chemistry- paper 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
what is a soluble?
a substance that can dissolve in a solvent
what is an insoluble?
a substance that cannot dissolve in a solvent
what is a solvent?
the liquid that dissolves in a solute
what is a solute?
the substance that is dissolved
what is a solution?
a mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent
what is an ion?
electrically charged atom or groups of atoms
how are ionic structures arranged?
lattice
what is Metallic bonding?
metal atoms bonding to each other
what is ionic bonding?
metals bonding to non-metals
what group are Alkali metals in?
Group 1
what group are Halogens in?
group 7
what group are the noble gases in?
group 8
what happens to group ones electrons?
lose
what is the order of electron shells?
2,8,8,2
what do metals form?
positive ions
what do non-metals form?
negative ions
what do metals do?
donate electrons to gain an empty outer shell
what do non-metals do?
accept electrons to gain a full outer shell
what is an isotope?
same element and different number of neutrons
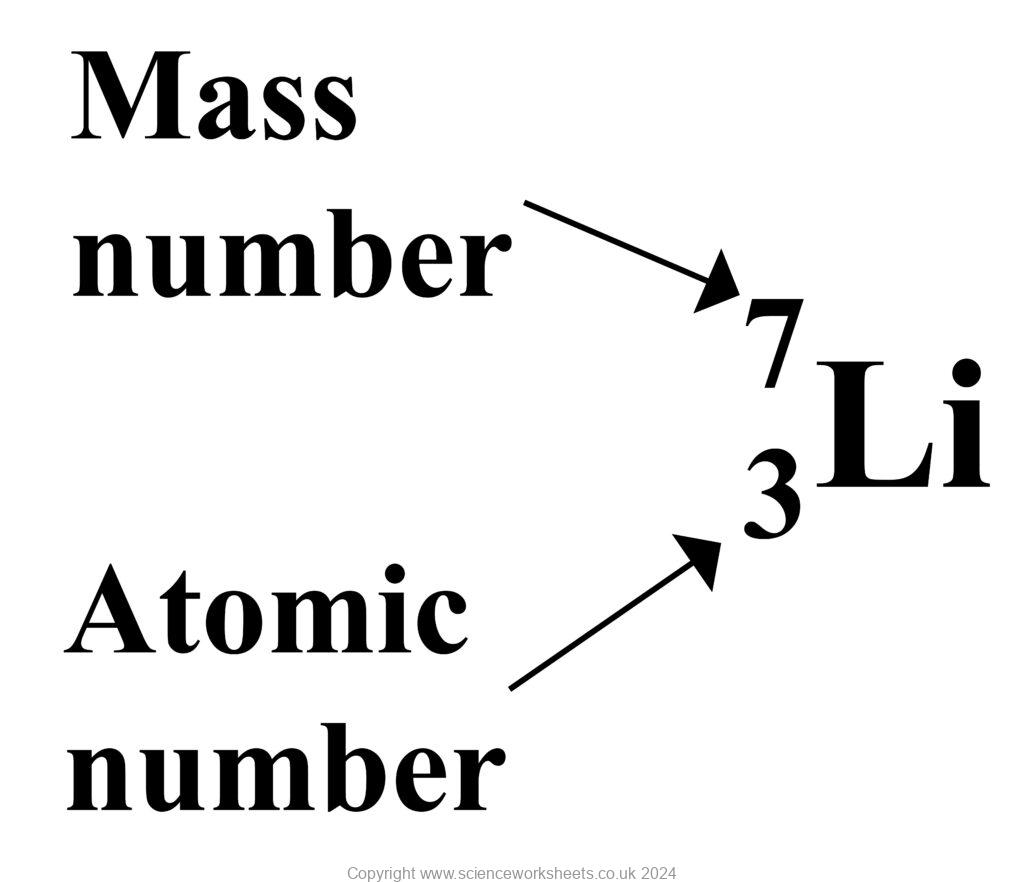
what is a mass number?
the number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus
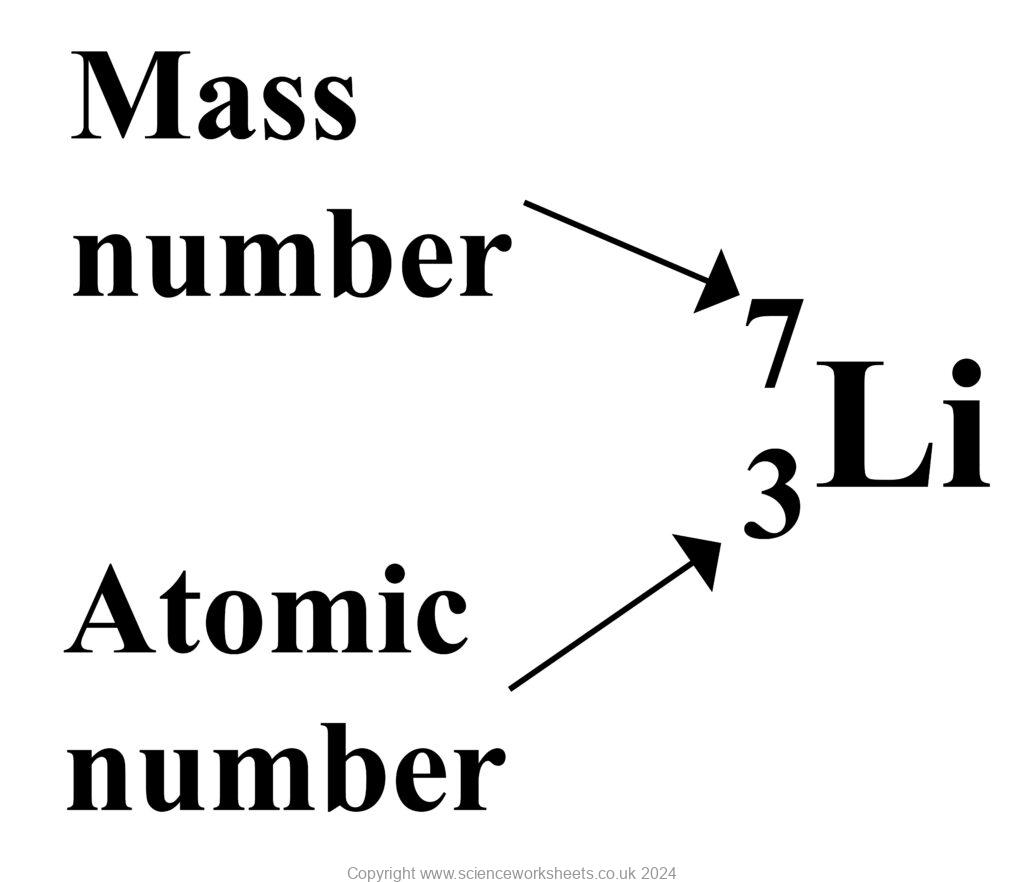
what is an atomic number?
number of protons in a nucleus
what does filtration do?
removes large, insoluble particles from a liquid
what is an example of filtration?
sand from water
what does evaporation do?
leaves behind crystals of a dissolved substance if heated gently
what does distillation involve?
condensing the evaporated solvent and collecting it
what is fractional distillation?
separating liquids due their different boiling points
what is chromatography?
causes substance to rise up due to capillary action
what was John Dalton’s theory about the atomic structure?
matter is made of invisible particles
what did JJ Thompson create?
plum pudding model
what did Ernest Rutherford discovered?
the nucleus and that most alpha particles went straight through
what did James Chadwick discover?
nucleus must contain neutrons as well as protons
what did Neil Bohr deduced?
electrons exist in shells
what is the relative charge for a proton?
+1
what is the relative mass for a proton
1
what is the relative charge for a neutron?
0
what is the relative mass for a neutron?
1
what is the relative charge for an electron?
-1
what is the relative mass for an electron?
0
what is an element?
a substance containing only one type of atom
give an example of an element?
mg
what is a compound?
a substance containing two or more different type of atoms
give an example of a compound?
H20
what is a mixture?
a substance made by mixing other substances together
what is an atom?
smallest unit of matter
what is (aq)?
indicates the substance is in a solution (aqueous)
what is an alloy?
mixture of two or more elements
why can graphite conduct electricity?
it has delocalised electrons
what does delocalised electrons means?
Delocalised electrons are electrons that are not associated with a single atom or a single covalent bond within a molecule.