Test 1: Autonomic Nervous System
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Homeostasis
Regulation and maintenance of bodily functions (i.e., metabolism, circulation, respiration, reproduction, etc.).
Behavioral modification
Motivation of involuntary and voluntary behavior to meet internal needs (i.e., thermoregulation and sweating).
Emotional-physiological link
Responsible for involuntary responses associated with a conscious emotional state (i.e., skin flush and embarrassment).
Mechanoreceptors
Responds to pressure and stretch (i.e., blood pressure).
Aortic baroreceptors, carotid sinuses, lung, veins, bladder, intestines
What are some examples of mechanoreceptors?
Chemoreceptors
Sensitive to chemical concentrations in the blood (i.e., monitoring blood pH).
Carotid and aortic bodies, medulla, hypothalamus, stomach, taste buds.
What are some examples of chemoreceptors?
Nociceptors
Respond to stretch, ischemia, and chemicals.
Viscera and arterial walls.
What are some examples of nociceptors?
Thermoreceptors
Respond to changes in circulating blood temperature and cutaneous temperature.
Hypothalamus and skin.
What are some examples of thermoreceptors?
CN VII, IX, X
______________________ and spinal cord convey sensory info from viscera to central processes.
Solitary nucleus; subcortical areas
CN VII, IX, X → Afferents synapse primarily with _____________________. → Solitary nucleus sends projections to other brainstem and _____________________ (i.e., pons/medulla, hypothalamus).
Brainstem; thalamus; hypothalamus
Explain the synaptic activity of dorsal root visceral afferents on each of the following:
Second order visceral afferent neurons → Origin of ascending pathways to ____________________, ____________________, and ____________________.
Emotion; hypothalamus
Second order visceral afferent neurons link ____________________ in cortex (limbic area) -and- send sensory info to _____________________ (master controller).
Reticular formation; cortex
Second order visceral afferent neuron synapse on 2nd order neuron → _____________________ in brainstem (synapse) → Hypothalamus (synapse) → Thalamus (synapse) → _____________________.
Nociceptive
Explain the synaptic activity of dorsal root visceral afferents on each of the following:
Second order somatic afferent neurons → Somatosensory ______________________ information.
Referred pain
Second order somatic afferent neurons are mechanism behind _____________________.
Substantia gelatinosa
VA info about inflammation from appendicitis synapses on _____________________ then goes up to cortex.
Pain
We have no conscious awareness of hypothalamic function so second order somatic afferent neurons going to the cortex allows us to perceive ______________________.
Reflex arcs
Explain the synaptic activity of dorsal root visceral afferents on each of the following:
VA info contributes to visceral ______________________ via synapses with visceral efferents.
Spinal cord
In appendicitis, shuts down appendicitis via ________________________ communication.
Interneuron
Explain the synaptic activity of dorsal root visceral afferents:
Somatic efferent neurons → VA synapses on an ___________________ that activates SE response.
Muscle guarding
In appendicitis, somatic efferent neurons activates _________________________ of abdomen.
Referred pain
Pain that is perceived as coming from a site that is distinct from the actual site of origin.
Second order neurons; dermatome
Theoretical origin of referred pain = visceral afferent fibers synapse on the same ______________________ as somatosensory afferents.
Ex: VA info uses arm ____________________ as road to get to cortex.
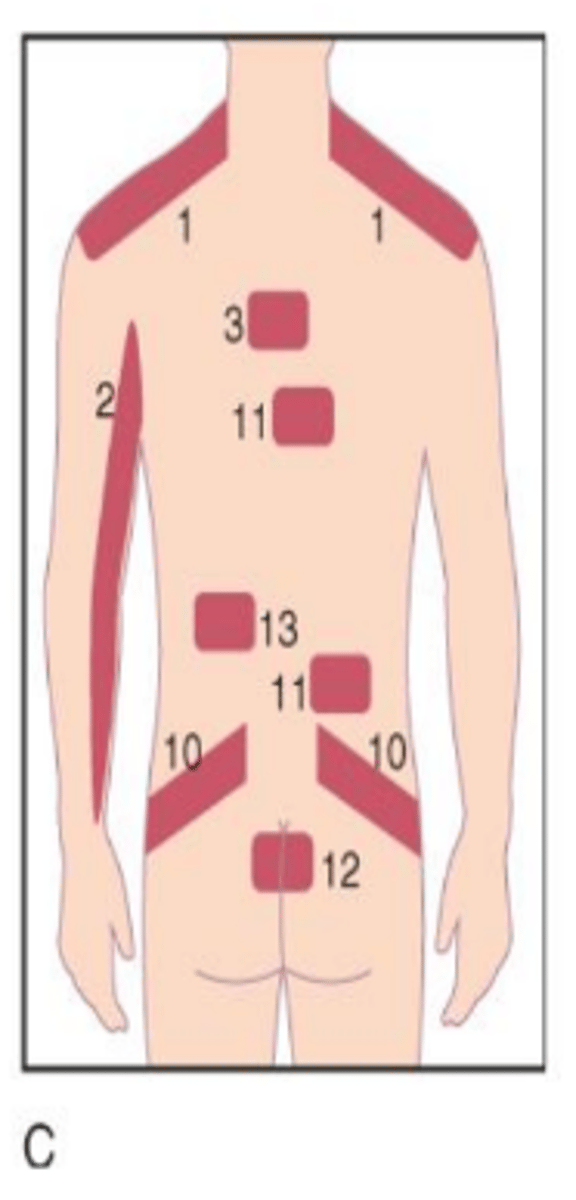
Heart
Across left side of chest into left shoulder and arm (2 in image).
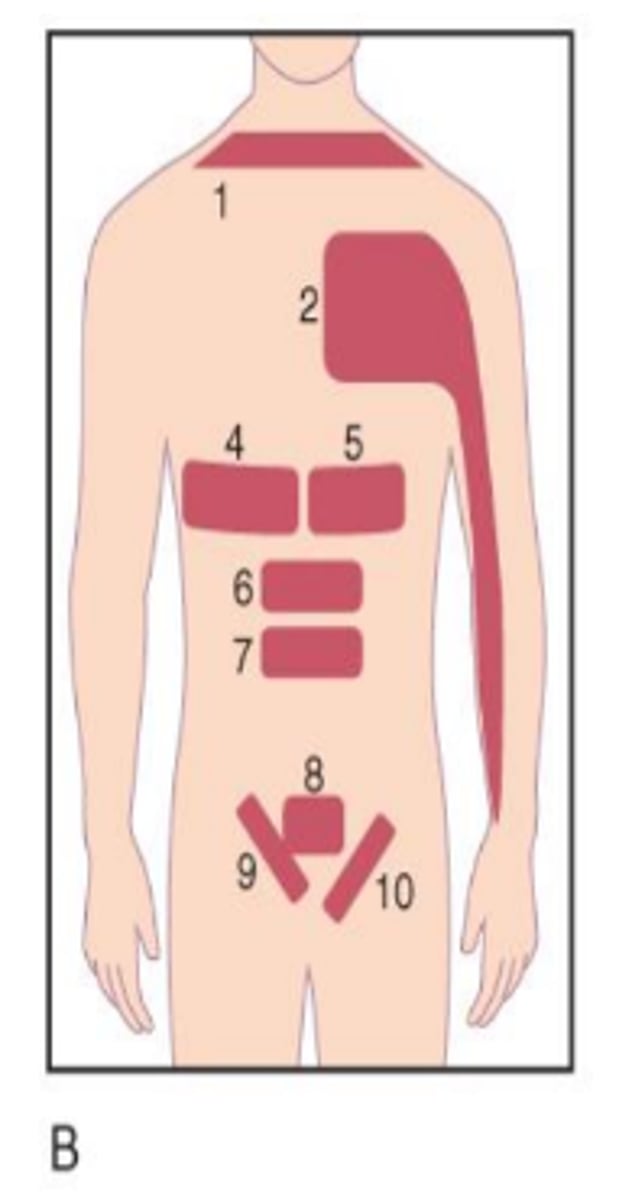
Stomach
Across left side of upper abdomen (5 in image).
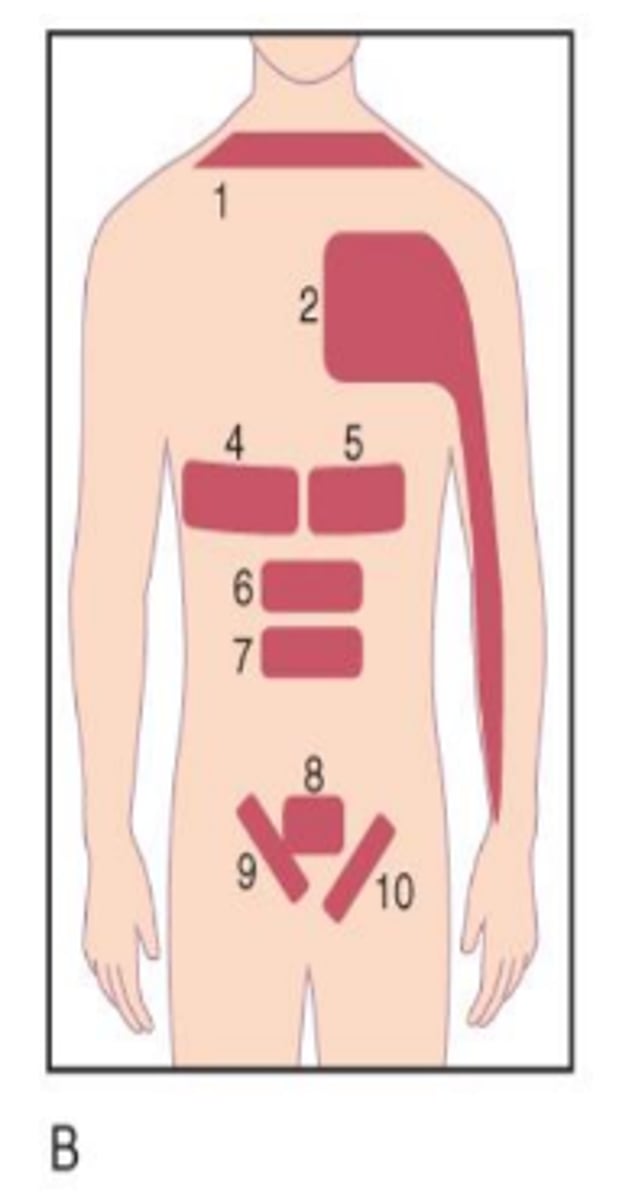
Liver
Across right side of upper abdomen (4 in image).
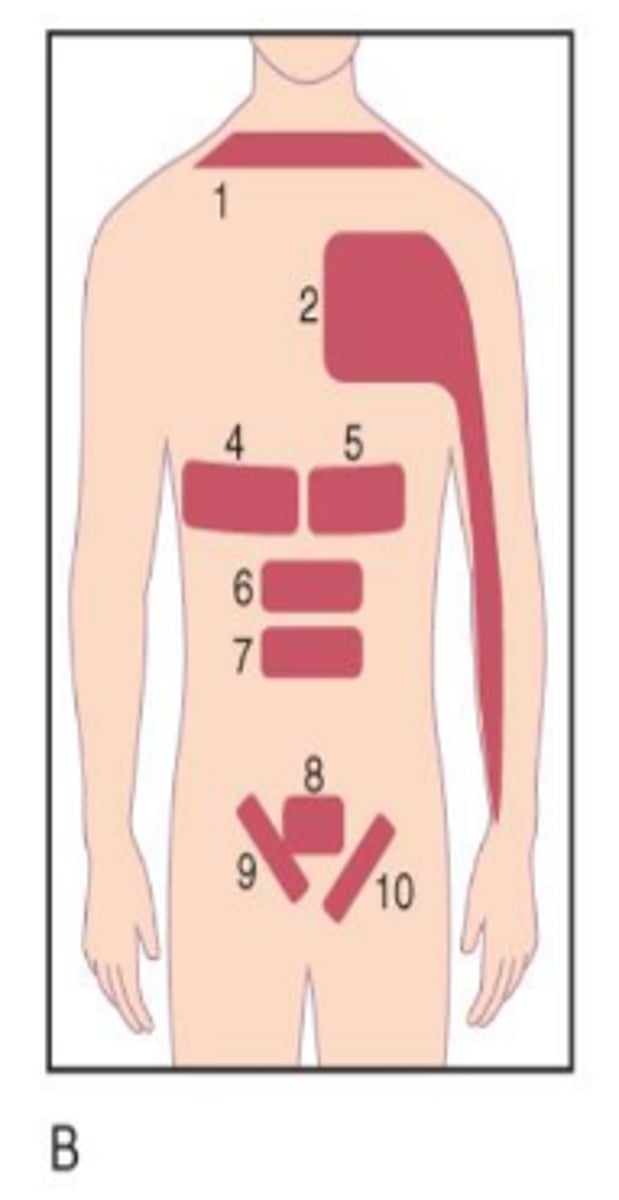
Gallbladder
Across right side of lower back (11 in image).
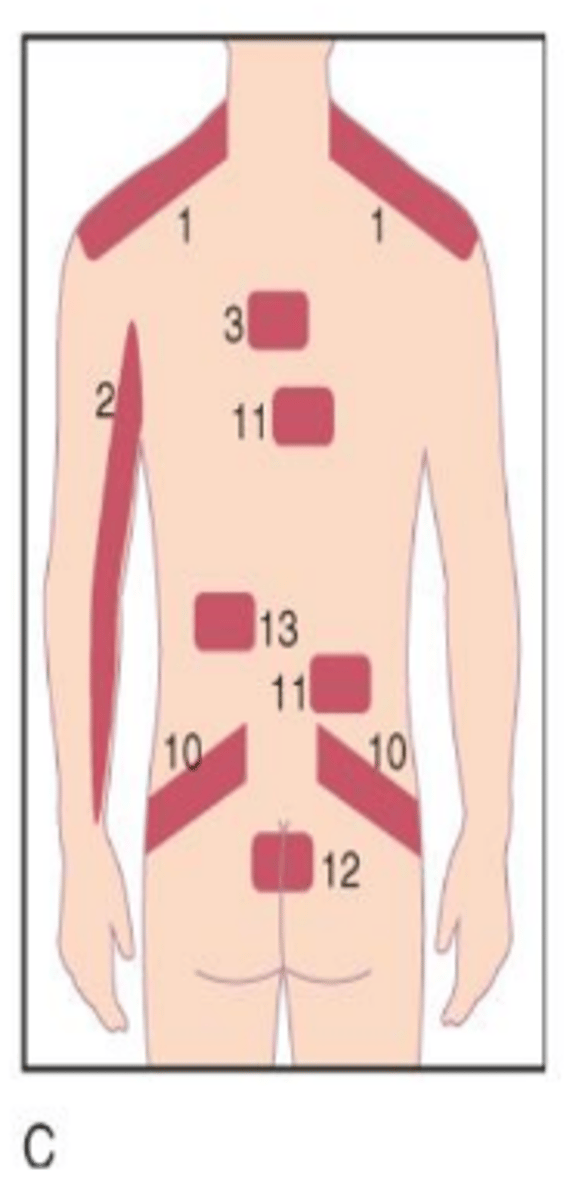
Kidney
Across left and/or right side of lower back into hip(s) (10 in image).
Medulla
Regulates essential functions (HR, RR, etc.).
Pons
Urinary and respiratory control.
Hypothalamus
Master controller of homeostasis; receives afferent autonomic info and exerts influence on nearly every body system and function (i.e., pituitary, spinal cord centers).
Limbic system
Receives information via thalamic relay and serves to link emotions with physiologic response.
Acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter is secreted by preganglionic fiber of sympathetic nervous system?
Norepinephrine
What neurotransmitter is secreted by postganglionic fiber of sympathetic nervous system?
Acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter is secreted by preganglionic fiber of parasympathetic nervous system?
Acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter is secreted by postganglionic fiber of parasympathetic nervous system?
Nicotinic; muscarinic
In PNS, acetylcholine uses _____________________ receptor. In CNS, acetylcholine uses _____________________ receptor.
Superior cervical ganglion
Innervates dilator muscles of pupil, nasal and salivary glands, facial arteries, elevator muscles of upper eyelid.
Middle cervical ganglion
Innervates heart, upper extremity.
Stellate ganglion
Innervates heart, aorta, upper extremity.
C8-T2
What is location of superior cervical ganglion, middle cervical ganglion, and stellate ganglion?
Paravertebral ganglion
Innervates trachea, heart, lungs.
T1-T5
What is location of paravertebral ganglion?
Celiac ganglion
Innervates esophagus → duodenum, spleen, liver.
Aorticorenal ganglion
Innervates kidneys.
Superior mesenteric ganglion
Innervates small intestine → proximal 2/3 of transverse colon.
Inferior mesenteric ganglion
Innervates distal 1/3 of transverse colon, bladder, and reproductive organs.
T5-L2
What is location of celiac ganglion, aorticorenal ganglion, superior mesenteric ganglion, and inferior mesenteric ganglion?
Spinal cord
Innervation of adrenal gland (medulla) is a direct connection to ________________________, no synapse!
Epinephrine
Adrenal medulla kind of functions like a postganglionic neuron. Acetylcholine (released by sympathetic nervous system preganglionic neuron) stimulates adrenal medulla to release ______________________ into bloodstream, thus increasing basal metabolic rate.
"Fight or flight"
Describe the general function of the sympathetic nervous system.
Epinephrine; ↑; sweat gland; piloerection
Sympathetic Nervous System Action: Thermoregulation:
Slow: Adrenal medulla releases ___________________, _____________________ metabolic rate.
Fast: Sympathetic skin innervation controls blood vessel diameter, ____________________ secretion, and _______________________.
↑
↑ blood vessel diameter, ______________________ heart release.
Remove
Goosebumps try to _____________________ heat.
Vasoconstriction
Sympathetic Nervous System Action:
Skeletal muscle blood flow: Prevents pooling of blood via _____________________.
↑; ↑; ↑; bronchodilation; ↓; ↓; ↓; bladder
Sympathetic Nervous System Action:
Visceral regulation:
- Cardiac = _____________ heart rate, _____________ contraction strength, ______________ cardiac output
- Pulmonary = _____________________
- Gastrointestinal = _______________ blood flow, _______________ peristalsis, ________________ digestion
- Genitourinary = Stimulates orgasm, __________________, and rectal wall relaxation/internal sphincter contraction.
Dilate; elevate; salivary glands
Sympathetic Nervous System Action:
Head innervation:
- Serves to ____________________ the pupil and ___________________ the eyelid (levator palpabrae).
- Innervation to _____________________ → inhibits secretion of digestive saliva (creates different type that is dry, thick).
Edinger-Westphal nucleus
What is CN III's nucleus of origin?
Superior orbital fissure
What is CN III's cranial exit?
Ciliary ganglion
What peripheral ganglia is CN III associated with?
Short ciliary nerve
What peripheral nerve is CN III associated with?
Ciliary body, iris
What is target structure of CN III?
Lens; constriction
Parasympathetic function of CN III is to manipulate shape of ___________________ (convexity) through ciliary body and control pupil diameter for ___________________.
Superior salivatory nucleus
What is CN VII's nucleus of origin?
Internal acoustic meatus
What is CN VII's cranial exit?
Submandibular ganglion, pterygopalatine ganglion
What peripheral ganglia is CN VII associated with?
Maxillary nerve
What peripheral nerve is CN VII associated with?
Lacrimal gland, submandibular gland, sublingual gland
What is target structure of CN VII?
Tear production
Function of CN VII at lacrimal gland is _____________________.
Saliva production
Parasympathetic function of CN VII at submandibular and sublingual glands is _______________________ for digestion.
Inferior salivatory nucleus
What is CN IX's nucleus of origin?
Jugular foramen
What is CN IX's cranial exit?
Otic ganglion
What peripheral ganglia is CN IX associated with?
Auriculotemporal nerve
What peripheral nerve is CN IX associated with?
Parotid gland
What is target structure of CN IX?
Saliva production
Parasympathetic function of CN IX at parotid gland is _______________________ for digestion.
Dorsal motor nucleus
What is CN X's nucleus of origin?
Jugular foramen
What is CN X's cranial exit?
Thoracic ganglion, abdominal ganglion, cardiac ganglion, etc.
What peripheral ganglia is CN X associated with?
Dorsal motor branches
What peripheral nerve is CN X associated with?
Lung, heart, digestive system, etc.
What is target organ of CN X?
Constriction
Parasympathetic function of CN X at lung is bronchiole ______________________.
↓; strength
Parasympathetic function of CN X at heart is to ___________________ heart rate and _____________________ of contraction.
Peristalsis; enzymes
Parasympathetic function of CN X on digestive system is to ↑ ____________________ and facilitate release of ____________________.
Glycogen; secretion; contraction
Describe the target structures and function of S2-S4 parasympathetic postganglionic fibers.
Gastrointestinal and genitourinary components of the S2-S4 (pelvic splanchnic nerves) function to increase peristalsis, ___________________ synthesis, and glandular ____________________, facilitate genital erection, and bladder/rectal _____________________.
"Rest and digest"
Describe the general role of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
Thoracolumbar cord (T1-L2)
What is location of preganglionic cell body in sympathetic nervous system?
Short
Is preganglionic axon of sympathetic nervous system short or long?
Acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter does preganglionic axon of sympathetic nervous system secrete?
- Paravertebral ganglia
- Prevertebral ganglia
- Superior cervical ganglion
- Middle cervical ganglion
- Stellate ganglion
What is location of postganglionic cell body in sympathetic nervous system?
Long
Is postganglionic axon of sympathetic nervous system short or long?
Norepinephrine
What neurotransmitter does postganglionic axon of sympathetic nervous system secrete?
Brainstem nuclei, sacral cord (S2-S4)
What is location of preganglionic cell body in parasympathetic nervous system?
Long
Is preganglionic axon of parasympathetic nervous system short or long?
Acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter does preganglionic axon of parasympathetic nervous system secrete?
- Ciliary ganglion
- Pterygopalatine ganglion
- Submandibular ganglion
- Otic ganglion
- Cardiac, pharyngeal, thoracoabdominal ganglia
What is location of postganglionic cell body in parasympathetic nervous system?
Short
Is postganglionic axon of parasympathetic nervous system short or long?