Extraction Lab (Midterm)
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
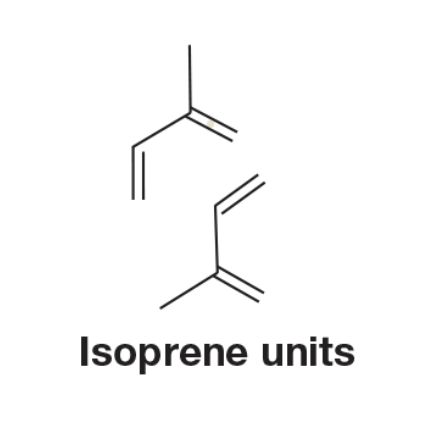
Terpenes are a general class of compounds which are composed from units of ___. Often in multiples of 5.
Isoprene
In steam distillation, the volatile oils distill along with the water and separate as they ___ back into the liquid phase.
Condense
More benign approach of extraction is the ues of liquid carbon dioxide or super critical carbon dioxide. Super critical fluid is a form of matter that is neither__ or ___ but __.
Liquid or gas, but has properties of both.
Liquid-liquid two-phase extraction involves partitioning compounds between ___. The classic two phases are __ and __.
Immiscible liquid phases (mutually insoluble). Aqueous and organic.
A variant of liquid-liquid extraction is the separation of different functional groups: __ can react with acids to form a salt, separating into the __. Then you can use an aqueous workup to reform the base.
Bases. Aqueous phase.
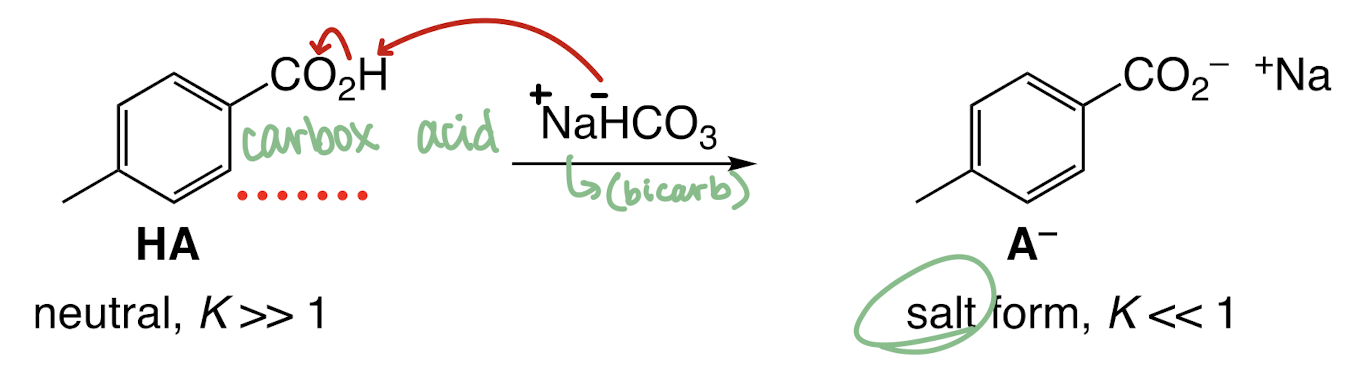
__ was converted to a salt by aqueous sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
p-toluic acid
p-toluic acid was converted into a salt by __ or __.
Aqueous sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) or Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
__ is converted into a salt by aqueous NaOH but NOT NaHCO3.
p-tert-butylphenol
p-tert-butylphenol is converted into a salt by __ but NOT __.
aqueous NaOH but NOT NaHCO3.
Acetanilide is a __ __ __ that __ be converted to a salt in aqueous solution.
Neutral functional group, cannot be converted
Using sequential extraction with __ then __, one can separate the three component organic mixture.
Aqueous NaHCO3, then aqueous NaOH.
The liquid-liquid extraction depends on the __ __ of different compounds in the two liquid phases.
Different solubilities
An organic compounds in the presences of two immiscible solvents, like water and diethyl ether, will split in two phases: the __ __ are in the __ __ __ and the __ __ are in the __ __.
Organic compounds are in the diethyl ether phase and the ionic salts are in the aqueous phase.

This is a __ __. Two phases identified by compound density, but the aqueous layers are usually __ than organic layers.
Separatory funnel. Denser.
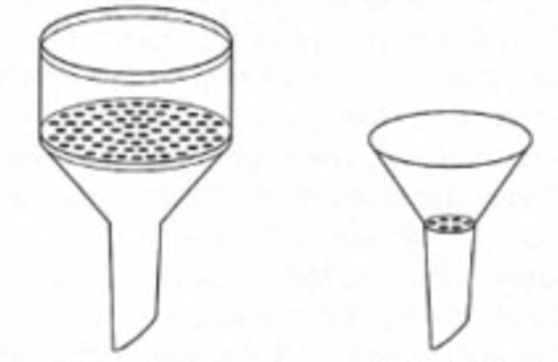
The big one is a __ __ and the small one is a __ __.
Buchner funnel. Hirsch funnel.
Buchner and Hirsch funnels are used for __ __ to separate the solid from __ __.
Vacuum filtration. Undesirable liquid
Recrystallization __ an organic solvent. The crystals grow into molecules in __ __ __ __ __.
Purifies. Tightly packed repeating lattice structure.
The desired organic solid is in a liquid mixture, __ __ by __ __ (ice bath) induces crystallization.
Lowering solubility by decreasing temperature
For gas chromatography, a mobile phase (an __ __) passes through the column at a controlled flow rate, and the injected samples are carried by the __ __ and __ as they emerge from the outlet.
Inert gas. Mobile phase and detected.
Compounds travel through the column at __ __ because they exist in equilibrium between the stationary and mobile phases, with different equilibrium constants for each compound.
Different rates
Compounds that stick more strongly with the __ __ __ take __ to get through the column.
Liquid stationary phase take longer
__ __ is the most important property for separation with GC.
Boiling point
__ __ molecules will come out of the GC __ if the compounds’ boiling points are similar.
Less polar. First.
A __ of p-toluic acid formed.
Precipitate.
Essential oil and Terpene features:
Produced via biosynthesis by plants and animals in nature. Attractive or defensive secretions. Valued for medicinal properties, flavors, fragrance.
Citrus oils are primarily which terpenes?
(R)(+) limonene / D-limonene
Disadvantages of steam distillation:
Essential oil is vaporized with steam then condensed. Oxidation in moist air converts limonene to carvone / limonene to terpinene. Heating with an acid converts limonene to terpinene. Energy intensive.
Disadvantages of pentane extraction:
Break up matric, mixes with pentane, filter insolubles, evaporate pentane. Volatile and flammable. Difficult to remove from products.
Four standard terpenes:
(R)(+) limonene. Myrcene. y-terpinene. (-) a-pinene.
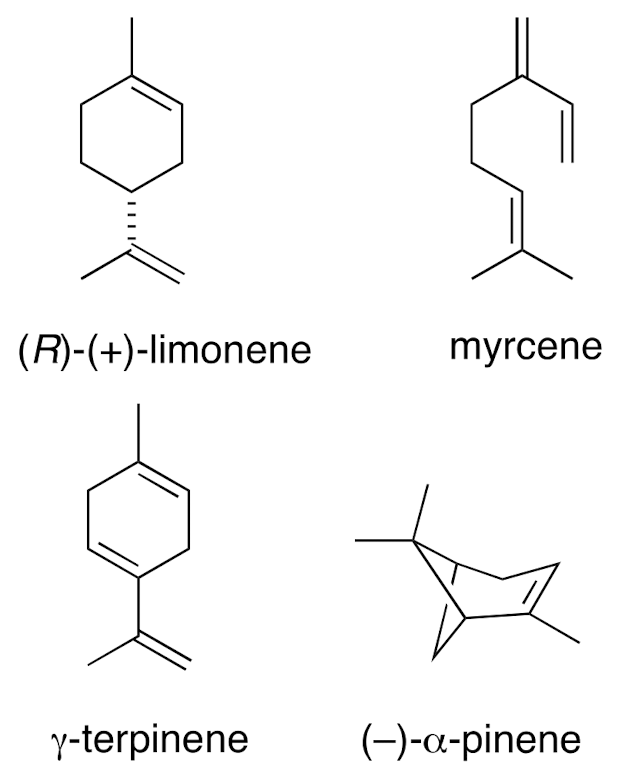
Liquid CO2 based on __ __ extractions of the terpenes.
Supercritical fluid.
Green Chemistry - Prevent Waste
To avoid producing waste, no need for treatment or cleanup.
Green Chemistry - Atom Economy
Incorporate all atoms from starting materials into products.
Green Chemistry - Low Toxicity
Design alternative processes/substances known to have lower toxicity.
Green Chemistry - Efficacy with low toxicity
Maintain function while lowering toxicity
Green Chemistry - Minimize Auxiliary Agents
Avoid solvents or separation agents whenever possible
Green Chemistry - Energy Efficiency
Minimize impacts by working at ambient temperature and pressure
Green Chemistry - Renewable Feedstocks
Avoid depleting natural resources whe able
Green Chemistry - Fewer Synthetic Steps
Avoid unnecessary derivatization (ie. adding protecting groups)
Green Chemistry - Catalytic Processes
Use of superior efficiency relative to stoichiometric
Green Chemistry - Innocuous after use
Avoid products which persist after use, and are unsafe after degradation
Green Chemistry - In-process monitoring
Control processes in real time, prior to formation of hazardous materials
Green Chemistry - Avoid accident prone materials
Avoid possibility of release, explosion, fire
Pentane replaced with __ in our extraction.
Liquid CO2
Why is supercritical CO2 better for extraction? (green chemistry)
Nonpolar organic solvent, nonflammable, readily available, nontoxic, able to be removed from product; recaptured and reused
Terpenes are __-__ organics that are __ in organic solvent, like pentane or liquid CO2.
Non-polar. Soluble.
Principle of Separations (extraction)
Break matrix, mix with liquid CO2, filter of insoluble materials (rest of peels), evaporate liquid CO2
Phases of CO2
Usually solid (dry ice) or gas. Above 5 atm = liquid. Above critical point = supercritical fluid
Cylinder use:
Protection in case the tube ruptures. Do not place anything above the cylinder with liquid CO2 present, contents under pressure.
Gas chromatography
Different compounds A and B travel through column, can associate with mobile and stationary phase in equilibrium process.
K value for gas chromatography
K = Astationary(liquid)/ Amobile(gas)
Gas chromatograph definition
Instrument used
Gas chromatogram definition
Plot of detector response (y-axis) versus time (x-axis), with peaks as a function of time
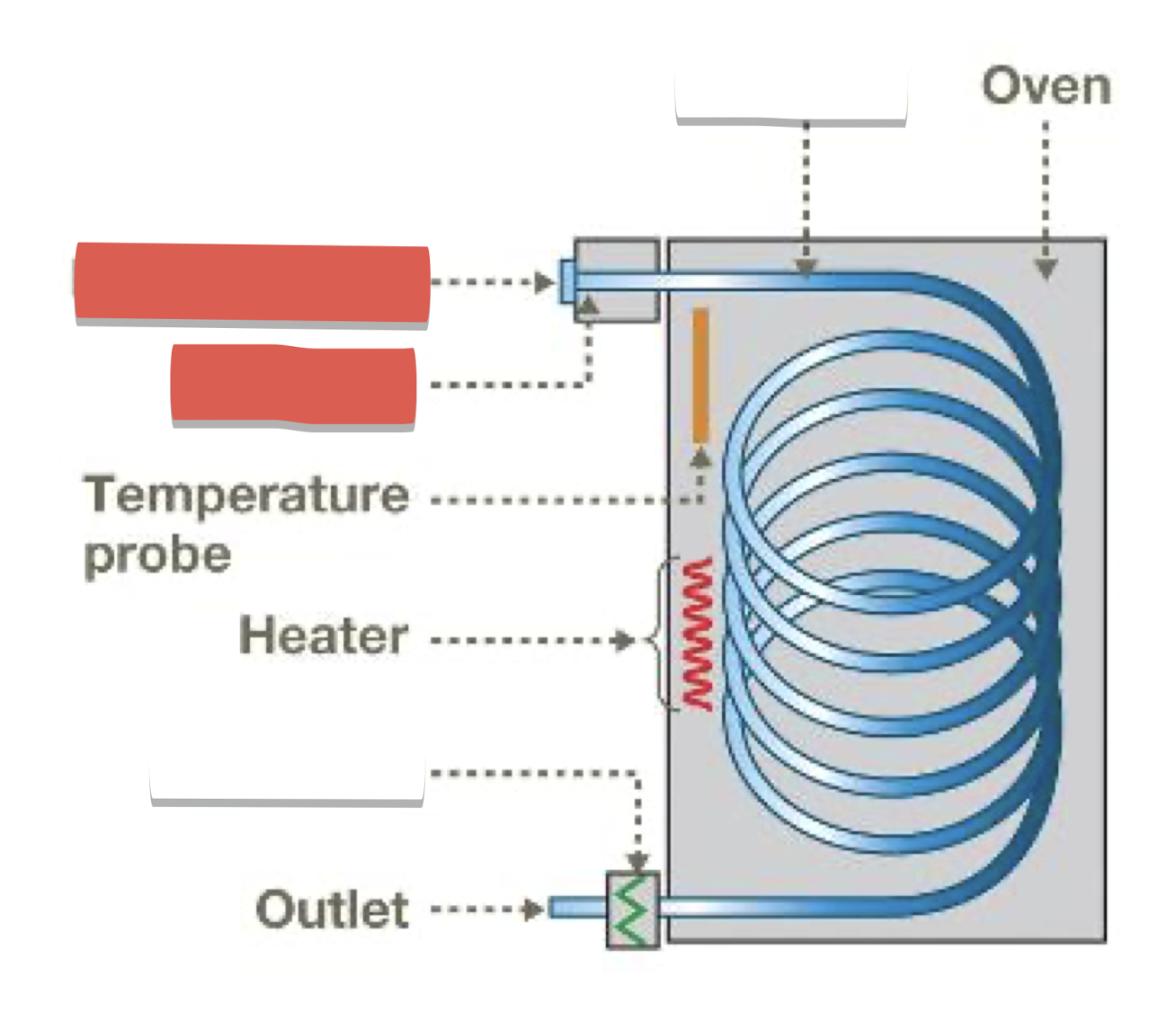
Injection port and gas inlet: introduce sample, vaporize, mix with carrier gas (He)
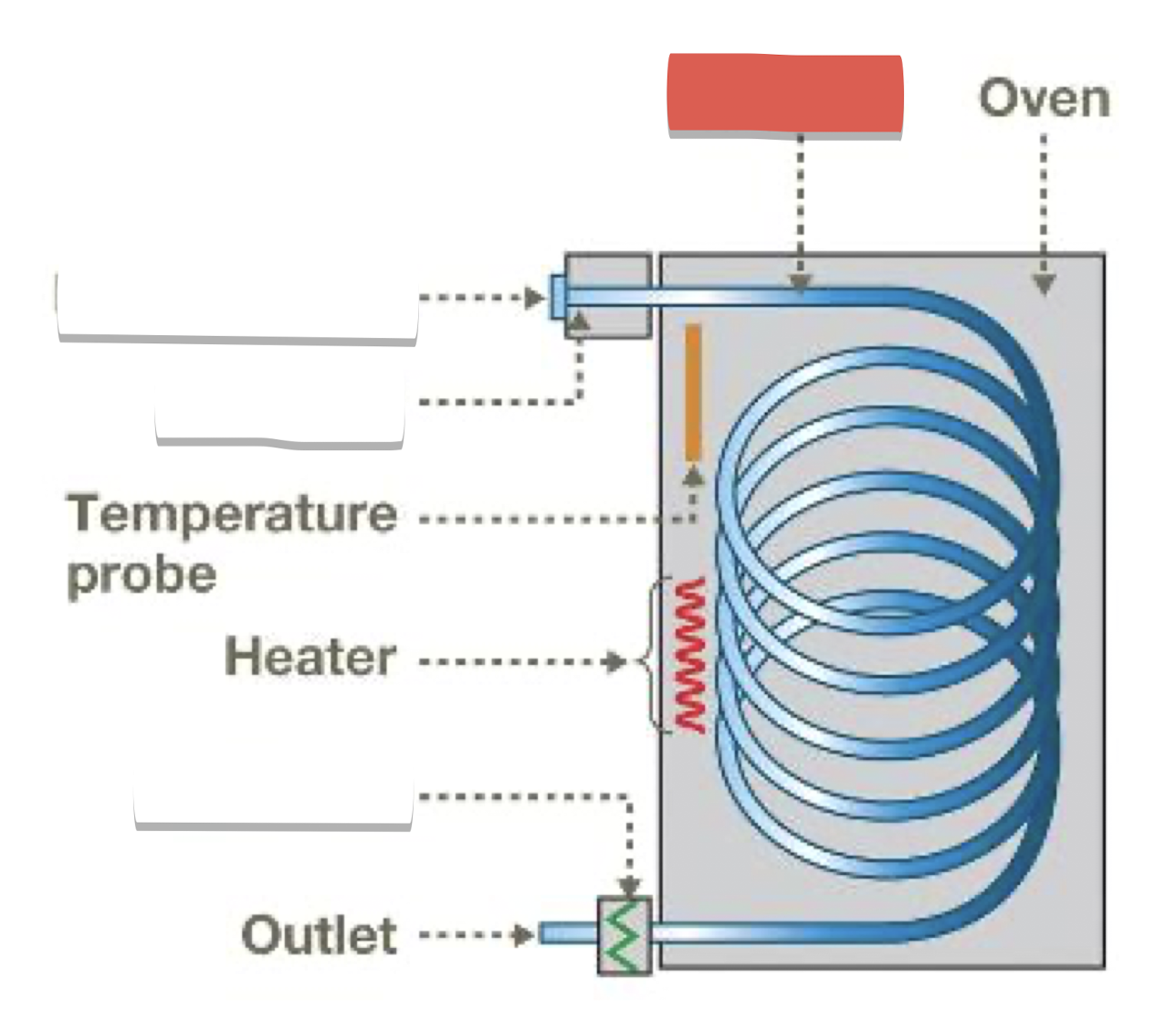
Column: where separation occurs, contains stationary phase (liquid attached to inert solid)
Detector: creates electronic signal when compounds emerge from column
Output chromatogram
Retention time (x-axis) can determine identity of compound by comparison with a known sample
Integration of chromatogram
Area under the peak = amount of compound present
Retention time
Time from injection point (t=0) to sample peak
Distribution coefficient (K) when liquid phases are immiscible
Concentration of X in organic solvent / concentration of X in aqueous solvent
Equation mechanism of part B (with sodium bicarbonate - NaHCO3)
Salt product in aqueous phase with NaHCO3
Mixture with p-toluic acid, p-tert-butylphenol, and acetanilide + aqueous NaHCO3
p-toluic acid salt in aqueous layer (NaHCO3), p-tert-butyl phenol and acetanilide in organic layer
p-toluic acid salt + HCl and vacuum filtrate
Neutral p-toluic acid precipitate
Organic layer with p-tert-butylphenol and acetanilide + aqueous NaOH
p-tert-butylphenol salt in aqueous layer (NaOH), liquid acetanilide in organic layer
p-tert-butylphenol salt + HCl and vacuum filtration
Neutral p-tert-butylphenol solid
Organic layer with liquid acetanilide + MgSO4 and rotovap
Water removed from solution, rotovap removes solvent; solid organic acetanilide
Incorrectly labeled samples from acid-base extraction Lab 2, how can they be identified?
Solubility in NaHCO3 and NaOH. Melting point. Smell (NO). IR spec. NMR (BEST)