Chapter 17: Special Senses from Human Anatomy Sixth Edition
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to the special senses as outlined in Chapter 17 of the Human Anatomy textbook.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
General Senses (Somatosensory)
Refers to the senses that perceive general stimuli from the body, including pain, temperature, touch, and pressure.
somatosensory
system responsible for processing sensory information from the skin and musculoskeletal system, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Free nerve endings
warm receptors
cold receptors
Nociceptor (pain)
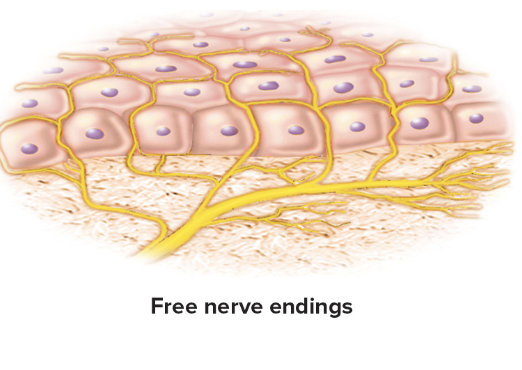
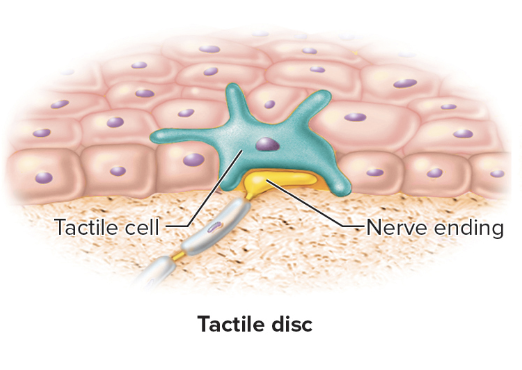
Tactile discs
light touch and pressure
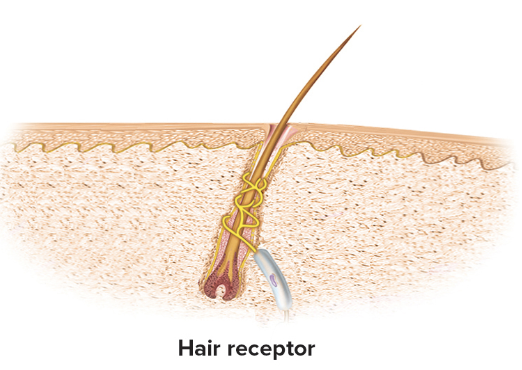
Hair root plexus (peritrichial endings)
mvmt of hairs
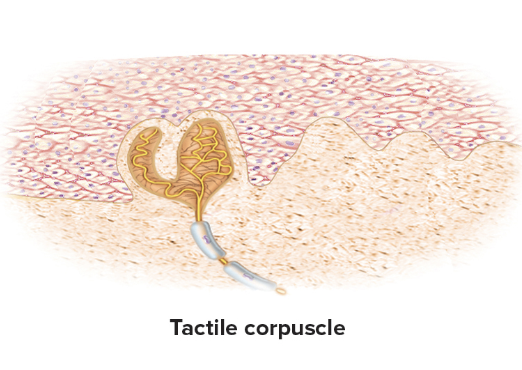
Tactile corpuscles
Oval mass in dermal papillae
sense light touch, texture perception
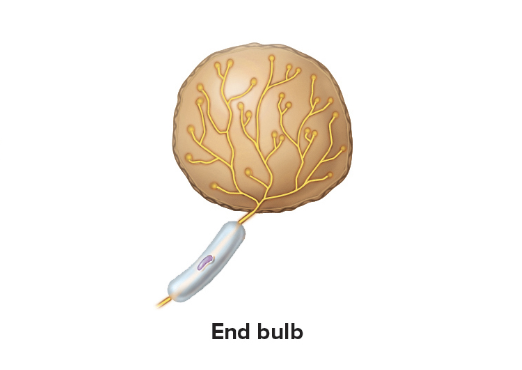
End bulbs
similar to tactile corpuscles but located in mucous membranes
bulbous corpuscles
lamellar corpuscles
muscles spindles
tendon ligament
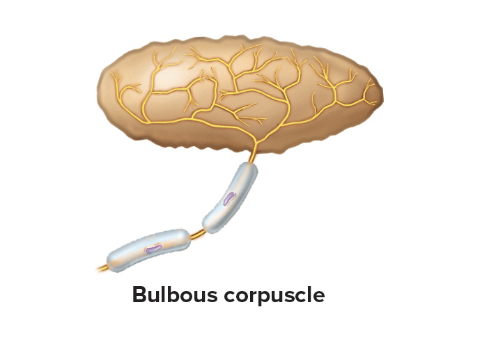
Bulbous corpuscles
Flat shape
Sense pressure, skin stretch, and joint movement
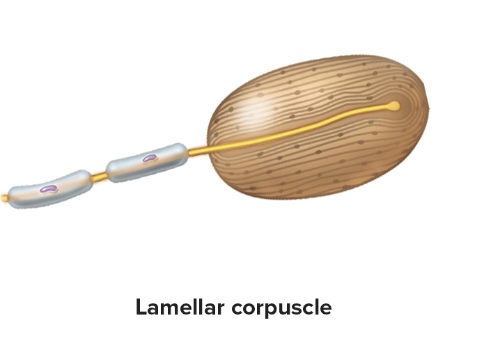
Lamellar corpuscles
onion like
Sense deep pressure, stretch, tickle, and vibration
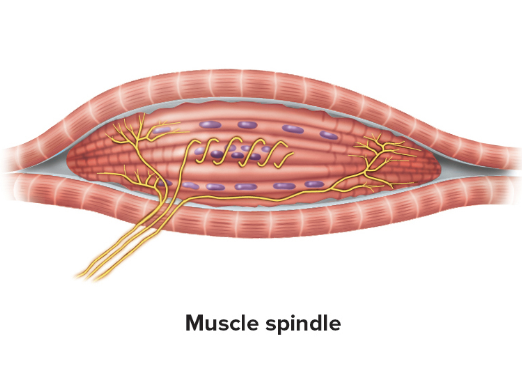
Muscle spindles
fusiform
sense skeletal muscle stretch
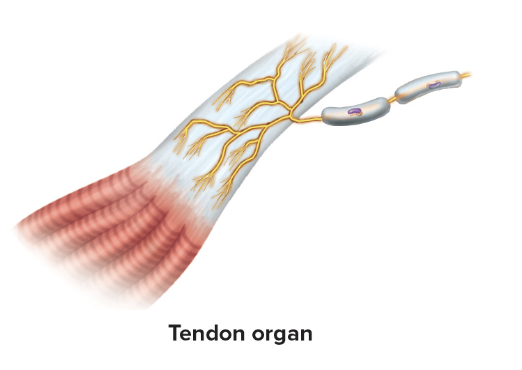
Tendon organs
leaflike
sense tendon stretch caused by muscle activity
Gustation
the sense of taste, detecting flavors through taste buds on the tongue.
Taste buds
tongue has the most
some in soft palate, pharynx, epiglottis, cheeks and testes
Lingual papillae
surface projection on tongue
Types
Filiform
folate
fungiform
Vallate
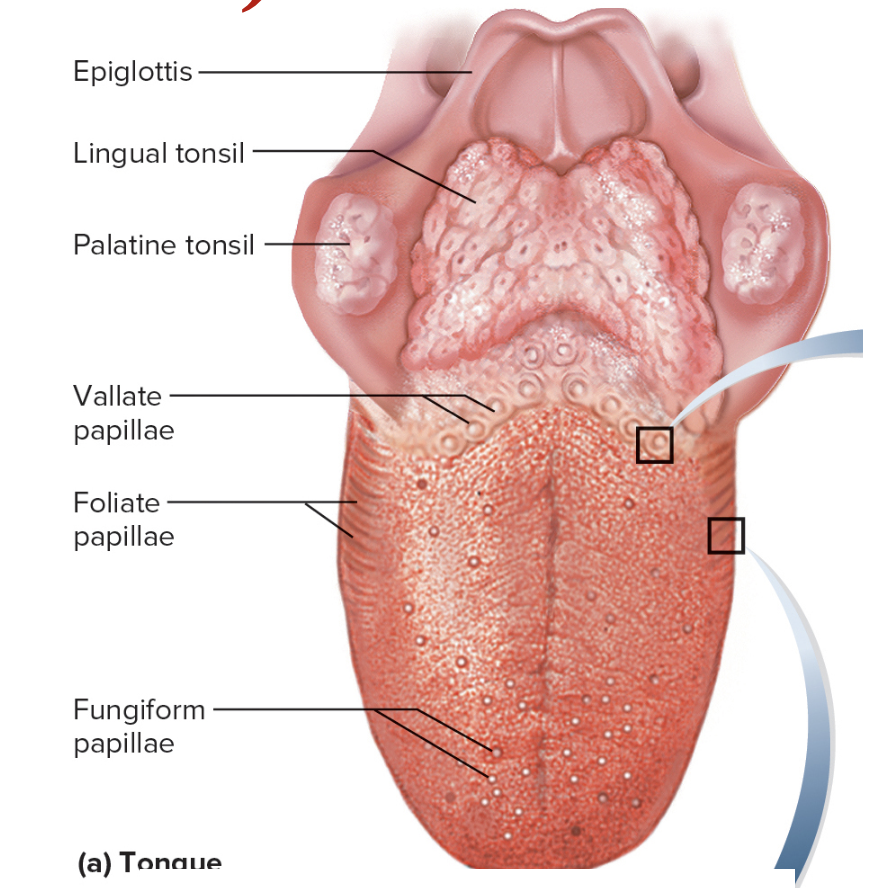
Filiform
most numerous
tiny spikes
no buds
Folate
ridges on tongue sides
buds in children
Fungiform
mushroom shaped bumps
have buds
Vallate
large bumps in a row at the back of the tongue, surrounded by trenches and containing many taste buds.
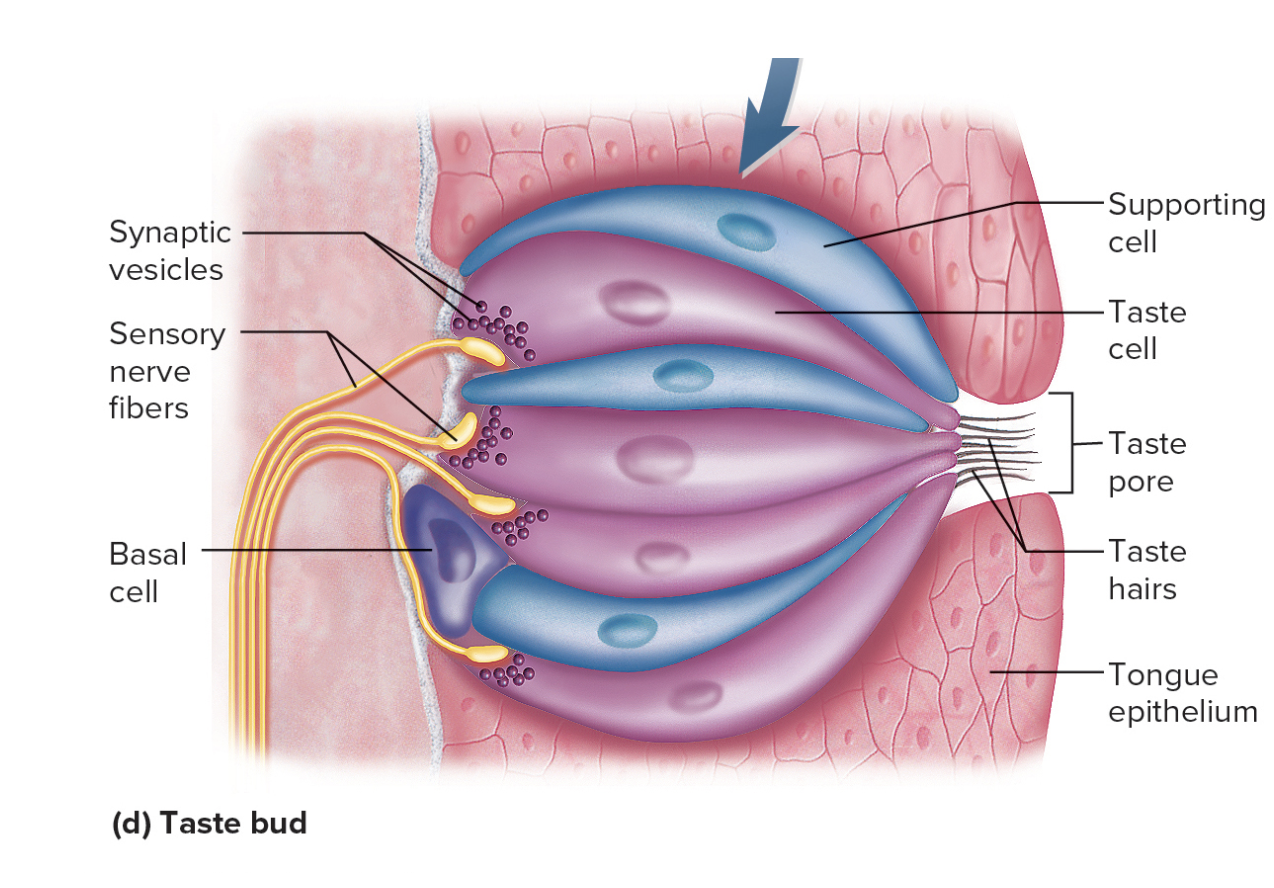
Taste buds contain taste celss:
Banana-shaped
Taste hairs
Receptor for taste
Synapse with sensory nerve
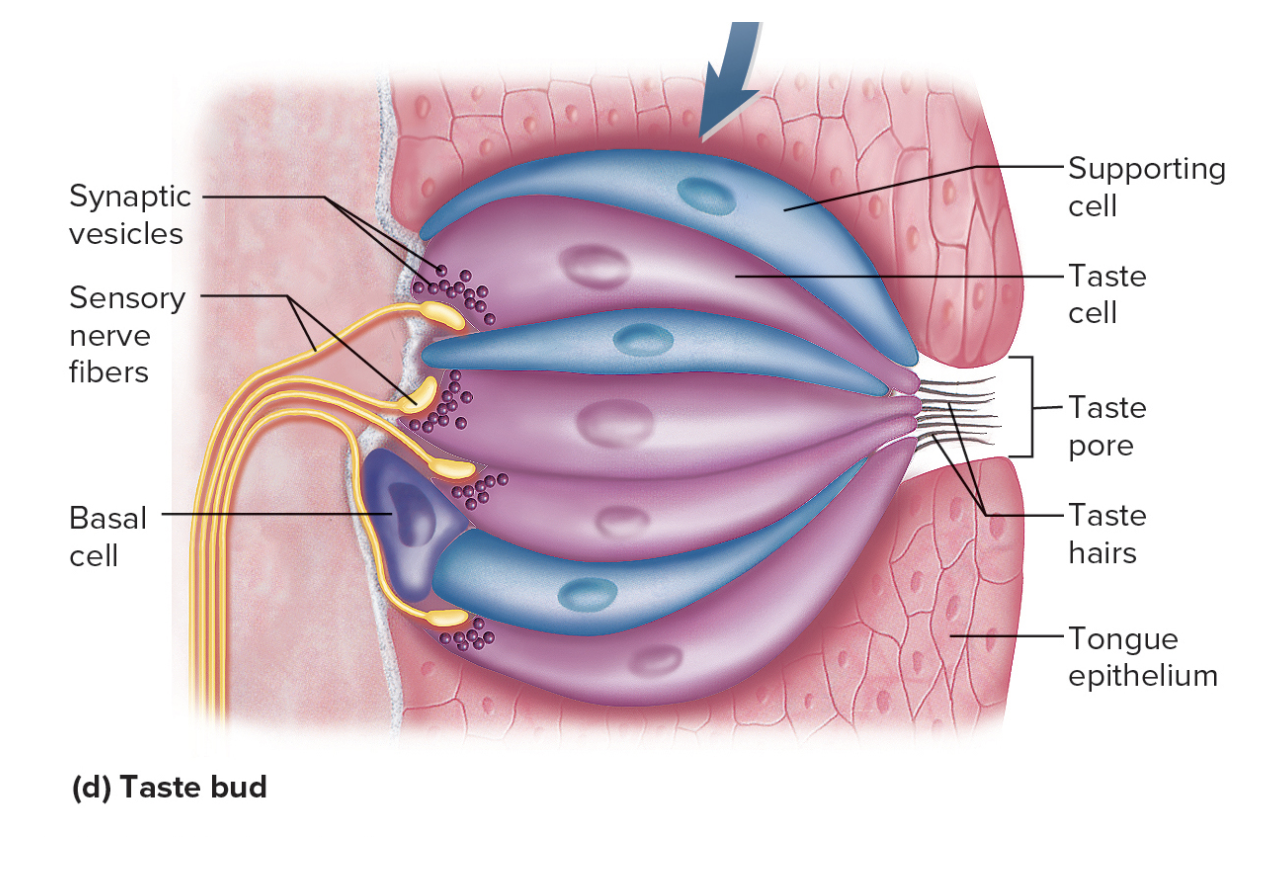
Taste Pore
Hole on epithelial surface of tongue
Olfaction
The sense of smell, involving olfactory neurons and olfactory receptors.
olfactory mucosa
Olfactory neurons
olfactory bulbs
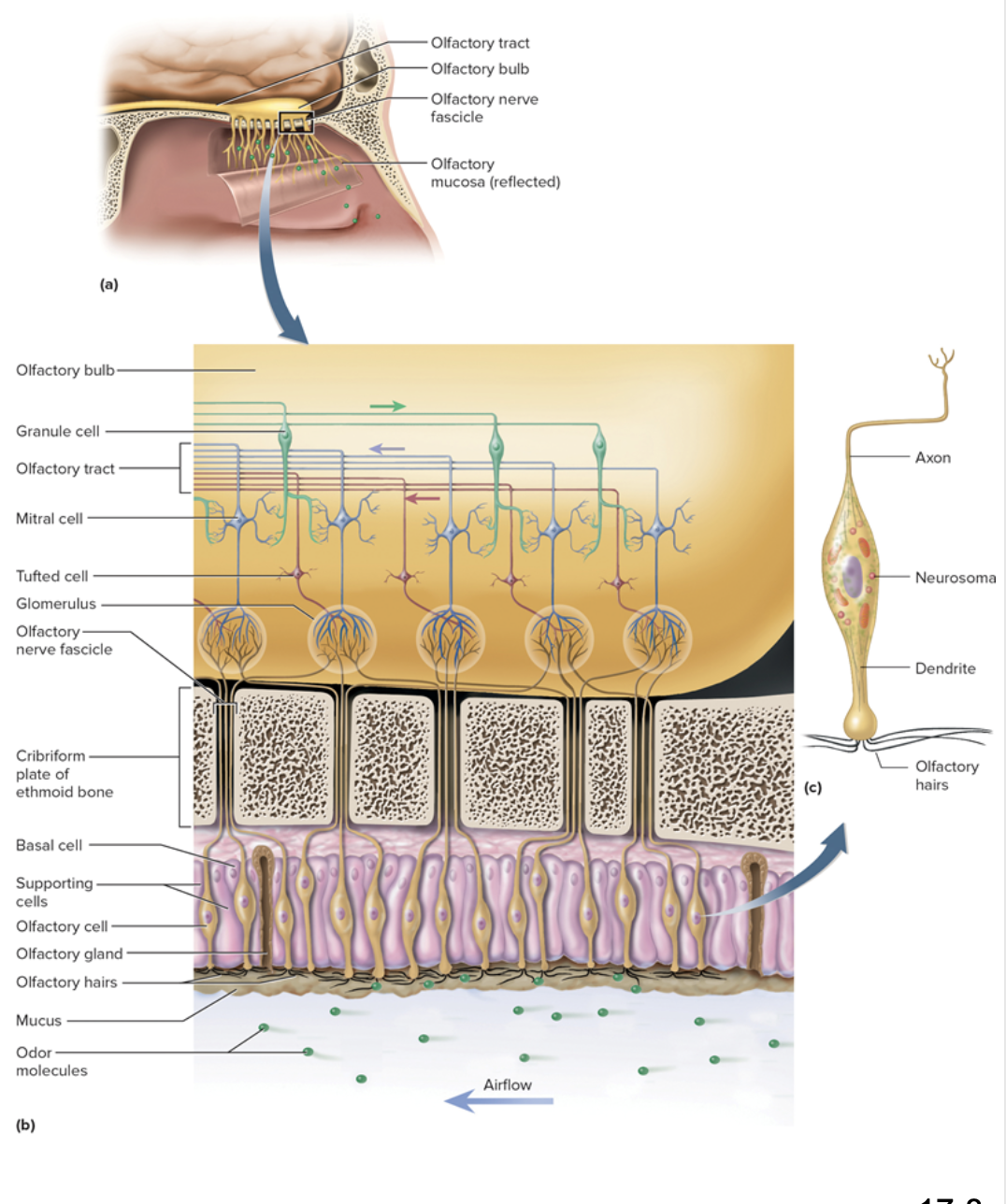
Olfactory mucosa
Roof of nasal cavity
Contains 10 to 20 million olfactory neurons
Olfactory neurons
have olfactory hairs (cilia) with binding sites for odor molecules
olfactory cell axons make olfactory nerve (CN I)
Olfactory bulbs
swollen tips of olfactory tracts at base of frontal lobes
Auditory ossicles
Three small bones in the middle ear, comprised of the malleus, incus, and stapes, that transmit sound vibrations.
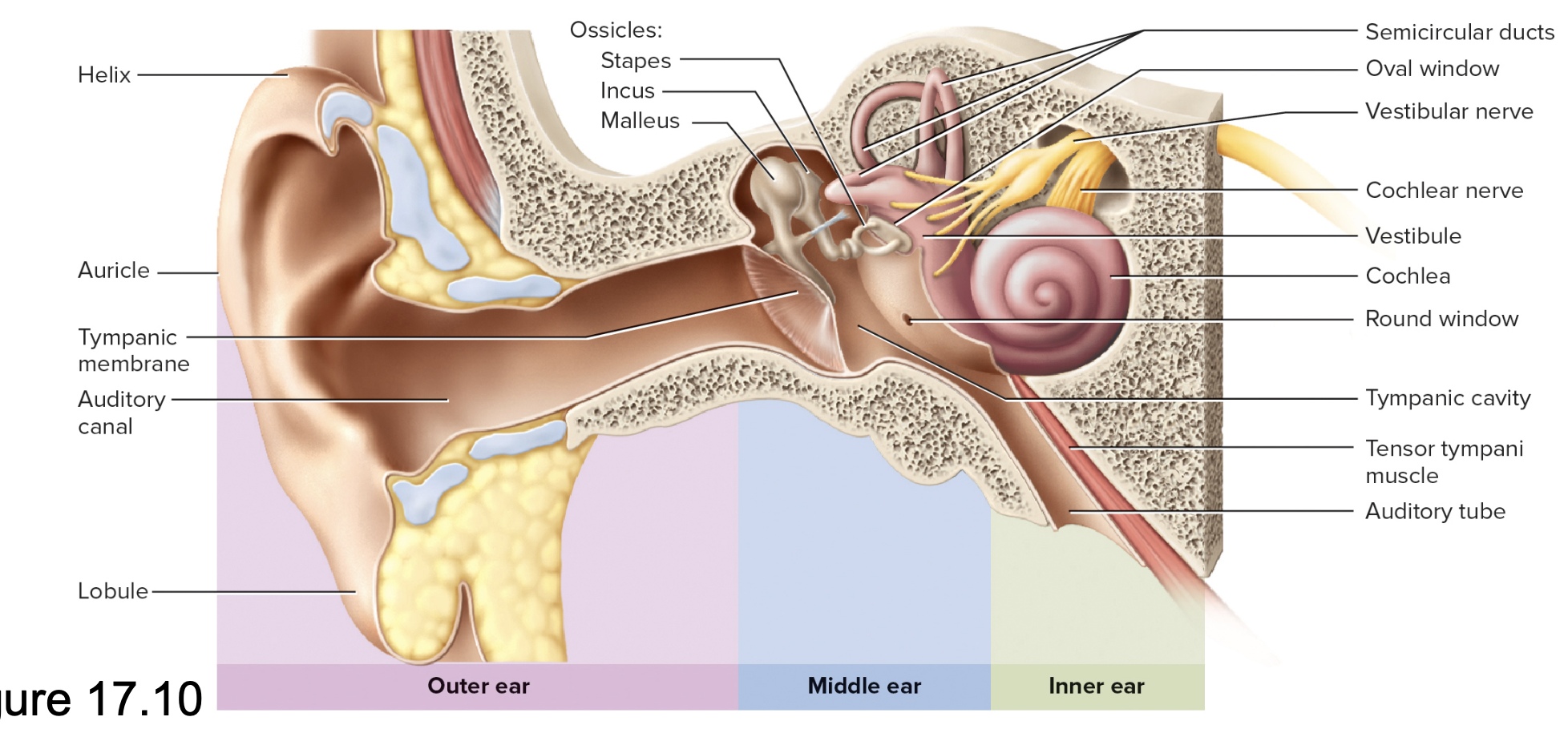
Outer ear included
Auricle (Pinna)
w/ helix and lobule
Auditory canal
w/ guard hairs, cerumen
Middle Ear
Tympanic membrane (eardrum)
Tympanic cavity of temporal bone
Auditory (eustachian) tube
Auditory ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes
Oval window on Cochlea (inner ear)
Muscles: stapedius, tensor tympani
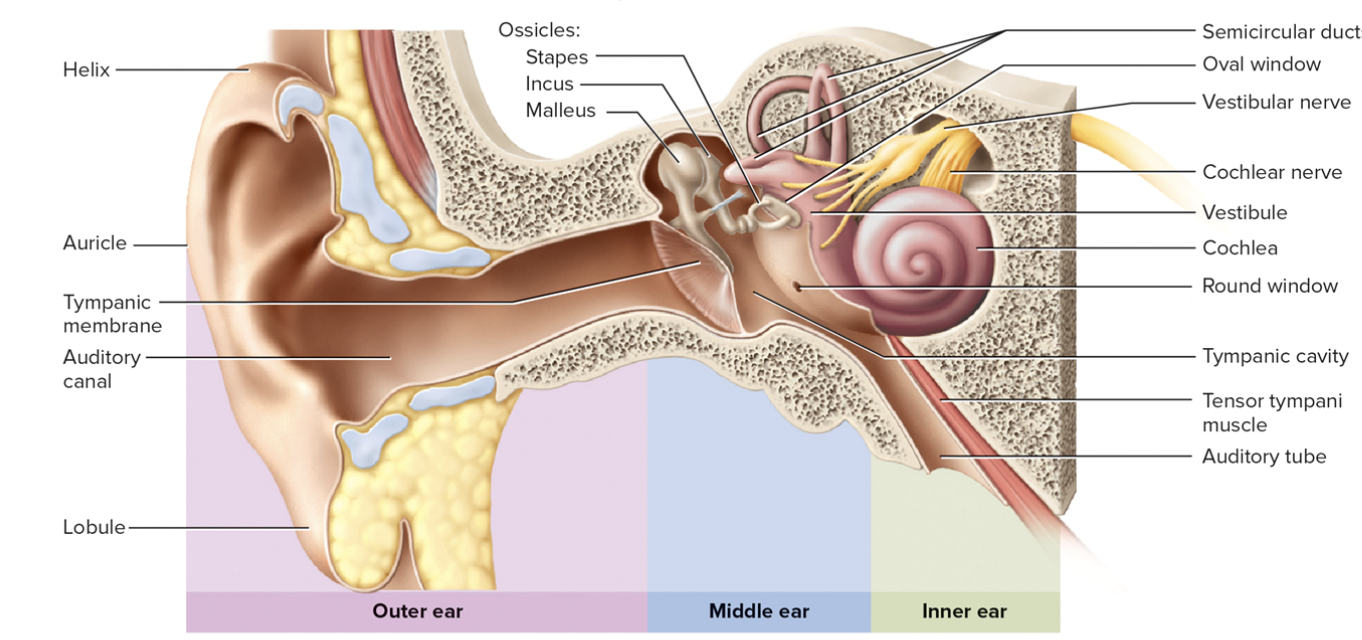
Inner Ear
Bony labyrinth – maze
in temporal bone
Membranous labyrinth – tube within maze
Endolymph – fluid in membranous labyrinth
Perilymph – fluid between membranous labyrinth and bone
Bony labyrinth – maze
in temporal bone
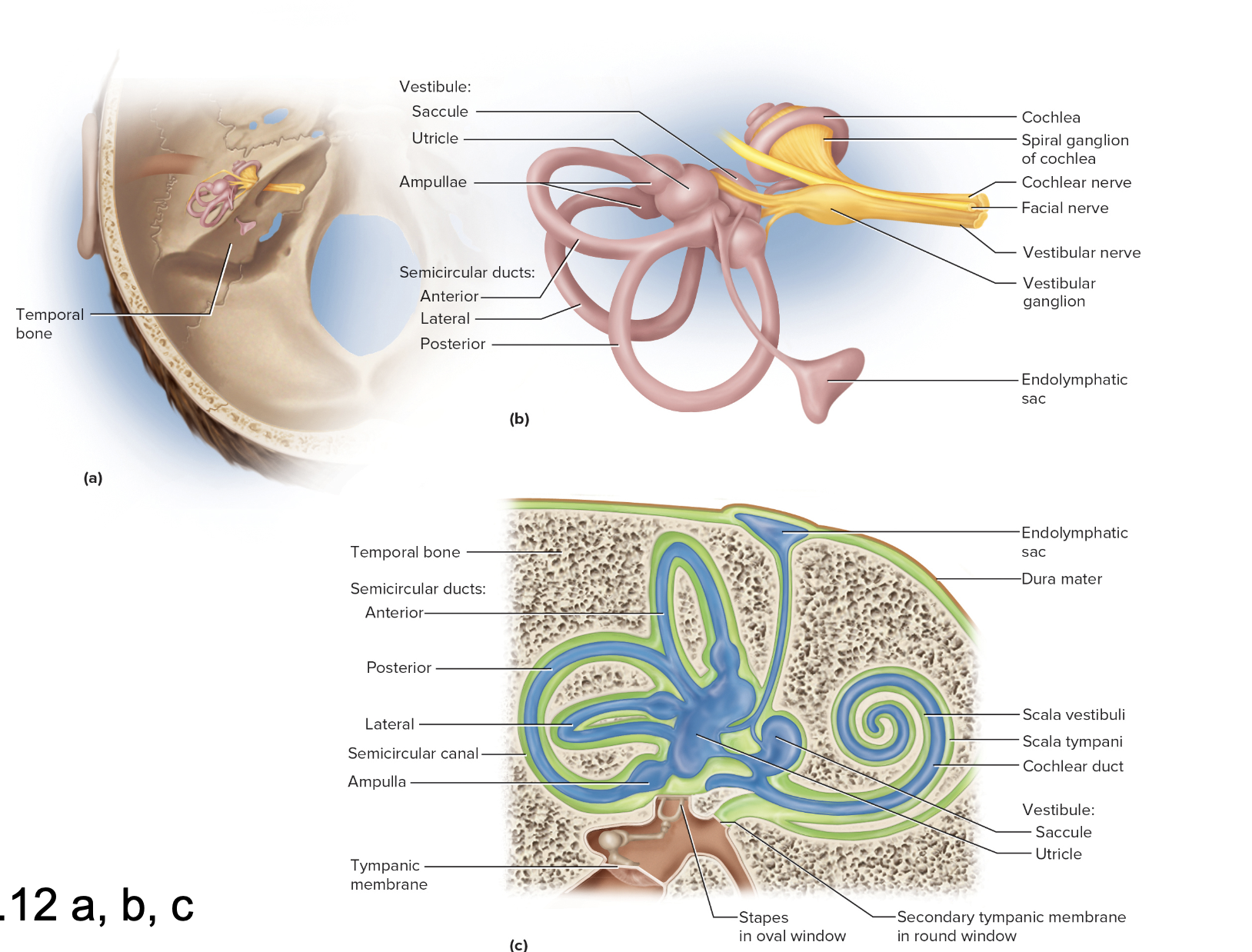
Vestibule
Utricle and saccule
Three semicircular canals
Cochlea – snail shaped
Anatomy of the Membranous Labyrinth
The membranous labyrinth is a complex system of interconnected tubes and sacs filled with endolymph, located within the bony labyrinth of the inner ear. It includes structures such as the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals, essential for hearing and balance.
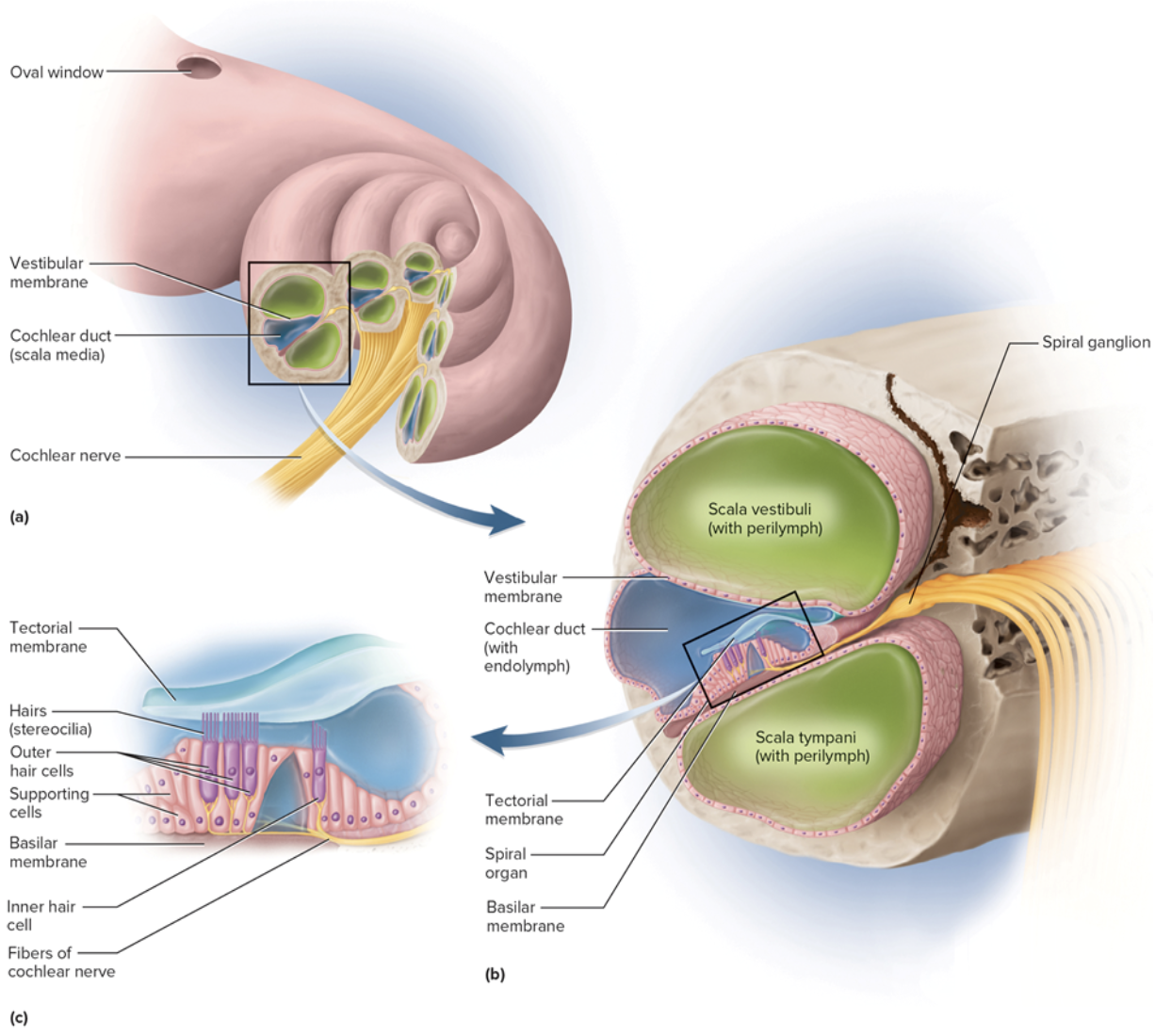
Cochlear duct (inner ear)
is an organ of hearing in the inner ear
Contains spiral organ w/ hair cells: inner hair cells and outer hair cells
Stereocilia of hair cells project into tectorial membrane
contain endolymph
Hair cells connect w/ sensory neurons that form the cochlear division of CN VIII
Equilibrium
coordinations, balance, orientation
Three semicircular canals
Utricle and saccule
Scala vestibuli (inner ear)
chamber above vestibular membrane
Begins near oval window
Contains perilymph
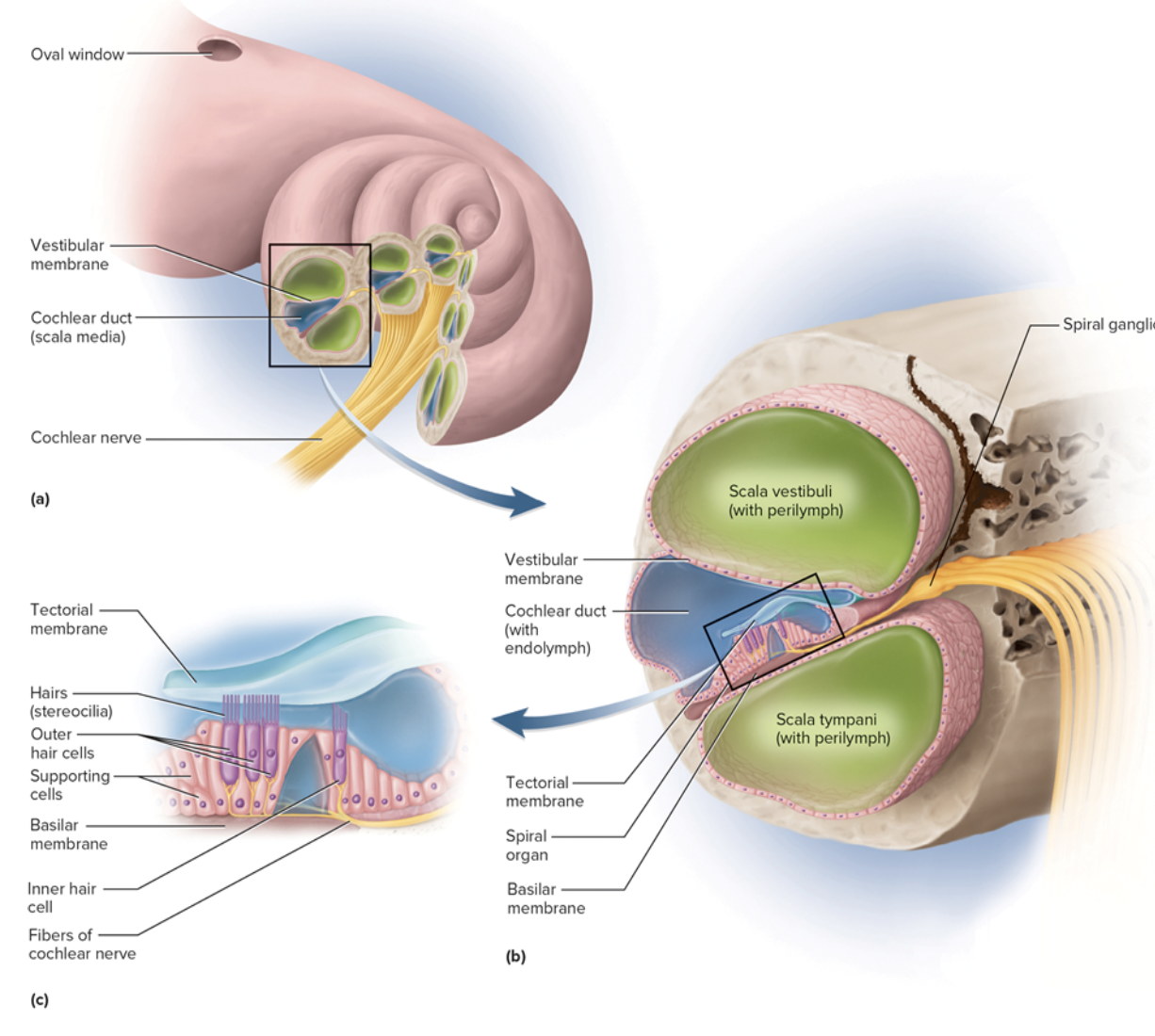
Scala Tympani
chamber below basilar membrane
Ends at round window that is covered by secondary tympanic membrane
Contains perilymph
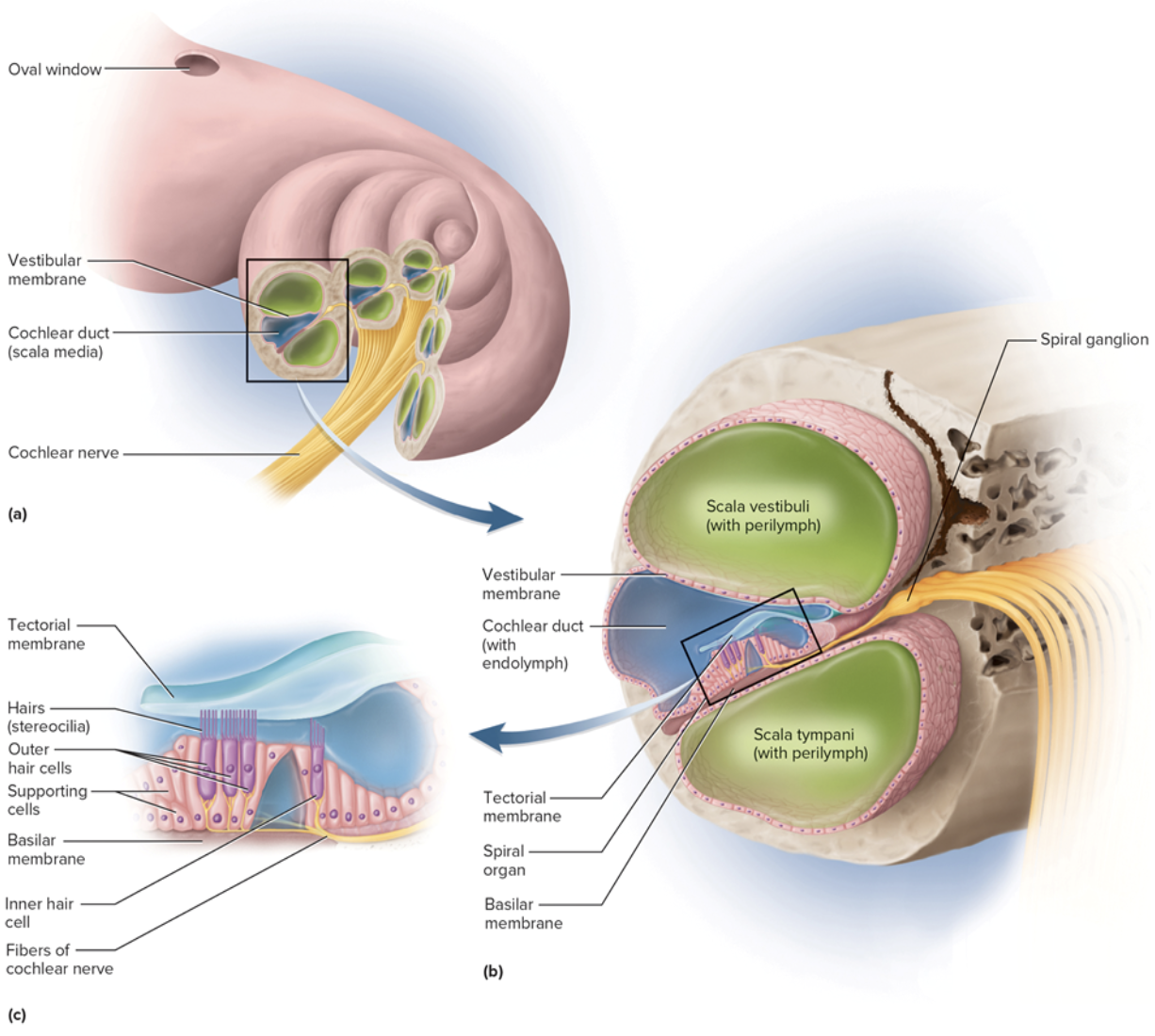
Vestibular Apparatus
Equilibrium- coordination, balance, orientation
Three semicircular canals
Utricle and saccule
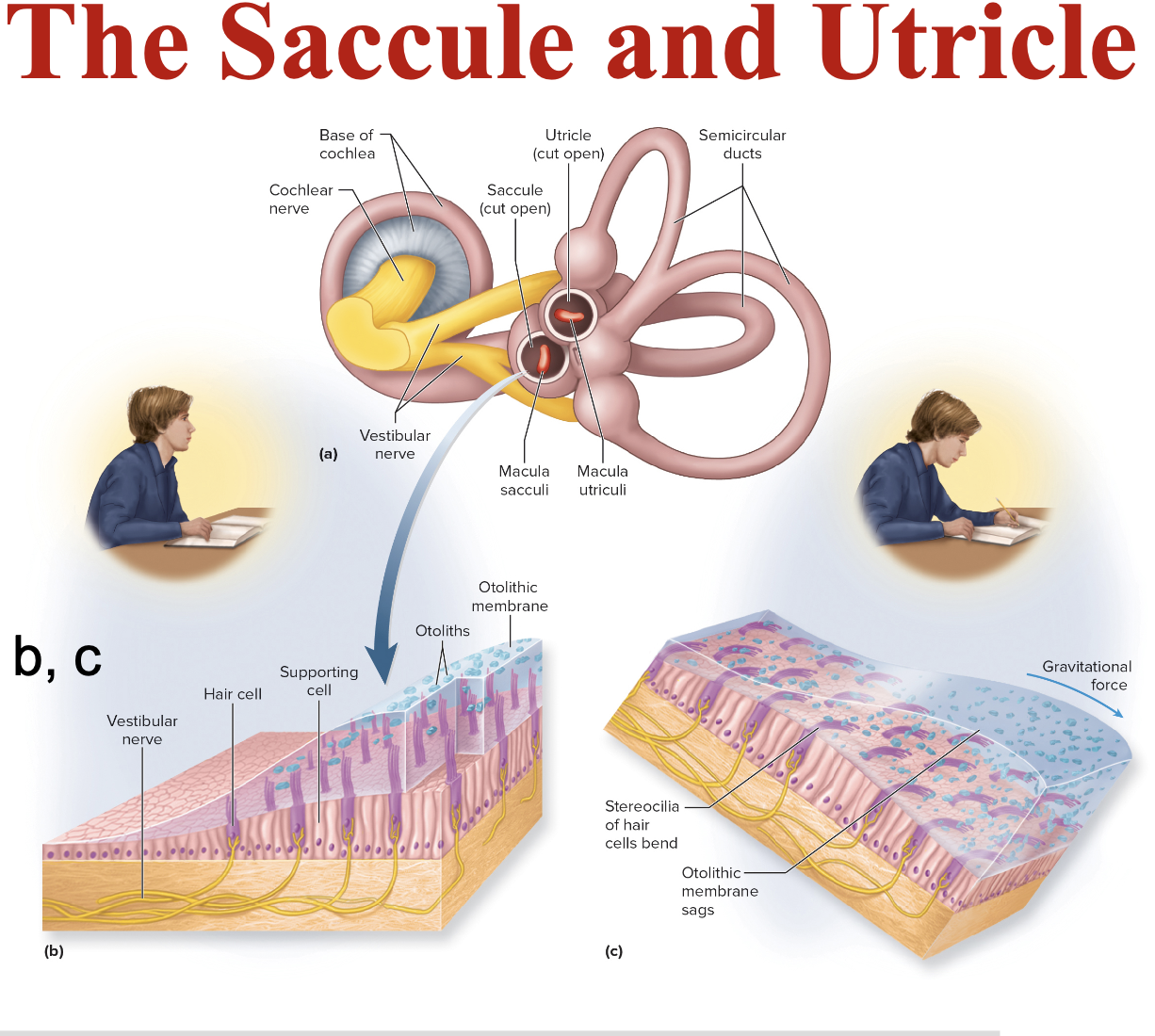
Saccule and Utricle
Saccule is vertical, utricle is horizontal
Each hair cell of a macula has a kinocilium embedded
in the otolithic membrane (Otoliths = Calcium stones)
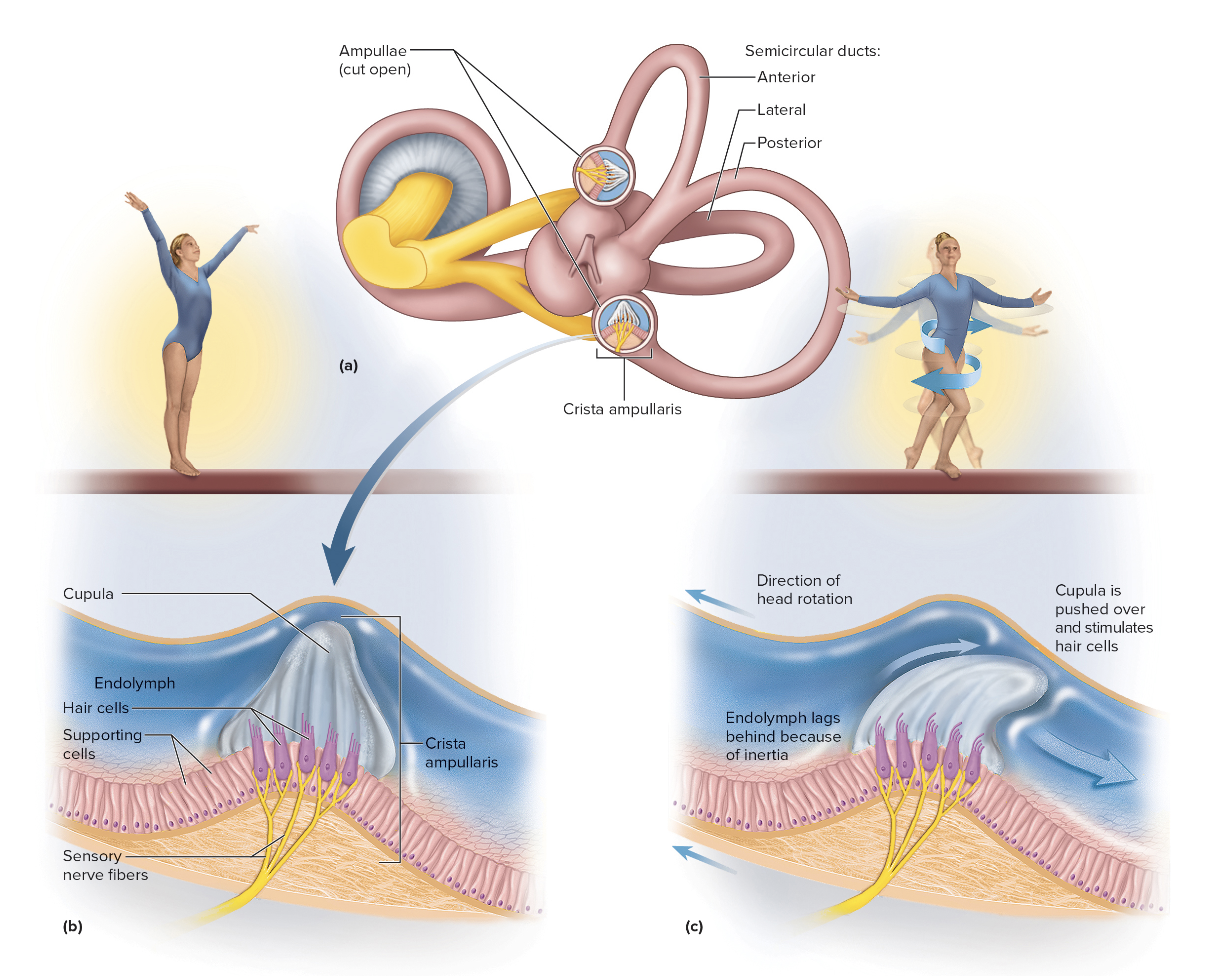
The semicircular ducts
Three semicircular ducts: anterior, posterior, and lateral
Each duct has an ampulla with a crista ampullaris
Hair cells project into gelatinous cupula and bend with fluid movement
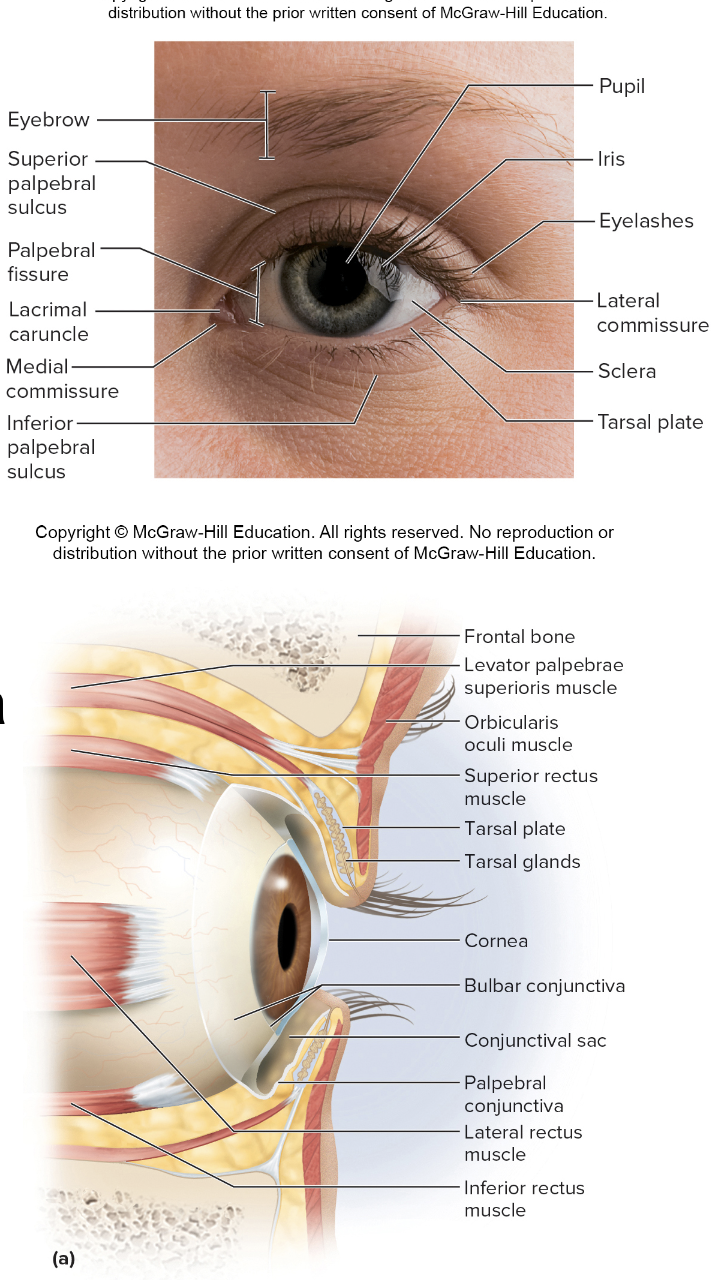
Accessory Structures of the orbit
keep foreign substances out of the eye
eyebrows
eyelids
conjunctiva
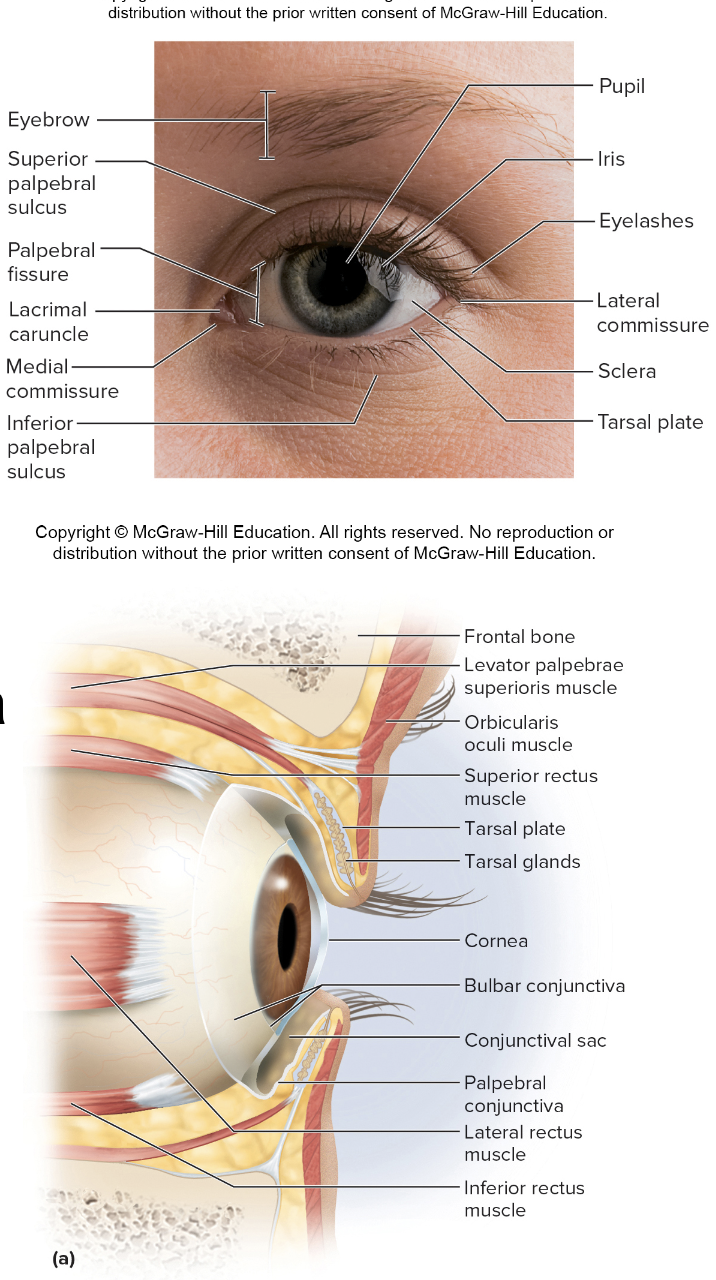
eyelids (palpebrae) include
Palpebral fissure
Medial/lateral commissures (canthi)
Tarsal gland
Eyelashes
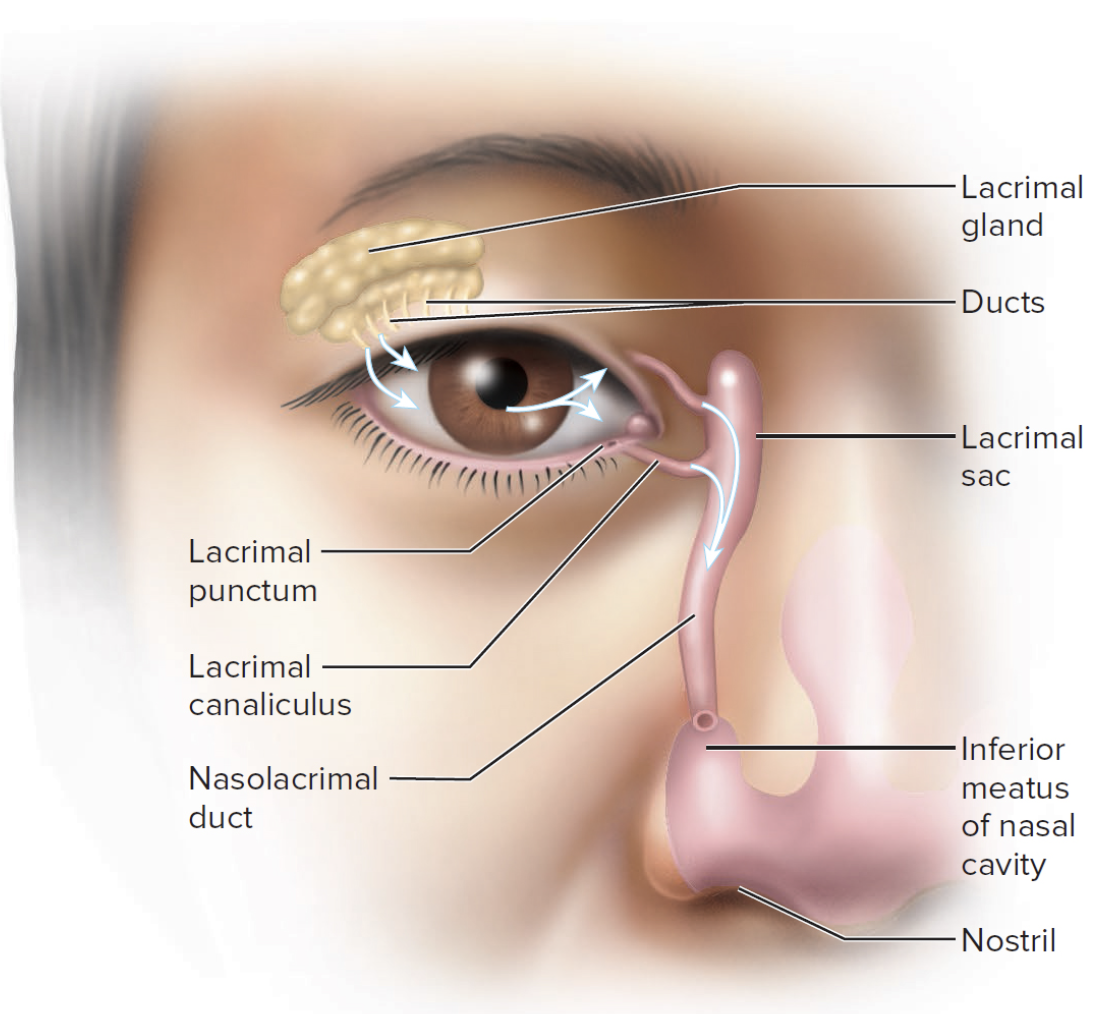
Lacrimal Apparatus includes:
Lacrimal gland
Tears travel across conjunctiva and cornea
Lacrimal punctum
Small pore in eyelid
Lacrimal canal
Lacrimal sac
Nasolacrimal duct
Drains to nasal cavity
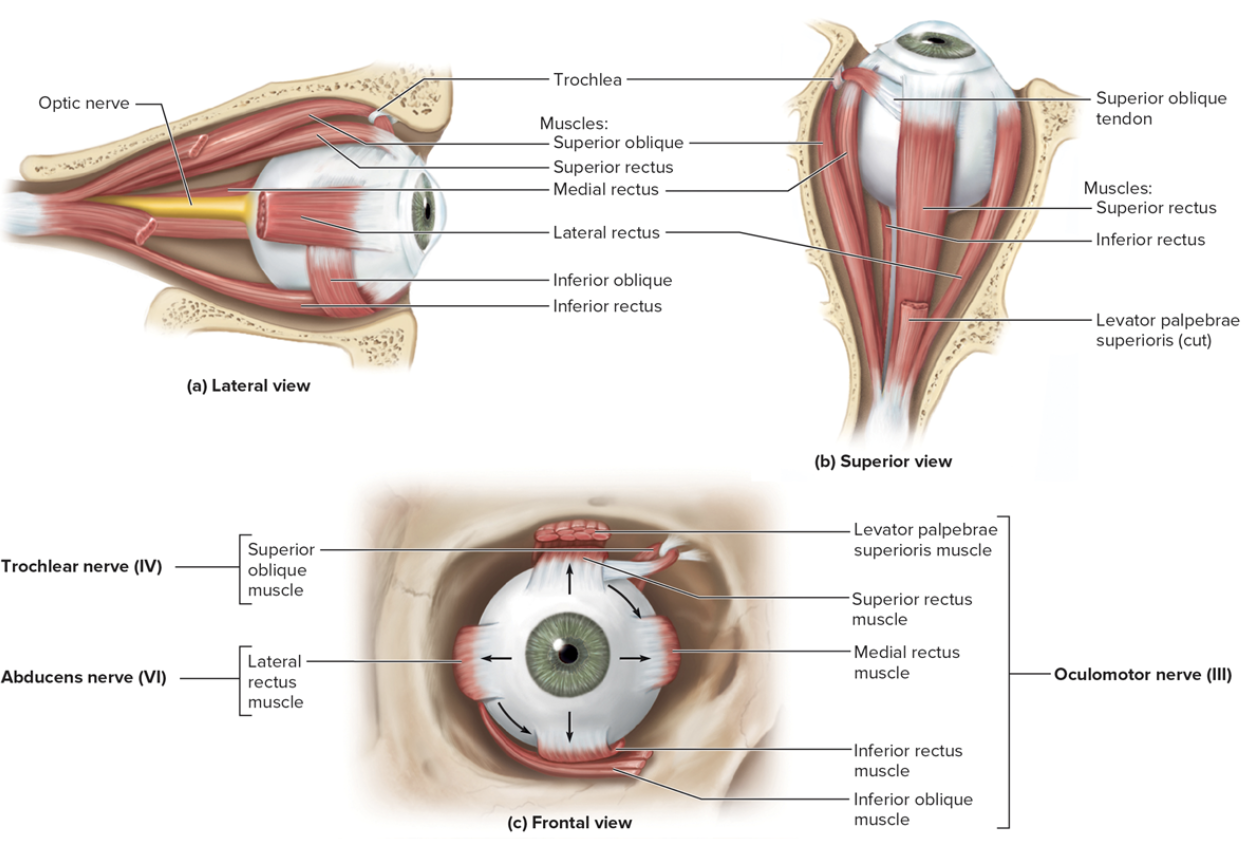
Extrinsic Eye muscle
Superior rectus
Moves gaze up
Inferior rectus
Moves gaze down
Medial rectus
Moves gaze medially
Lateral rectus
Moves gaze laterally
Superior oblique
Tendon through trochlea
Inferior oblique
Anatomy of the eyeball (Fibrous tunic)
Sclera – white fibrous tissue
Cornea – transparent, anterior
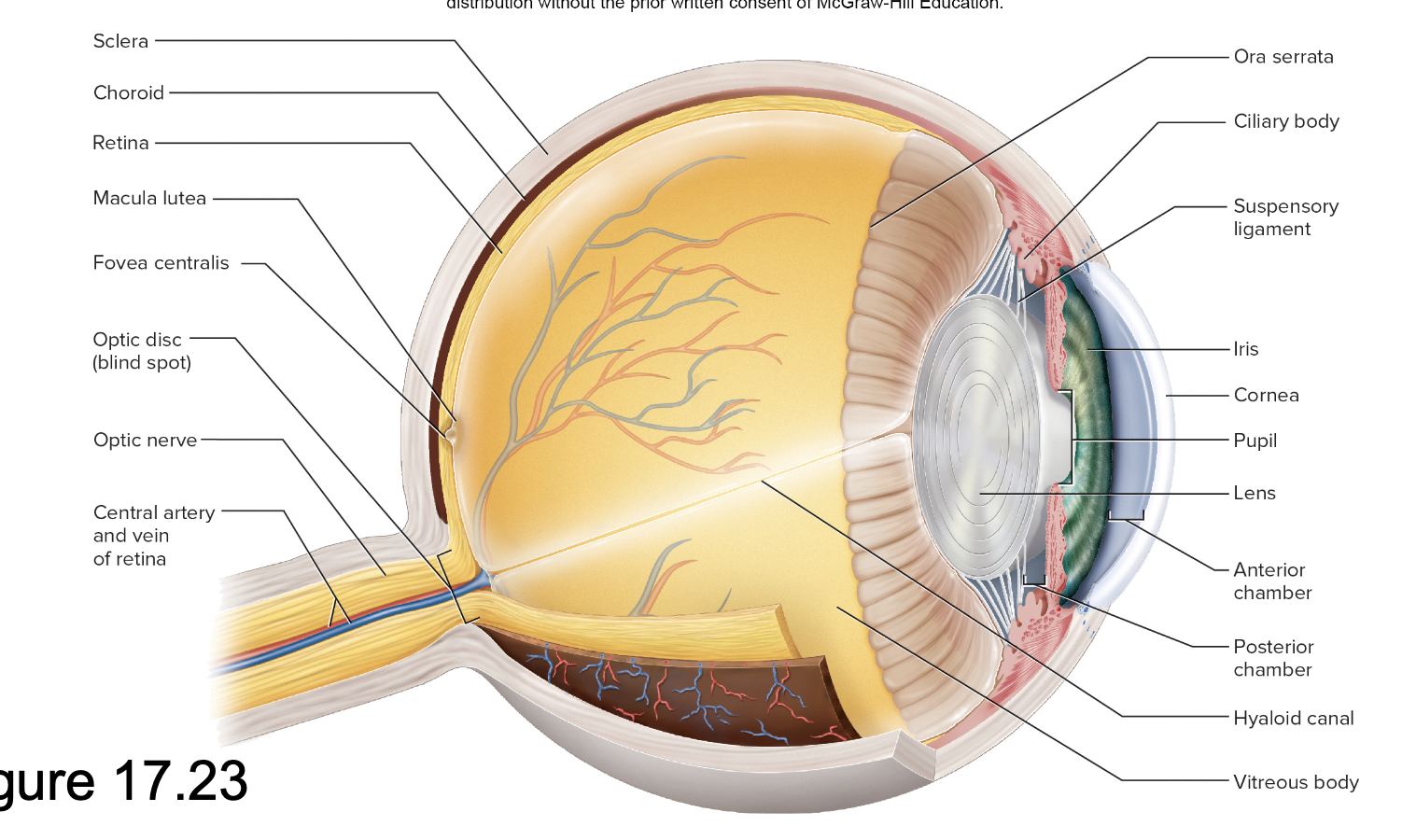
Anatomy of the eyeball (Vascular tunic)
Choroid – pigmented layer behind retina
Ciliary body – ring of smooth muscle around lens
Suspensory ligaments – holds lens in place and stretch/loosen when ciliary body contracts/relaxes
Iris – pigmented diaphragm controlling pupil diameter
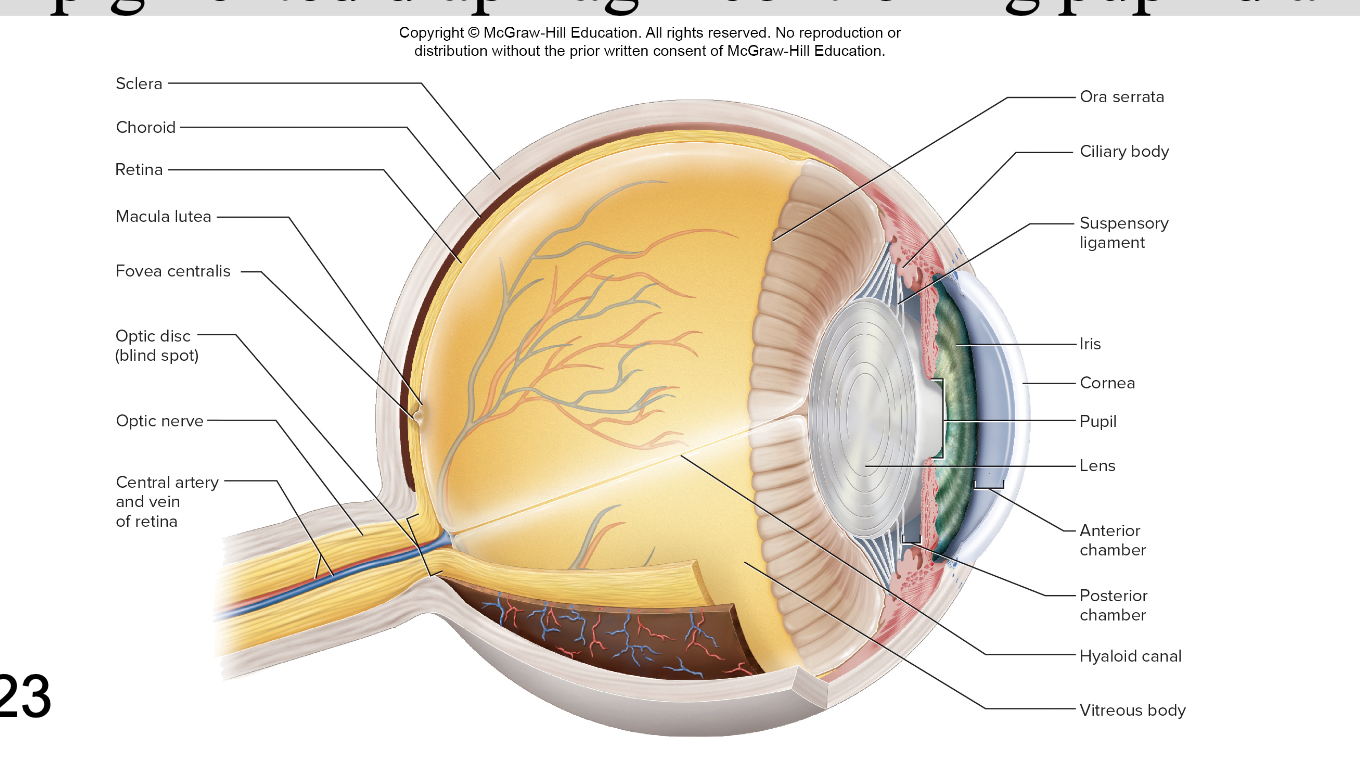
Anatomy of the eyeball (Tunica interna)
Retina – lines posterior two-thirds of eye contains the neural layer
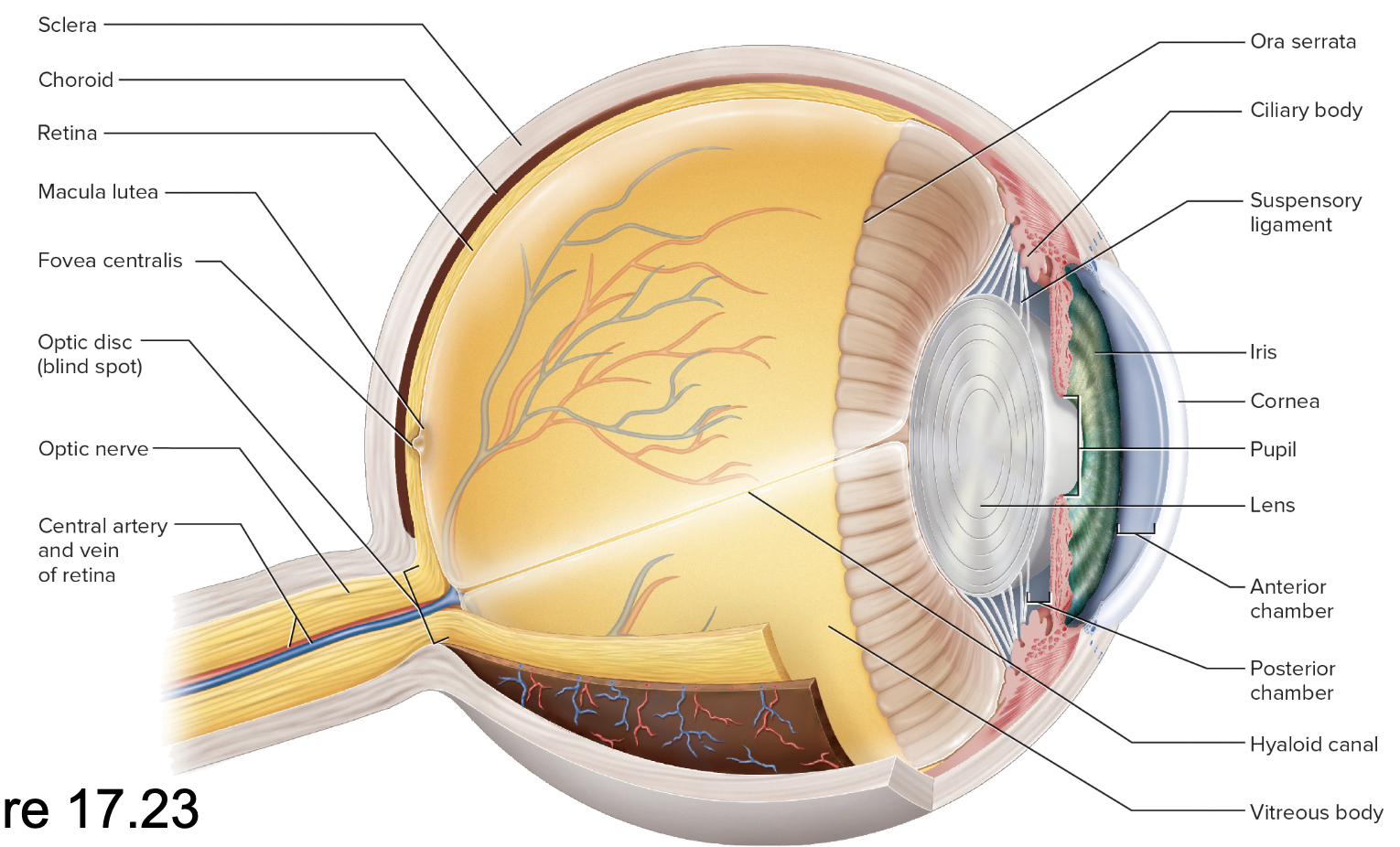
Optical Chambers and Humors
Aqueous humor
Lens
Vitreous body
Aqueous humor
Posterior chamber – from lens to iris
Anterior chamber – from iris to cornea
Scleral venous sinus – drains aqueous humor back to blood
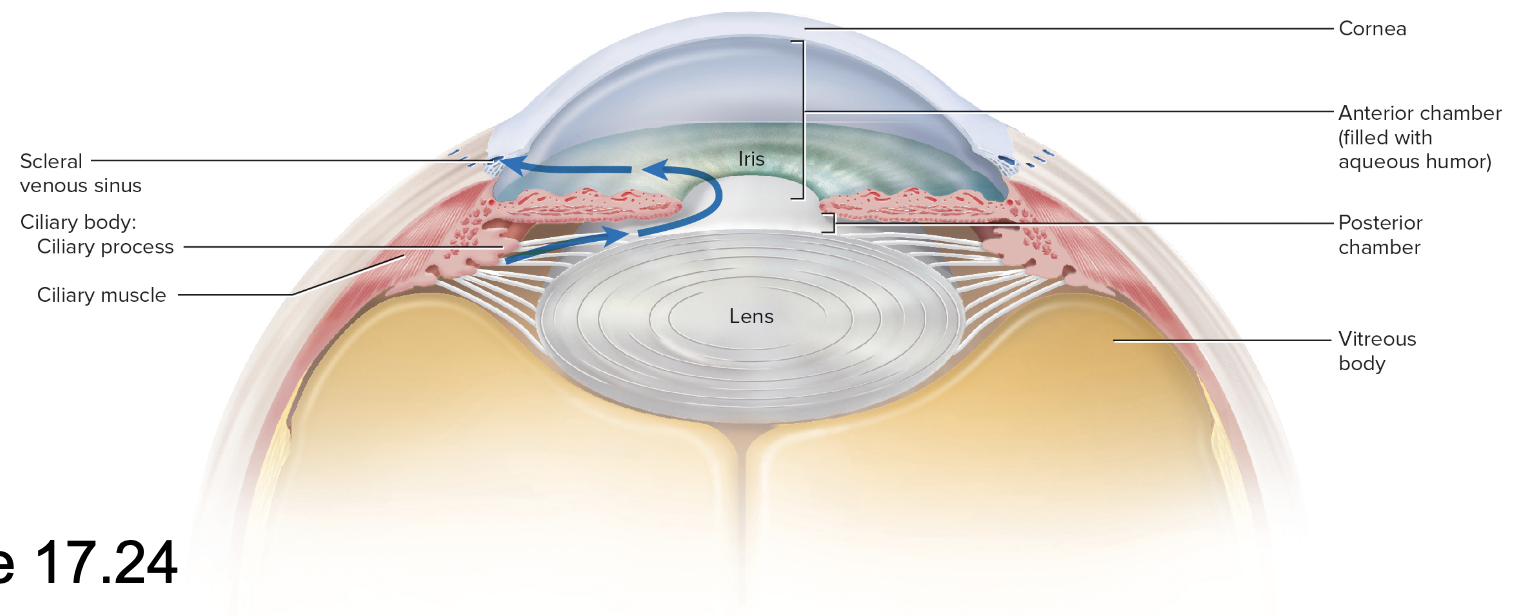
lens
Ciliary body- aqueous humor
Neural components of the eye
Retina
optic nerve
Macula lutea
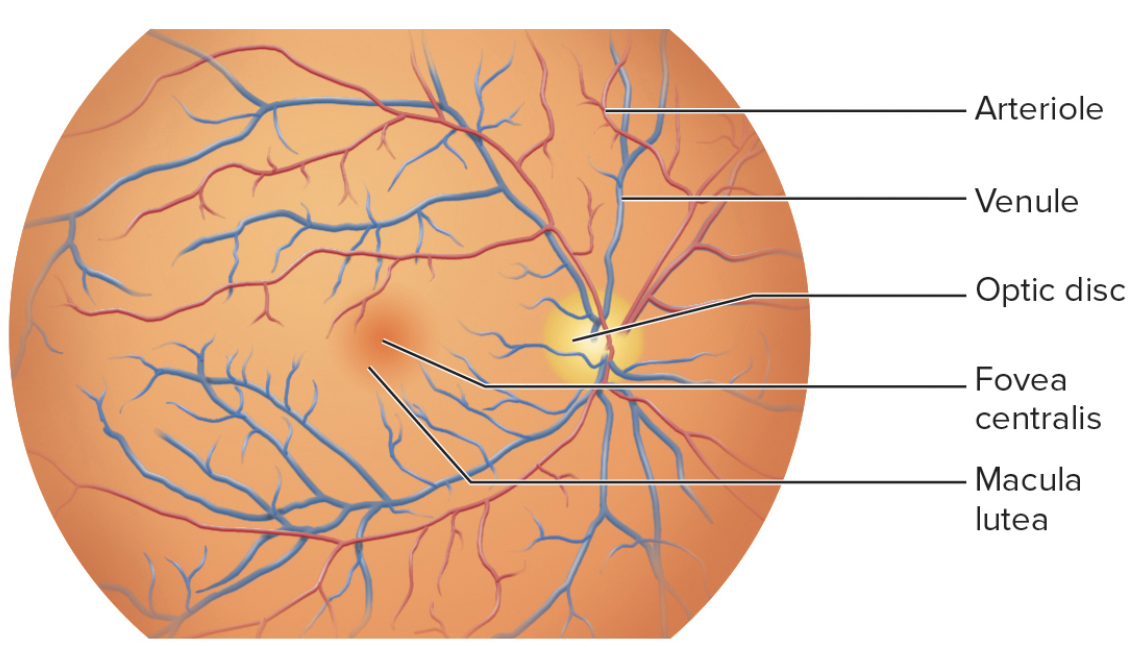
Retina
Ora serrata – anterior
Optic nerve
exits at optic disc
Is the “blind spot” without receptors
Macula lutea
Central patch for detailed vision
Fovea centralis – pit within macula
Vitreous body (vitreous humor)
Vitreous chamber – behind lens
Retina
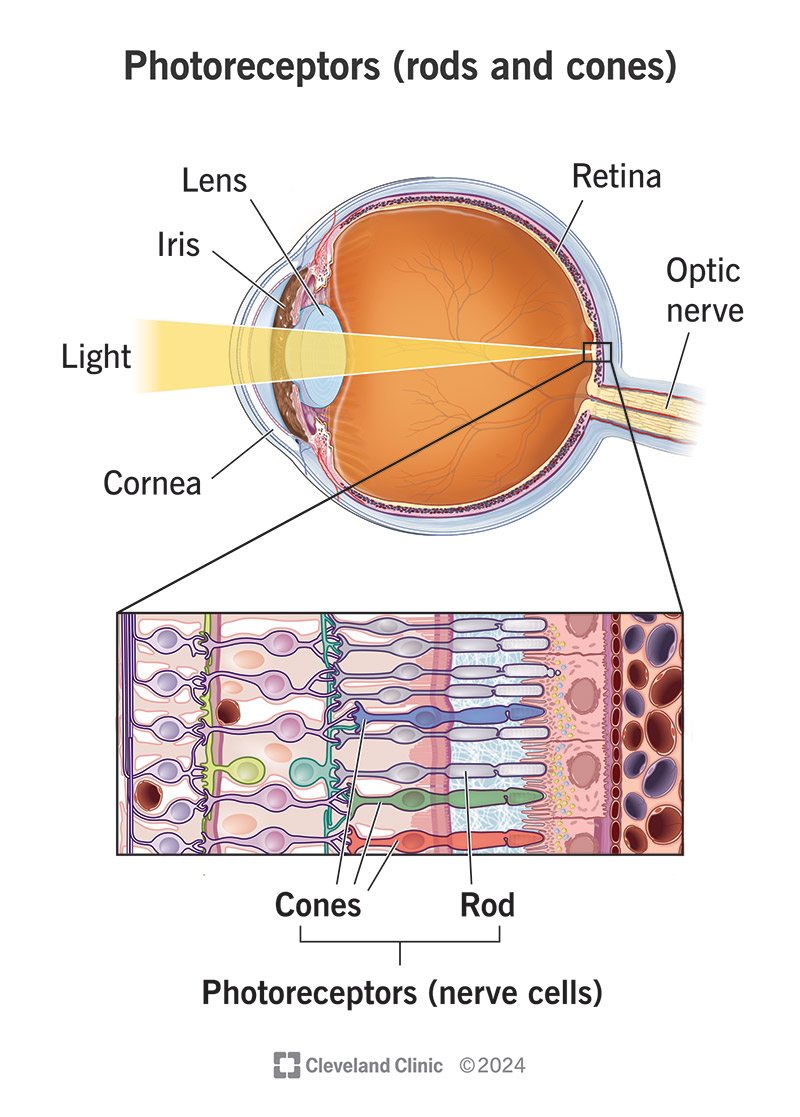
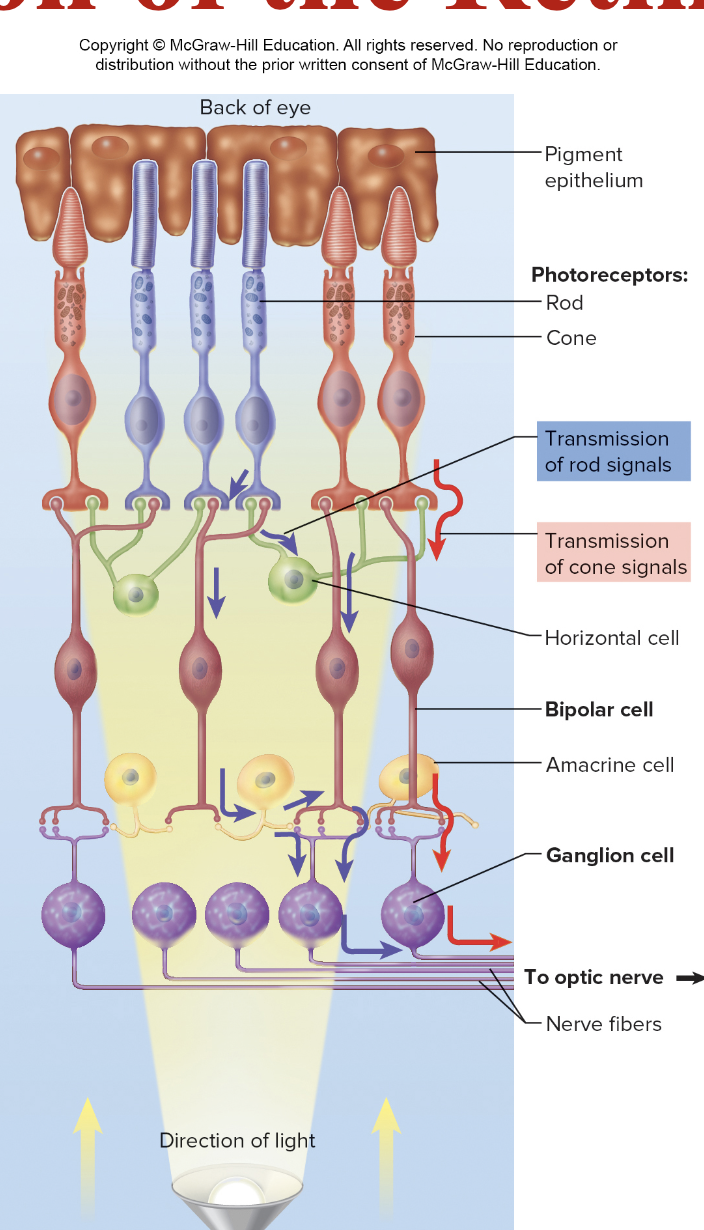
The neural layer of the eye responsible for receiving light and containing photoreceptors (rods and cones).
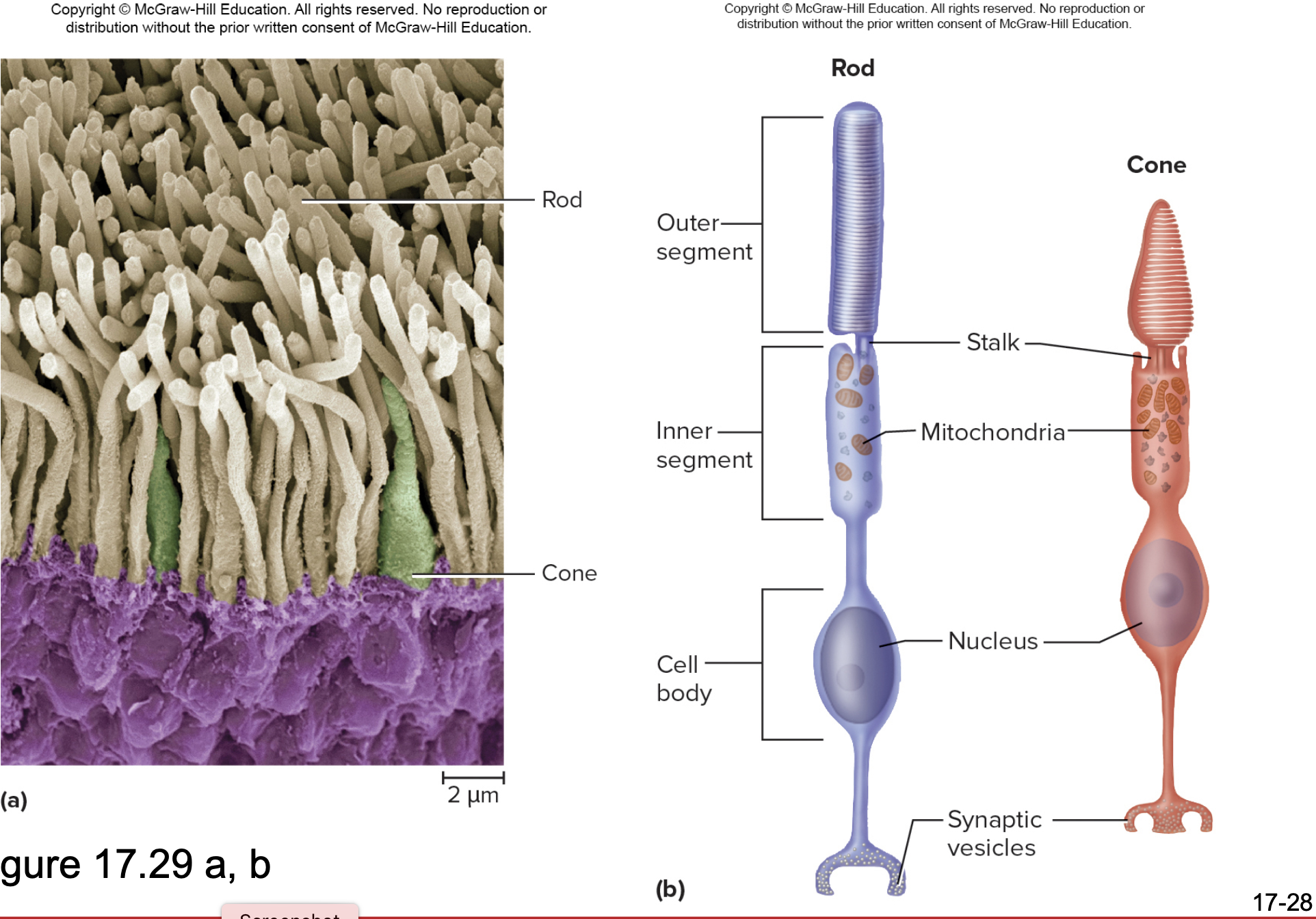
Rods
Photoreceptors in the retina that are responsible for night (scotopic) vision and monochromatic
Rhodopsin- pigment
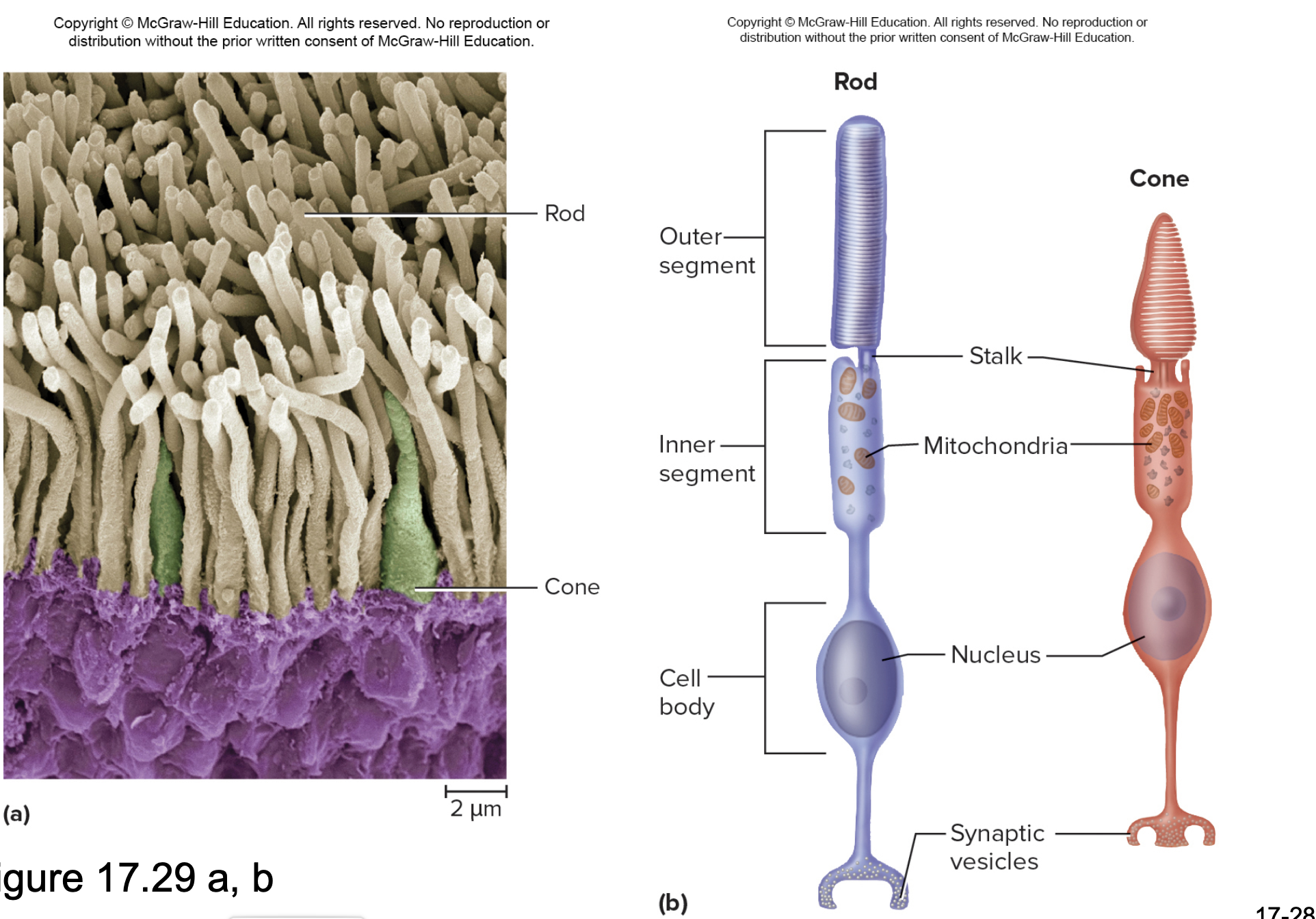
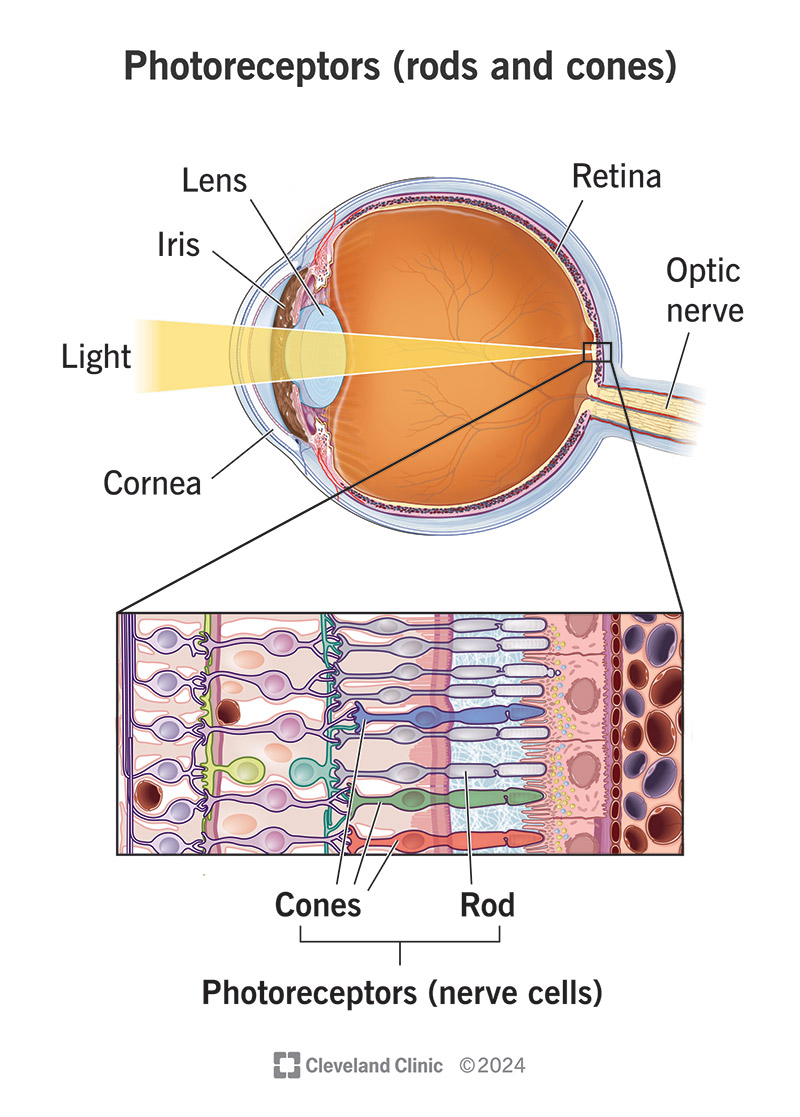
Cones
Day (photopic) vision, trichromatic
Photospins- three different pigments
red, blue, green
Bipolar cells
interneurons
receive input from rods and cones
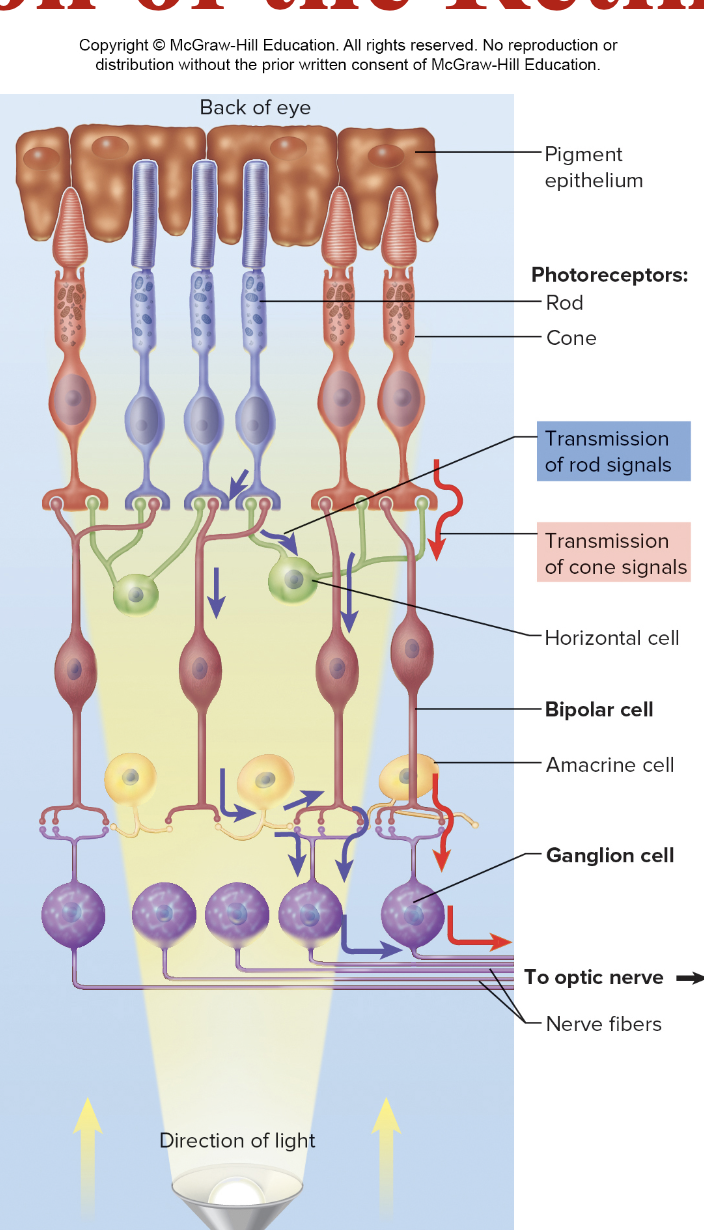
Ganglion cells
Receive input from bipolar cells
Axons form optic nerve
Cochlea
The spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear that plays a critical role in hearing by converting sound vibrations into nerve impulses.
Tactile discs
Nerve endings located in the stratum basale of the epidermis that sense light touch and pressure.
Lacrimal apparatus
The structure involved in tear production and drainage, including the lacrimal gland and lacrimal sac.
Ciliary body
A ring of smooth muscle in the eye that controls the shape of the lens and produces aqueous humor.
Vitreous body
The clear gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina in the eyeball.
Macula lutea
The central region of the retina that is responsible for high acuity vision, containing a high density of photoreceptors.
Otoliths
Calcium stones in the otolithic membrane; they play a crucial role in the sense of balance by responding to gravitational changes.
Semicircular canals
Three canals in the inner ear that help maintain balance by detecting rotational movements of the head.
Eustachian tube
The tube that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx and helps equalize pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane.
Sclera
The white outer layer of the eyeball that provides structure and protection.
Pupil
The opening in the center of the iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
Tectorial membrane
The membrane in the cochlea that interacts with hair cells and is crucial for the process of hearing.
Fovea centralis
A small pit in the retina that contains a high concentration of cones and provides the sharpest vision.