Plant Taxonomy: Angiosperms: Flowers
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
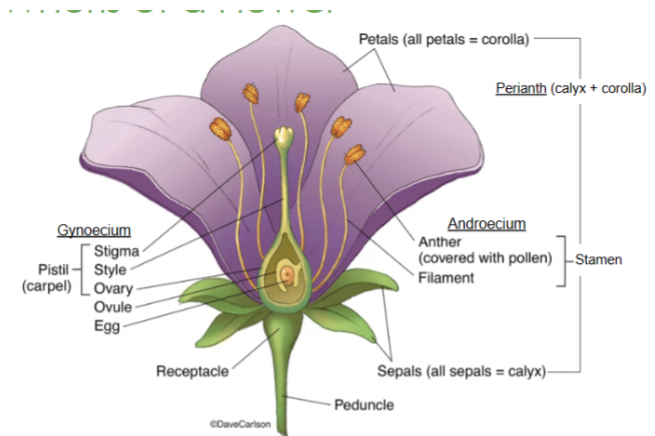
Calyx
The lowest whorl of the flower, made up of sepals
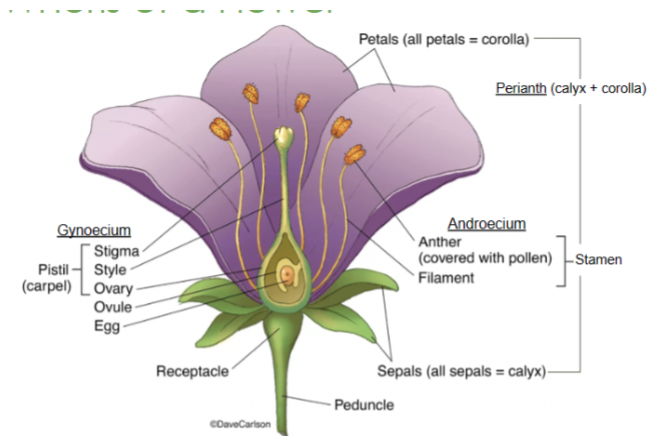
Corolla
All of the petals
If the petals and sepals look the same, they’re called tepals
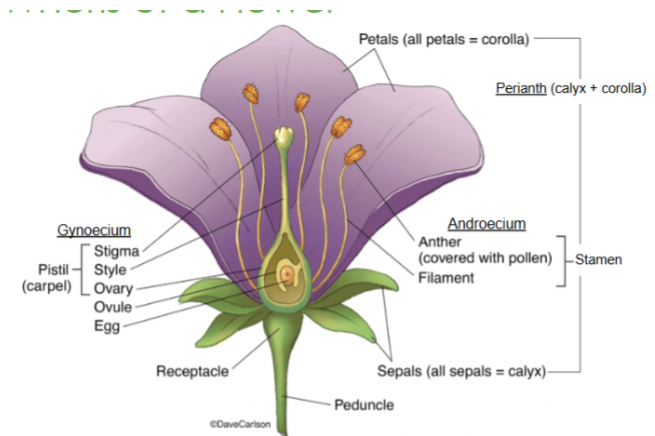
Androecium
All of the male parts, or stamens
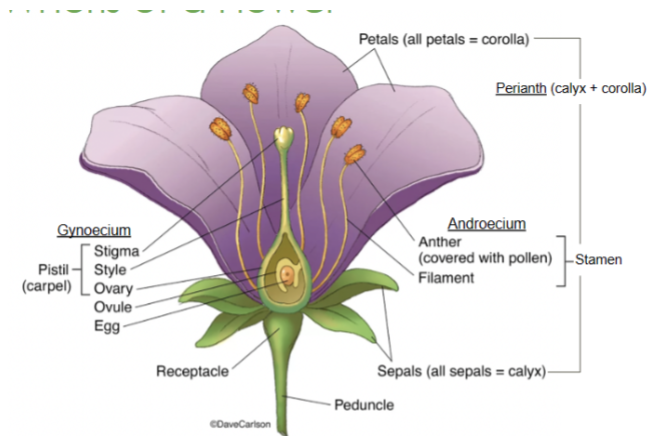
Gynoecium
All of the female parts, or pistil/carpel(s)
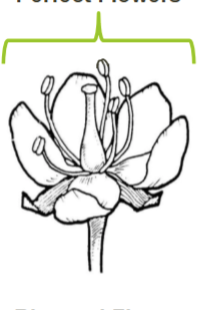
Perfect flower
Has both male (anthers) and female (pistils/carpels) parts
Plants with perfect flowers are always monoecious
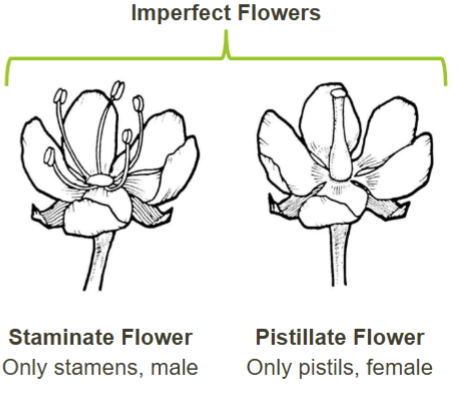
Imperfect flower
Has male or female parts, not both
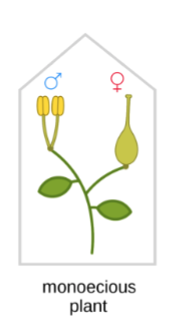
Monoecious plants
Can have either perfect flowers, or both types of imperfect flowers on one plant
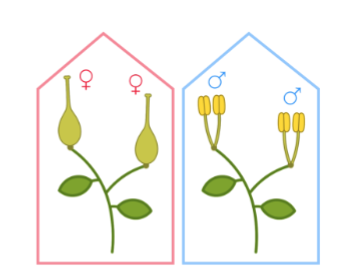
Dioecious plants
Only have imperfect flowers, with different plants holding different types of imperfect flowers
They cannot have perfect flowers and still be dioecious
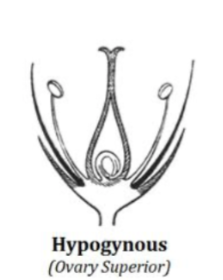
Hypogynous
The corolla, calyx, and androecium originate below the gynoecium
Ovary superior

Perigynous
The corolla, calyx, and androecium are attached to a hypanthium surrounding, but not attached to, the ovary
Ovary half-inferior
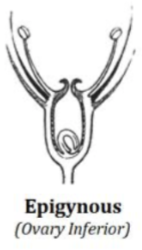
Epigynous
The corolla, calyx, and androecium are attached to the top of the ovary
Ovary inferior
Hypanthium
A cup or strap of tissue the rim of which the corolla, calyx, and androecium are attached to
It usually surrounds or encloses the ovary
Adnate
Fusion of different types of flower parts

Connate
Fusion of the same flower parts
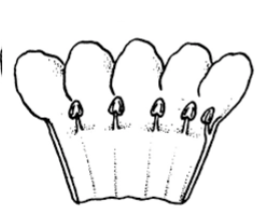
Sympetalous petals
Petals that are fused together
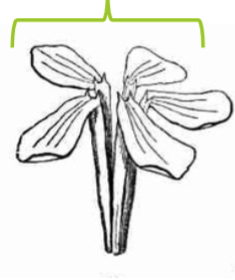
Polypetalous petals
Petals that are completely separate from each other
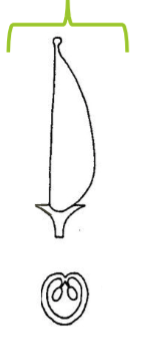
Monocarpous
One carpel on its own
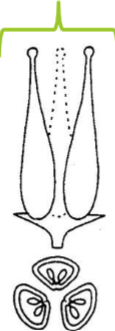
Apocarpous
Multiple unfused carpels
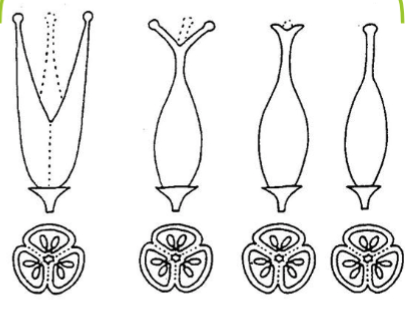
Syncarpous
Multiple fused carpels
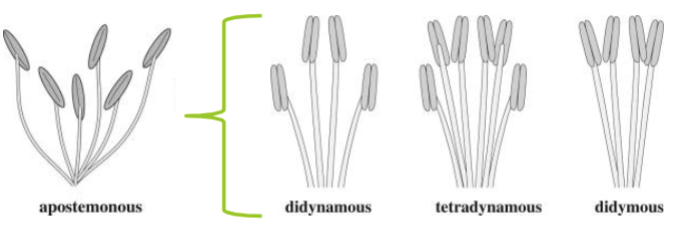
Apostemonous
Unfused stamens
Didynamous, tetradynamous, didymous
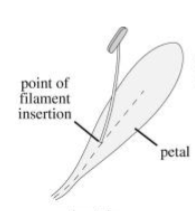
Epipetalous
A stamen fused to a petal
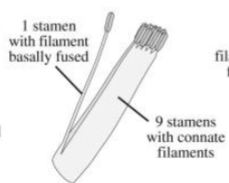
Diadelphous
9 stamens with fused filaments and one stamen basally fused
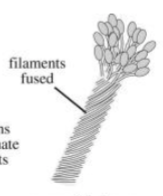
Monadelphous
All stamens with filaments fused
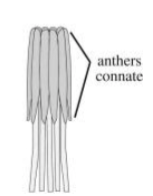
Syngenesious
Multiple stamens with anthers connate
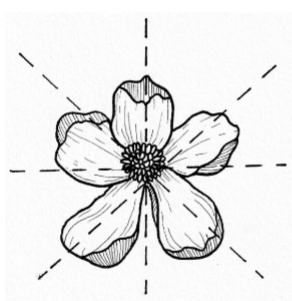
Actinomorphic
Multiple lines of symmetry
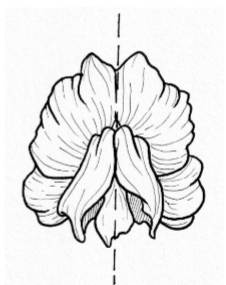
Zygomorphic
One line of symmetry

Sepals
The lowest whorl on a flower
Collectively called the calyx

Petals
The second whorl on a flower
Collectively called the corolla

Tepals
Collective term for identical sepals and petals
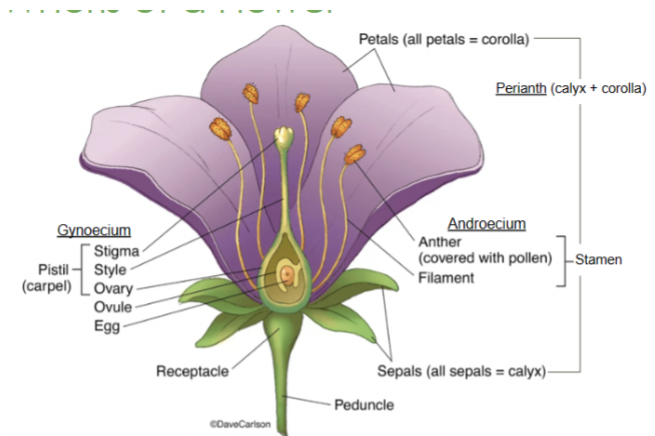
Receptacle
Part of the stem where the floral organs are attached
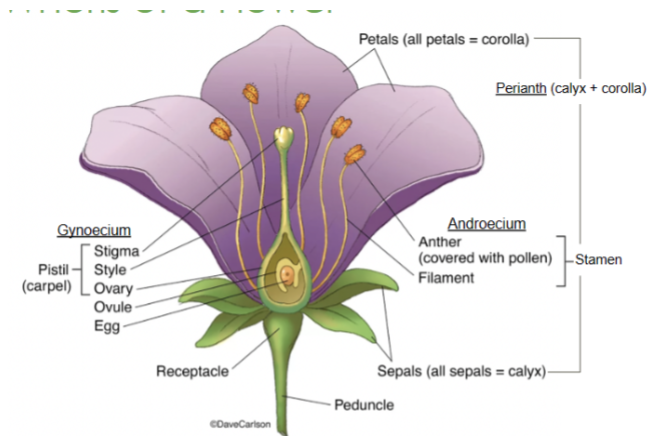
Anther
Part of the stamen that produces and releases pollen
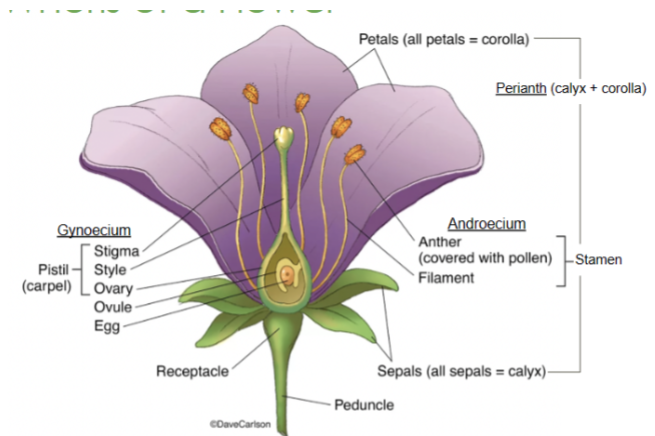
Style
Slender stalk in the pistil that connects the stigma to the ovary
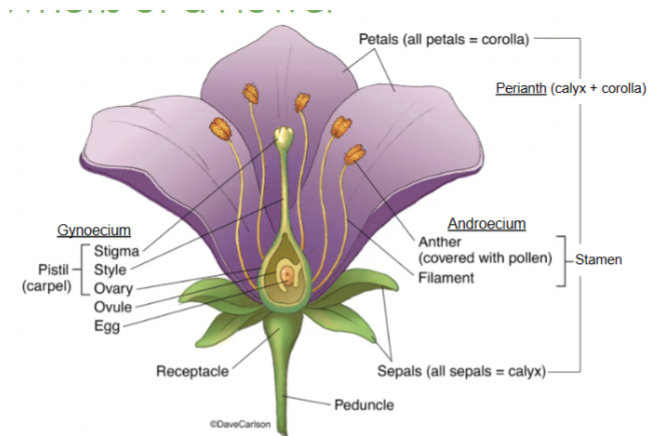
Ovary
Base of the pistil that contains ovules and develops into fruit after fertilization
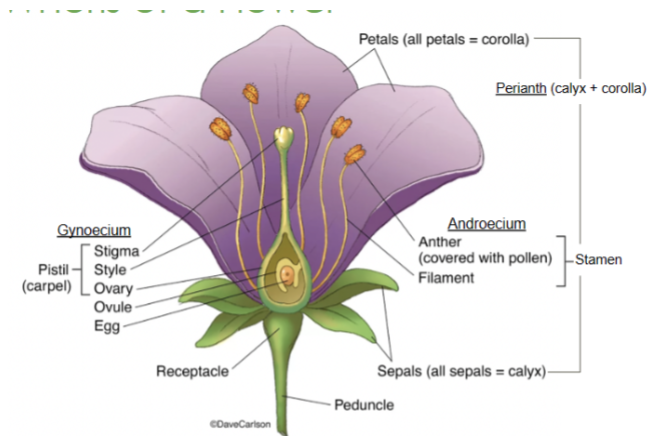
Stigma
The sticky tip of the pistil where pollen lands and begins germination
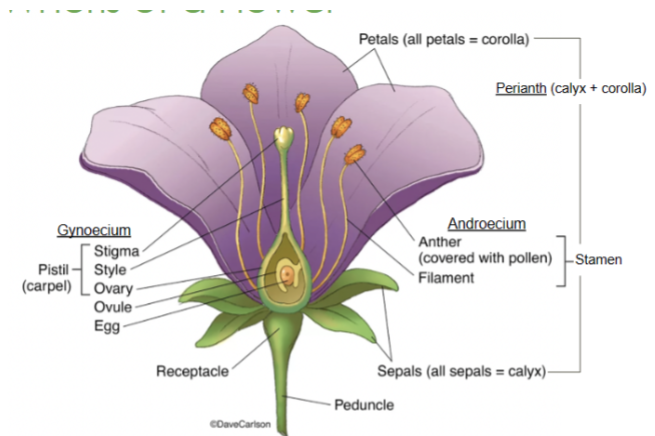
Filament
Stalk that supports the anther in the stamen
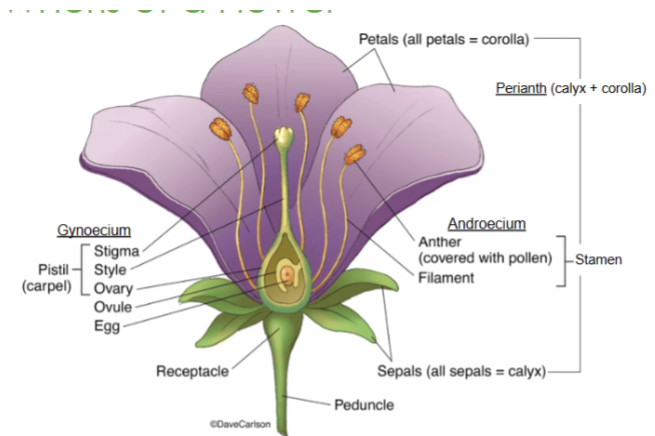
Perianth
Collective term for the petals and sepals of a flower