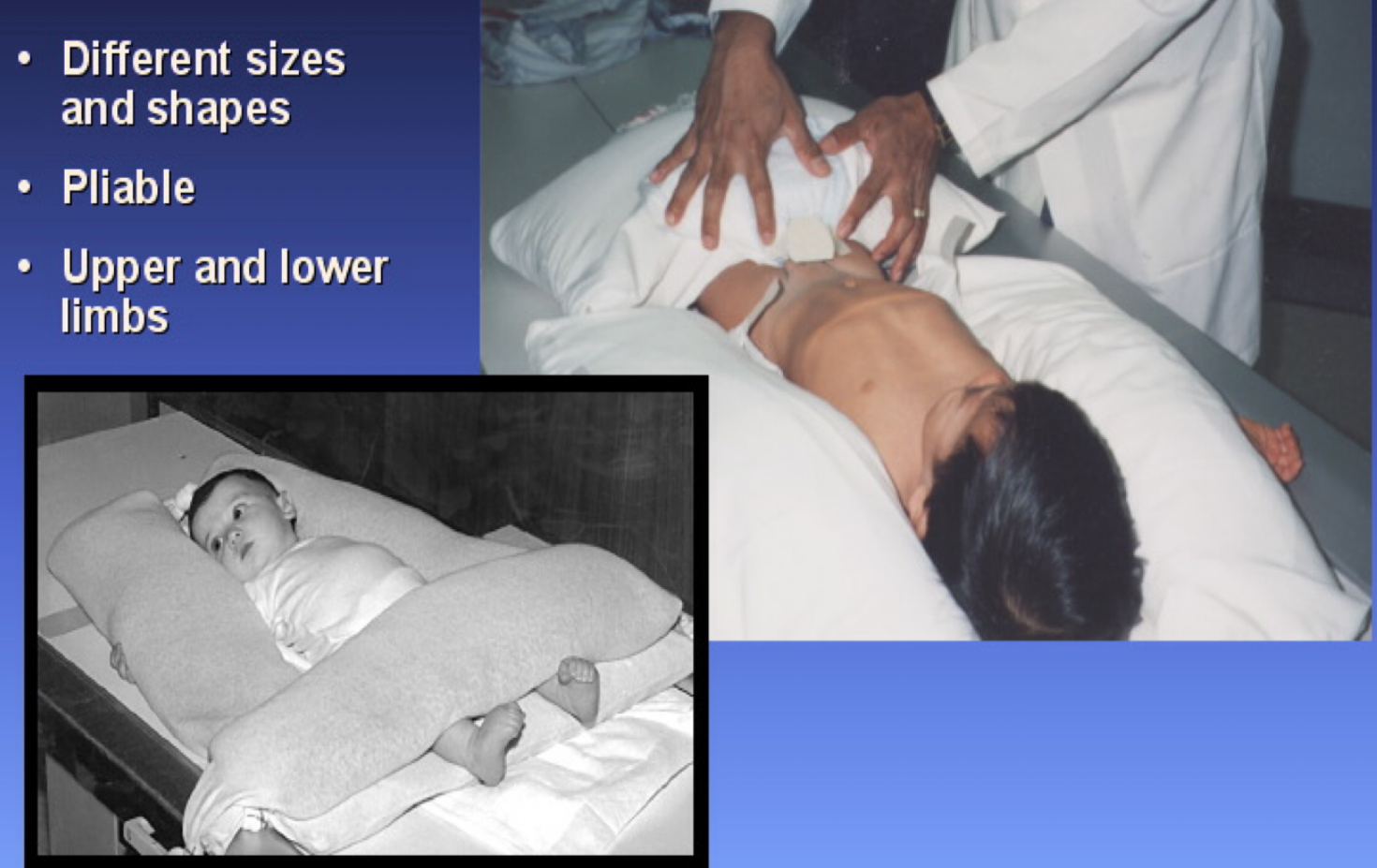
What type of immobilization device is this?
Sandbags
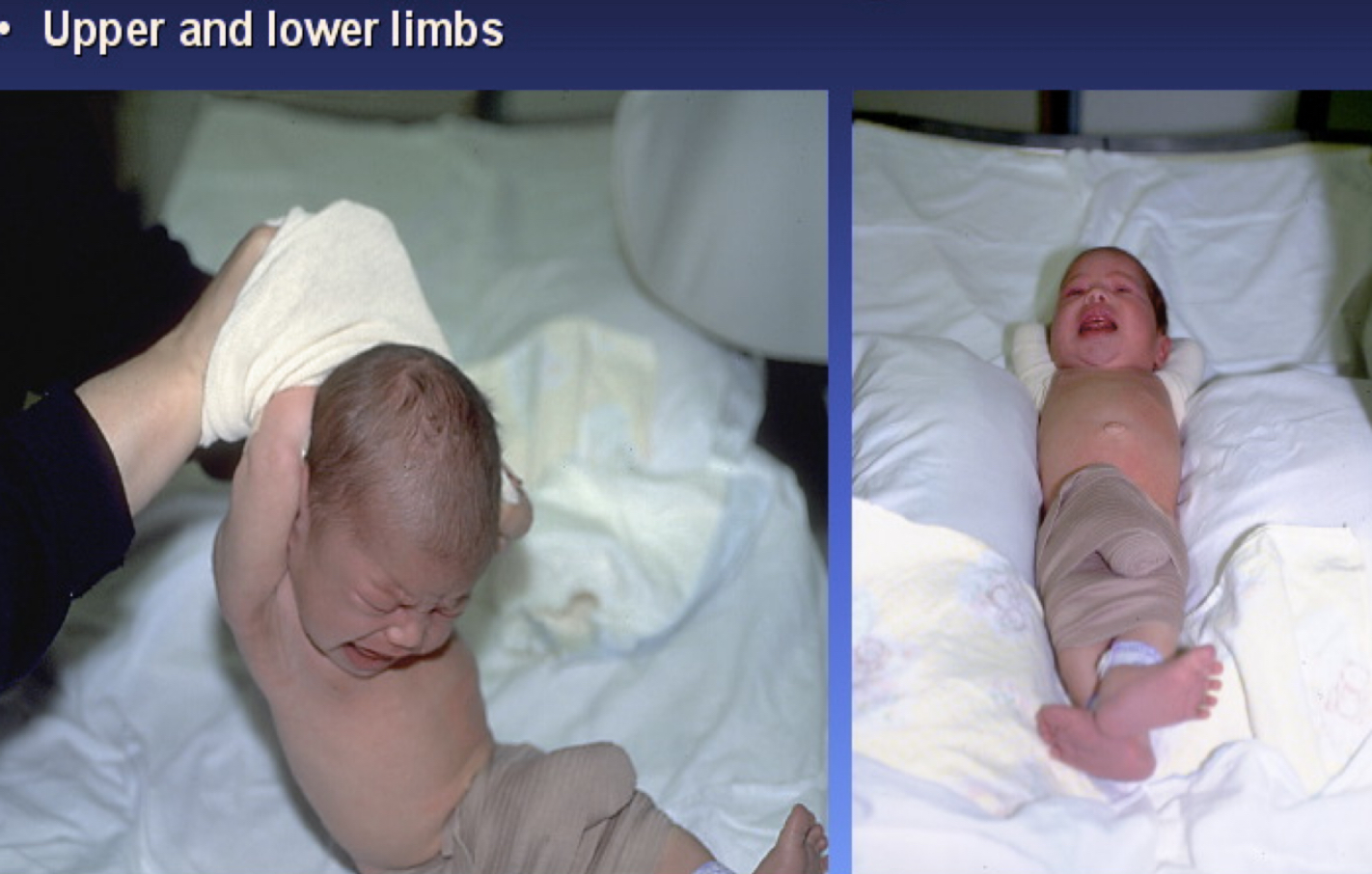
What type of immobilization device is this?
Stockinette and ace bandage
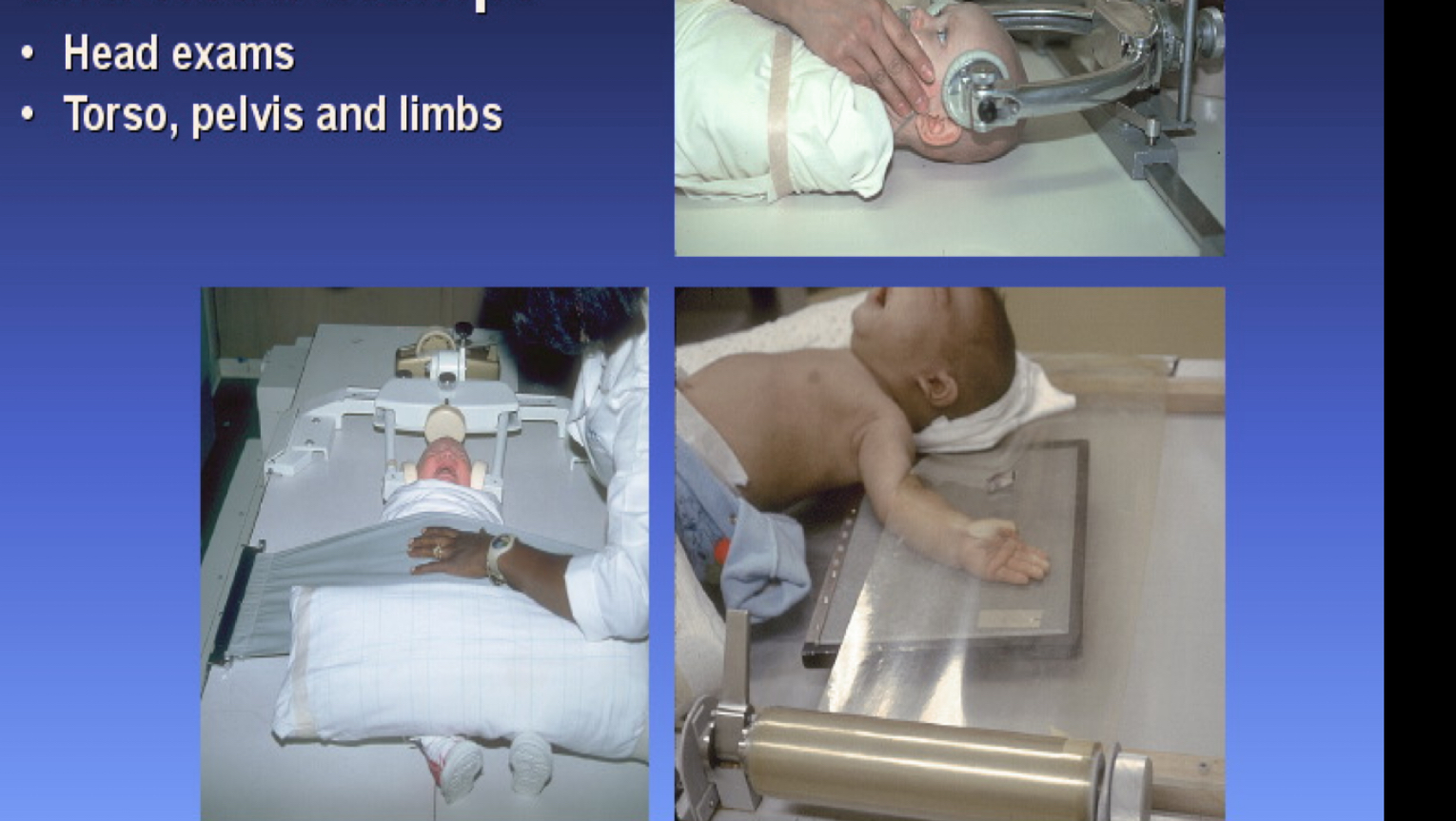
What type of immobilization device is this?
Compression band and head clamps
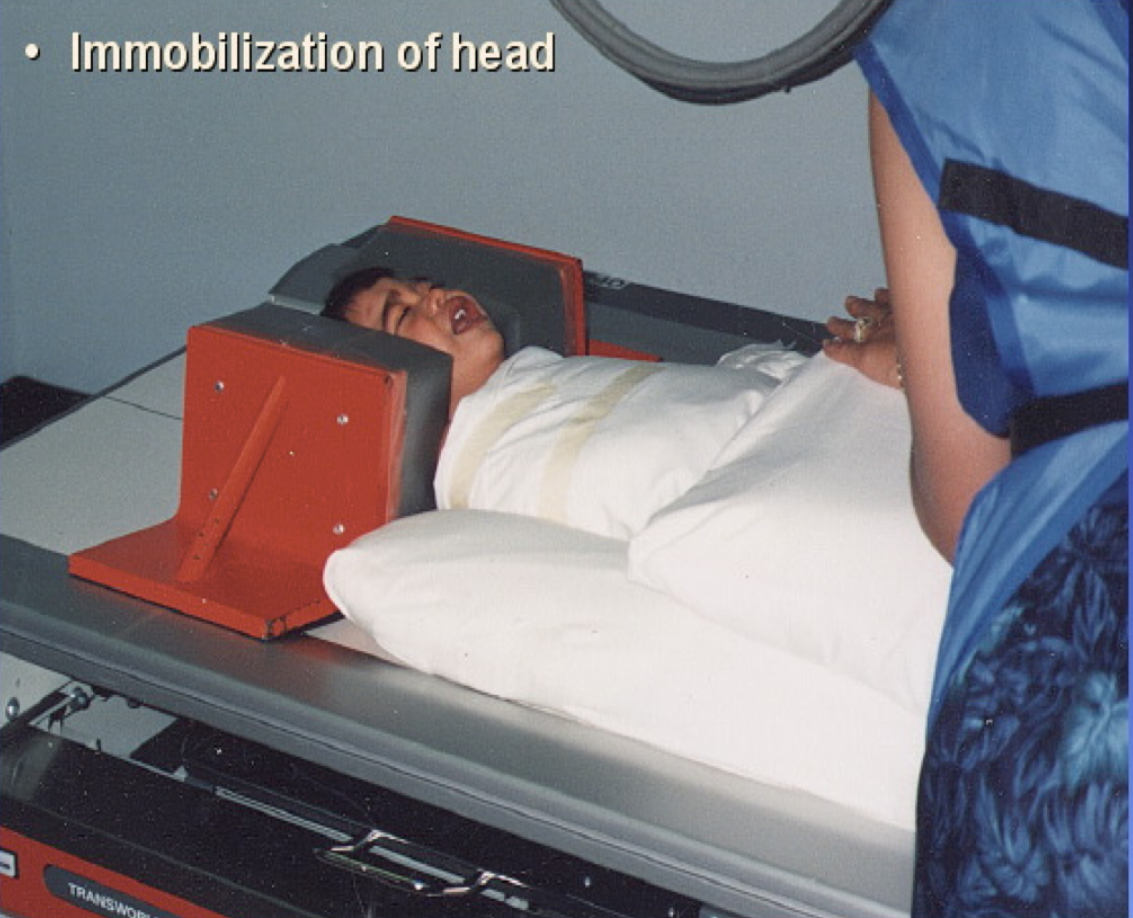
What type of immobilization device is this?
Weighted angle blocks
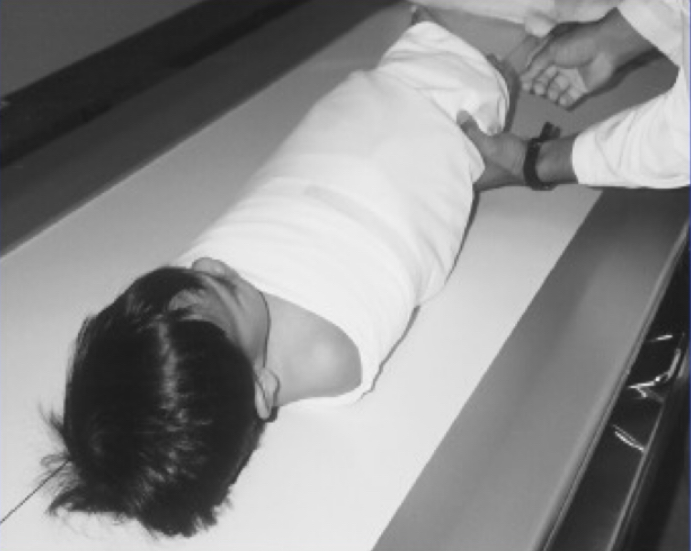
What type of immobilization device is this?
Mummifying
What are the steps for mummifying?
prepare sheet
place patient and immobilize right arm
immobilize left arm and wrap body
pull sheet tightly
tape sheets at arms
immobilize legs, tape sheet at knees
Primary centers of bone formation involve what area?
Mid shaft area and appear before birth
What is the diaphysis of long bones?
Primary centers of bone formation that involve the mid shaft area
What are the ends of diaphysis called?
Metaphysis
What is the metaphysis?
Area where bone growth occurs
What is the epiphysis?
secondary center of bone formation that involves the ends of long bones
What is the epiphyseal plate?
Space between the diaphysis and epiphysis, made up of cartilage
The reduction of what is critical in young children whose developing cells are particularly sensitive to the effects of radiation
Repeat exposures
What will reduce your chances of repeats in pediatrics?
Proper immobilization and short exposure times
True or false: accurate technique charts with body weights should be used
True
True or false: most examinations for pediatrics will have reduced views for children under a certain age
True
What type of gonadal shielding should be used for children?
Contact type
What other safeguards should be used and explained to the parent?
Close collimation, low dosage techniques, and a minimal number of exposures
What should be given to the parent if they are staying in the room during a child’s exam?
Radiation protection such as aprons and lead gloves
True or false: you should make sure that the person staying with the child is not pregnant
True
What all should be removed off the child before the exam and why?
Any clothing, bandages, embroidery, buttons, and diapers because due to the low exposure factors, these will show as artifacts
Salter-Harris fractures
involve the epiphyseal plates, classified based on the location of the fracture and the involvement of surrounding anatomy
What is type I of salter-harris fractures?
Transverse fracture along the epiphyseal plate; may involve slipping of the epiphyses such as seen with slipped capital femoral epiphyses
What is type II of salter-harris fractures?
Fracture though the metaphysis and epiphyseal plate
What is type III of salter-harris fractures?
Fracture through the epiphyseal plate and epiphysis
What is type IV of salter-harris fractures?
Fracture though the metaphysis, epiphyseal plate, and epiphysis
What is type V of salter-harris fractures?
Compression fracture of the epiphyseal plate
What does NICU stand for?
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
NICU
special care for infants that are considered high-risk
usually premature birth
inquire on isolation procedure before working on infant
sanitize equipment
nurse will sometimes assist
watch lines and catheters
What is the greatest danger to premature infants?
Hypothermia
True or false: infants can tolerate minimal movement without their heart rate become irregular
True
Whenever possible, how should chest x-rays be done?
Erect (if they can hold their head up)
How can the lateral chest x-rays be done on infants?
pt on side
pt on back and shoot through (x-table)
If you’re using AEC on infants what should you be sure to do?
Decrease your kVp
Where is your CR for chest x-rays?
To mid thorax (mammary line)
How many ribs should you see on a peds chest x-ray?
Minimum of 8-9 ribs
What size IR should you use for peds chest x-rays?
10 × 12
What can you sometimes do for extremities on infants?
Can sometimes be done in one shot
What should you do if your patient has clubfeet?
Do not attempt to straighten abnormality, just shoot as is
What views should you do on a patient with clubfoot?
Two projections at 90 degrees from each other
What is another name for club foot?
Bilateral talipes varus
What will typically be ordered for the pelvis and hips?
Pelvis and bilateral frog leg
What should always be removed for pelvis and hip peds imaging?
Diaper, snaps, other artifacts
What can you use for the upright abdominal x-rays?
Pigg-o-stat
What can you use for the flat plate abdomen x-rays?
Brat board
Where is your CR for infants for KUB x-ray?
1 inch above umbilicus
Where is your CR for children for a KUB x-ray?
1 inch above iliac crest
When do you exposure for the AP erect abdomen on a child?
On expiration
How many techs should you have when doing headwork on a child?
Two
Where is your CR for a AP skull projection on a child?
Parallel to OML
What might you have to do to your barium for a child?
Diluted
Who puts the tip in when doing a BE on a child?
Radiologist
What should you do with the child before beginning a fluoro procedure?
Demonstrate how it works and explain it to them
How much barium should be used for an upper GI study on a NB- 1 year old?
2-4 oz
How much barium should be used for an upper GI study on a 1-3 year old?
4-6 oz
How much barium should be used for an upper GI study on a 3-10 year old?
6-12 oz
How much barium should be used for an upper GI on a child over 10 years?
12-16 oz
What views are typically done on a child for a barium enema?
start with pt supine
left lateral
LPO
RAO
right lateral
end on prone
Who should start the IV on a child for urography?
The best in the department (or call lab)
Contrast for IVUs for children depends on?
Body weight, usually 1 cc per pound
What does a bone age study determine?
Skeletal maturation in children
What views are typically done for a bone age study on a child?
left PA hand/wrist
sometimes AP of the knee