Oligopolies
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Oligopoly - definition
An imperfectly competitive industry with a high level of market concentration
Examples of oligopolies
Airlines, broadband, banks, cinemas, fizzy drink, pharmaceuticals, car manufacturers
Concentration ratio - what is it
The combined market share of the leading 3-5 firms in a market
Generally what does the 5 firm concentration ratio need to be for an oligopoly?
>60%
5 firm concentration ratio of supermarket industry uk
75%
Tesco: 27%
Sainsburys: 15%
Asda: 14%
Aldi: 10%
Morrisons: 9%
Key characteristics of oligopolies
Few dominant firms
Interdependence
Relatively high barriers to entry
Non-price competition
Interdependence - what does this mean in oligopolies?
Each firm’s pricing and output decisions directly impact the profit of its rivals.
If one lowers prices, other may be forced to lower to compete. This creates a competitive and volatile market structure
Barriers to entry - examples
Economies of scale, vertical integration, brand loyalty, expertise/ reputation, patents, control of important platforms (eg aws)
Non-price competition - what is it in oligopolies
The use of other competitive strategies to gain an advantage over rivals, as price is less effective due to interdependence.
Types of product branding
Product brand - associated with particular products
Service brands - add perceived value to service
Umbrella brands - assigned to multiple products
Corporate brands - promoting the name of the business
Own label - when shops assign their name to branding
Global brand - household names across the world.
What’s the Hirfindhal-Hirschman Index?
An alternative and more accurate measure of market concentration
Price stickiness definition
If a firm lowers prices this will cause a price war and all parties lose profit
If a firm raises prices, others will keep theirs the same so that firm will lose customers
Therefore, pricing strategy generally remains constant
Why does the kinked demand curve arise?
As firms in oligopoly are more likely to match price decreases by a competitor than price increases
Kinked demand curve graphed
At high price rivals are assumed not to follow a price rise therefore PED is price elastic
However, rivals are assumed to follow a price fall therefore at lower prices demand is price inelastic
This shows how in oligopolies firms are likely to maintain their prices
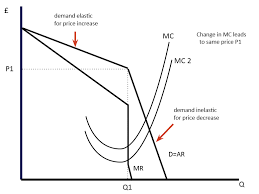
What happens at the point where elasticities change?
This is the point of profit maximisation as MR equals MC at this equilibrium any change in price leads to a fall in total revenue
A shift in the MC curve does not necessarily lead to a change in price.
Collusion definition
When two or more firms work together to set prices or output levels at the expense of consumers and the market
What’s explicit collusion
Formal agreements
What’s tacit collision?
This is subtle collusion, for instance when firms follow the actions of rivals and act accordingly
Is collusion legal?
No, in the UK and many countries it is illegal
How is corporation different to collusion?
This is when firms work together to achieve mutual benefits in a way that does not harm consumers like industry standards
Key example of collusion
OPEC – oil producing and exporting countries they artificially restrict supply to ensure a higher price for oil
What are the two conditions that make collusion more likely?
small number of supplies producing a homogenous product
High barriers to entry and established firms have similar objectives of profit maximisation
Collusion – graph for market and firm.
The cartel output is lower than that of market equilibrium which is where MC equals AR
For firms this leads super normal profits at the output quota
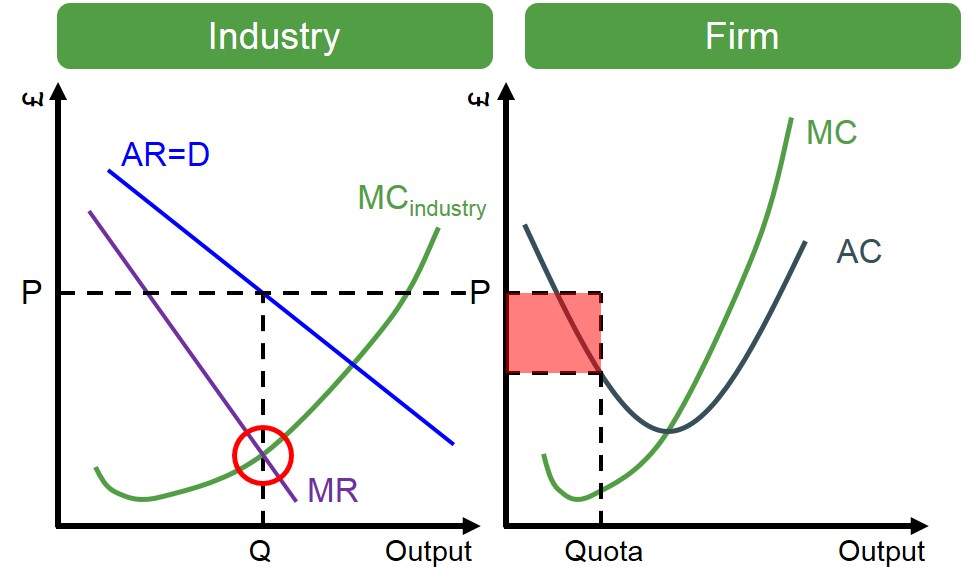
What is a quota in collusion?
An agreed upon output for firms
Why do cartels often fall apart?
Although the cartel is maximising profit each individual firm could increase their own profits by expanding output and undercutting the cartel price by small margin so members cheat their quotas