Unit 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Notochord
rod-like structure that supports and protects the spinal cord in chordate animals
'Ostracoderms'
jawless fishes, not monophyletic, body covered in dermal bone, cartilaginous skeletons
Anadromous
fish migrating up raivers from the sea to spawn
Otolith
stones in ear, registers gravity and linear acceleration
Horizontal septum
transverse wall of tissue that can occur anywhere in the body
Ampullae of Lorenzini
special sensing organs called electroreceptors, forming a network of jelly-filled canals; these organs help sharks sense electric fields in the water
Heterocercal tail
In some fishes, a tail with the upper lobe larger than the lower, and the end of the vertebral column somewhat upturned in the upper lobe, as in sharks.
Natural History
the study of animals, plants and their environment, focused more on observation than experiments
Taxonomy
the science of classification of living and extinct organisms
Homoplasy
shared characteristic that evolved independently in different groups of animals
Myomeres
muscle segments found in aquatic chordates
Chondrocranium
the cartilaginous skeletal structure of the fetal skull that grows to envelop the rapidly growing embryonic brain
Dermatocranium
portion of the cranium that is composed of dermal bone, part of the skull that develops int he form of membrane bone
‘Dunkleosteus’
jointed neck fish, covered in dermal bone
'Acanthodians'
spiny sharks, spines on most fins
Ammocoetes
filter-feeding larval form of a lamprey
Batoidea
flat-bodies, cartilaginous fish, suborder of cartilaginous fishes known as rays
Cephalic claspers
found on the head or near the cephalic region, assist in making by providing grip or positioning during copulation
Pelvic claspers
male anatomical structure used in mating, formed from the posterior portion of their pelvic fin, serves as a channel for semen into the female's cloaca
Prismatic calcification
buildup of excess calcium in the body
Lechithotrophy
little maternal input, nutrition -> yolk, oviparous
Matrotrophy
high maternal input, nutrition -> mother's reproductive track
Oviparity
describes organisms that produce eggs that develop and hatch outside the body of the mother
Trophonemata
long filaments extending from the uterine wall of some elasmobranchs that secrete a fluid that nourishes their embryos
Hair cells
The hairlike sensory receptors for sound, which are embedded in the basilar membrane of the cochlea.
Monobasic fins
one bone connecting the fins
Ganoid scales
diamond shaped scales, comprised of bone
Urohyal bone
median dermal bone
Postanal tail
posterior elongation of the body, extending past the anus
Dermal bone
bone that forms directly in the skin rather than from cartilage, process is called intramembranous ossification
Endochondral bone
bone development that occurs by replaying hyaline cartilage
Centrum
solid, central part of each vertebra that gives strength to the vertebral column
Gas bladder
an organ in fish that provides buoyancy and prevents sinking
Binomial Nomenclature
a system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both using latin grammatical forms
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Linnean Ranks
Monophyletic group (clade)
a group of organisms that share a most common recent ancestor and include all its decendants
Paraphyletic group
a group that contains a common ancestor and some but not all of the descendants
Homology
any characteristic of biological organisms that derived from a common ancestor
Convergent evolution
organisms that are not closely related develop similar features independently
Hemichordate
phylum of marine invertebrates, closely related to both echinoderms and chordates
Pharyngeal arches
early embryonic structures found in developing embryos, bilateral tissues that grow from the cephalic part of the neural crest, develops into cartilage, bone, nerves, muscles, glands, and connective tissue
Dorsal Hollow Nerve Chord
unique structure found in chordates, hollow tube of nervoud tissue located along the dorsal side of the body, basis for central nervous system
Endostyle
organ found in chordate animals, assists in filter-feeding, it evolved into the thyroid, secretes mucus to trap food particles in water drawn into the pharynx
Cephalization
evolutionary trend in animals where special sense organs and nerve ganglia become concentrated towards the rostral end of the body
‘Haikouella’
chordate fossil
Splanchnocranium
portion of the cranium that is derived from pharyngeal arches, forms the supporting structure of the jaw and consists of cartilage and endochondral bone
Neural crest
will form things line bones and muscles in cranium, unique germ layer in vertebrates
Hox genes
genes that help organize the development of an animal
Perichondral bone
bone that forms around cartilage
Neural arch
encloses the canal that the spinal cord passes through
Devonian
geological period and system of the Paleozoic era
'Placoderms'
jawed fish, anterior of body covered in think boney shield
Tidal ventilation
allows organisms to breathe while feeding
Flow-through ventilation
water goes through the mouth and over its gills
Vestibular apparatus
the organs in your inner ear that sense information your body needs to maintain balance
Semicircular canals
act as detectors for angular acceleration in their respective planes
Mandibular arch
mandible, mastication muscles, trigeminal nerve, gives rise to malleus and incus bones. Plays a role in feeding a speech
Hyoid arch
The second branchial arch, which forms the styloid process, stapes of the ear, stylohyoid ligament, and part of the hyoid bone.
Palatoquadrate
dorsal component of the mandibular arch
Meckel's cartilage
Cartilage that forms within each side of mandibular arch and that disappears as bony mandible forms
Spiracle
small opening located along the side of the body through which air enters and leaves the body of many terrestrial arthropods
Pelvic fins
used for turning, balance, and stopping
Pectoral fins
navigate, stop, back up, and help orient the body when at rest
Epaxial musculature
dorsal muscles associated with the vertebrae, ribs, and base of the skull
Hypaxial musculature
lie ventral to the horizontal septum of the vertebrae
Squalimorphii
super order of cartilaginous fishes, lacking traits like anal fin, nictitating membrane, suborbital shelves in the cranium
Galeomorphii
superorder of sharks
Ceratotrichia
slender soft or stiff filaments of an elastic protein, supporting tissue of the fins
Placoid scales
they are scales that protect fish from predators, the reduce drag so they are able to swim faster and quieter
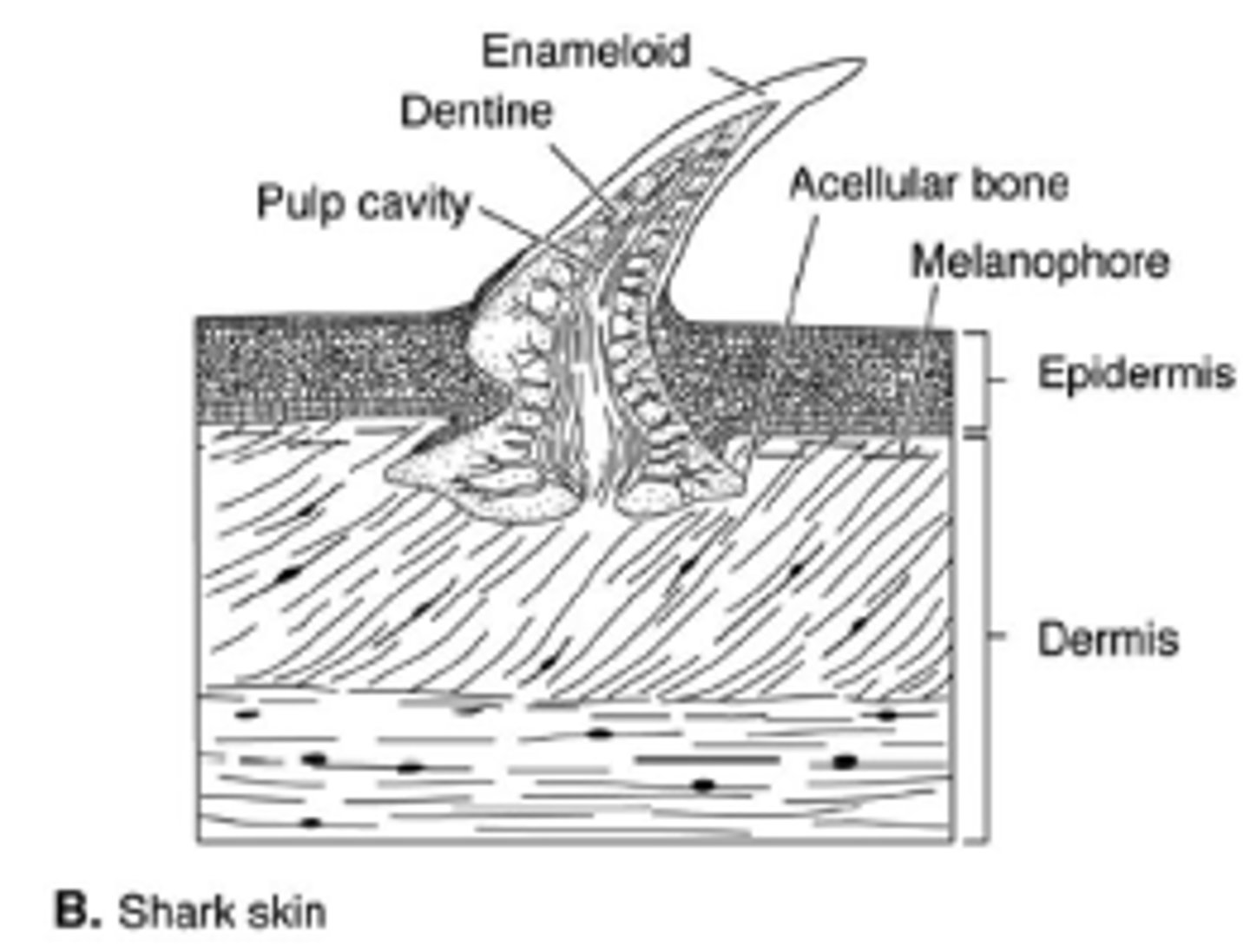
Viviparity
giving birth to live young
Yolk sac vivparity
eggs retained inside, low maternal input, but live birth
Histotrophy
Developing embryos absorb maternal secretions
Placental Viviparity
development of a placenta
Oophagy
occurs only in Lamniformes sharks; nutrition is provided by the mother to developing embryos within the uterus by continuing to ovulate new eggs that are then consumed by the embryos
Branchiostegal rays
a fanlike series of dermal bones on the underside of the skull, forming the floor of the gill chamber
Latimeria chalumnae
West Indian Ocean Coelacanth
Cosmoid scales
scales that consist of two basal layers of bone, a layer of dentine-like cosmine and an outer layer of vitrodentine or enamel-like substance
Pharyngeal jaws
jaws contained within an animals throat
Obligate air breather
respire entirely from atmosphere
Facultative air breather
breathe air when it is convenient but otherwise do not use lungs
Homocercal tail
A tail with the upper and lower lobes symmetrical and the vertebral column ending near the middle of the base, as in most telost fishes.
Premaxilla
Bony area of the upper jaw that includes the alveolar ridge for the incisors and the area immediately behind it.
Maxilla
upper jaw