midterm 3 true/false
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
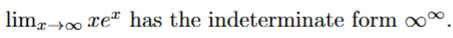
false → anything that is infinity^infinity will just go to infinity
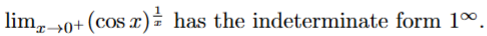
true → 1/0 will go to infinity and cos(0) = 1 so it will be 1^infinity
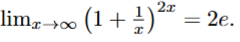
false → this is the definition of e^x; therefore, it would result in e²
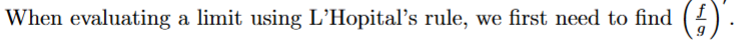
false → l’hopital’s rule finds the derivative of each the numerator and denominator, you do NOT use the quotient rule to find it
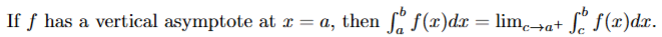
true → definition
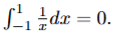
false → you have to split it where it does -1 to 0 + 0 to 1
if one side diverges, they both diverge
saying that an improper integral converges means that the integral must evaluate to a finite number
true → converges = finite number
indefinite integrals can be improper
false → must evaluate to either infinity or a finite number
If {An} is bounded, then it converges
false → sequence must be BOTH monotonic and bounded to converge
if {An} converges, then it is monotonic
false → sequence must be BOTH monotonic and bounded to converge
An unbounded sequence diverges
true → unbounded = diverge
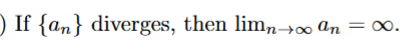
false → it can also oscillate
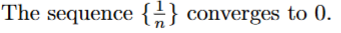
true → long term limit
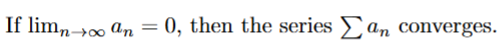
false → harmonic series
the series always diverges

true → definition
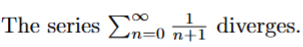
true → harmonic series
the sum of two divergent series also diverges
true
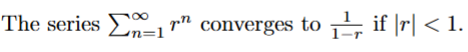
false → geometric series
the majority of this statement is correct BUT n must equal 0 for the statement to be 100% correct
integral test & nth term test
statement regarding test you are using and any/all conditions
math step
conclusion statement
Integral Test
positive
decreasing
continuous