B9.3 Blood vessles
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the three blood vessles in a mammalian circulatory system?
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
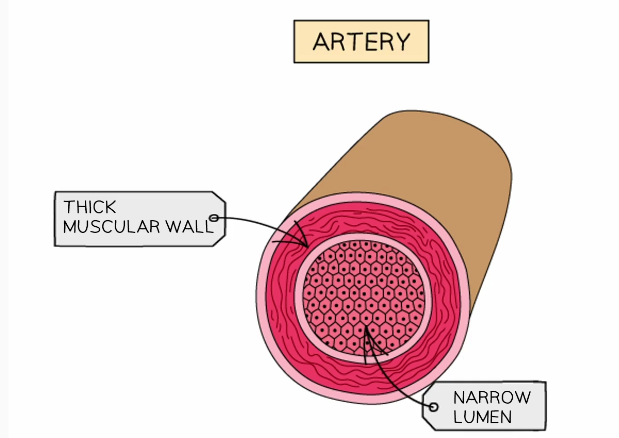
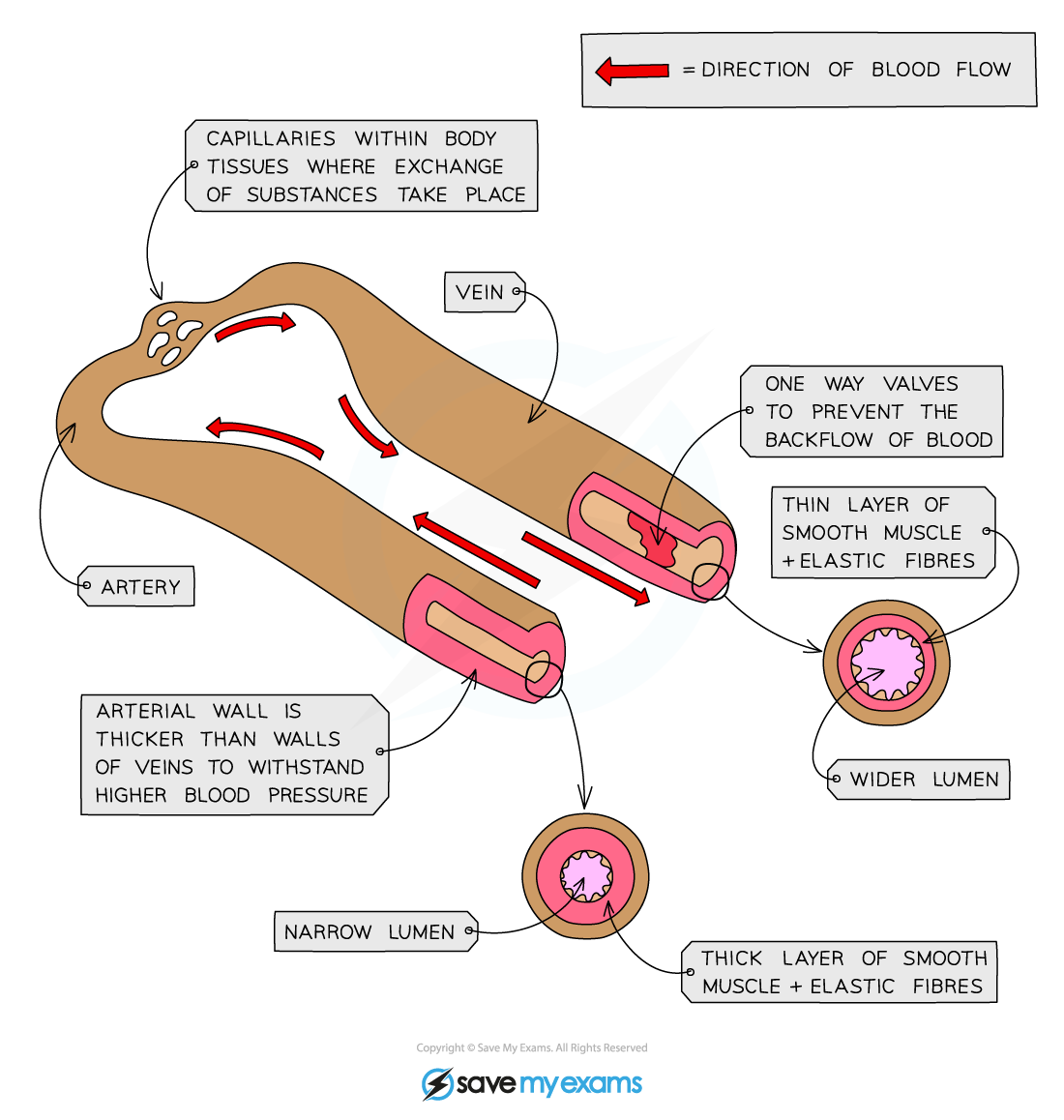
Describe the structure of an artery
Thick muscular walls containing elastic fiber
Narrow diameter of lumen
What is the sole artery that carries deoxygenated blood?
Pulmonary artery.
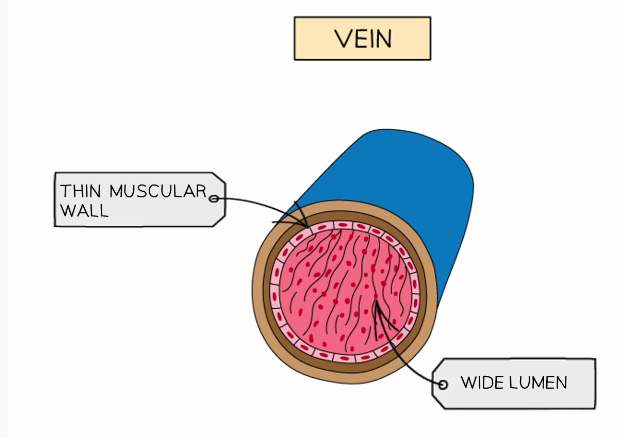
Describe the structure of a vein
Thinner layer of muscular wall containing elastic fiber
Wide diameter of lumen
Presence of valves
What is the sole vein that carries oxygenated blood?
Pulmonary vein.
What type of blood do cappilaries carry throughout the body?
Oxygenated from arteries to cells
Deoxygenated from cells to veins
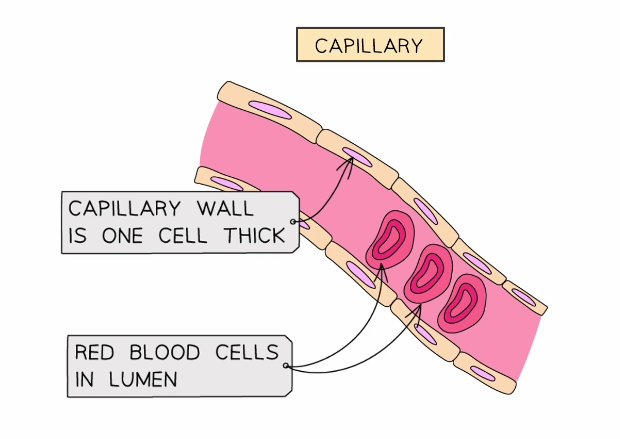
Describe the structure of capillaries
Very thin relative thickness, one cell thick & contain gaps
Do not contain muscle or elastic fiber layers
Very narrow diameter of lumen
What is the function of capillaries?
Deliver oxygen, glucose & nutrients to respiring cells
Collect & remove carbon dioxide and other waste products from respiring cells
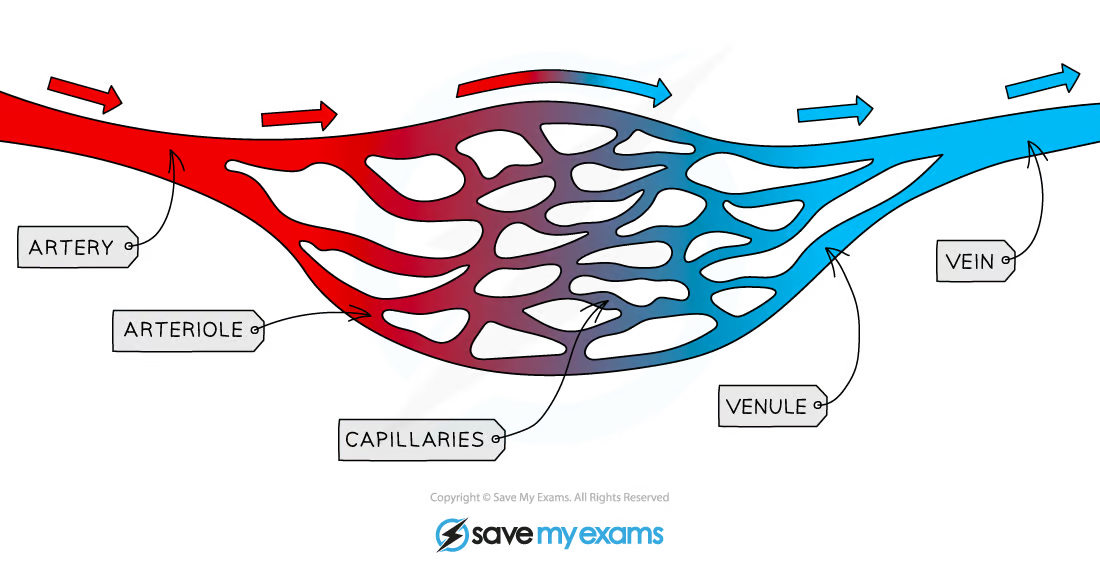
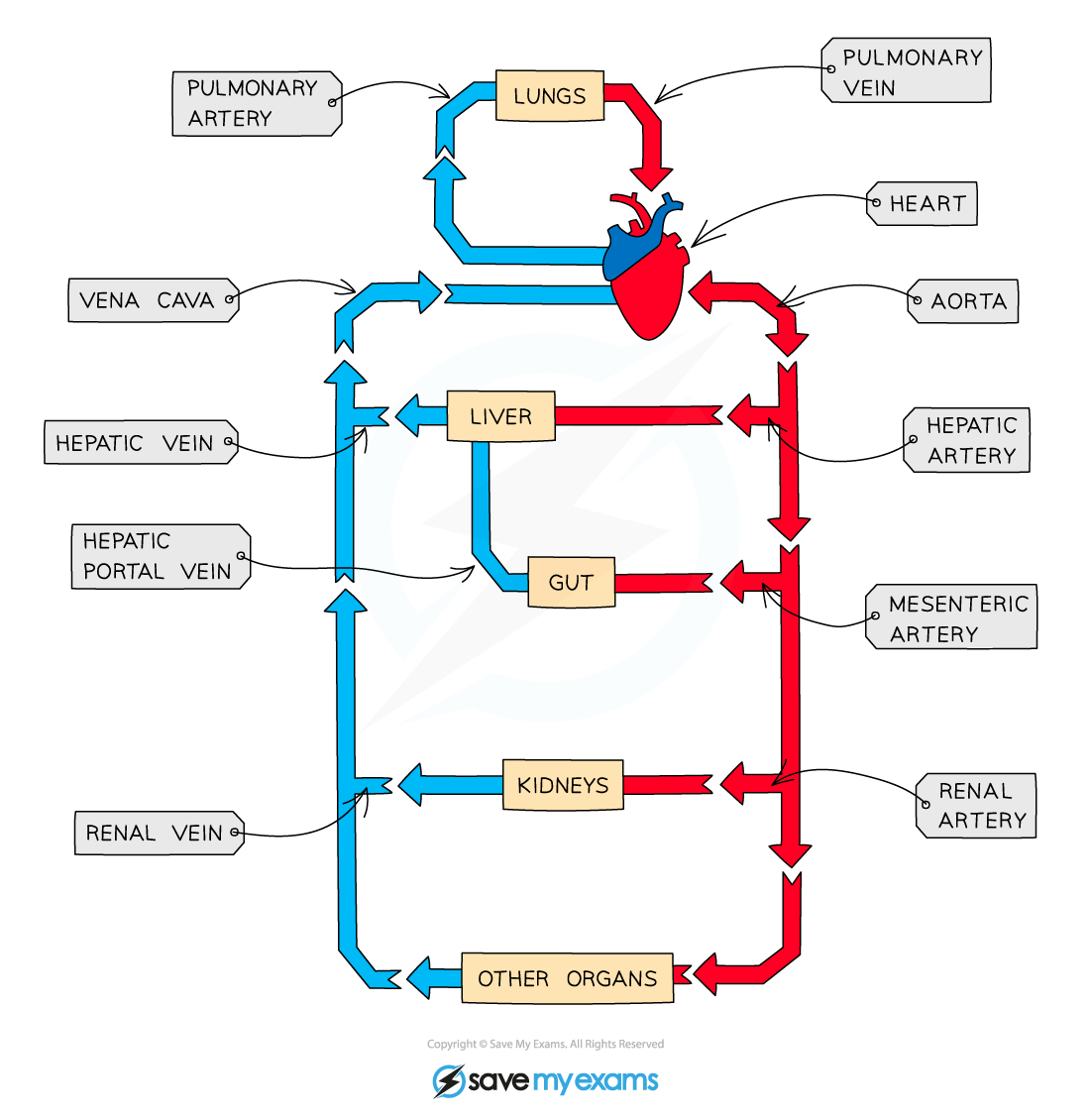
Describe the circulation of blood around the body in terms of the blood vessles
Blood is carried away from the heart and toward organs in arteries
These narrow to atrioles and to capillaries as they reach the target organs
The capillaries then widen to venules and finaly to vein before carring the blood back to the heart
What blood vessle carries blood into the right atrium?
Vena cava
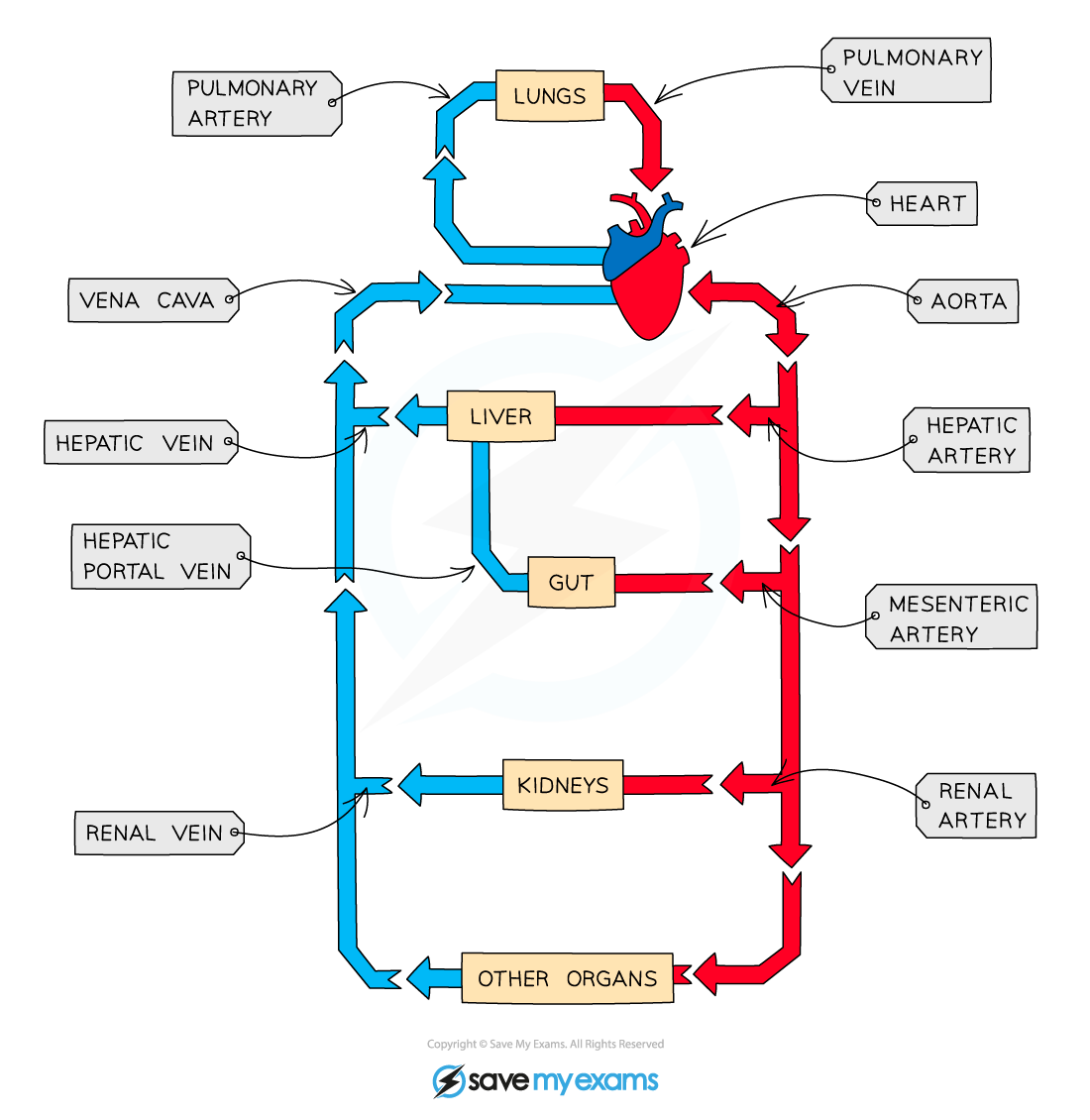
Which blood vessle carries blood away from the right ventricle?
Pulmonary artery
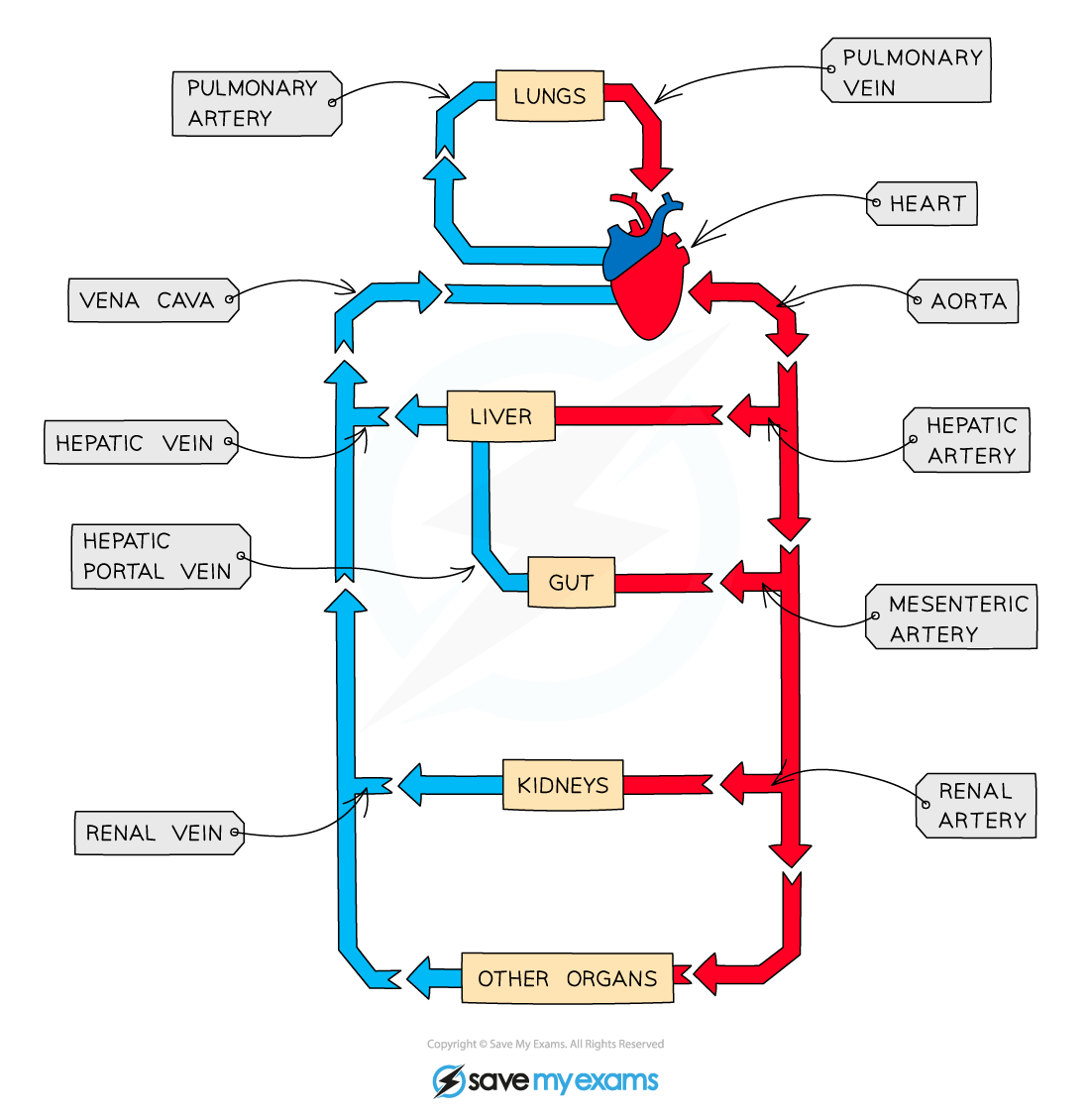
Which blood vessle carries blood into the left atrium?
Pulmonary vein
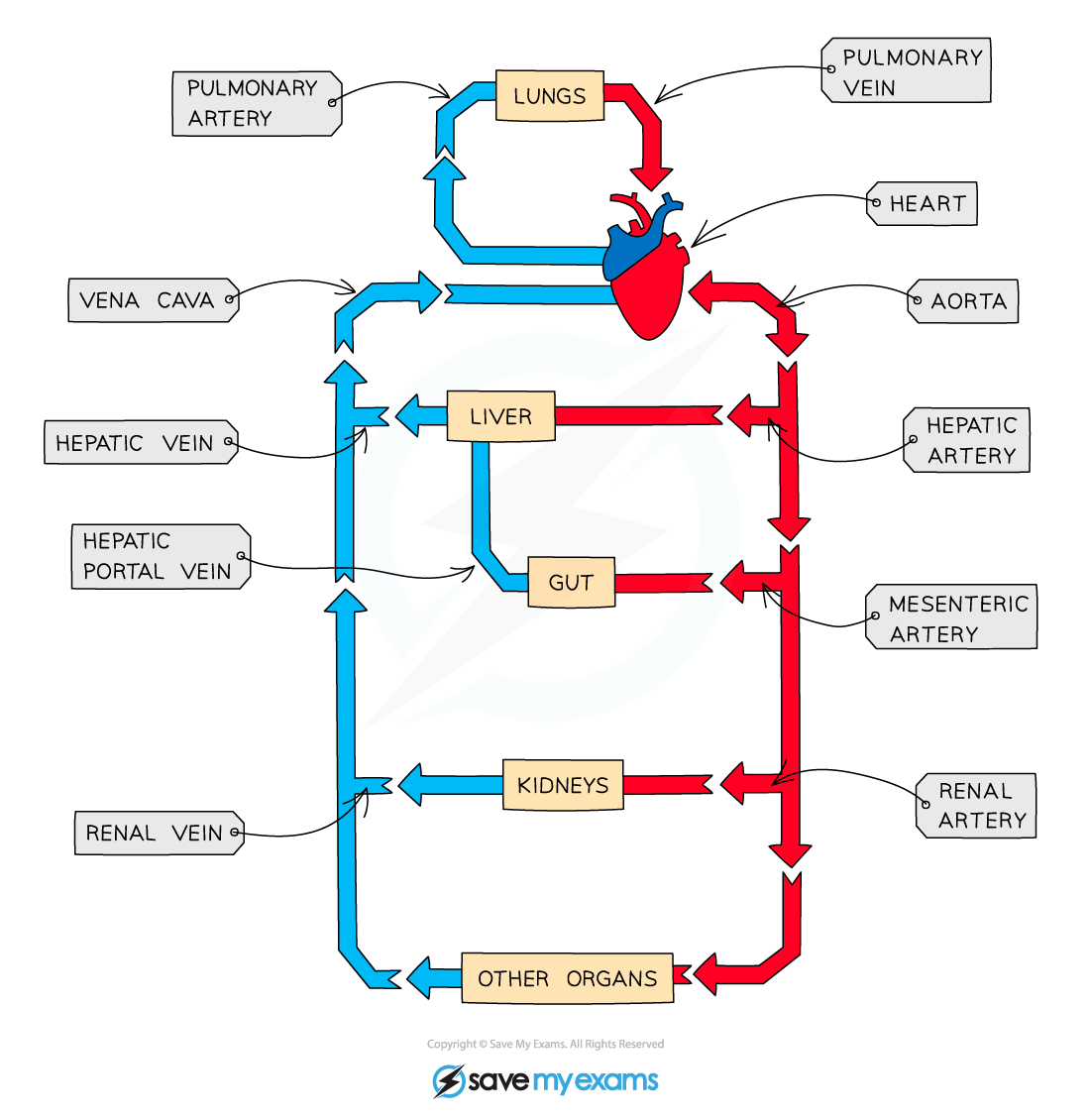
Which blood vessle carries blood away from the left ventricle?
Aorta
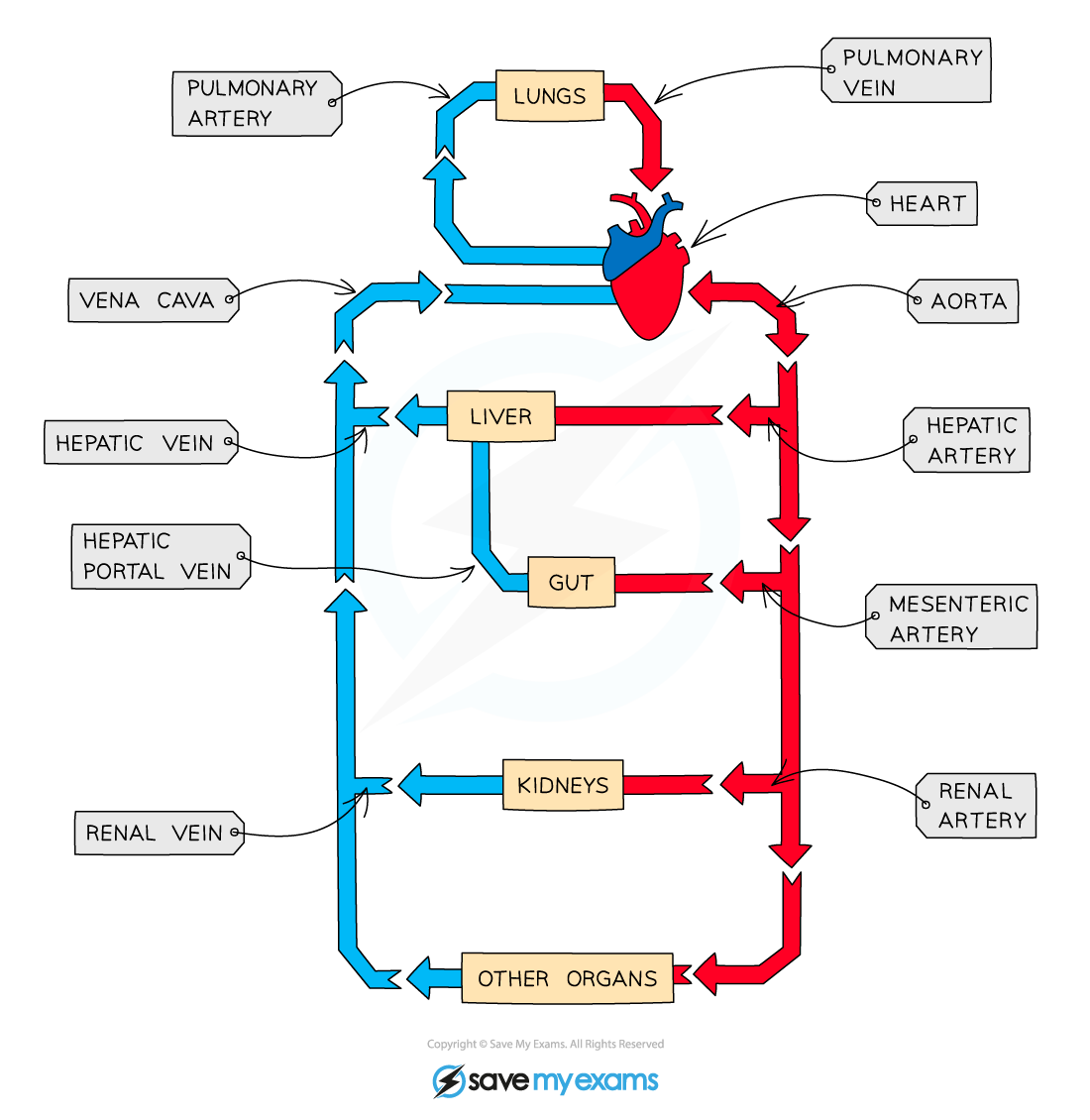
Which blood vessle carries blood toward the lungs?
Pulmonary artery
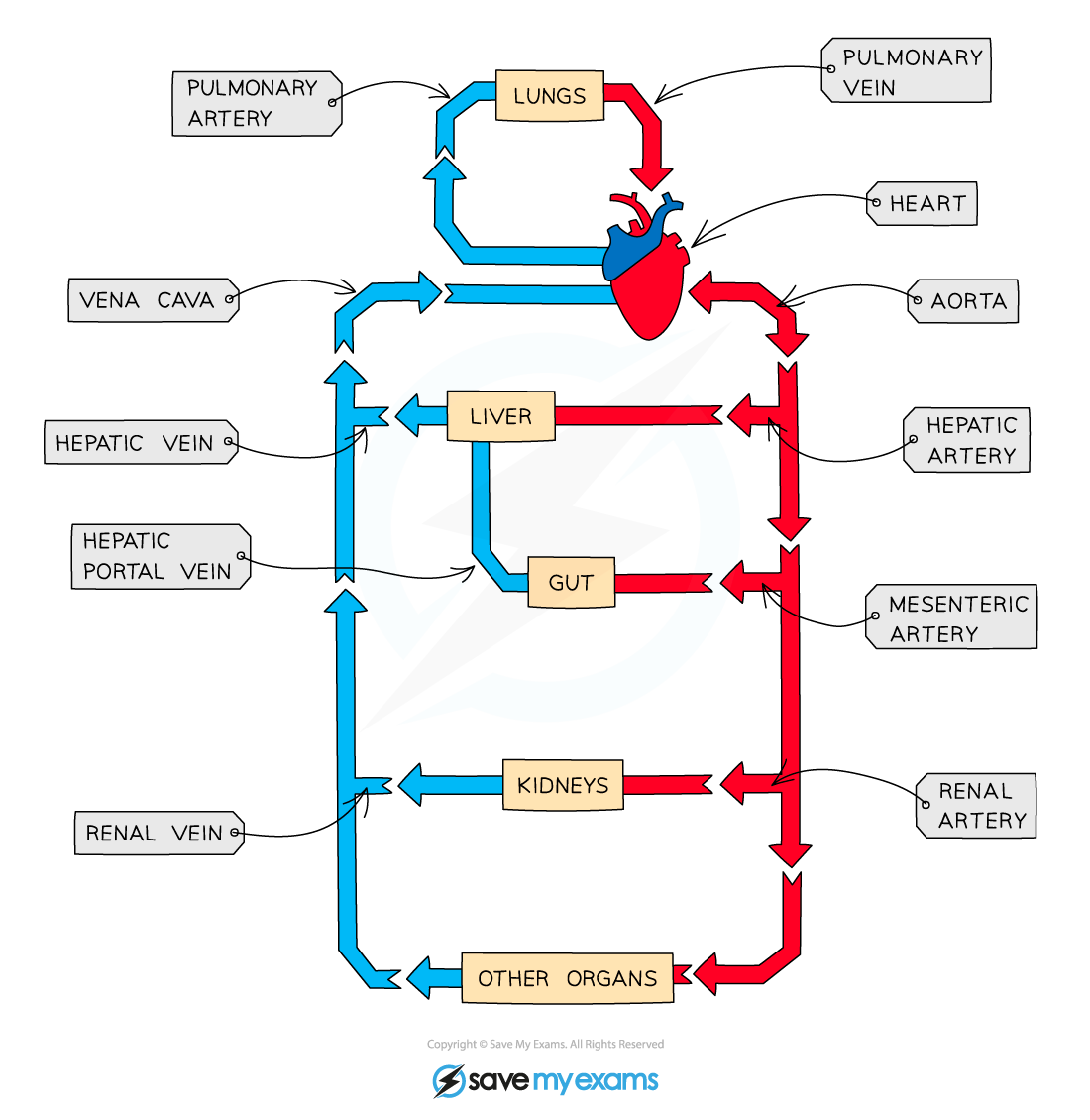
Which blood vessle carries blood away from the lungs?
Pulmonary vein
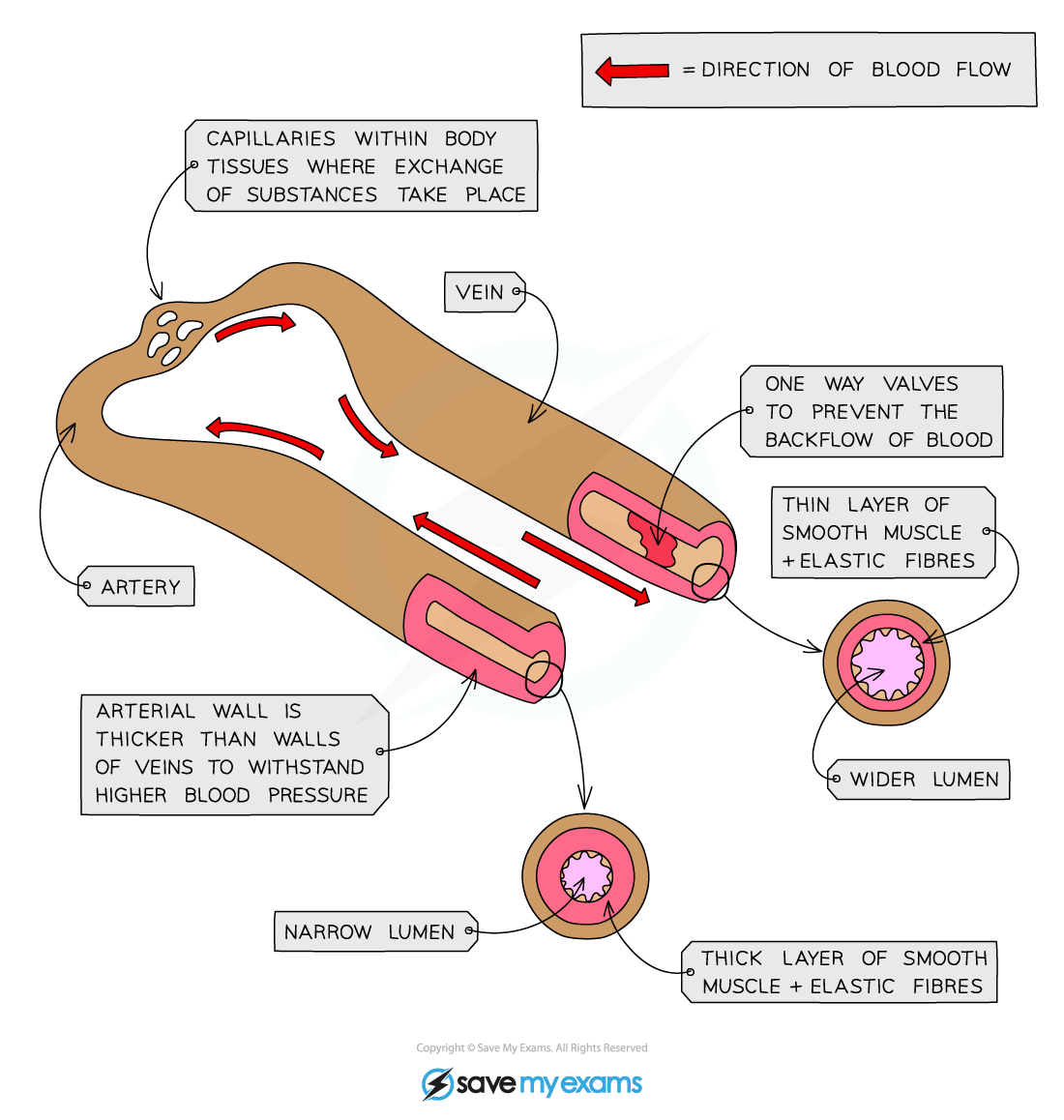
How does the structure of an artery relate to its function?
Thick arterial walls and elastic fiber:
Withstand & maintain high blood pressure enabling the vessle to stretch & recoil
Muscle changes lumen diameter:
Direct blood toward target organs
Maintain high blood pressure throughtout its length
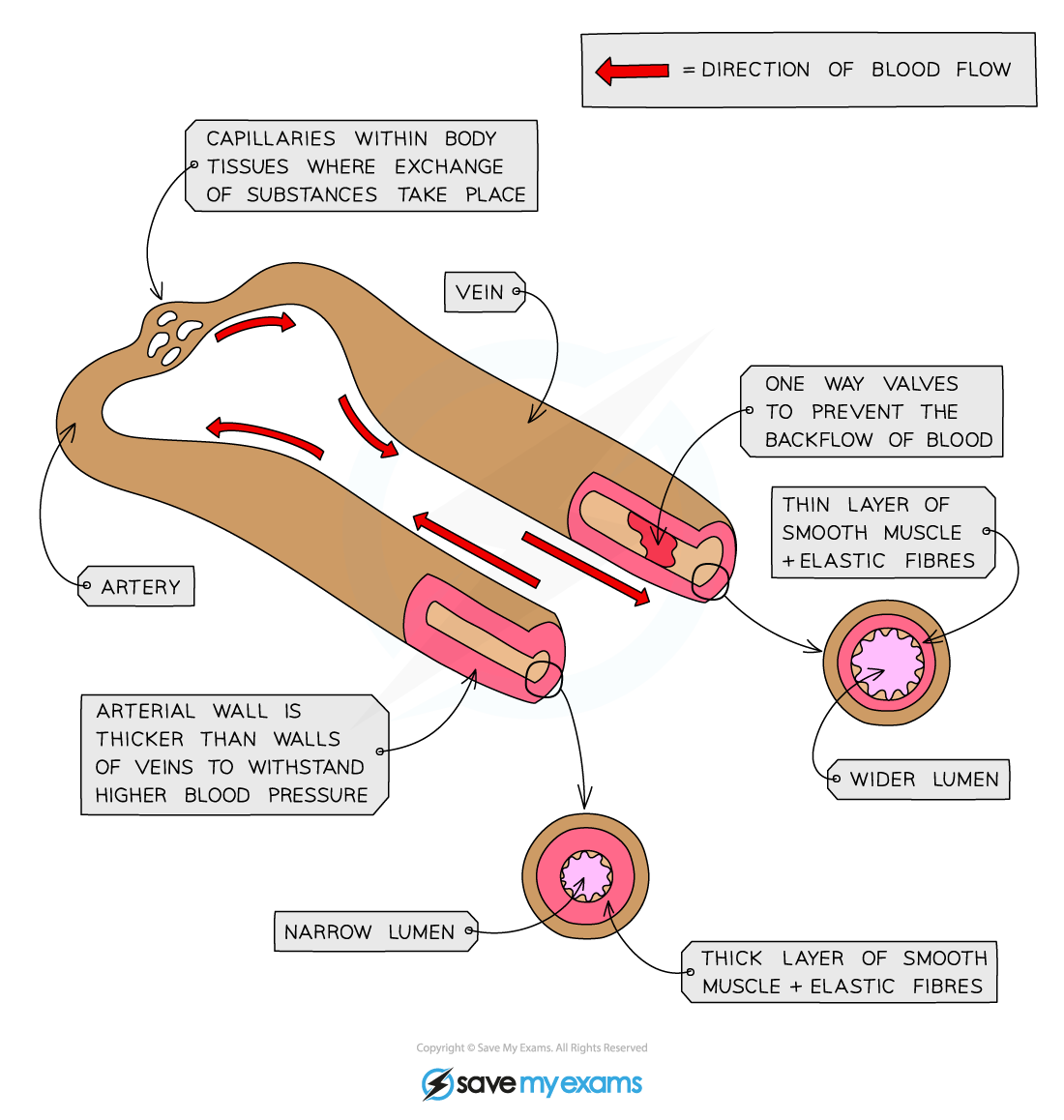
How does the structure of a vein relate to its function?
Large lumen diameter:
Less resistance to the low pressure
Thin muscular & elastic wall:
No need to withstand high pressure of blood
Presence of valves:
Prevent backlof of the low presure blood
How is the structure of a capillaty relate to its function?
One cell thick wall containing gaps:
Maximises rate of diffusion by decreasing distance
Blood plasma can leak out & form tissue fluid surrounding cells
Narrow lumen diameter:
Allow passage of one blood cell which gives time for the diffusion with respiring tissues
Name the narrow vessle that connects arteries to capillaries
Atrioles
Name the narrow vessle that connects capillaries to veins
Venules