LES 2.2: The Practice Specialty of Nursing Informatics (Models & Theories)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Models
Are representations of some aspect of the real world; show particular perspectives of a selected aspect and may illustrate relationships
False
True or False: There is one right model for NI.
Clinical-Information-System (CIS)
This model shows how modeling can be used to organize different concepts into a logical whole. The purpose of this model is to depict system components, influencing factors, and relationships that need to be considered when attempting to capture the complexities of professional nursing practice.
Graves & Corcoran’s Model
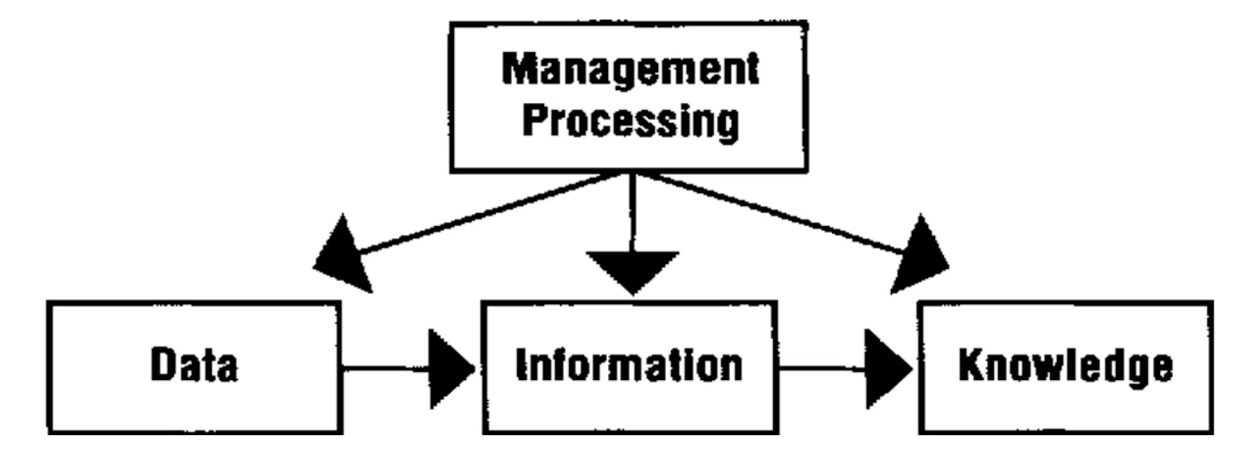
Model that places data, information and knowledge in sequential boxes with one-way arrows pointing form data to information to knowledge. The management processing box is directly above with arrows pointing in one direction from management processing to each of the three boxes.
Graves & Corcoran Model
Identify the model.
Patricia Schwirian’s Model
Model of NI intended to stimulate and guide systematic research in this discipline.Provides a framework for identifying significant information needs.
Patricia Schwirian’s Model
Identify the model.
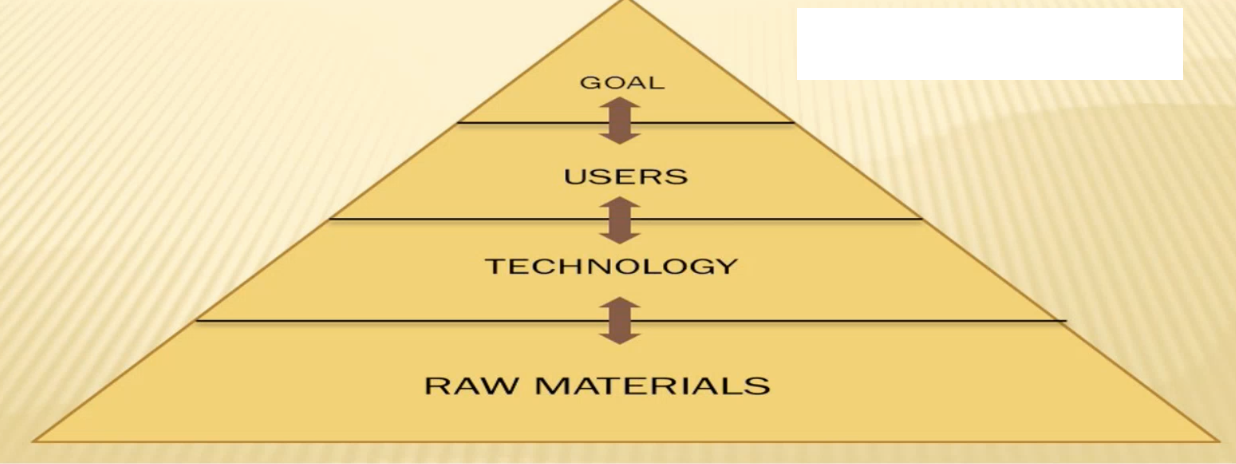
Raw Materials
Component of Patricia Schwirian’s Model
Nursing related information
Technology
Component of Patricia Schwirian’s Model
A computing system comprised of hardware and software
Users
Component of Patricia Schwirian’s Model
Surrounded by context which are the nurses and students
Goal
Component of Patricia Schwirian’s Model
Toward the preceding elements are directed
Turley (1996)
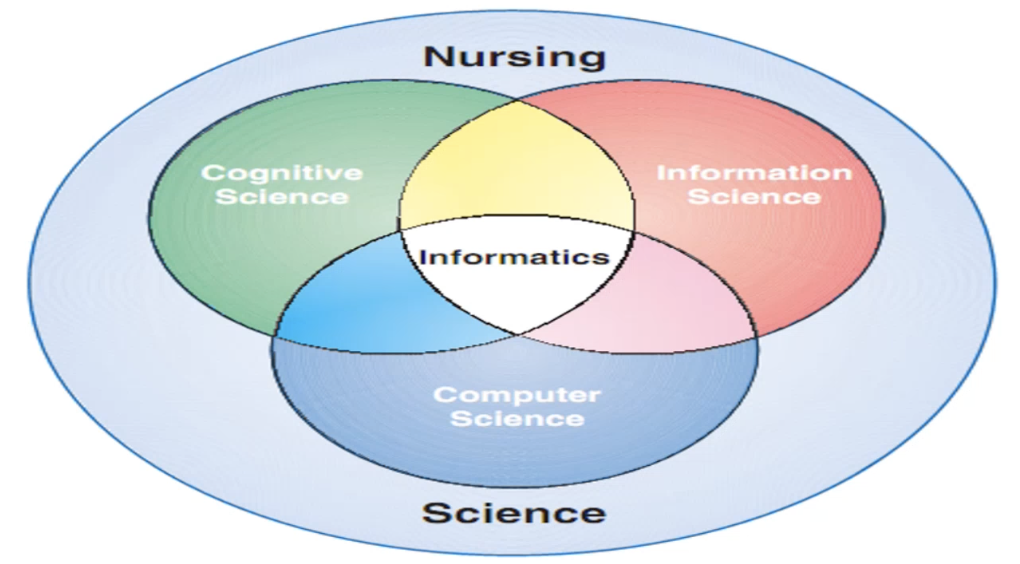
Model in which the core components of informatics (cognitive, information, and computer sciences are depicted as intersecting circles. NI is the intersection between the discipline-specific science (nursing) and the area of informatics
Turley’s Model (1996)
Identify the model.
McGonigle & Mastrian’s Foundation of the Knowledge Model
Base of this model shows data and info distributed randomly. From this base, transparent cones grow upward and intersect. The upward cones represent acquisition, generation, and dissemination of knowledge. knowledge processing is represented by the intersections of these three cones. Circling and connecting all the cones is feedback. The cones and feedback circle are dynamic in nature
McGonigle & Mastrian’s Foundation of the Knowledge Model
Identify the model.
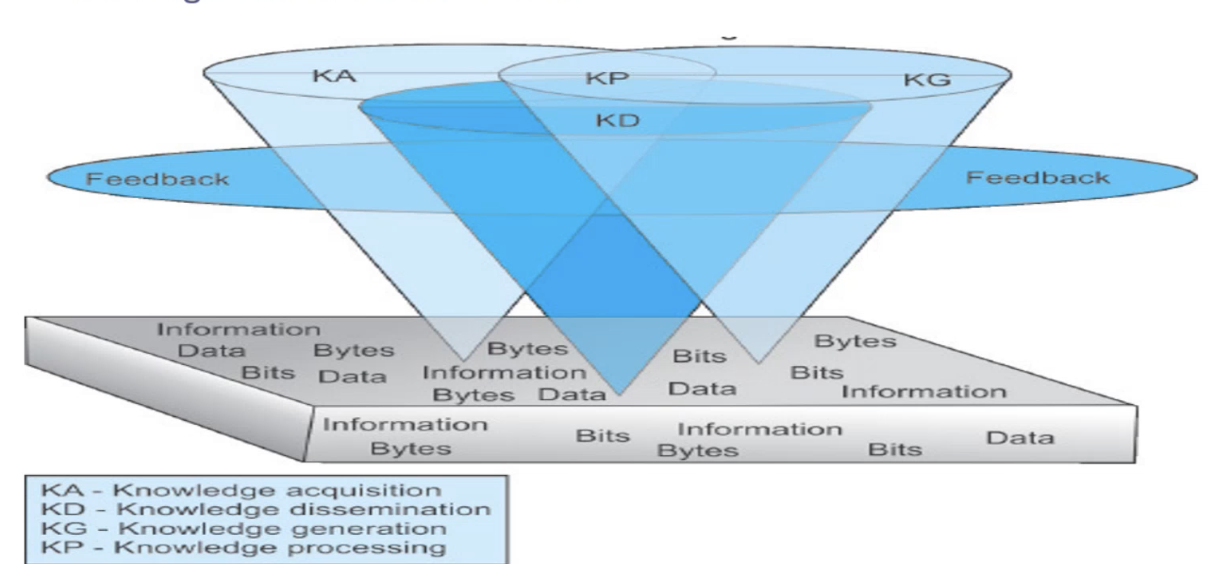
Knowledge
Acquisition
Generation
Dissemination
In McGonigle & Mastrian’s Foundation of the Knowledge Model what do the upward cones represent?
Knowledge Processing
In McGonigle & Mastrian’s Foundation of the Knowledge Model what do the intersection of the three cones represent?
Feedback
In McGonigle & Mastrian’s Foundation of the Knowledge Model what circles and connects the cones?
Theory
A scholarly, organized view of some aspect of the world (reality); can describe, explain, predict, or prescribe selected phenomena within this reality
Grand
Middle-Range
Situation-Specific or Practice Theories
Theory Classifications
Grand Theories
Theory Classification
Are broad in scope and the most complex of the 3
Situation-Specific/Practice Theories
Theory Classification
Are the most specific of the 3; Usually provide prescriptions or directions for practitioners
Middle-Range Theories
Theory Classification
Are somewhere in the middle of the 2; are more specific than grand but not as prescriptive as practice theories
Nursing Theories
Are about nursing practice-a nurse’s interactions or relationships with individuals, groups, or communities (aka patients or clients) focused on applying the nursing process
Grand Nursing Theories
Discuss nursing practice in broad terms, providing different worldviews of how, when, and why nurses relate to clients
Middle-Range Nursing Theories
Might describe a particular phenomenon of interest to nurses, explain how one phenomenon relates to one or more other phenomena or predict how a phenomenon impacts nurses and or clients
Practice Nursing Theories
A particular approach to breast feeding or a set of specific principles for the care of preterm infants that improves heir health outcomes are two examples of this.
Patricia Benner’s Novice to Expert
Model to explain how nursing students and professional nurses acquired nursing skills
Novice
Advance Beginner
Competent
Proficient
Expert
5 Stages of Novice to Expert
Novice
Stage of Novice to Expert
Follow rules provided for each situation and is not flexible in real life situations
Advanced Beginner
Stage of Novice to Expert
When one acquires real-life experiences and can appreciate environmental influences on rule sets
Competent
Stage of Novice to Expert
A learner is able to tell what is important and what is not important in assessing a given situation-a learner has gained perspective
Proficient
Stage of Novice to Expert
Able to see a situation in terms of the larger setting or environmental situation and begins to use intuition in decision-making
Expert
Stage of Novice to Expert
Intuitively understands a situation and immediately connects action to this understanding
Computer Science
Study of algorithms for solving computation problems; if an algorithm can be identified for solving a particular problem, an automated solution to the problem can be developed
False
True or False: A computer is the focus of comp sci, rather than a tool.
Information Science
Focuses on the gathering, manipulation, classification, storage and retrieval of recorded knowledge; can be socially oriented, focused on humans and machines and closely linked to communications and human behavior
Information Retrieval
Human-computer interactions from the perspective of knowledge manipulation
Information handling within a system (human or machine)
3 Important Branches of Information Science
Communication Theory
Uses the concept of communication channel and additional principles developed since then to analyze information transfer and effectiveness and efficiency of communication
below
If the sender’s entropy rate is ___ the channel capacity, there is a way to encode the information so that it can be received without errors
Bruce I. Blum
Within a communication model, who presented a taxonomy?
Data
Communication Model
Discrete entities that are described objectively without interpretation; facts without context; sometimes referred to as being “raw”
Information
Communication Model
Data that are interpreted, organized, or structured; brings in the idea of processing data so that it can be displayed or presented for human use
Knowledge
Communication Model
Information that has been synthesized so that interrelationships of data and information are identified and formalized
Wisdom
Many informatics theorists have added this to Blum’s theory; the appropriate use of knowledge in managing and solving problems
Cognitive Science
Study of the mind of how we think
Computers, phones, web browsers
What are examples of cognitive technologies that are emerging from cognitive science that help in learning, memory, problem solving, and living faily life in modern society?
Biological-Base Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
What are two significant branches of cognitive technologies?
Systems Theory
Theory that relates to the properties of ____ as a whole; focuses on the organization and interdependence of relationships within a ____
System
Any set (group) of interdependent or temporarily interacting parts
Parts
Are systems themselves and are composed of other parts
Closed
Open
Boundary of a system may be:
Closed System
Systems theory
Has an impermeable boundary and does not interact with the surrounding environment
Example: Human circulatory system since the blood never leaves the system of blood vessels
Open System
System theory
Can be influence by events outside of the actual or conceptual boundaries; have semipermeable boundaries that restrict the exchange of selective components but allow free exchange of all other components
Example: Information systems and people, although there can be the opposite systems within these systems
Behavior
Can include emotions, cognitions, motivation
Social Processes & Acts
Can be status (demographic, economic, or cultural), levels of social context, and biosocial interaction
Behavioral and Social Sciences
Study of behavior; examining how people act alone and with others
Change
Entail not only structures and ways of doing tasks but also the performance, expectations, and perceptions of all involved parties
Informatics Nurse Specialist (INS)
Who is often the primary change agent in facilitating the implementation of clinical information systems (CIS) in healthcare settings?
Planned Change
A collection of ideas about modifications to an organization or social system that are explicitly designed and put into place
Lewin’s Theory on Planned-Change Model
Rogers’ Diffusion of Innovations Model
What are the 2 most familiar change perspectives?
Unfreezing
Changing
Refreezing
3 Stages of Lewin’s Theory on Planned Change Model
Unfreezing
Stage of Lewin’s Theory on Planned Change Model
Involves overcoming inertia and dismantling the existing mindset. Defense mechanisms or resistance patterns have to be bypassed.
A change agent must uncover reasons or rewards that will be influential in __ or changing a behavior.
Moving
Stage of Lewin’s Theory on Planned Change Model
Behavioral change occurs; typically is a period of confusion
People are aware that the old ways are being challenged but do not have a clear picture yet of how to replace the old ways
Refreezing
Stage of Lewin’s Theory on Planned Change Model
A new mindset has formed and the comfort level is returned to previous levels
Everett Rogers
Who formalized the diffusion of innovation theory?
Diffusion of Innovations (1962)
In what book did Everett Rogers formalize the diffusion of innovation theory?
Innovators
Early Adopters
Early Majority
Late Majority
Laggards
5 Specific Groups of Innovation Adopters
Knowledge
Persuasion
The Adopter Makes a Decision
Implementation
Confirmation
5 Stages of Diffusion of Innovations Model
1: Knowledge
Stage of Diffusion of Innovations Model
Learning about the existence and function of the innovation
2: Persuasion
Stage of Diffusion of Innovations Model
Becoming convinced of the value of the innovation
3: The Adopter Makes a Decision.
Stage of Diffusion of Innovations Model
Committing to the adoption of the innovation
4: Implementation
Stage of Diffusion of Innovations Model
Putting it to use
5: Confirmation
Stage of Diffusion of Innovations Model
The ultimate acceptance (or rejection) of the innovation.
Learning
Process of acquiring KSA, or values through study, experiences or teaching
Organizational Behavior
In this field, organizations are examined, using methods drawn from economics, sociology, political science, anthropology, and psychology
Management Science
Uses mathematics and other analytical methods to help make better decisions
Group Dynamics
Is a social science field that focuses on the nature of groups; urges to belong or to identify may make for distinctly different attitudes
Bruce Tuckman (1965)
Who proposed a 4 stage model for ideal group decision making process?
Forming
Storming
Norming
Performing
4 Stages for ideal group decision making process
1: Forming
Stage for ideal group decision making process
Pretending to get on or get along with others
2: Storming
Stage for ideal group decision making process
Letting down the politeness barrier and trying to get down to the issues even if tempers flare up
3: Norming
Stage for ideal group decision making process
Getting used to each other and developing trust and productivity
4: Performing
Stage for ideal group decision making process
Working in a group to a common goal on a highly efficient and cooperative basis