Second & Third Trimesters
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
What is the protocol for second and third trimester sonography?
1. fetal viability
2. fetal presentation
3. fetal number (anatomy/growth of each, placenta, membranes, AFI, etc.)
4. amniotic fluid index
5. evaluate placenta grade, location, relationship to cervical os
6. cervical length
7. fetal age
8. evaluation of uterus, adnexa, cervix
9. 3VC
10. gender
11. establish systematic protocol
What are growth parameters for assessing fetal age?
- BPD
- head circumference (HC)
- femur length (FC)
- humerus length
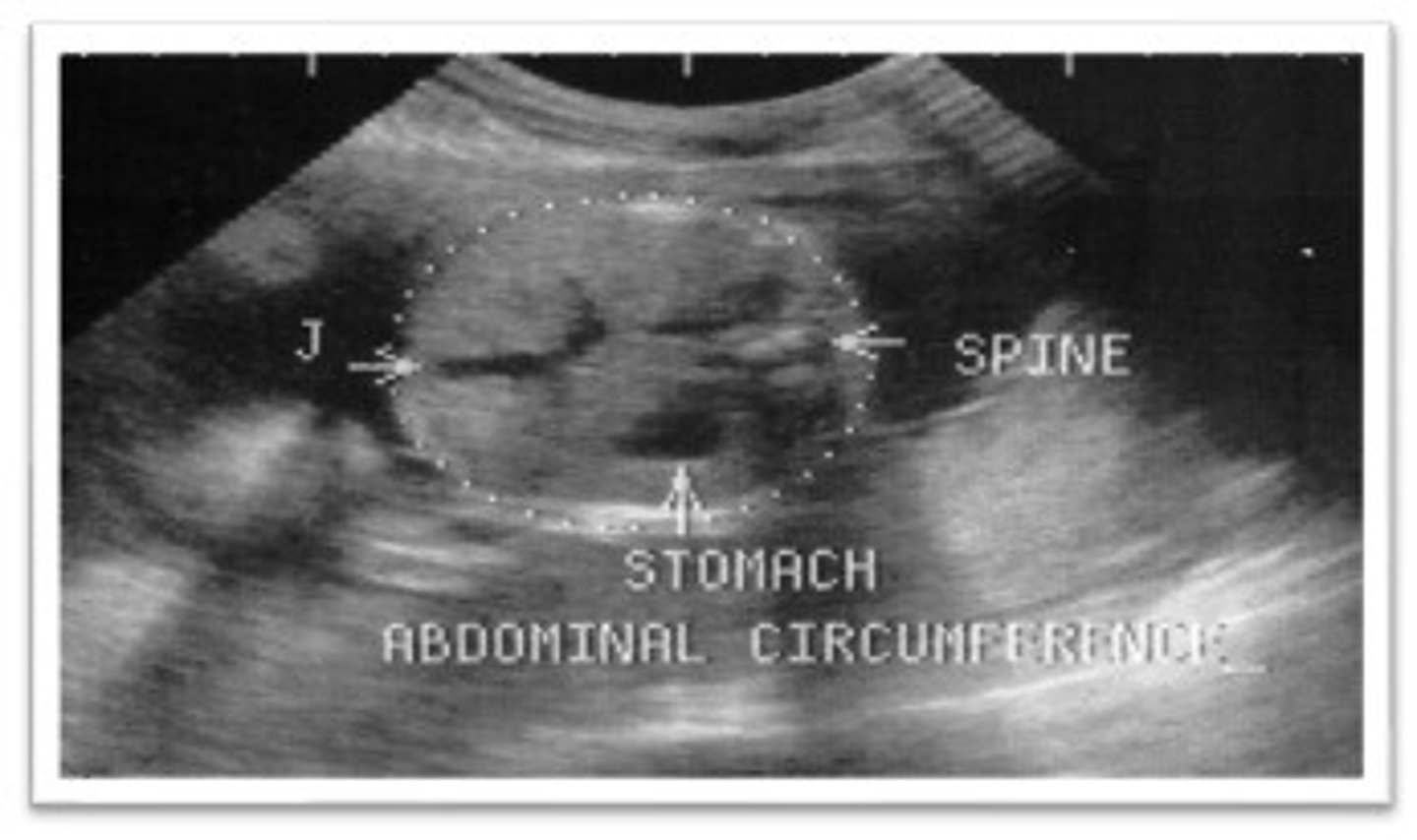
- abdominal circumference (AC)
- HC/AC ratio (head to abdomen size)
What does abdominal circumference measure?
fetal weight
What is typically not seen in second and third trimesters?
ovaries
What is included in a fetal anatomic survey?
head
spine
stomach
heart
kidneys/bladder
What is 3VC?
umbilical cord insertion into abdomen and placenta (2 arteries, 1 vein)
When is the gender of fetus medically indicated?
with multiple gestations
A human pregnancy lasts around __ weeks beginning from the LMP
40
Ovulatory age pregnancy lasts around __ weeks
38
An unknown LMP requires an ultrasound for ___, aka ___
EDC; EDD
(estimated date of confinement/delivery)
First trimester = ___ weeks
Second trimester = ___ weeks
Third trimester = ___ weeks
0-12
13-26
27-40
Post-term pregnancy is greater than __ weeks
40
What is the equation for estimated delivery date called?
nagele's rule
What is the equation for estimated delivery date?
EDD = LMP - 3 months + 7 days (+ 1 year)
What is EDD of an LMP of 3/17/2012?
12/24/2012
What is gravidity?
number of all pregnancies
(includes abortion, ectopic, stillbirths)
What is parity?
number of births to a fetus at or beyond 20 weeks
(includes full-term, premature, abortions, living)
G4P2103 describes what?
4 gravidity
2 parity
1 premature
0 abortions
3 living children
Fetal presentation determines the position of the fetus in relation to the position of the ___
mother
After fetal position is understood, determine the ___ and ___
direction; orientation
What are the fetal positions?
vertex/cephalic
breech
transverse
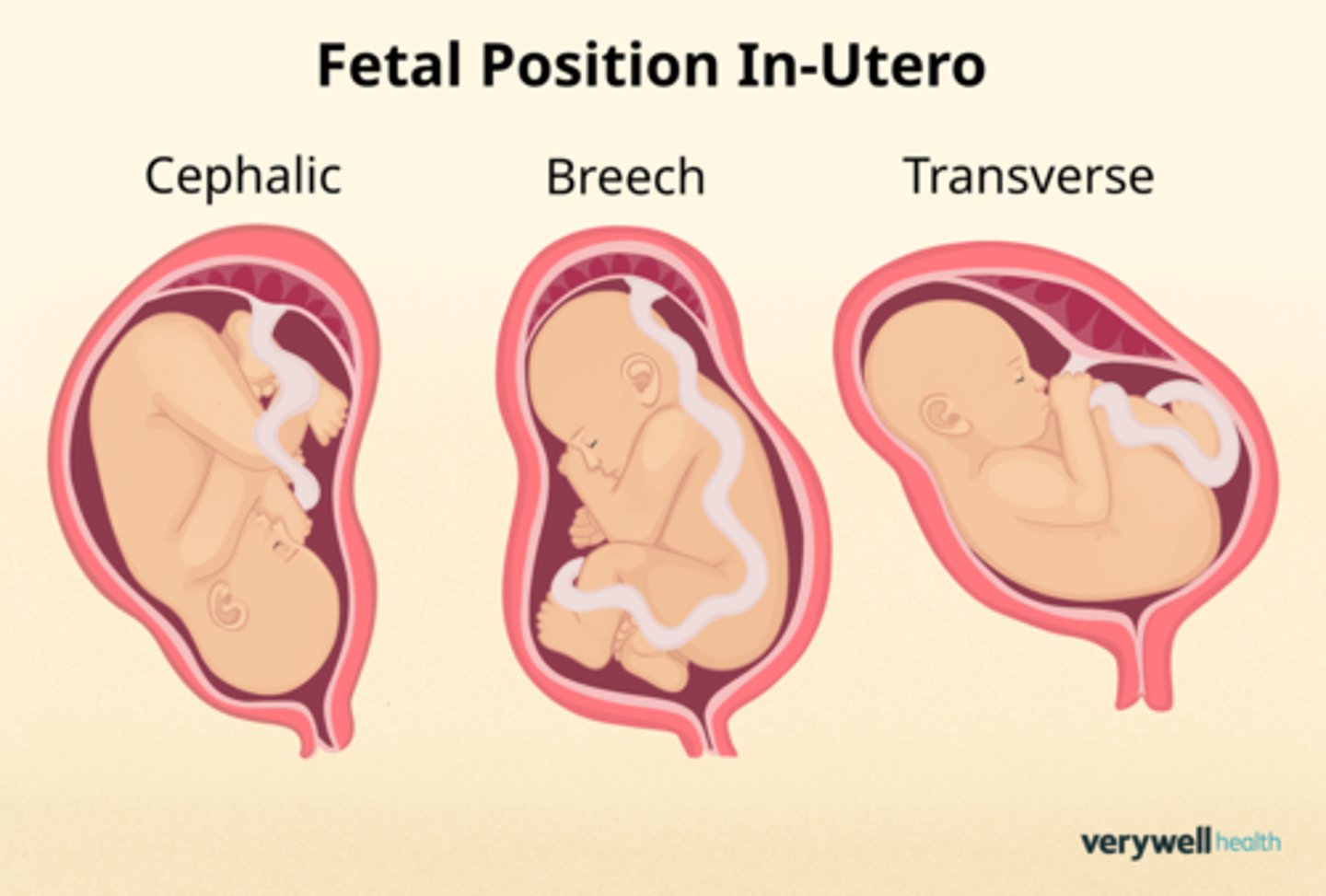
In a vertex/cephalic position, the fetal head is located at level of the ___ and ___
bladder; lower uterine segment
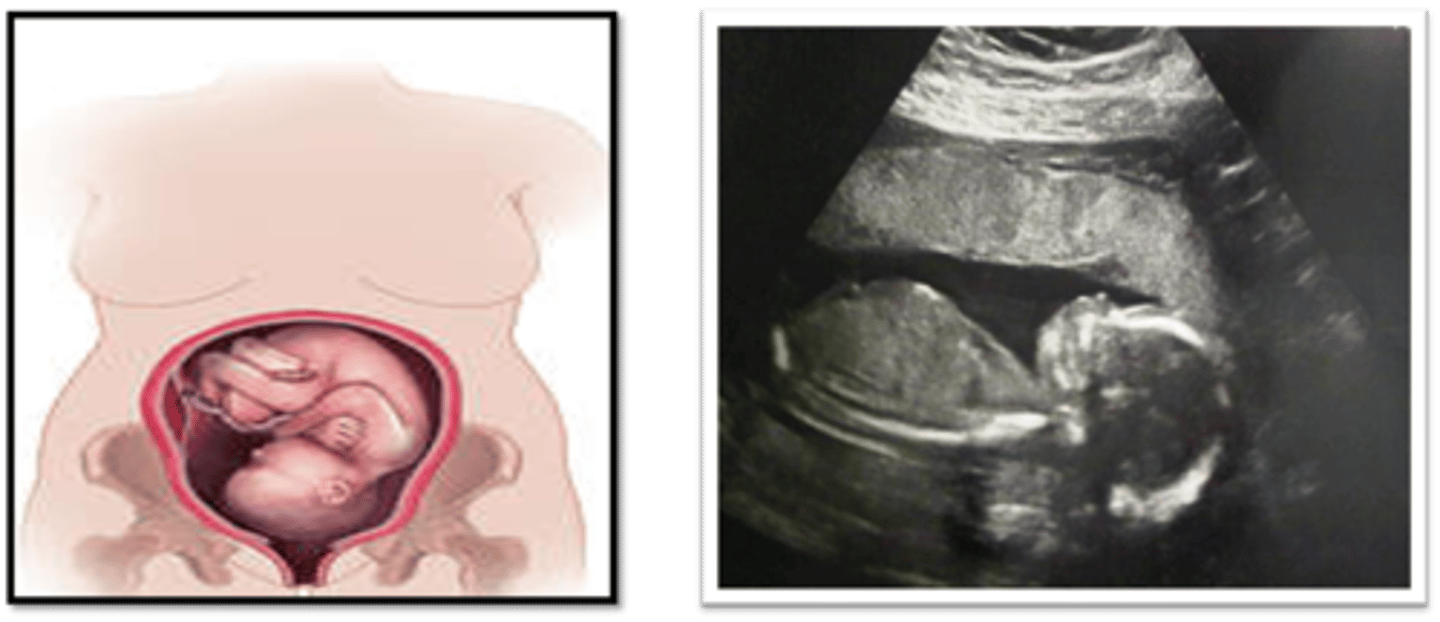
In a vertex/cephalic position, the fetal body is in the ___
uterine fundus
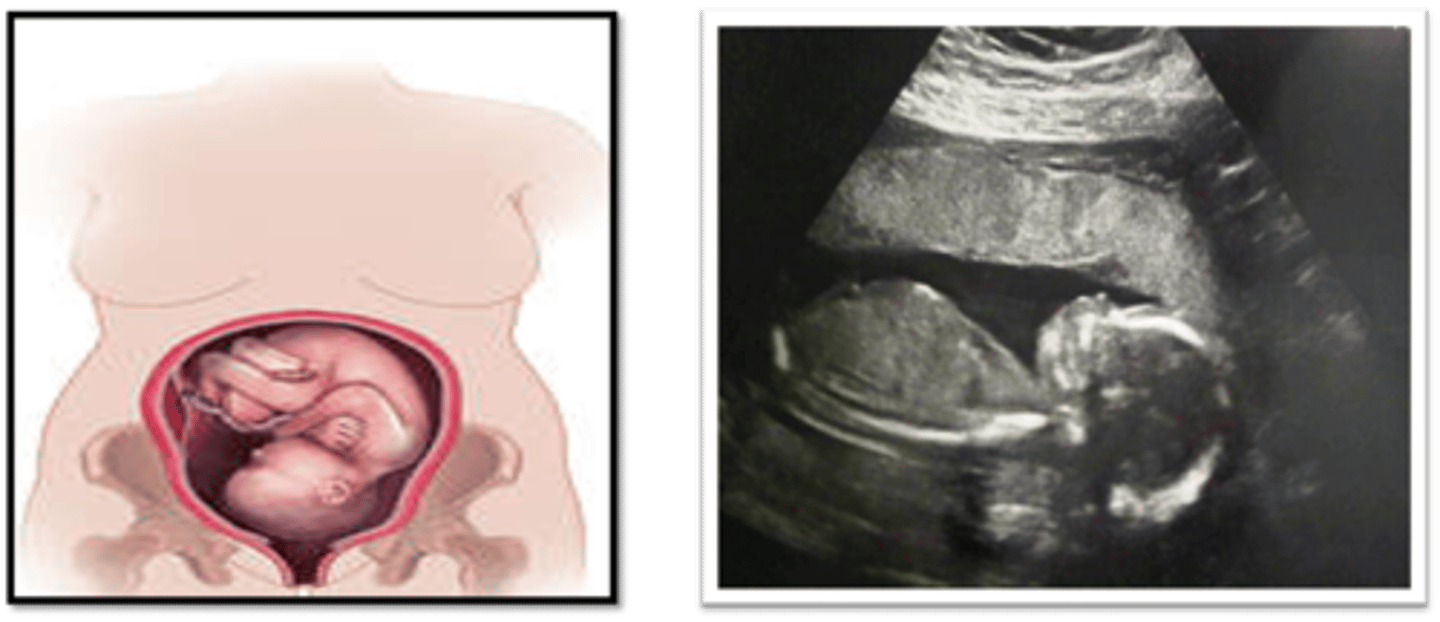
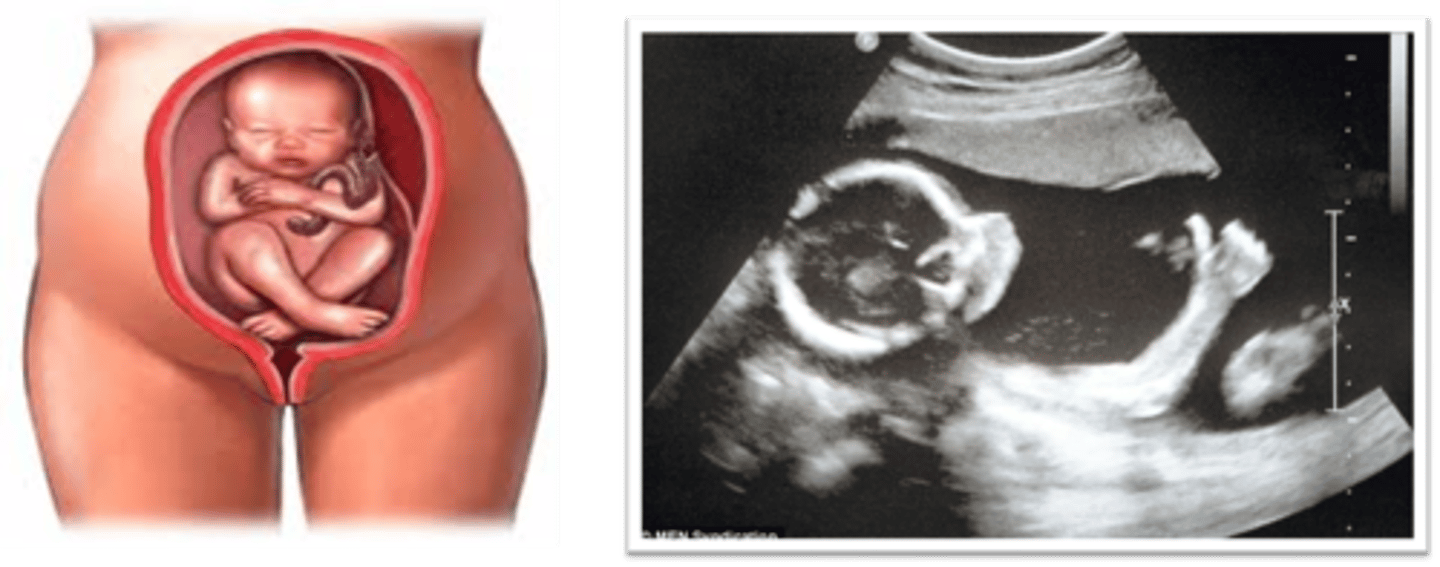
In a breech position, the fetal body/lower extremities are in the ___
lower uterine segment
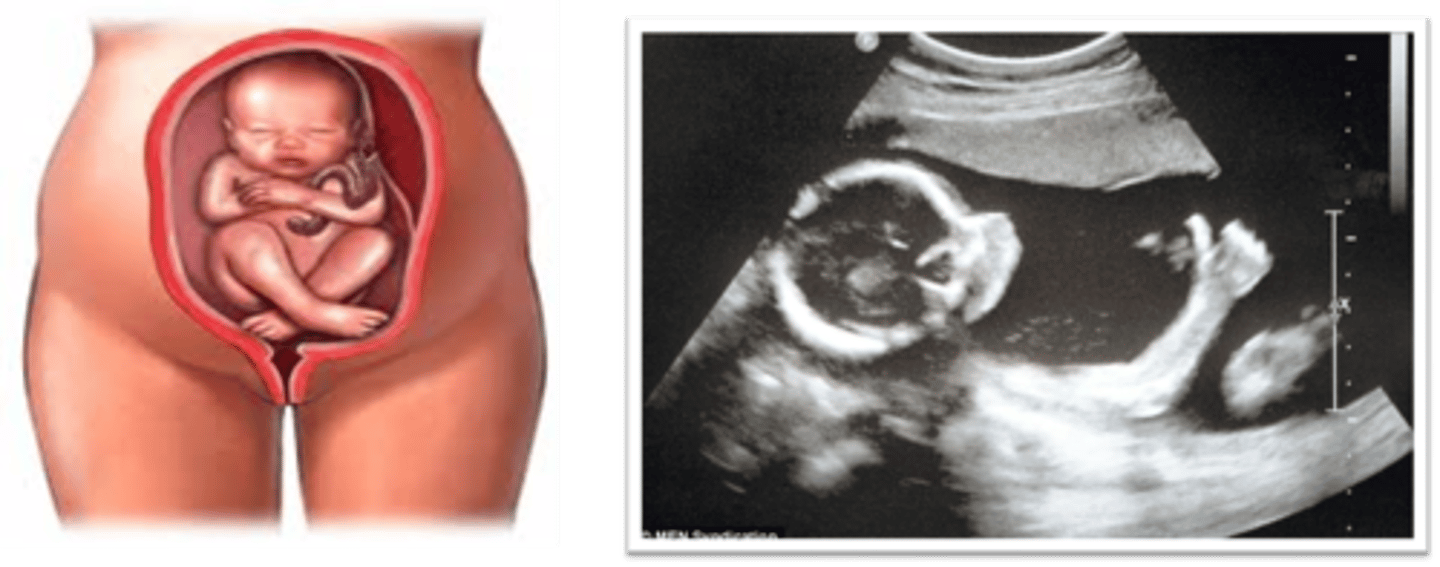
In a breech position, the fetal head is seen in the ___
uterine fundus
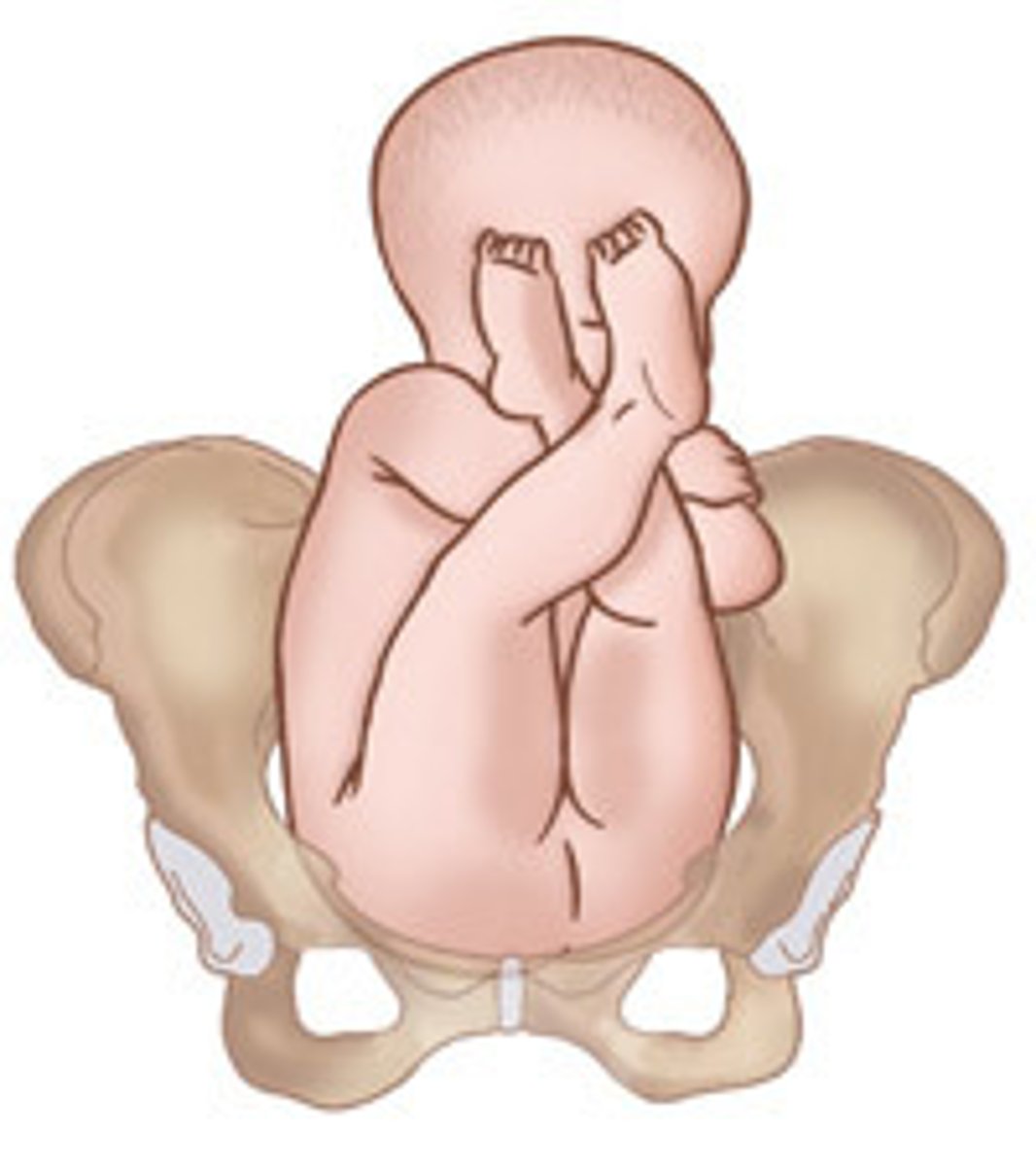
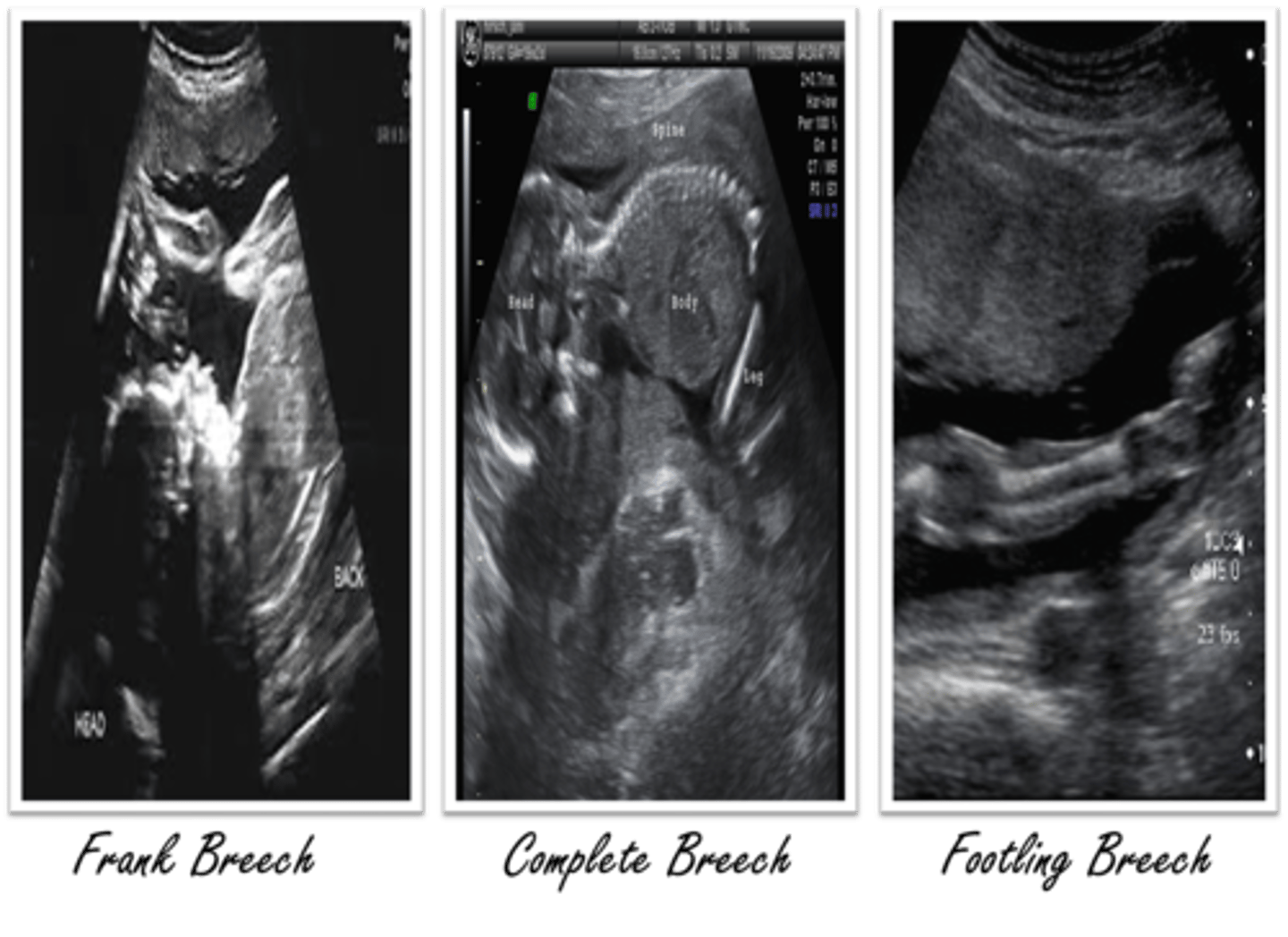
Frank breech is when fetal thighs are flexed at the ___ and the lower legs are extended ___ the head
hips; in front of
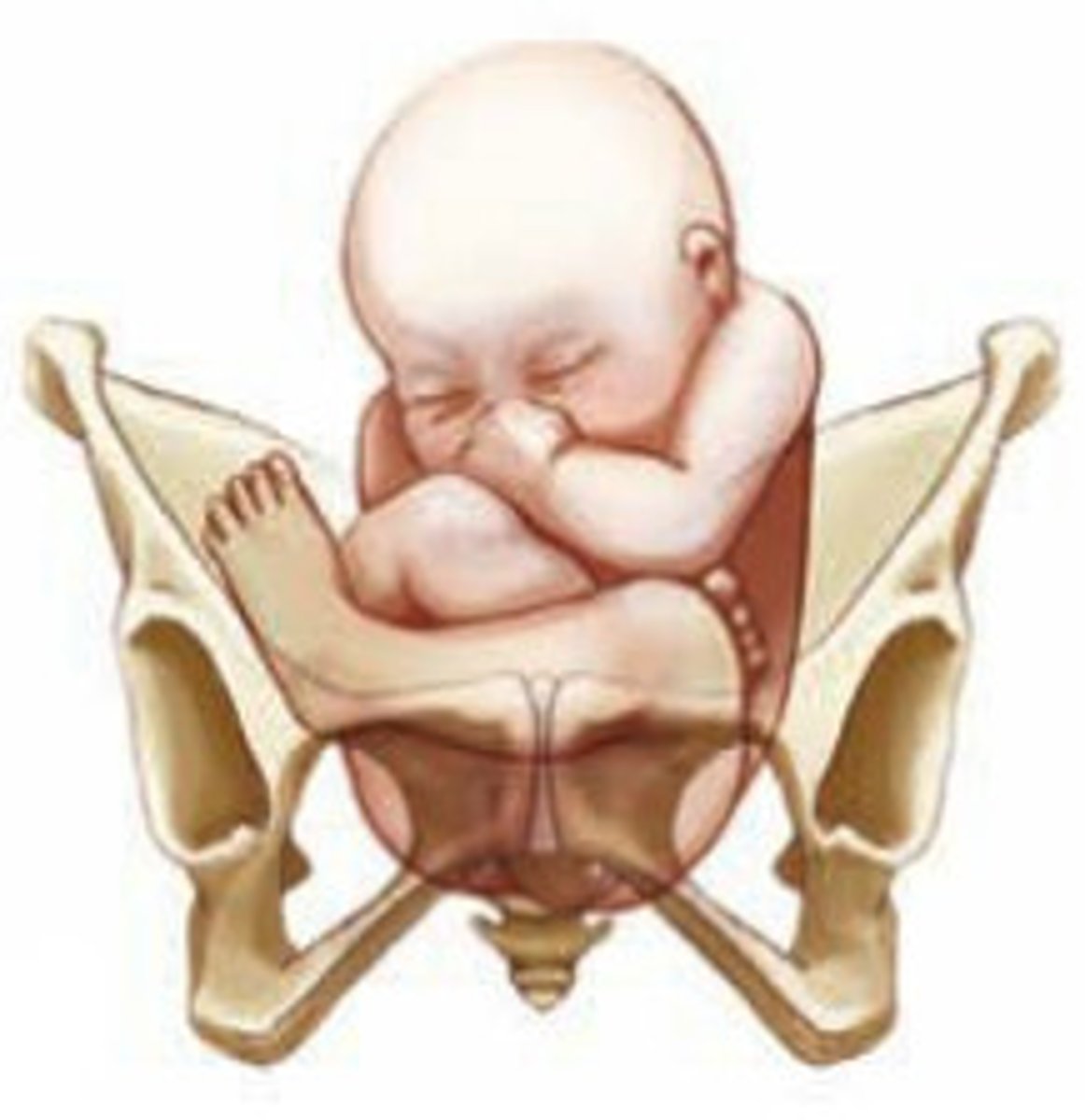
Complete breech is when fetal hips and lower extremities are ___ than the pelvis and legs are ___
lower; crossed
Footling breech is when fetal hips are ___ and one or both feet are closest to the ___
extended; cervix
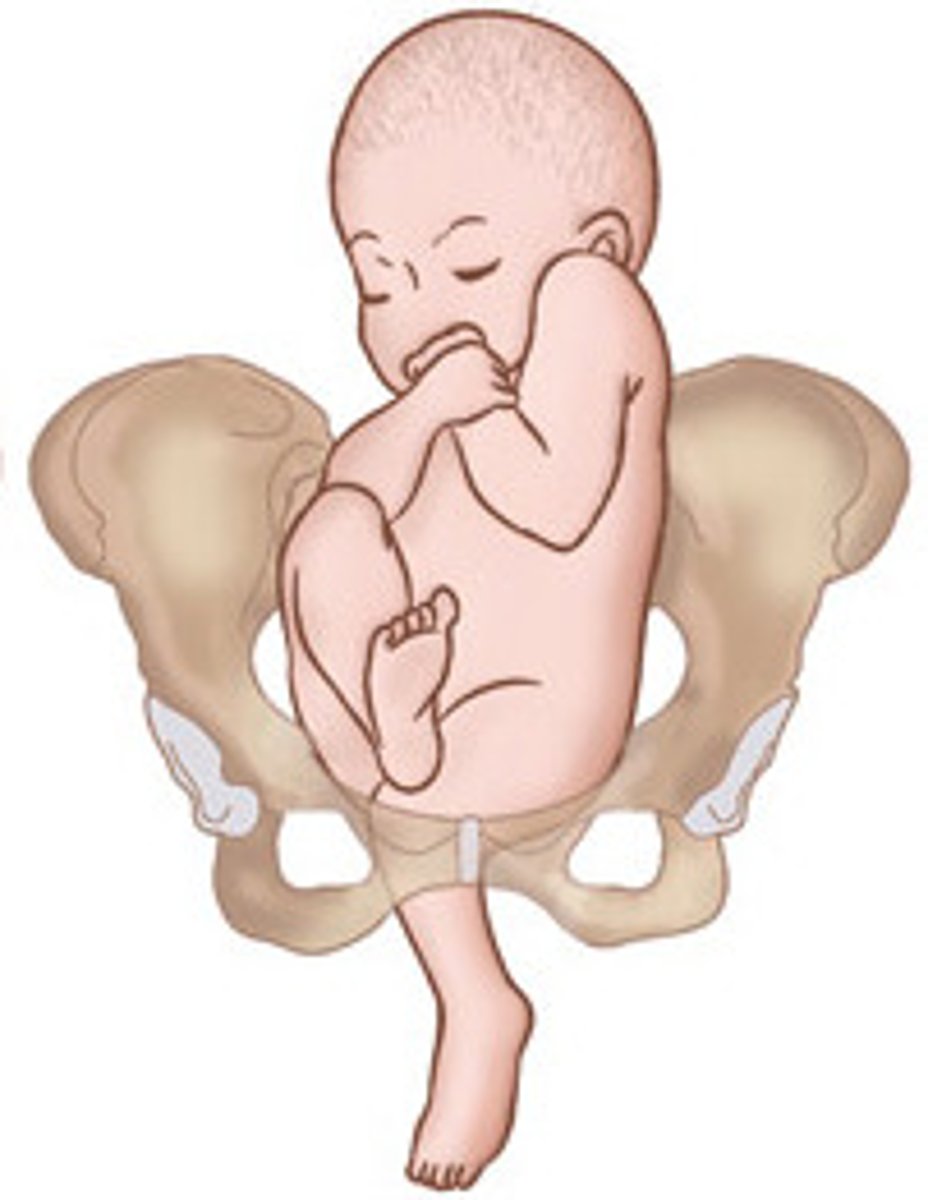
What is footling breech also called?
incomplete breech
What breech position can be turned?
frank breech
What breech position requires a c-section?
footling/incomplete breech
Breech positions on ultrasound
What is a transverse fetus position?
fetus lies across uterus
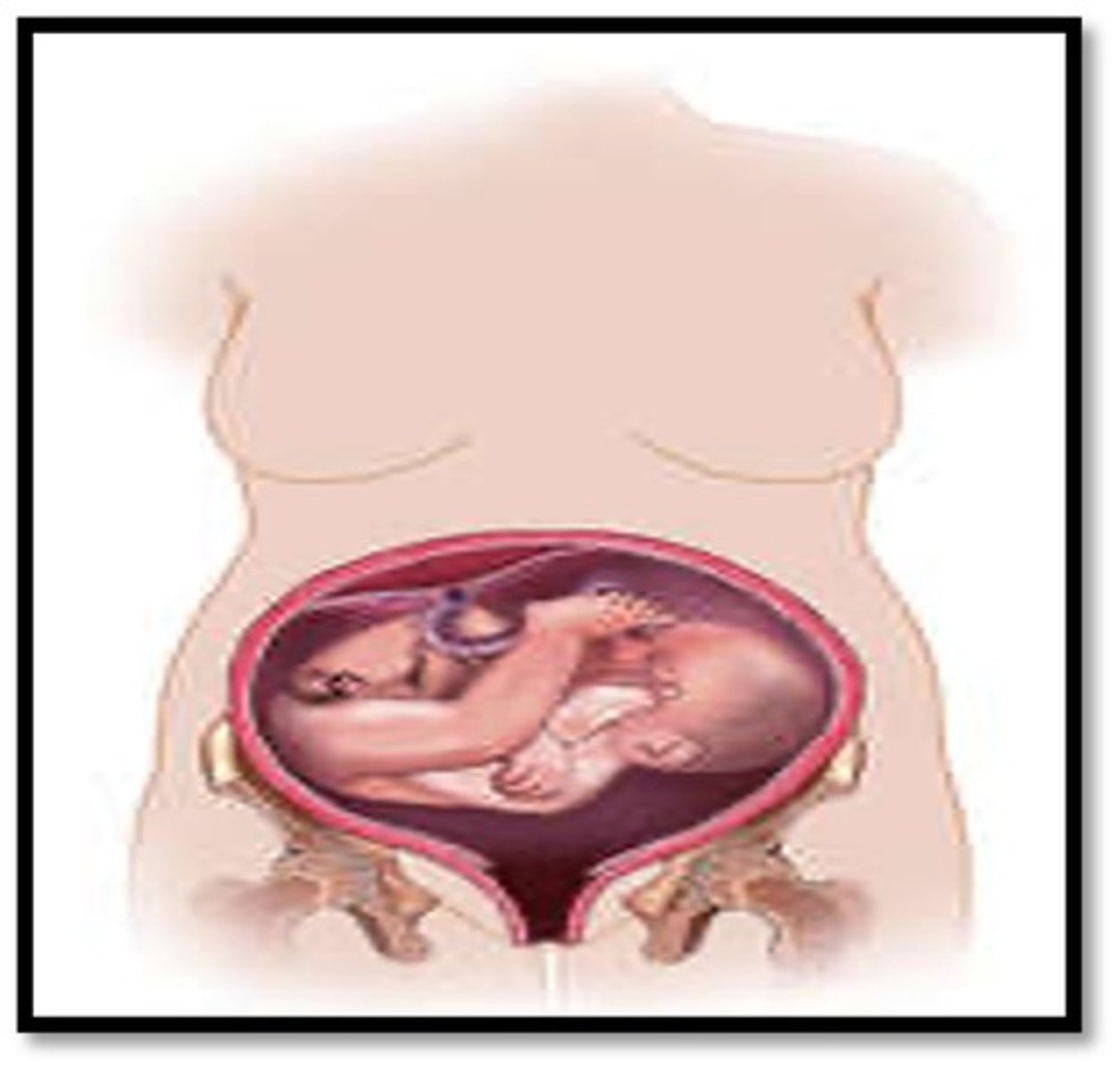
In a transverse fetal position, a sagittal transducer will show a ___ fetus
transverse
In a transverse fetal position, a transverse transducer will show a ___ fetus
sagittal
When labeling twin fetuses, twin A will always be closest to the ___
cervix
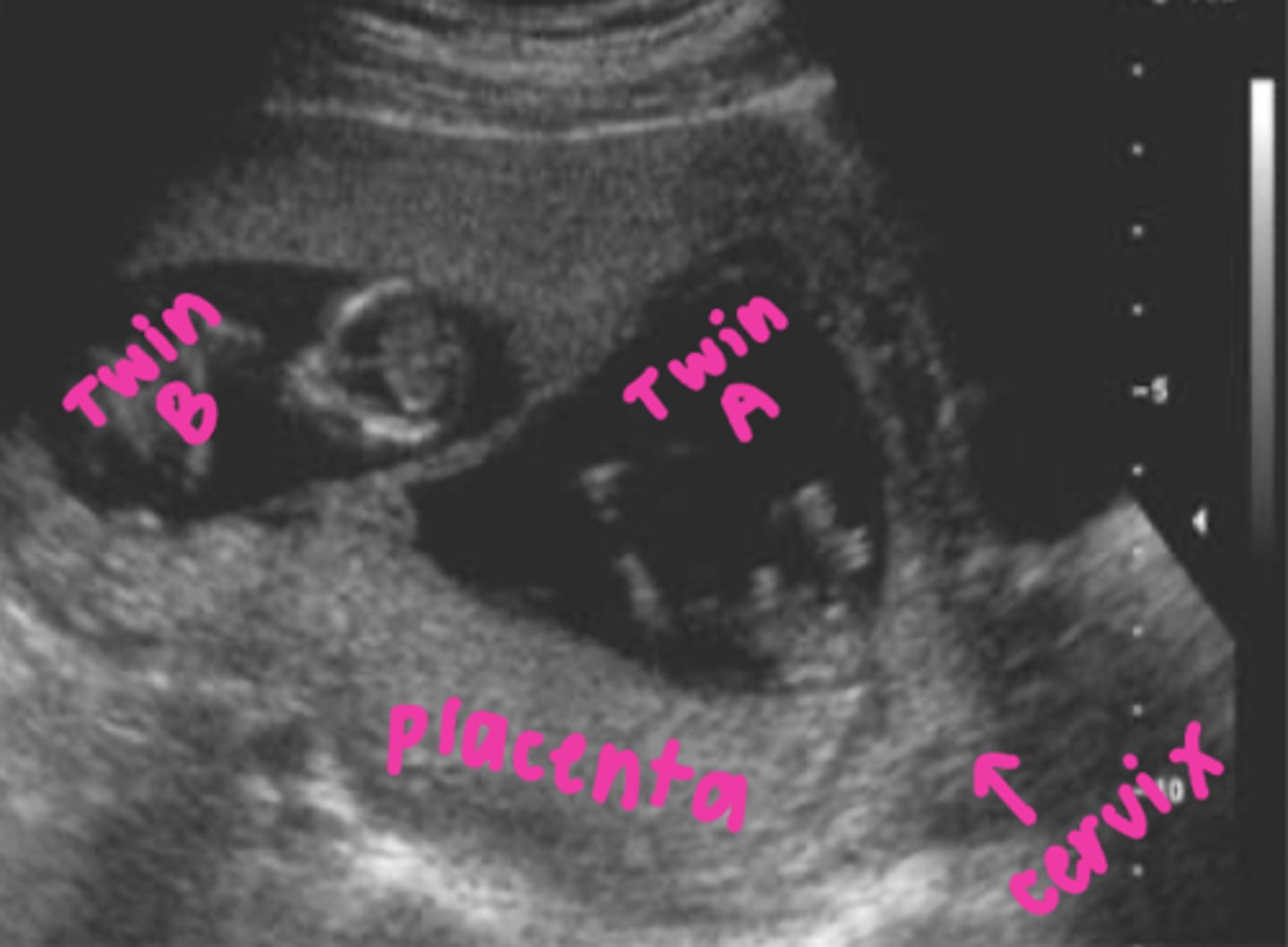
What is situs?
positional arrangement of a fetus's organs (right vs left sides)
The right and left sides of the fetus are determined by identifying ___
landmarks
Review fetal presentation (slides 20-22)
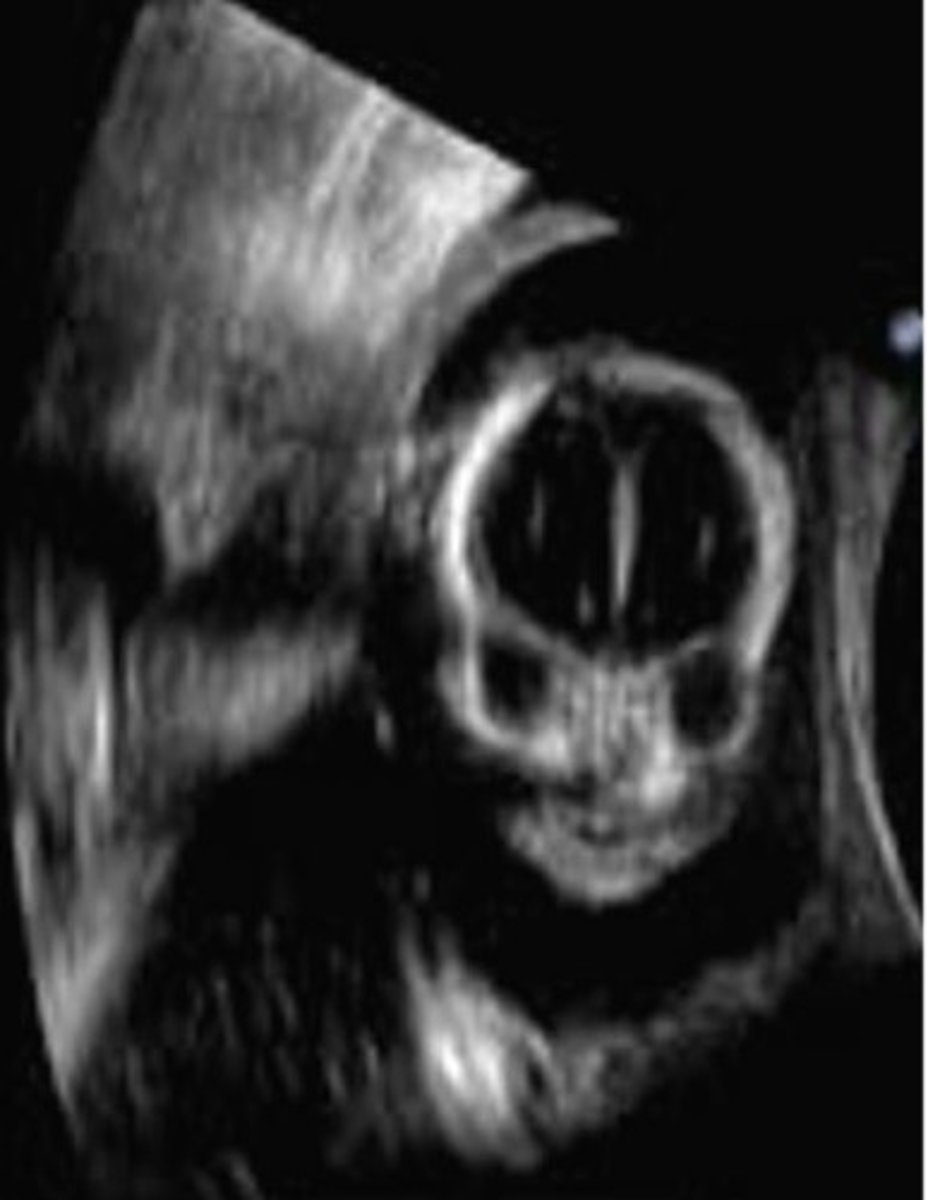
Fetal brain tissue may appear ___ or ___
hypoechoic; cystic
When do fetal cranial bones ossify?
12 weeks
The dura mater and pia mater within the fetal cranium appear ___
echogenic
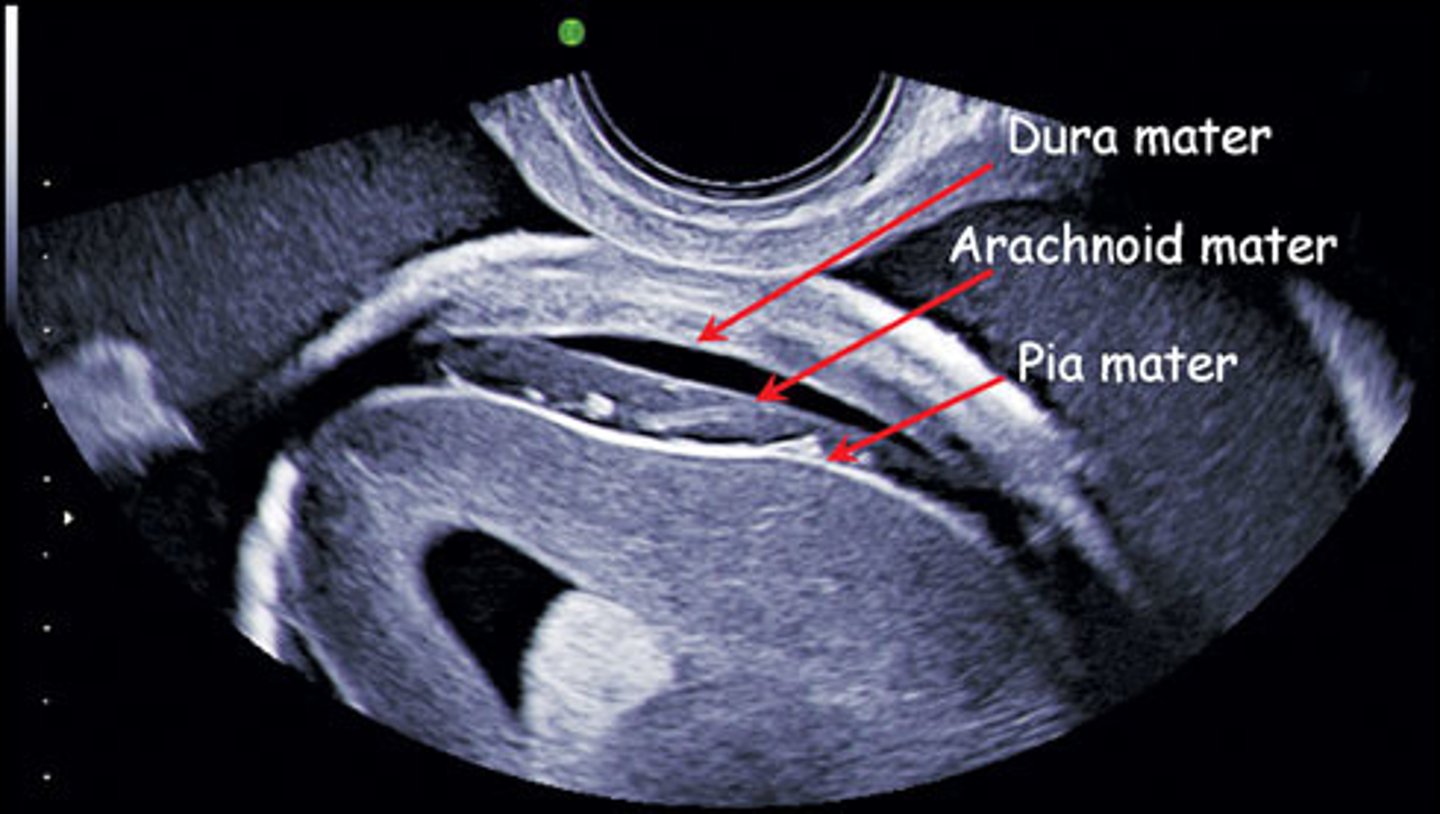
CSF within the fetal cranium appears ___
cystic
What scanning plane are fetal brain anatomy and measurements assessed in?
transverse
Why is the fetal cranium difficult to evaluate in the late third trimester?
bc of deep pelvic positioning
At the most cephalad (upper) level, the contour of the fetal skull should be ___ with a ___ surface
oval; smooth
What is the interhemispheric fissure / falx?
membrane separating the fetal brain into right and left hemispheres
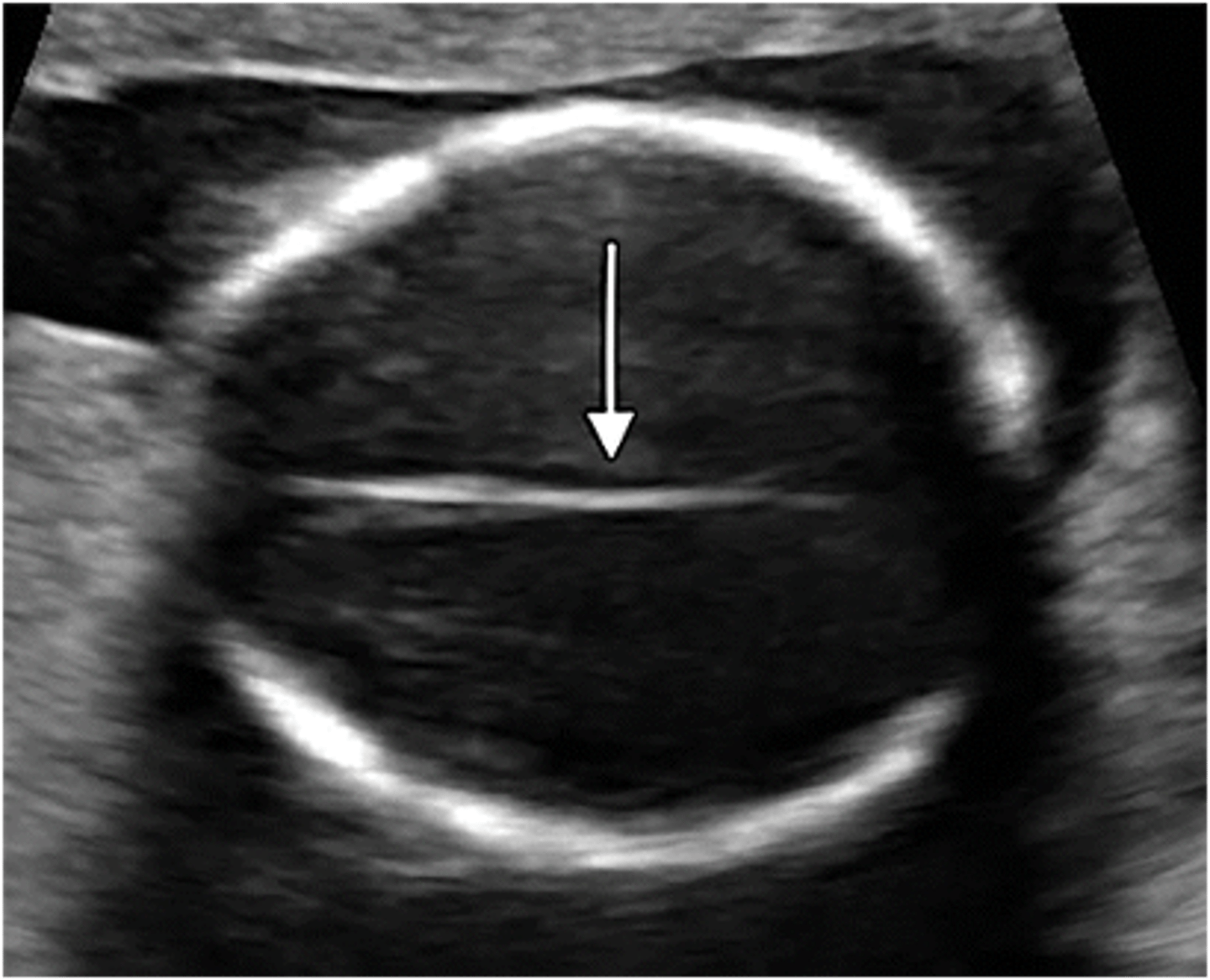
At the most cephalad level within the fetal skull, the falx should be ____
continuous
___ and ___ to the falx, two linear echoes representing deep venous structures (white matter tracts) are viewed
lateral; parallel
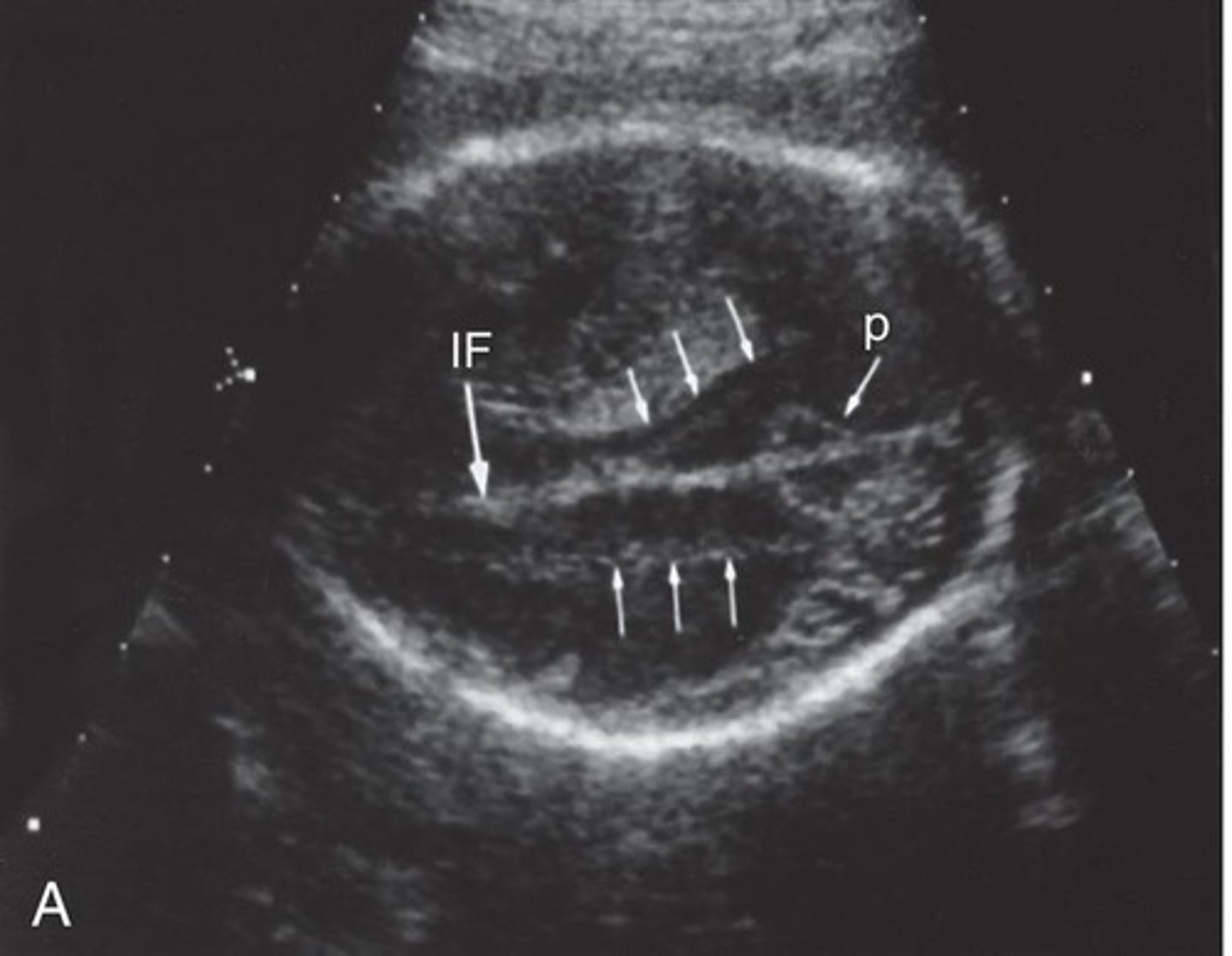
White-matter tracts are positioned ___ the lateral ventricles
above
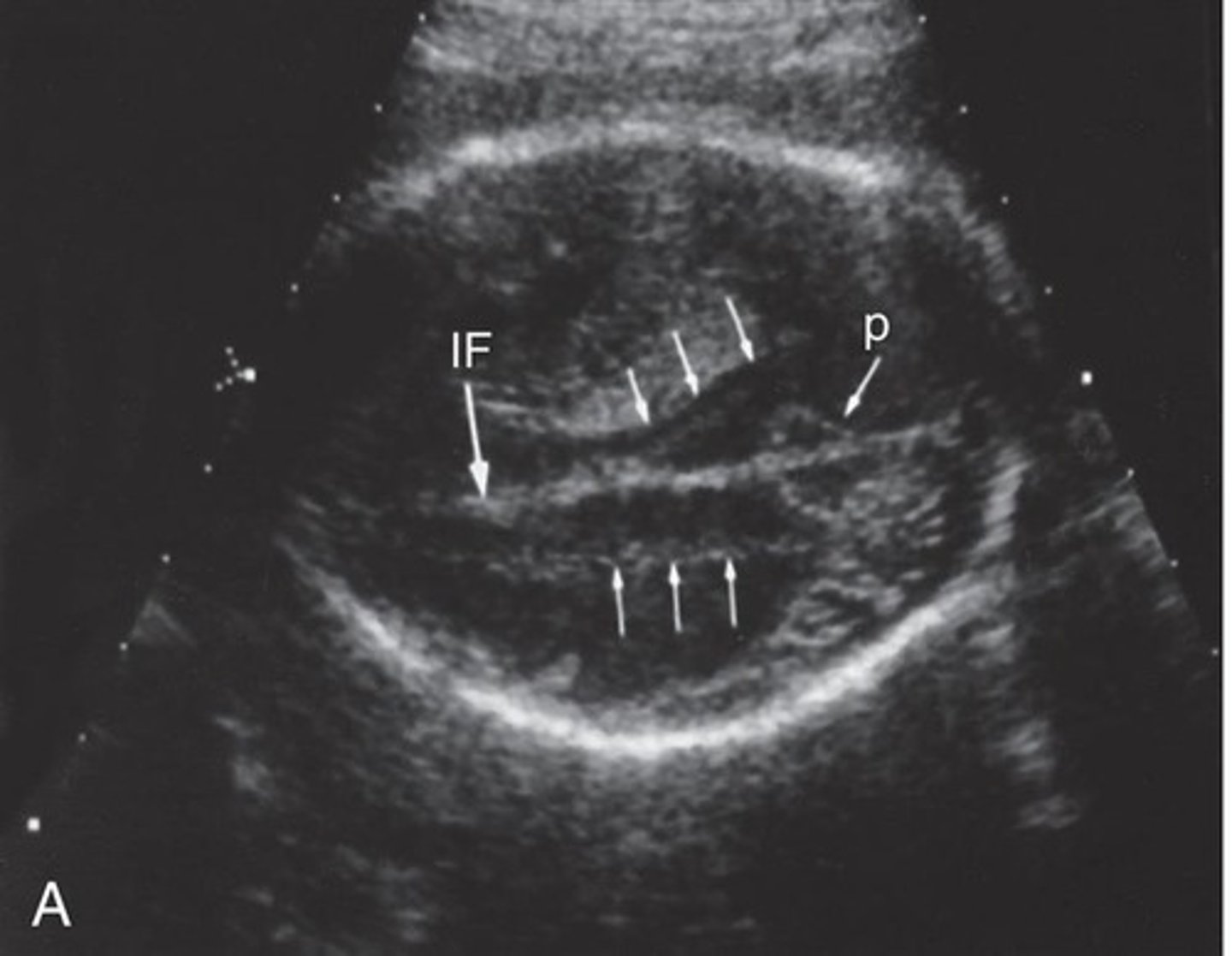
What ventricles are in the fetal ventricular system?
2 lateral ventricles
3rd ventricle
4th ventricle
The ventricles are filled with ___ produced by the ___
CSF; choroid plexus
Choroid plexuses are located within the ___ of each ventricle
roofs
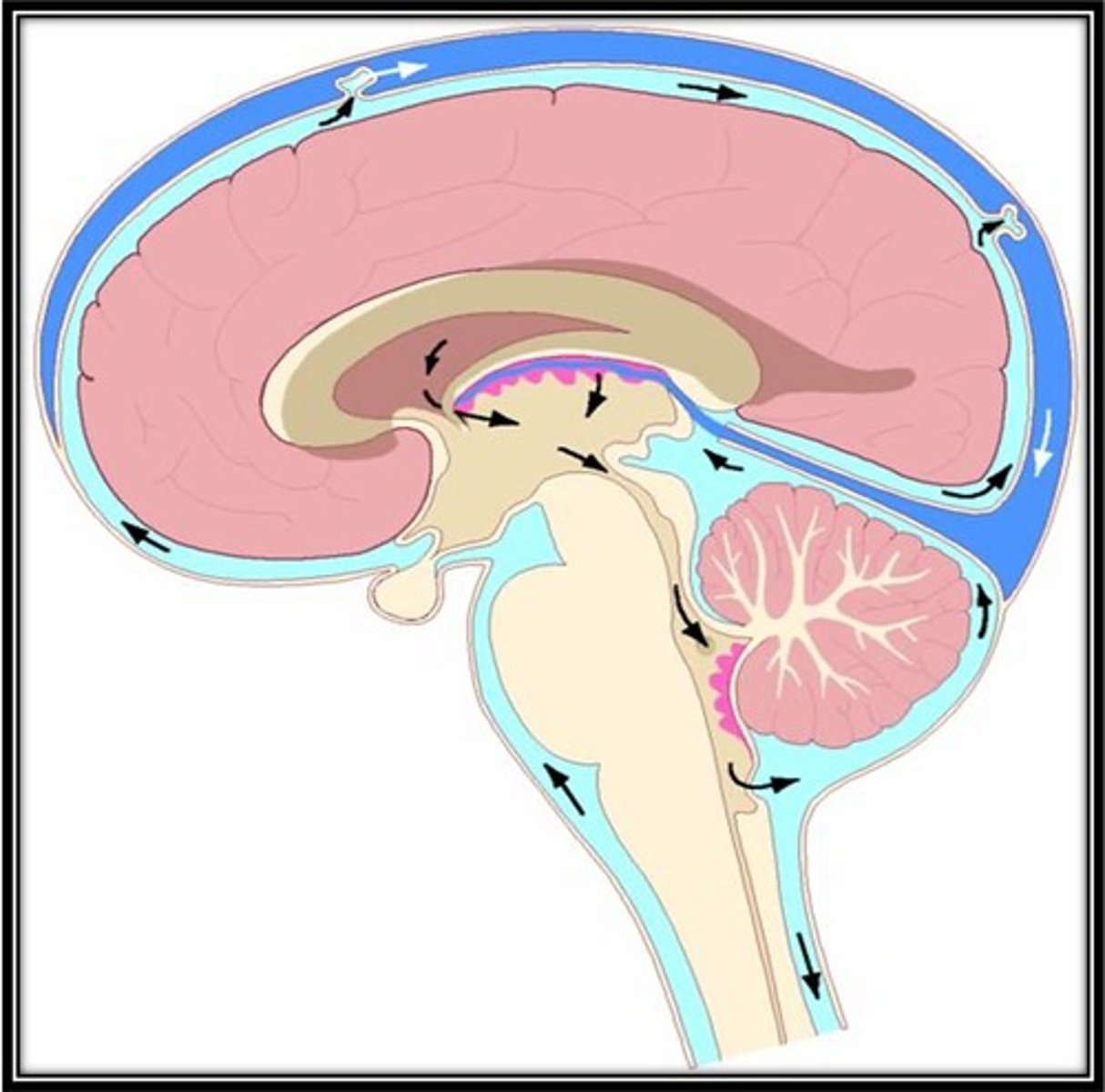
What is the flow of CSF?
lateral ventricle
foramen of Monroe
3rd ventricle
aqueduct of Sylvius
4th ventricle
foramina of Luschka
cerebral and spinal subarachnoid spaces
venous system
What is one of the most common fetal neural tube defects?
ventriculomegaly
(enlarged ventricles)
Lateral borders of the ventricular chambers are seen as ___ lines coursing ___ to the falx
echogenic; parallel
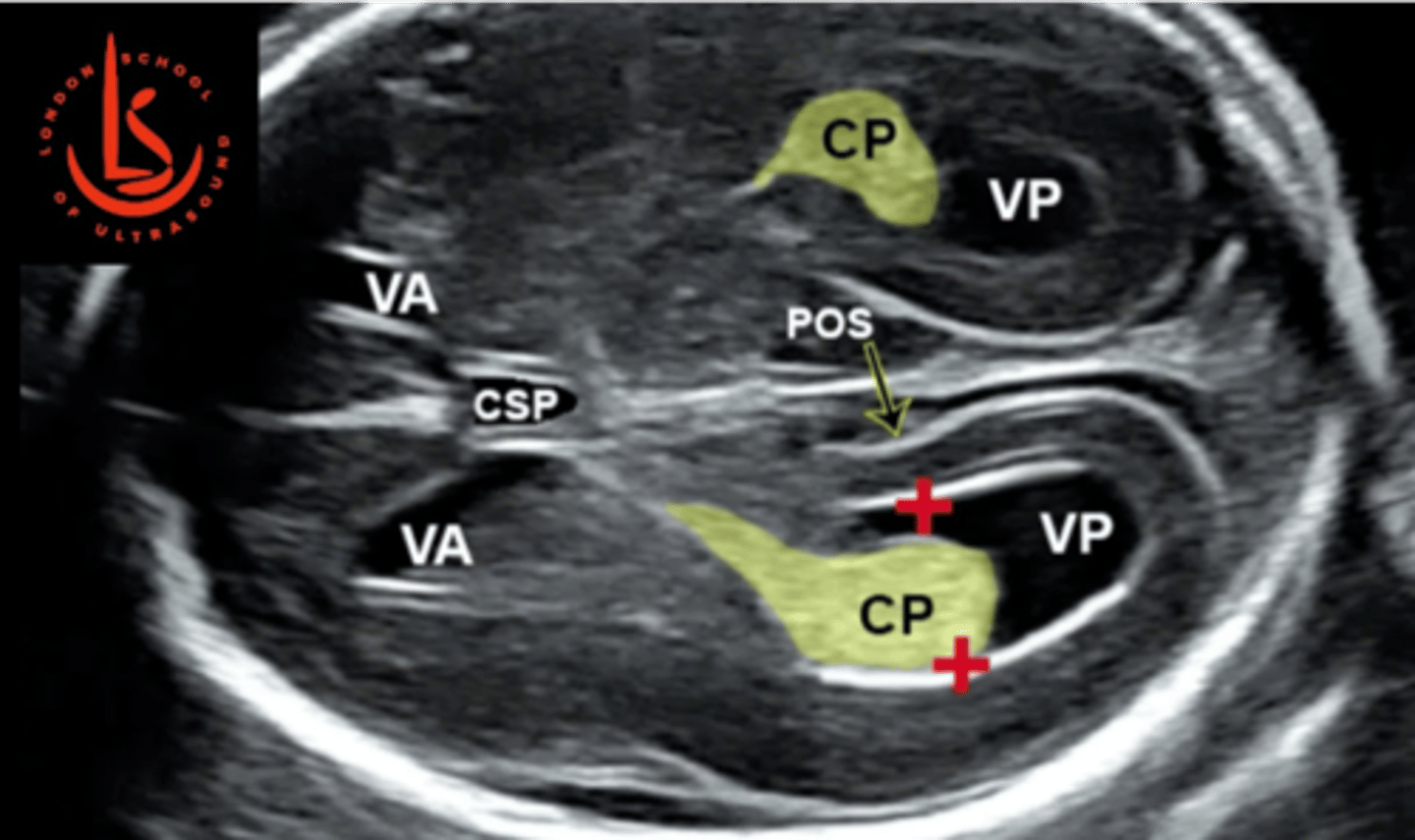
At ___ weeks gestation, the lateral borders appear to be large in relationship to the developing ___ ___; moves more ___ later in pregnancy
12-22; cranial hemispheres; medial
The body (glomus) of the choroid plexus marks the site at which the ___ are measured
ventricles
If the glomus of the choroid plexus appears to float or dangle within the ventricular cavity, ___ may be present
ventriculomegaly
Does ventricular size vary throughout gestation?
no - it remains the same
How do you measure fetal ventricles?
place calipers at junction of ventricular wall and lumen of ventricle (inner to inner)
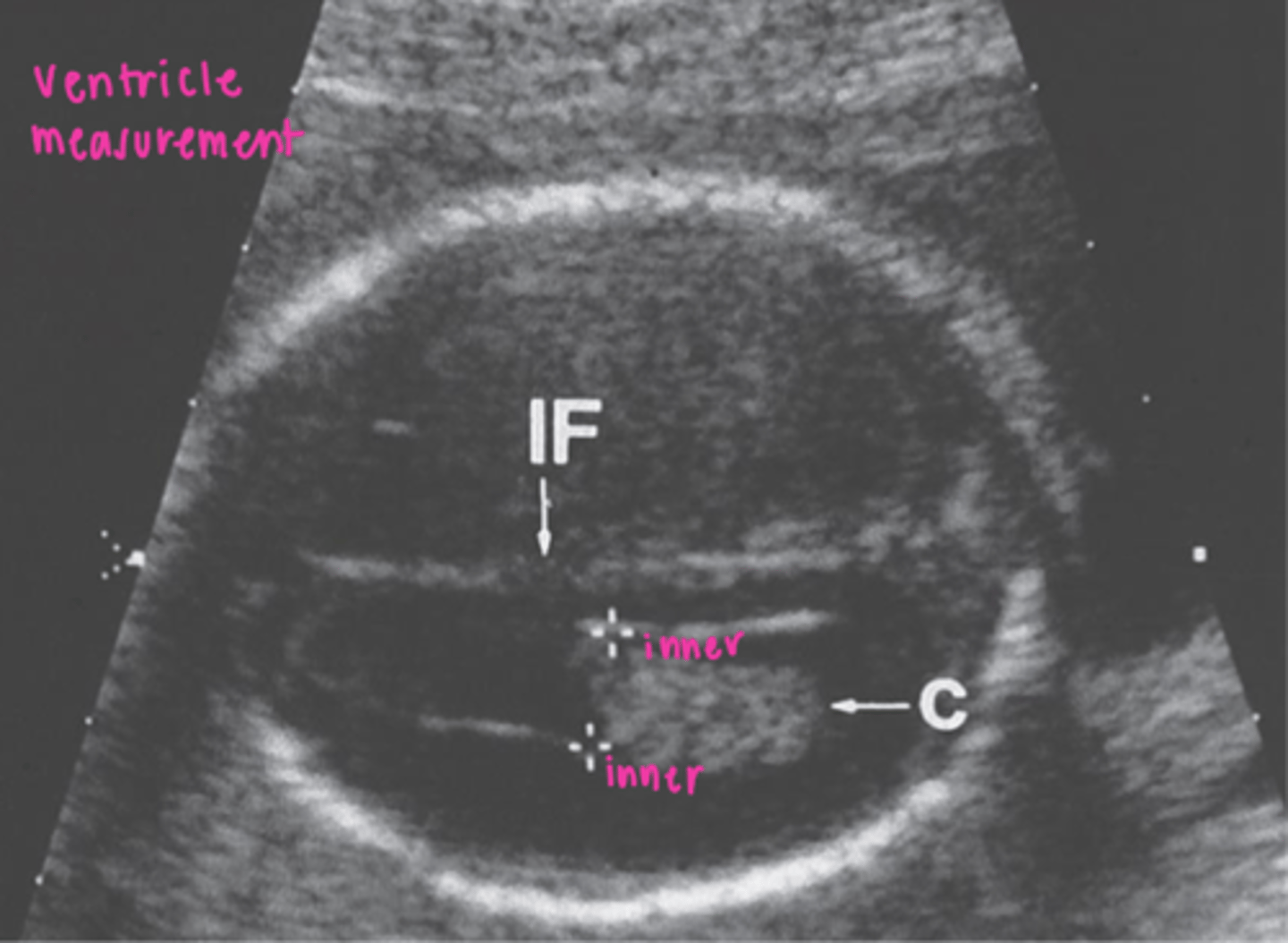
What is normal ventricular measurement?
6.5 mm
Abnormal ventricular measurement is above ___
10 mm (1 cm)
What part of the skull do you measure BPD?
midline echo complex
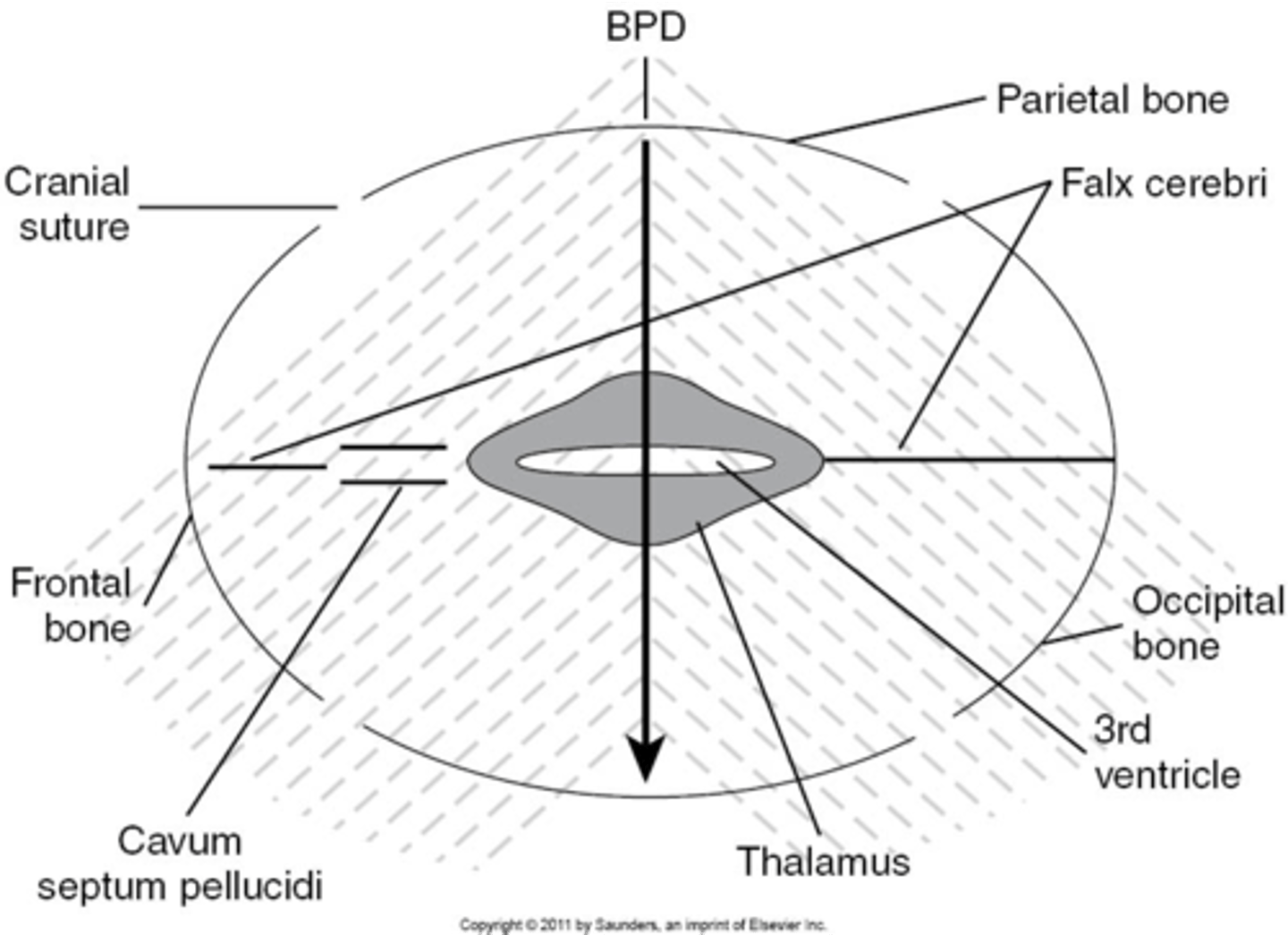
How do you find midline echo complex on ultrasound?
move the transducer caudally from lateral ventricles
When measuring BPD, paired ___ will be seen on either side
thalamus
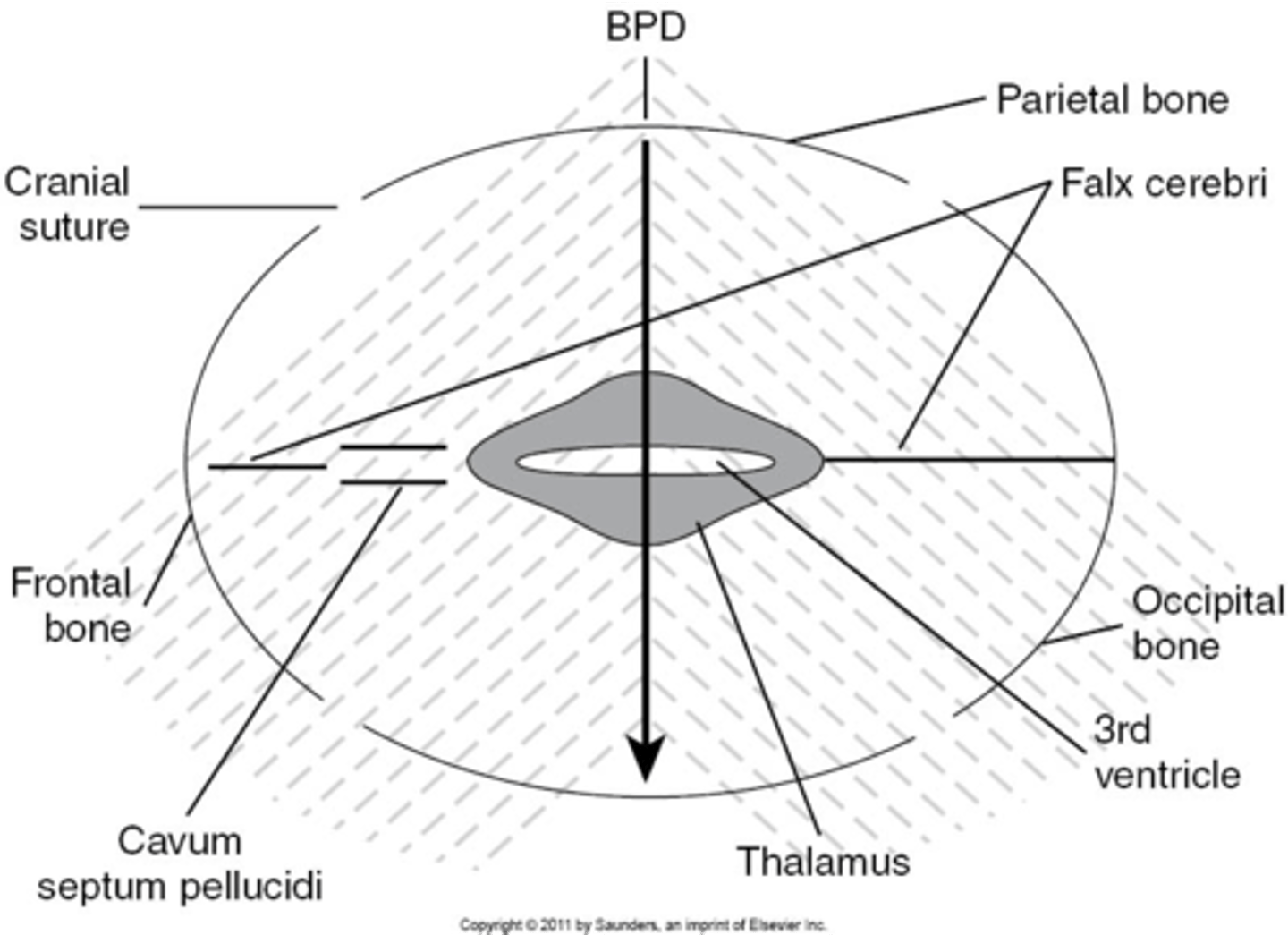
When measuring BPD, what is located between the thalamus?
3rd ventricle
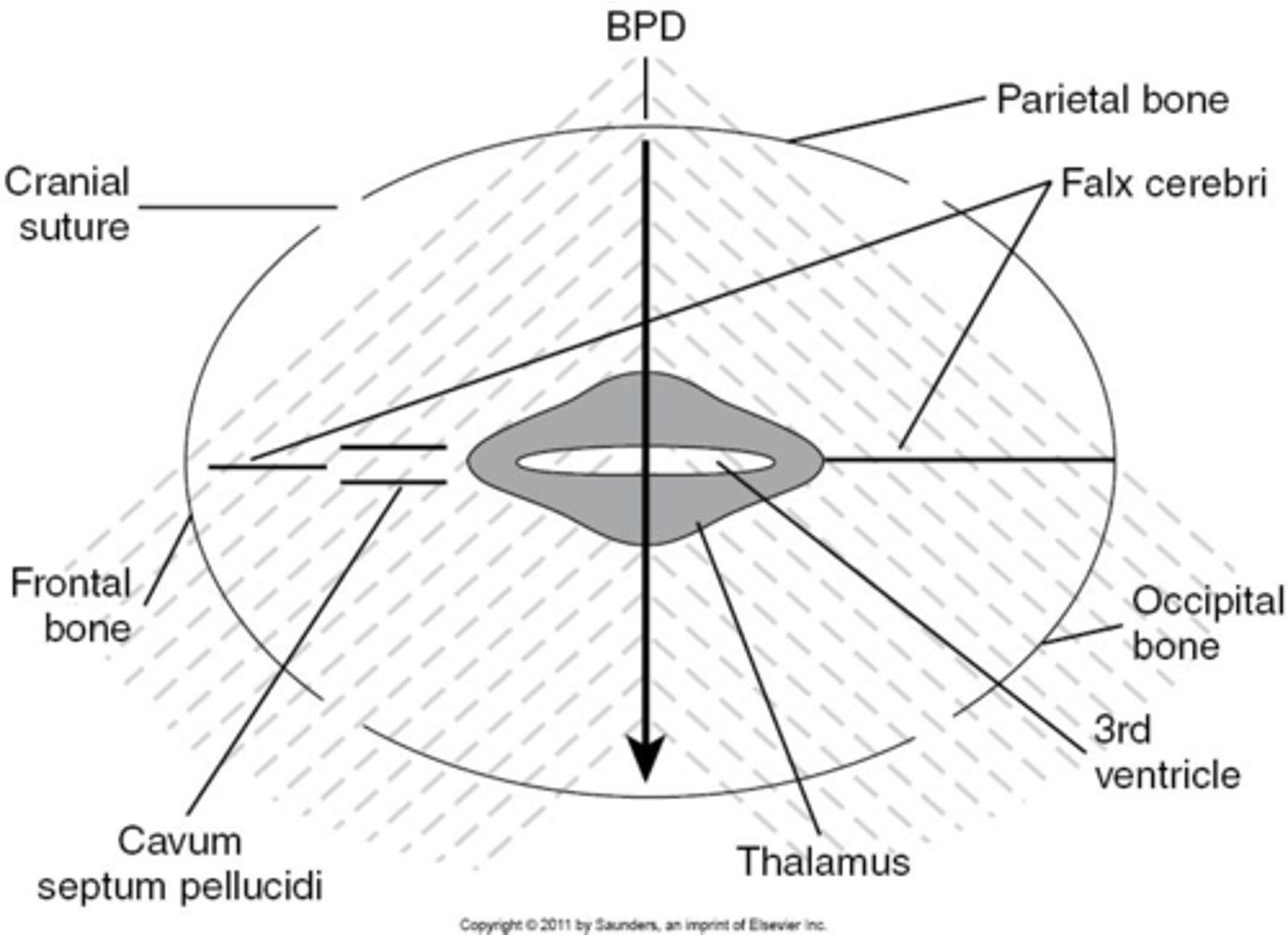
When measuring BPD, what is seen in front of the thalamus?
cavum septum pellucidum (CSP)
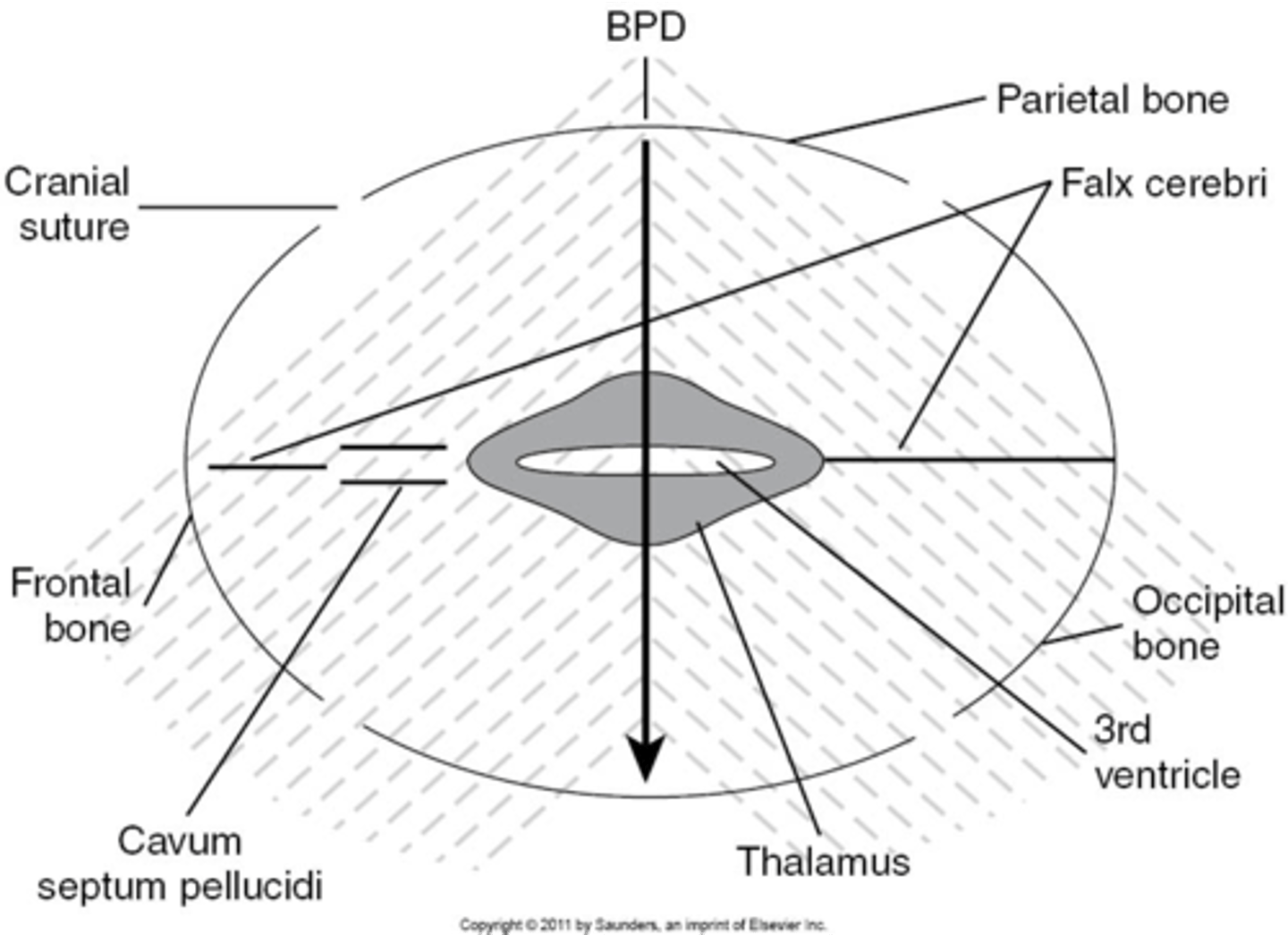
At the midline echo complex, frontal horns of the lateral ventricles may be seen as ___ ___ ___ structures within the ___ ___ of the brain
2 diverging echo-free; frontal lobes
What is the corpus callosum?
band of tissue between the frontal ventricular horns
The corpus callosum is ___ sonographically
ill-defined
The cisterns are ___ structures bordering the thalamus ___
pulsatile; posteriorly
Moving transducer more caudally from midline, what heart-shaped structures smaller than the thalamus are visualized?
cerebral peduncles
Moving transducer more caudally from midline, ___ artery pulsations can be seen
basilar
Moving transducer more caudally, the circle of Willis may be seen ___ to the midbrain and appears ___ and highly pulsatile because of ___
anterior; triangular; cerebral arteries
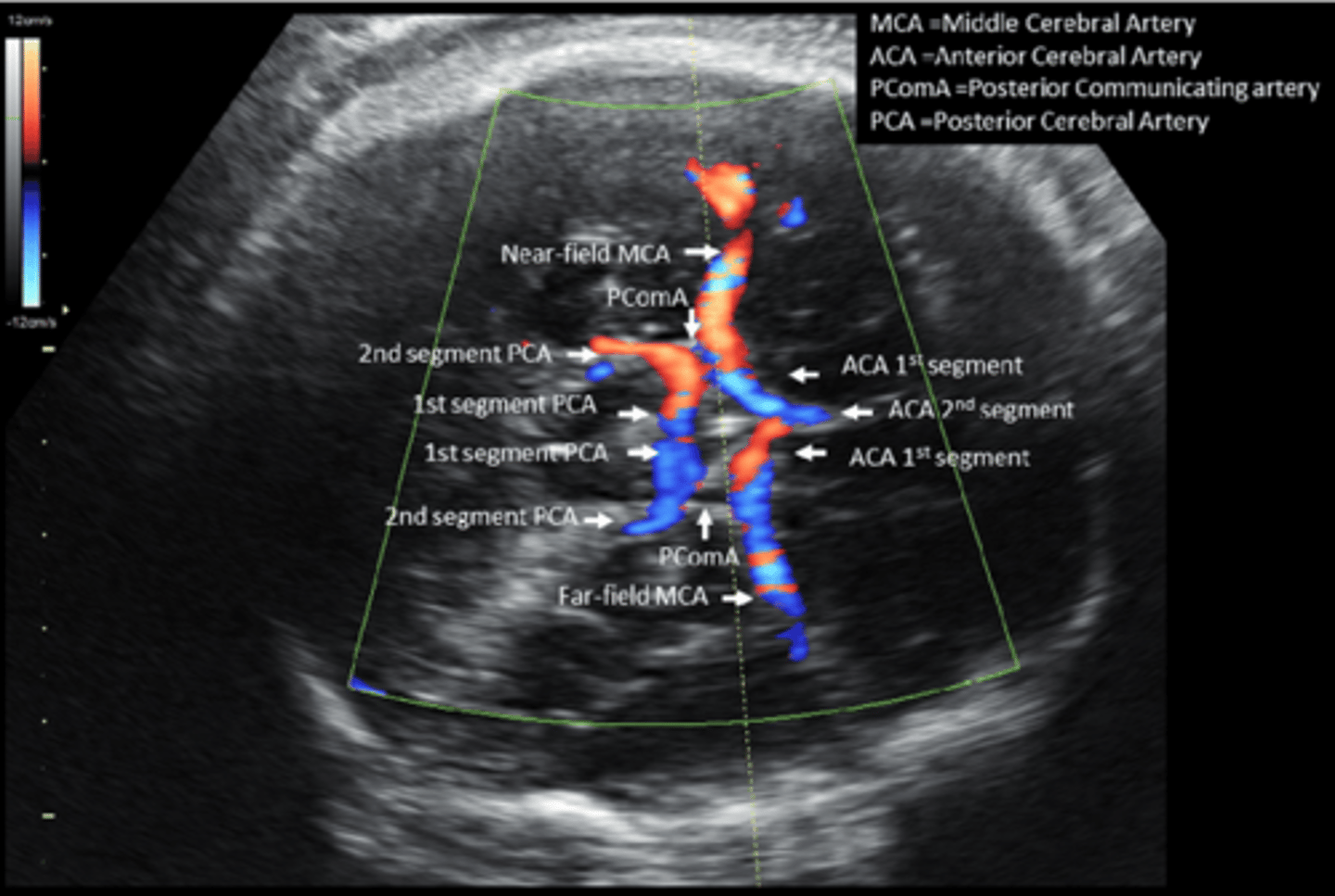
What may be visualized in the center of the circle of Willis?
suprasellar cistern
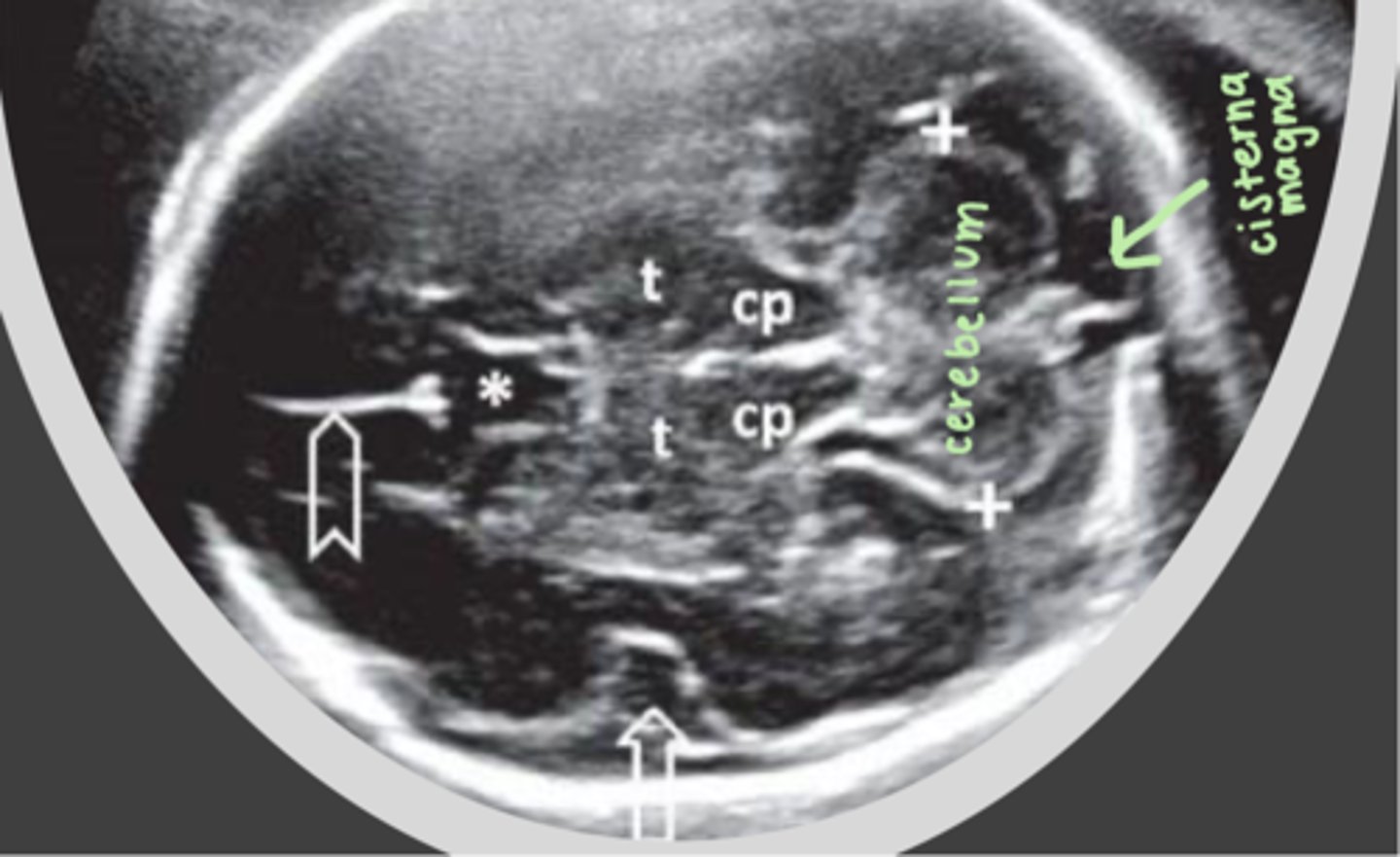
The cerebellum is located ___ to the cerebral peduncles, within the ___
posteriorly; posterior fossa
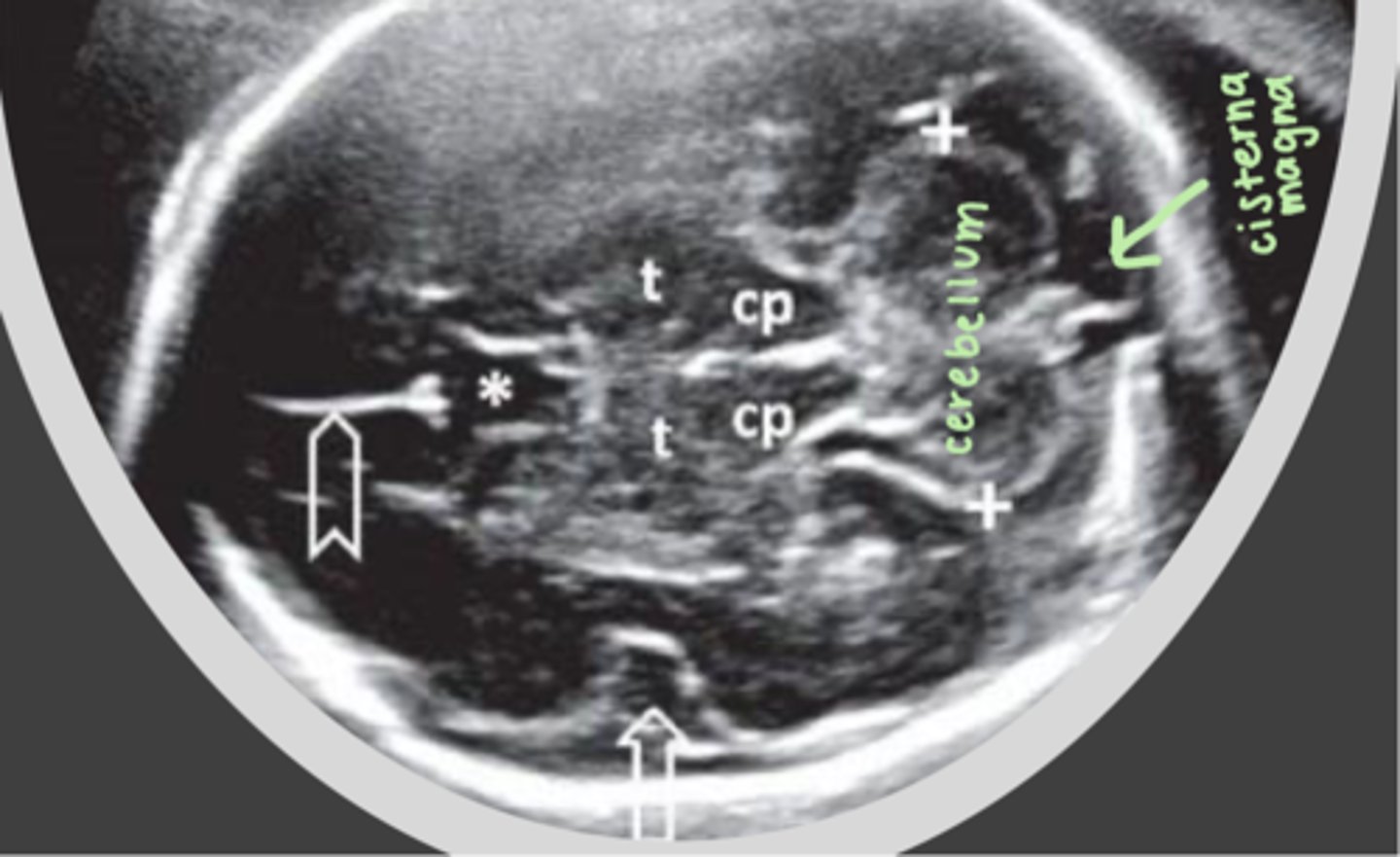
The cerebellar hemispheres are joined together by the ___
cerebellar vermis
The ___ lies directly behind the cerebellum
cisterna magna / posterior fossa
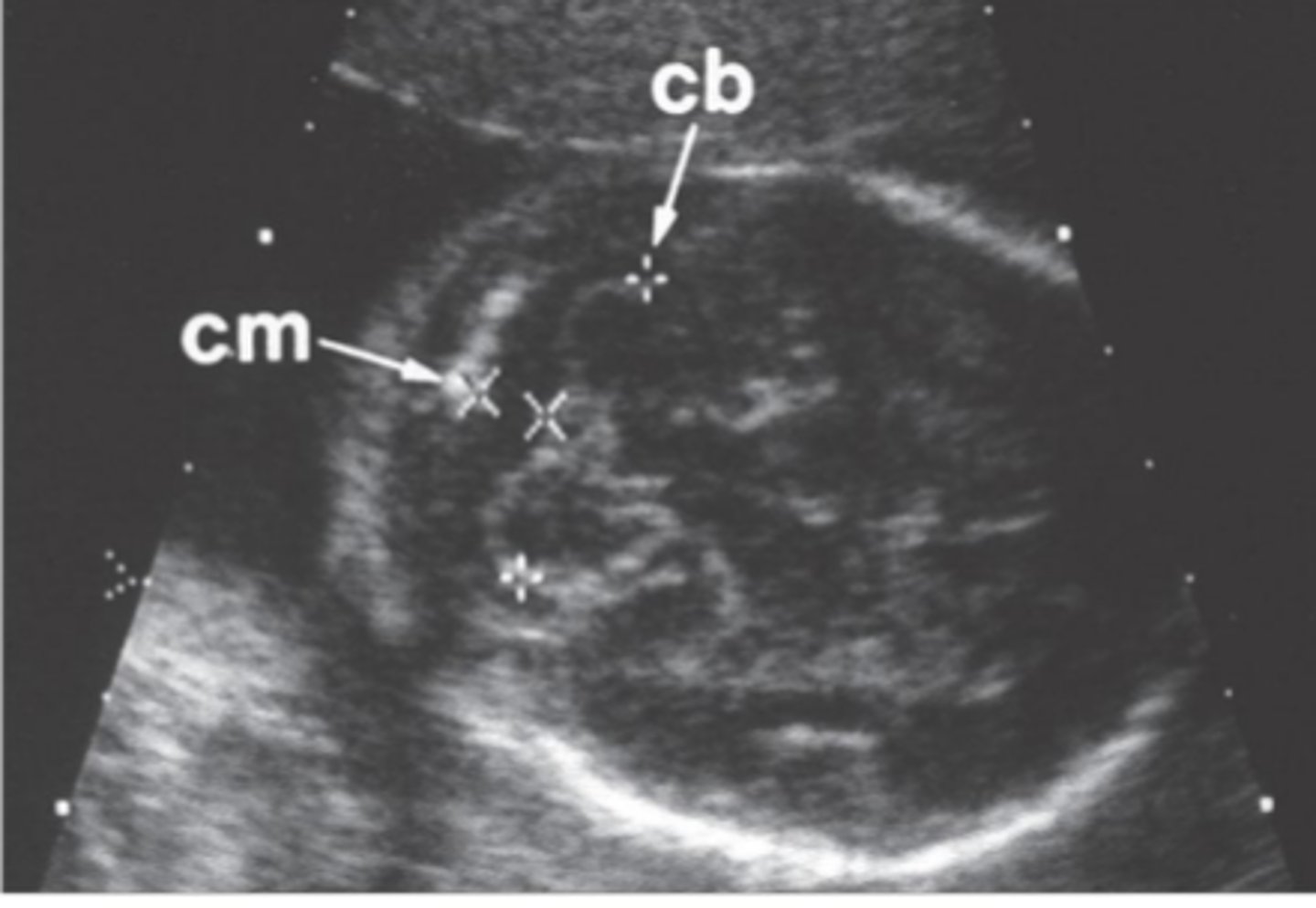
Normal cisterna magna measures ___; and averages ___
3-10 mm; 5-6 mm
When measuring cisterna magna, measure from the ___ to the inner ___ bone
vermis; occipital
Within the cisterna magna space, ___ can be seen as linear echoes within
dural folds
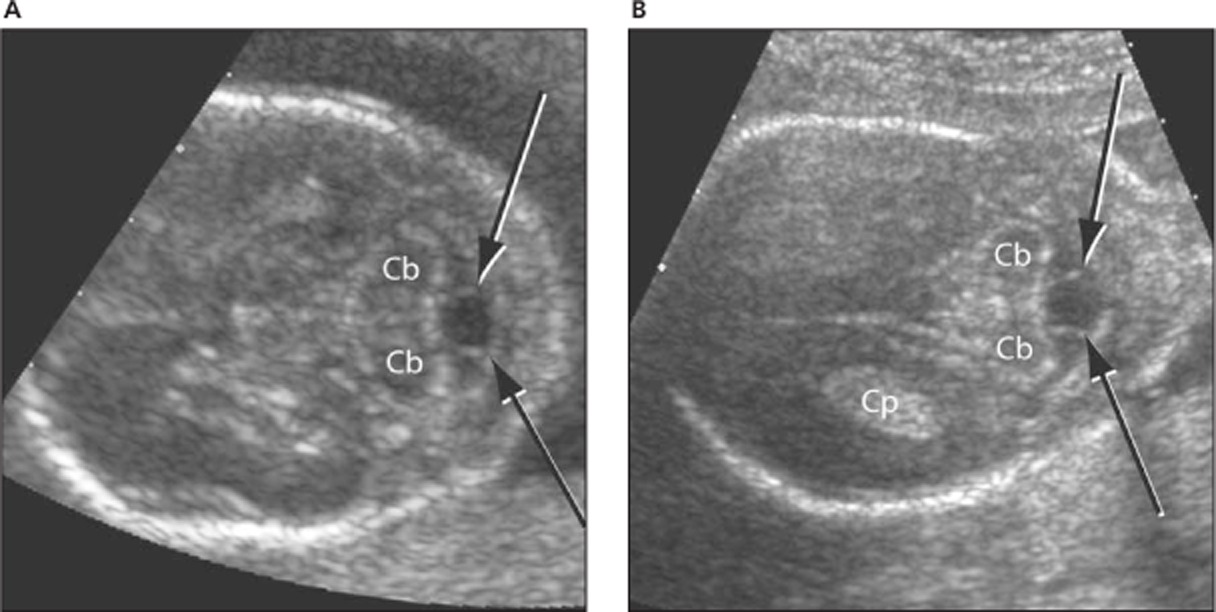
When scanning inferior to the cerebellar plane, what may be visualized?
orbits
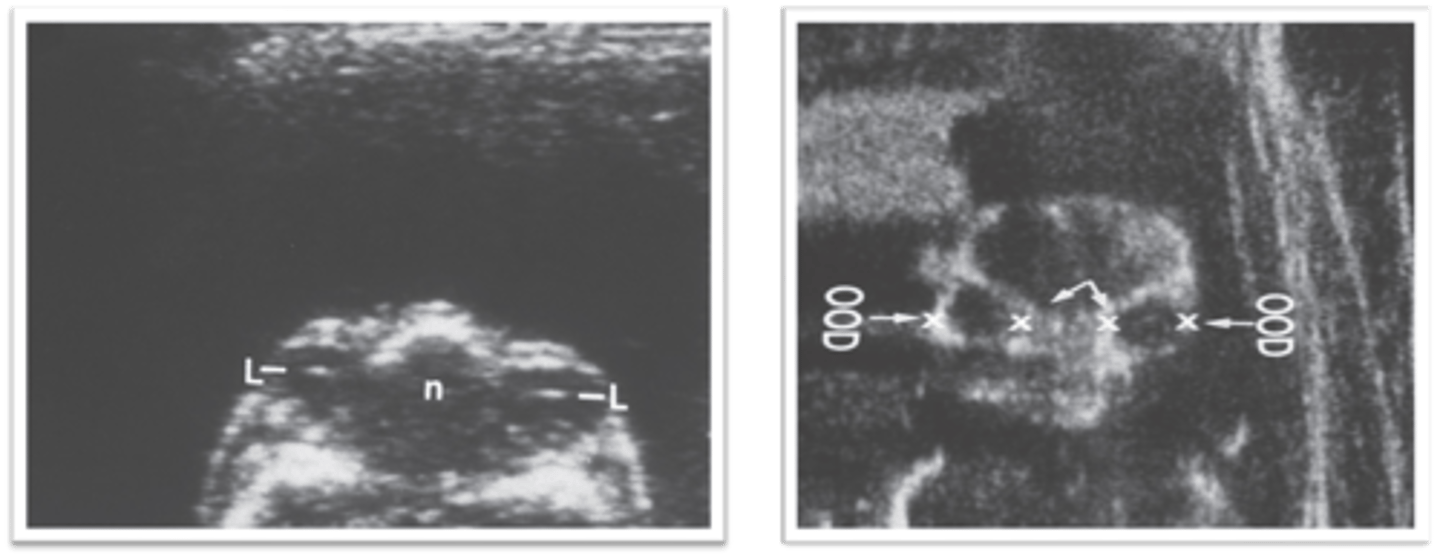
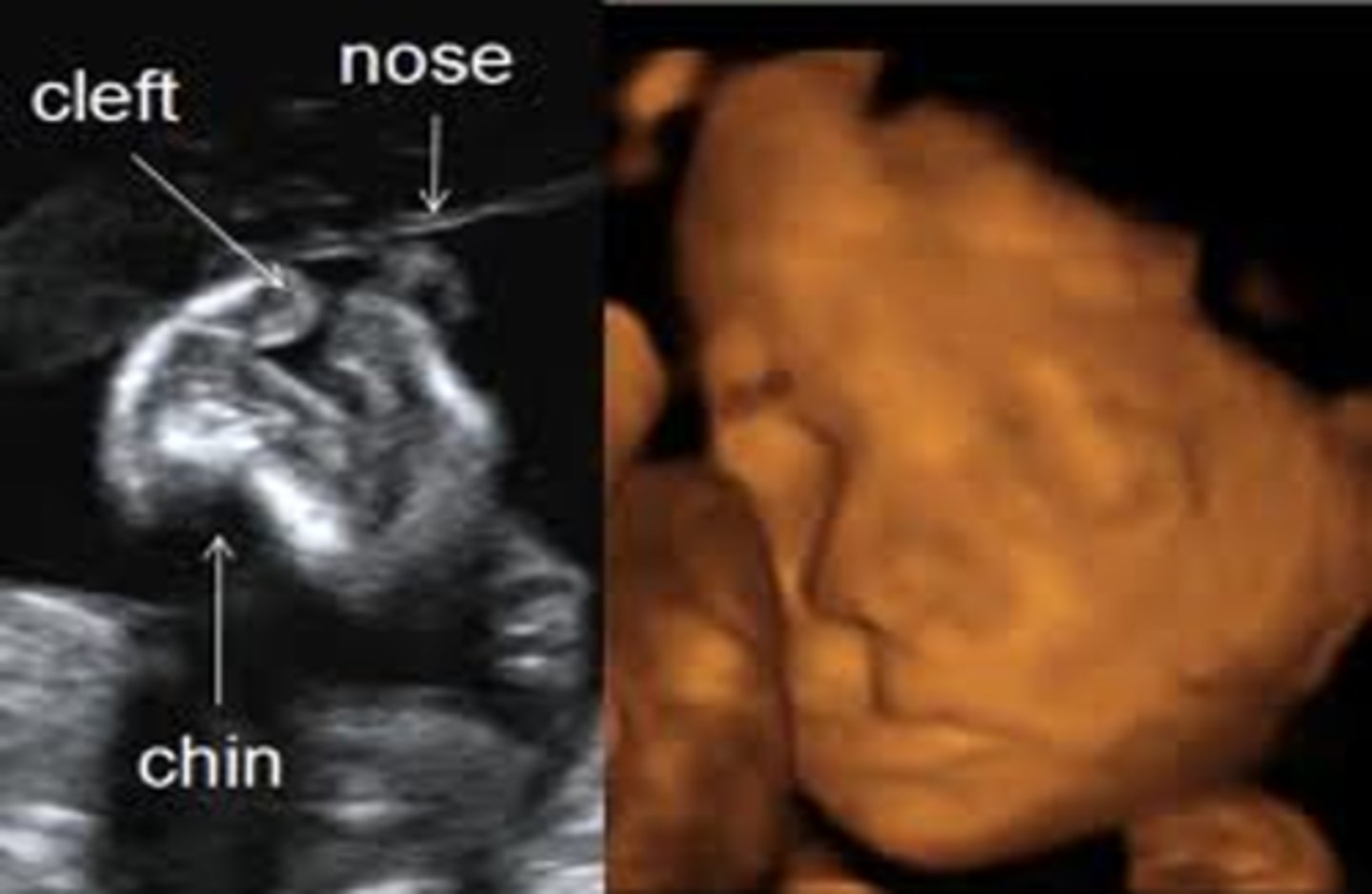
When scanning fetal facial profile, what should you assess?
frontal bone
nose
lips
chin
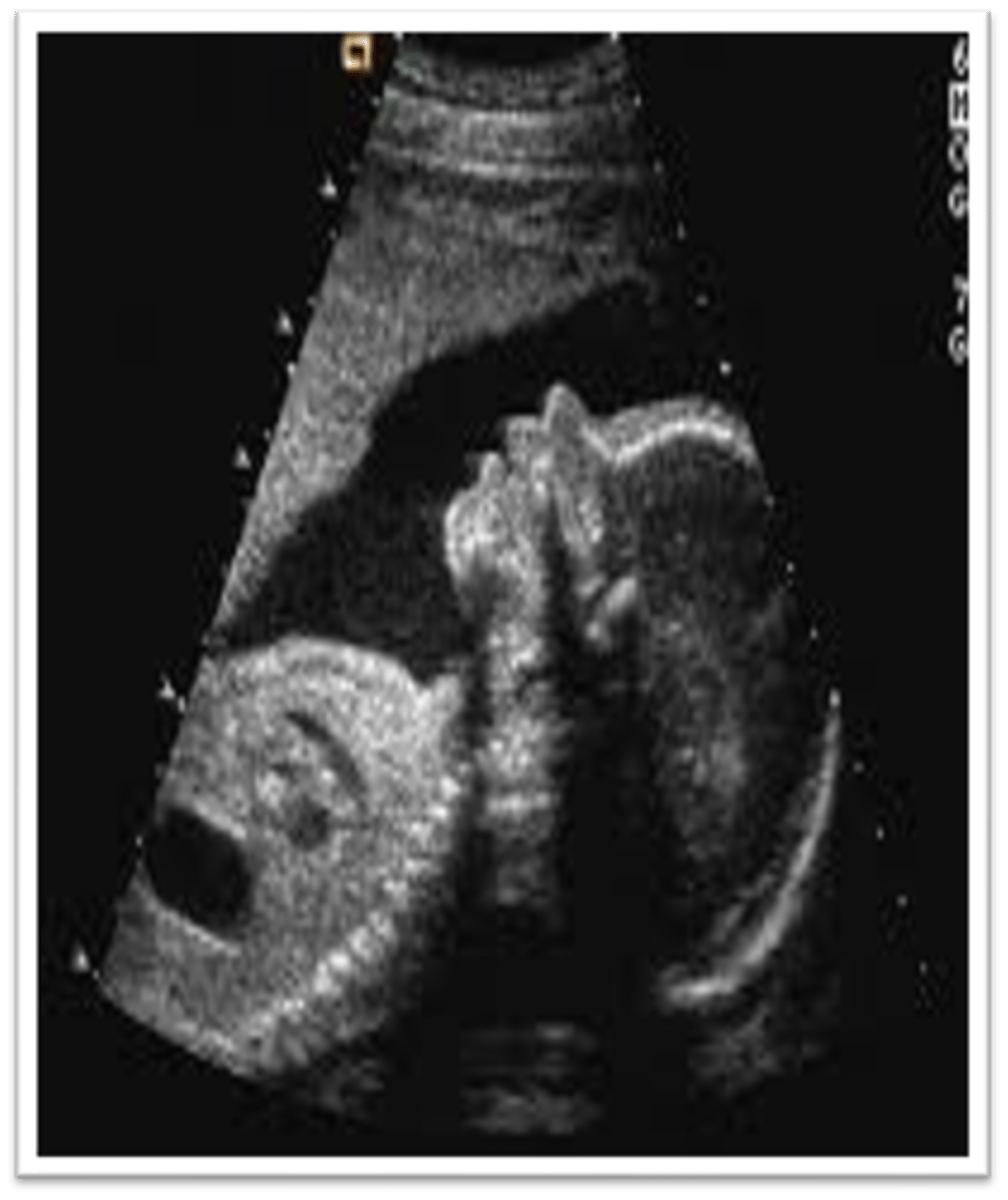
Fetal facial profile determines the relationship of the ___ and ___ and assesses the formation of the ___
nose; lips; chin
What does a coronal facial view demonstrate?
both orbital rings
parietal bones
ethmoid bones
nasal septum
zygomatic bone
maxillae
mandible
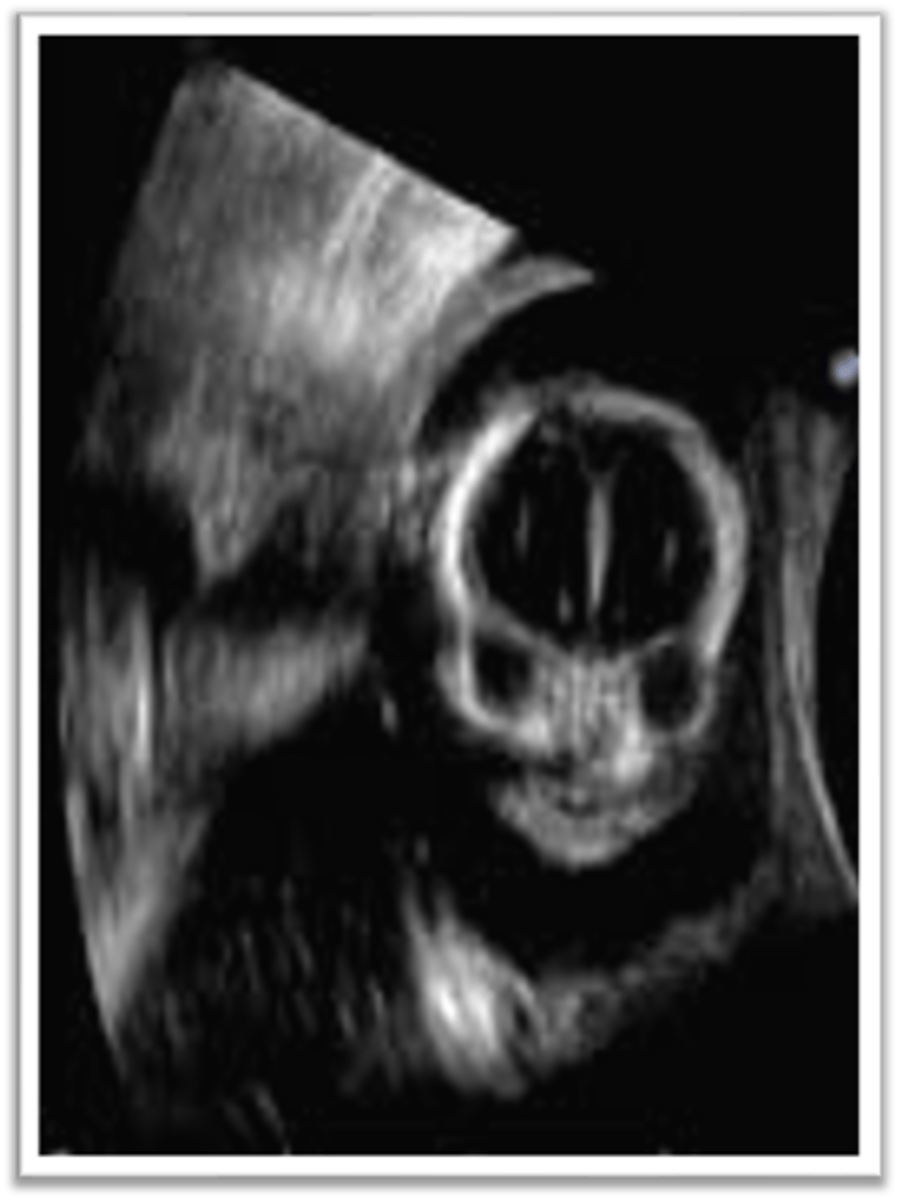
The coronal facial view is scanned in the anterior plane over the orbits to demonstrate the ___ and the ___
eyelids; orbital lens
In a coronal facial view, what is frequently outlined during fetal swallowing?
oral cavity and tongue
What do tangential views demonstrate?
nostrils/nares
nasal septum
maxillae
mandible
What view is helpful in diagnosing a cleft lip?
coronal facial view
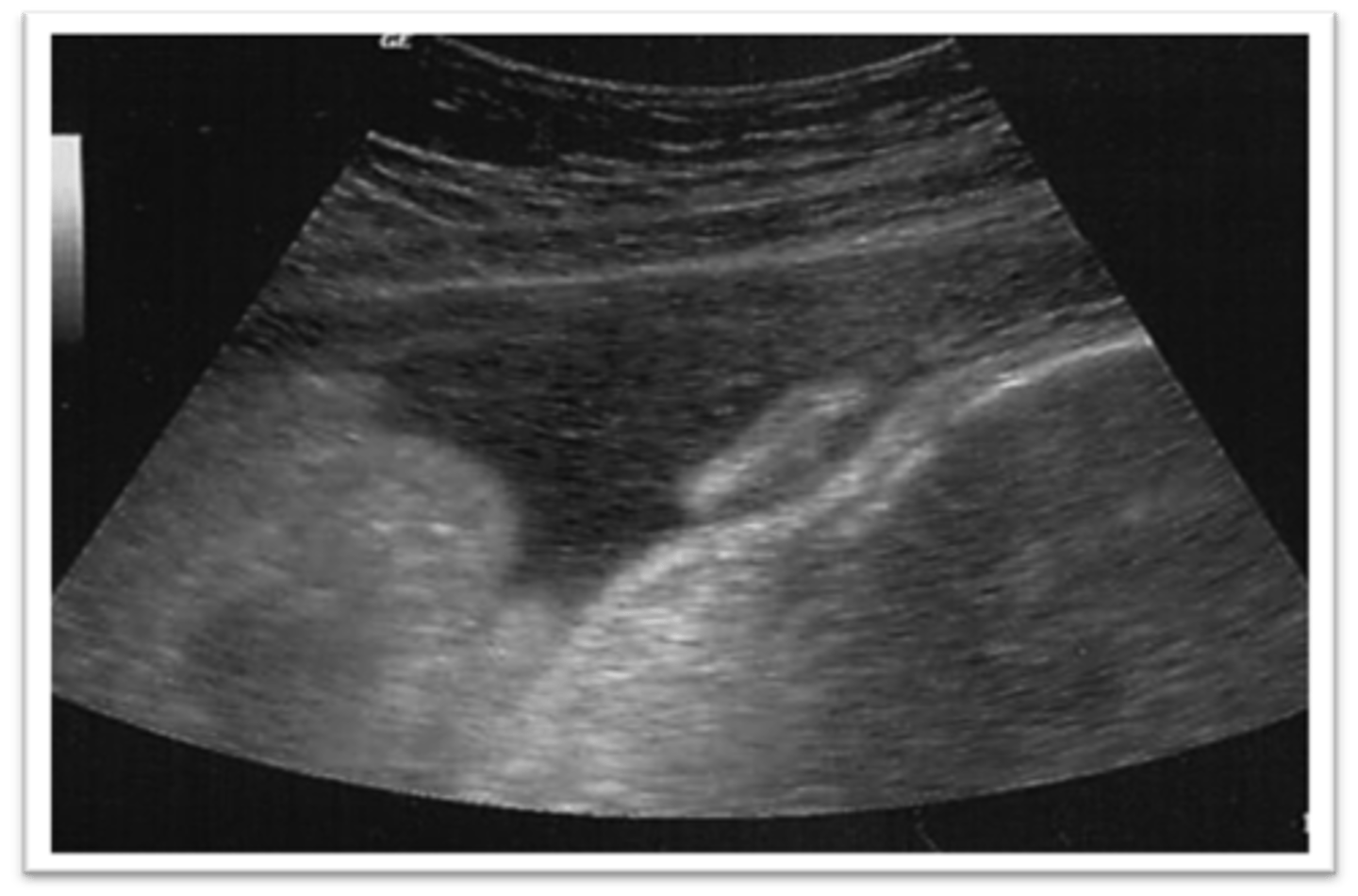
Ears may be defined as ___ protuberances emerging from the ___ bones
lateral; parietal
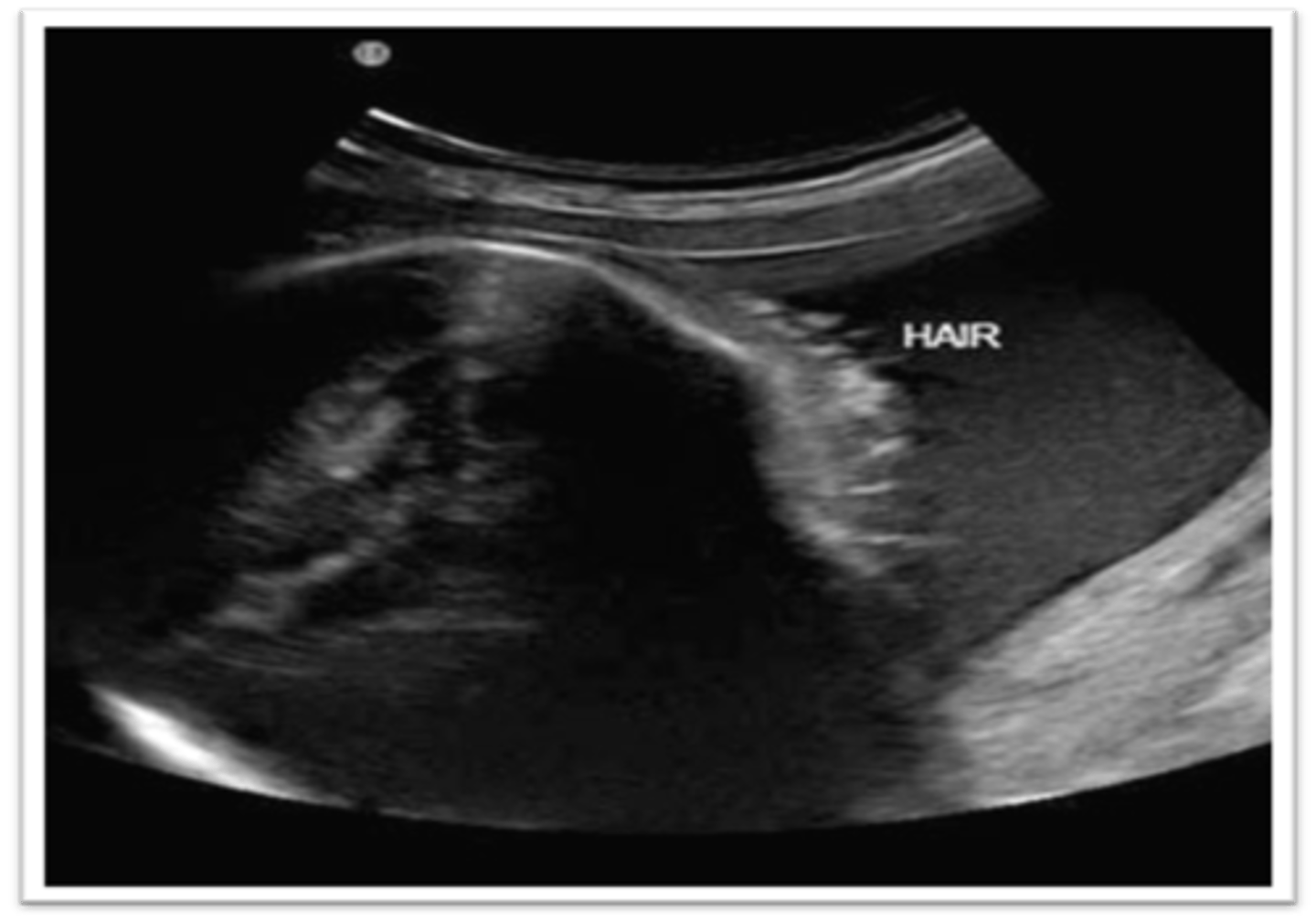
Fetal hair is often observed along the ___ of the skull; not to be included in the ___
periphery; BPD measurement
What scanning planes is the vertebral column evaluated in?
sagittal
coronal
transverse
In sagittal, the spine appears as ___ extending from the ___ to the ___
2 curvilinear lines; cervical spine; sacral spine
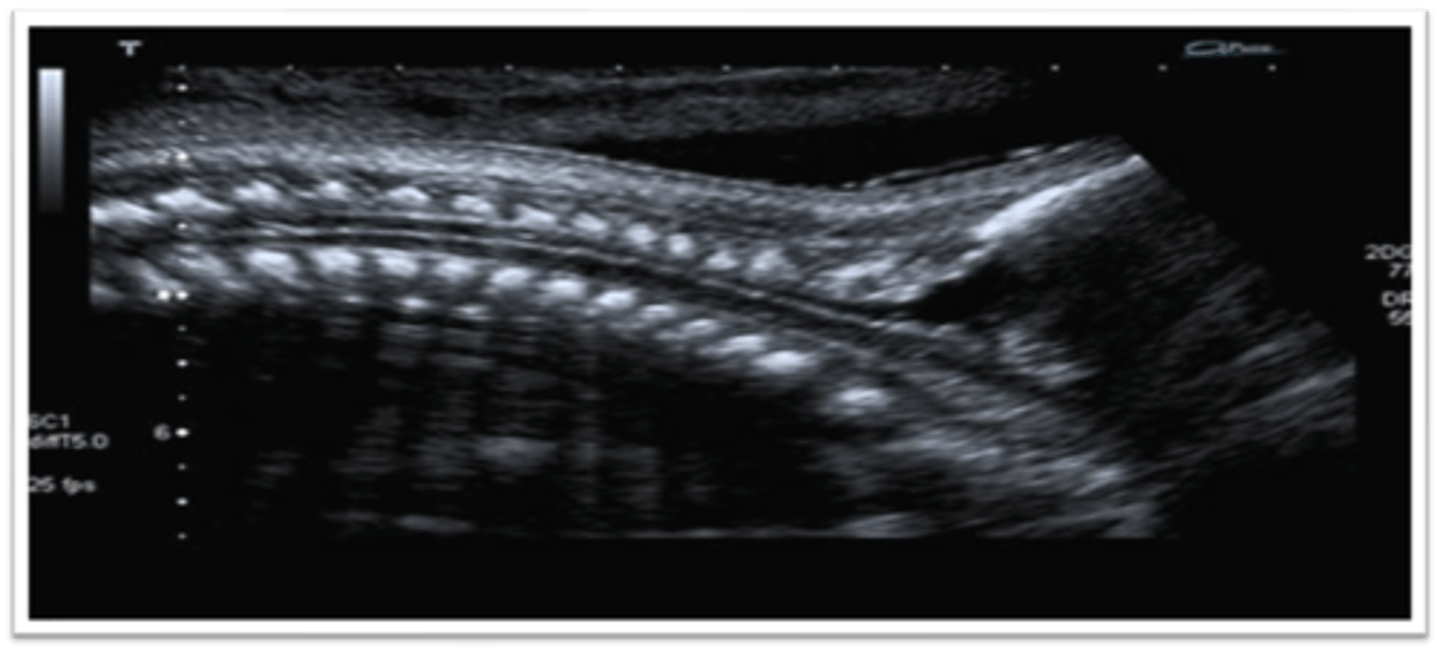
The cervical spine is ___ than the sacrum
wider
The normal fetal spine tapers near the sacrum and widens near the base of the skull. This double-line appearance of the spine is referred to as the ___ sign
railway
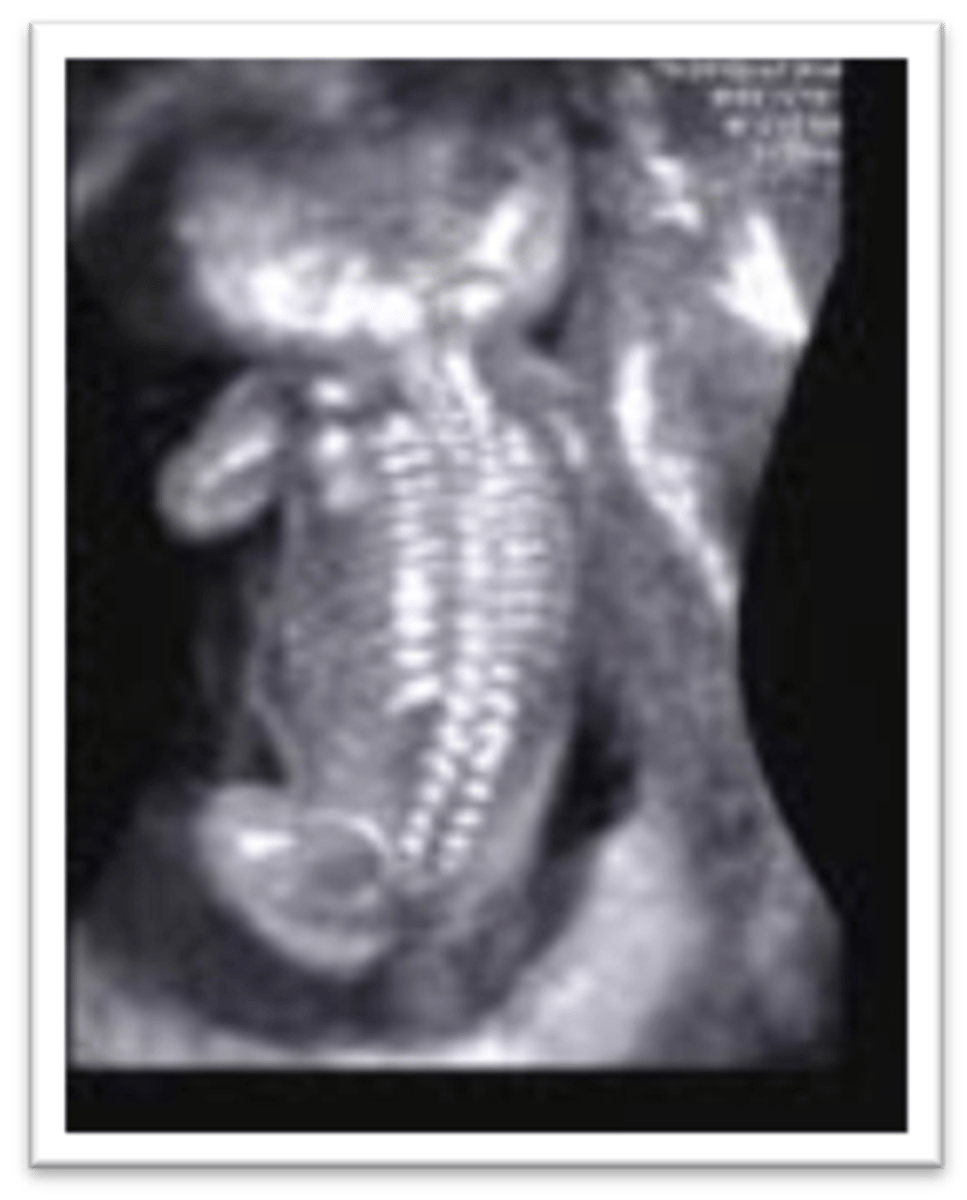
In transverse, the spinal column appears as a closed ___, indicating closure of the ___
circle; neural tube
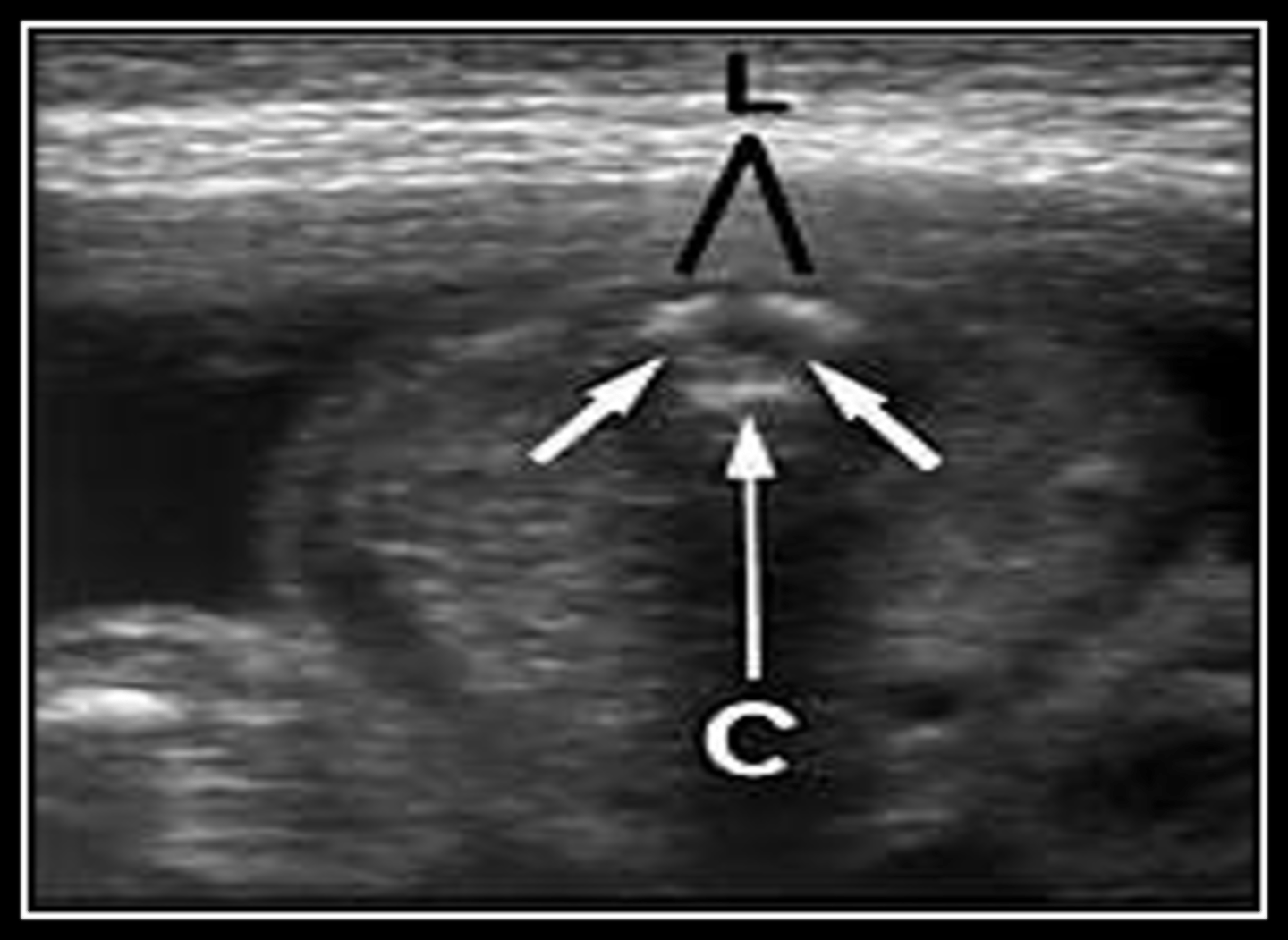
The circle of echoes in transverse represents the center of the ___ and the ___
vertebral body; posterior elements
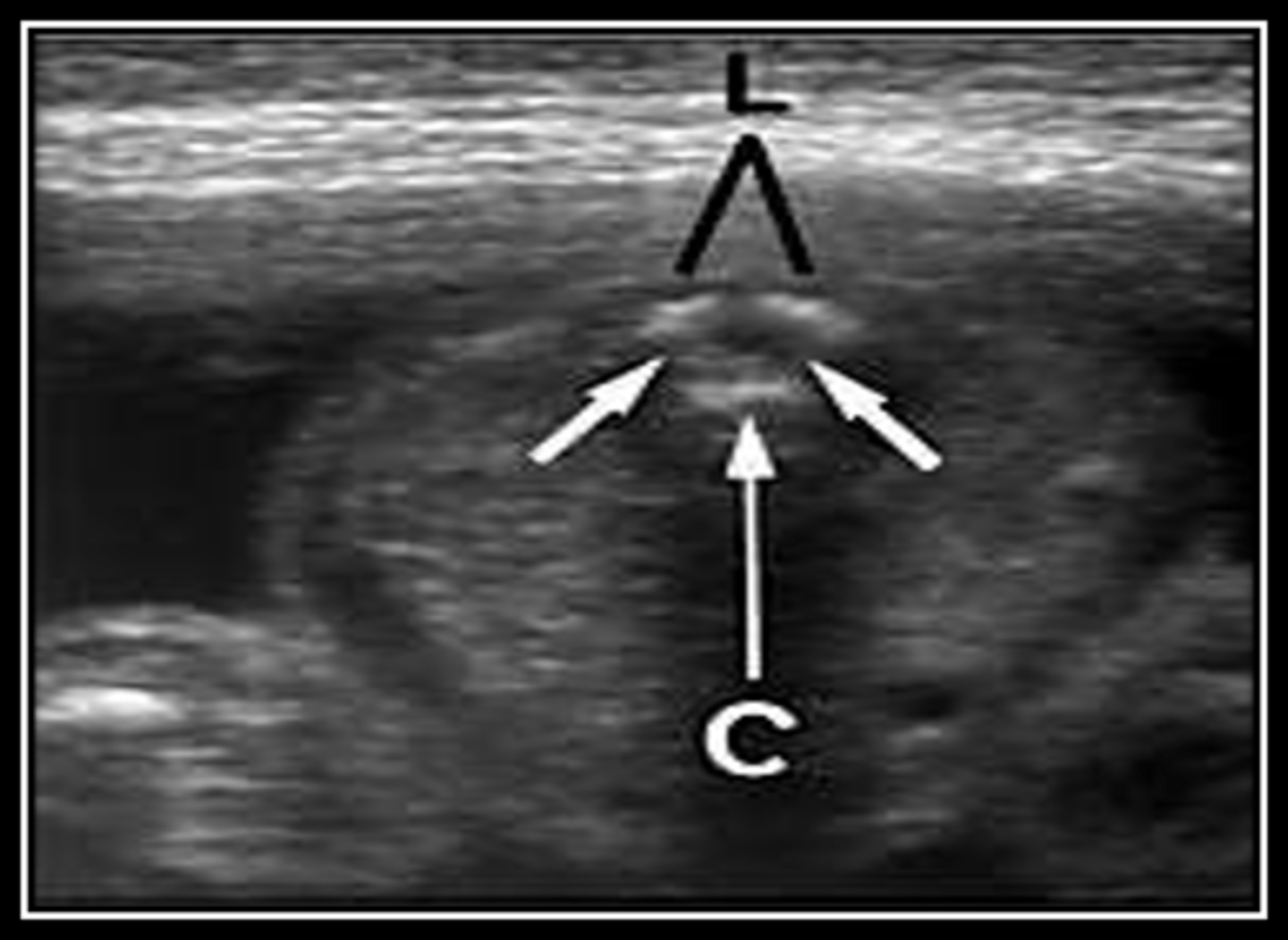
When evaluating the spine, it is important for the sonographer to align the transducer in a ___ axis to the spinal elements so that any interruption of skin surface can be detected
perpendicular
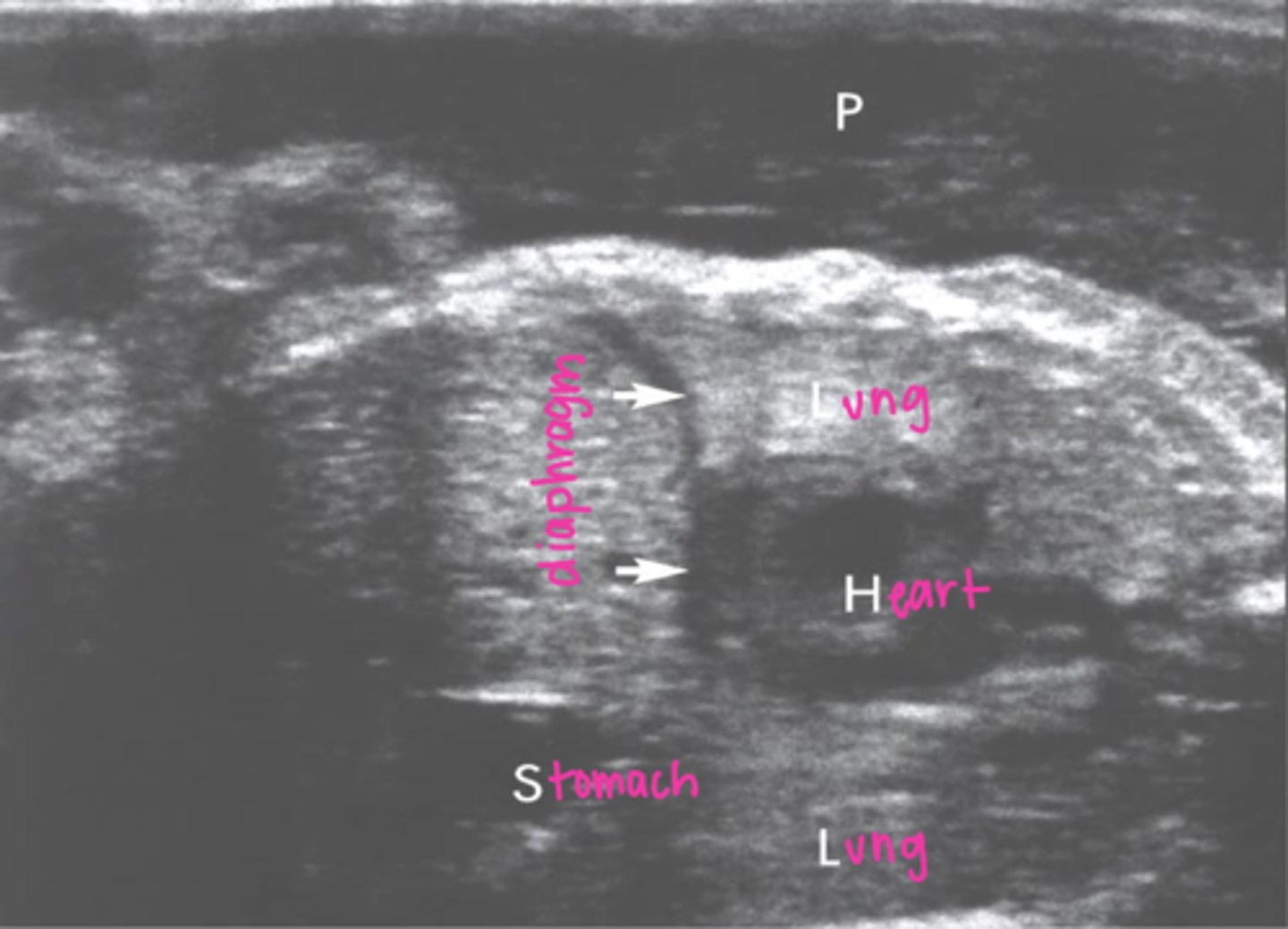
Lungs serve as ___ borders for the fetal heart
lateral