Anatomy exam 5 pt 2 (ch 26, ch 27 slides 1-6)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:17 AM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
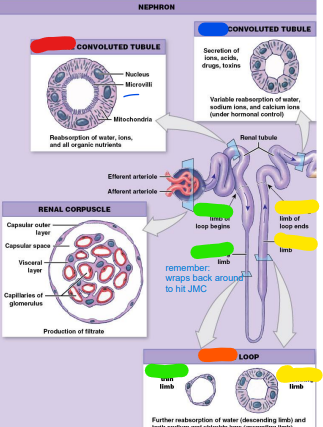
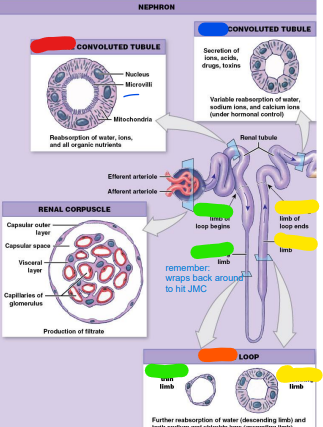
proximal convoluted
______ convoluted tubule (PCT)
– Begins at tubular pole
of renal corpuscle
– Lined with simple
cuboidal epithelium
containing microvilli
– Major site of
reabsorption
(red)
– Begins at tubular pole
of renal corpuscle
– Lined with simple
cuboidal epithelium
containing microvilli
– Major site of
reabsorption
(red)
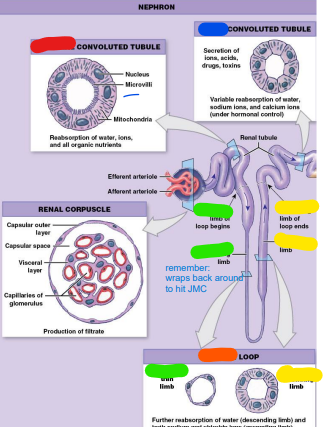
2
New cards
henle/nephron
Loop of _____ (LOH)
or ______ Loop
– Descending limb
– Ascending limb
– Both loops simple
squamous epithelium
– Drained by vasa
recta (orange)
or ______ Loop
– Descending limb
– Ascending limb
– Both loops simple
squamous epithelium
– Drained by vasa
recta (orange)
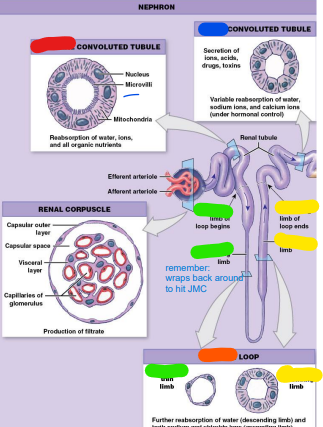
3
New cards
ascending
______ (thick) limb-
reabsorption of ions;
impermeable to
water (yellow)
reabsorption of ions;
impermeable to
water (yellow)
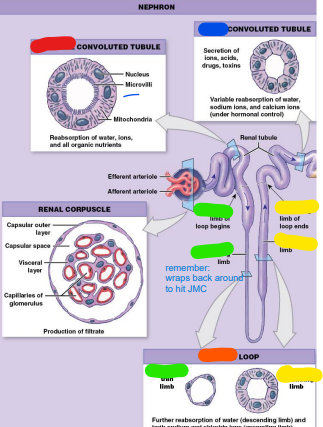
4
New cards
descending
_____ (thin) limb-
reabsorption of
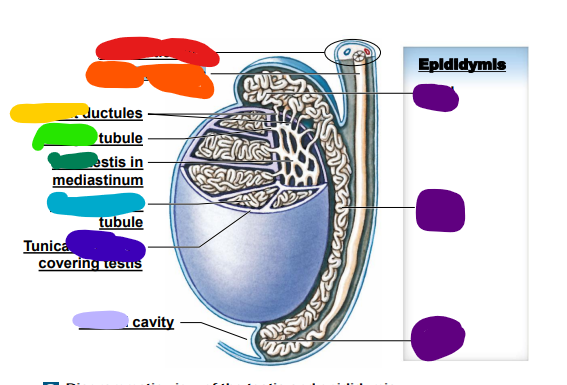
water; only
permeable to water (green)
reabsorption of
water; only
permeable to water (green)
5
New cards
Distal Convoluted
________ convoluted tubule
Tubule (DCT)
Active, regulated
secretion of ions, acids,
toxins
– Selective reabsorption
of sodium & calcium
ions
– Reabsorption of water
– Section used in
regulation of
glomerular filtration
rate (GFR)
(blue)
Tubule (DCT)
Active, regulated
secretion of ions, acids,
toxins
– Selective reabsorption
of sodium & calcium
ions
– Reabsorption of water
– Section used in
regulation of
glomerular filtration
rate (GFR)
(blue)
6
New cards
proximal
______ convoluted tubule rabsorbs materials we want to keep (proteins, water)
7
New cards
microvilli
the ______ in the proximal convoluted tubule help to excrete and absorb
8
New cards
nephron
the _______ is the smallest functional unit of the kidney.... functions great but not based off of size!
9
New cards
nephron
________ tissue in kidney
10
New cards
absorption
loop of henley correlates w what process
11
New cards
thick (ascending)
loop of henly-
____ limb is important for excreting sodium-... helps to regulate water intake/loss
____ limb is important for excreting sodium-... helps to regulate water intake/loss
12
New cards
high
too much sodium --> too much water diffusion --> _____ blood pressure
13
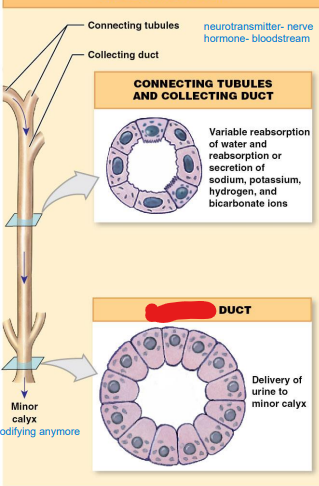
New cards
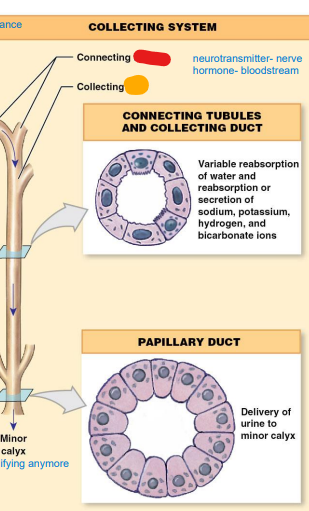
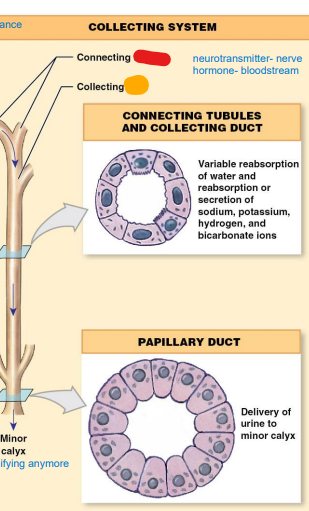
collecting
______ System (still reabsorbing things, final chance)
• Connecting tubules
• Collecting ducts
• Both of these sections will
reabsorb water; secrete or
reabsorb ions
– Last adjustments to
filtrate before excretion
• Papillary ducts
• Connecting tubules
• Collecting ducts
• Both of these sections will
reabsorb water; secrete or
reabsorb ions
– Last adjustments to
filtrate before excretion
• Papillary ducts
14
New cards
tubules
collecting ____:
DCT
of each nephron empties
filtrate to this (red)
DCT
of each nephron empties
filtrate to this (red)
15
New cards
duct
collecting ______: Several
connecting tubules drain
into this tube (orange)
connecting tubules drain
into this tube (orange)
16
New cards
papillary
____ ducts: excrete
filtrate; now urine
filtrate; now urine
17
New cards
minor
once we hit the ________ calyx, not modifying anymore
18
New cards
juxtaglomerular
_____ complex:
• Macula densa cells
• Juxtaglomerular cells
• Extraglomerular mesangial cell
(repeat)
• Macula densa cells
• Juxtaglomerular cells
• Extraglomerular mesangial cell
(repeat)
19
New cards
BP
juxtaglomerular complex: will alter arteriole & systemic ___
– Monitor Arteriole BP
– Monitor DCT filtrate ion concentration
– Monitor Arteriole BP
– Monitor DCT filtrate ion concentration
20
New cards
arterioles
Arteriole BP ∆ via
1. Constriction & dilation of ________; afferent & efferent
1. Constriction & dilation of ________; afferent & efferent
21
New cards
angiotensin
contraction & dilation of arterioles
-breaks _____ down (1 and 2 )
-2 stimulates aldosterone
-aldosterone increase blood pressure
-breaks _____ down (1 and 2 )
-2 stimulates aldosterone
-aldosterone increase blood pressure
22
New cards
renin
2. _____: precursor for angiotensin (lin liver); raises BP
23
New cards
erythropoietin
3. _______: (JMC/juxtamedullary complex) regulate density of RBCs (MORE)
24
New cards
GFR
b/c of arteriole BP change-
____ (glomuler filtration rate will be altered due to these changes
____ (glomuler filtration rate will be altered due to these changes
25
New cards
ureters
_______: drain urine from kidneys to bladder; exits at hilum;
• enters bladder at trigone via ureteal orifices
• Peristaltic contractions & gravity move urine toward urinary
bladder
• enters bladder at trigone via ureteal orifices
• Peristaltic contractions & gravity move urine toward urinary
bladder
26
New cards
peristaltic
ureter
__________ contractions & gravity move urine toward urinary
bladder
__________ contractions & gravity move urine toward urinary
bladder
27
New cards
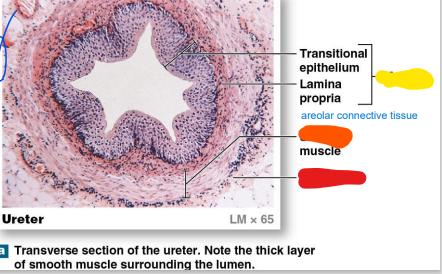
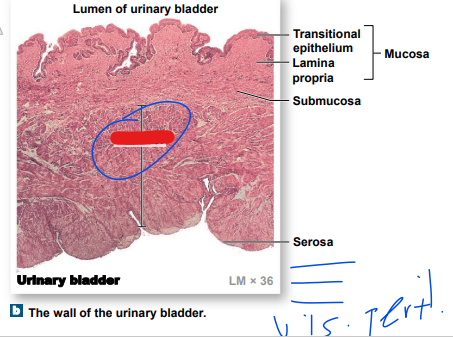
mucosa
Inner _______: Lined with transitional epithelium (yellow)
-areolar connective tissue
-areolar connective tissue
28
New cards
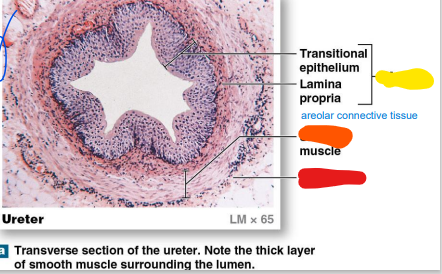
middle (smooth)
_____ muscular layer: longitudinal & circular smooth muscles (orange)
29
New cards
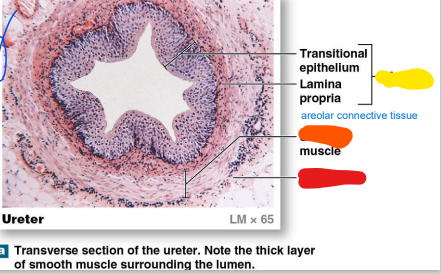
adventitia
ureter
_______: continuous with fibrous capsule & parietal
peritoneum (red)
_______: continuous with fibrous capsule & parietal
peritoneum (red)
30
New cards
rugae
allows increase in bladder size (red)
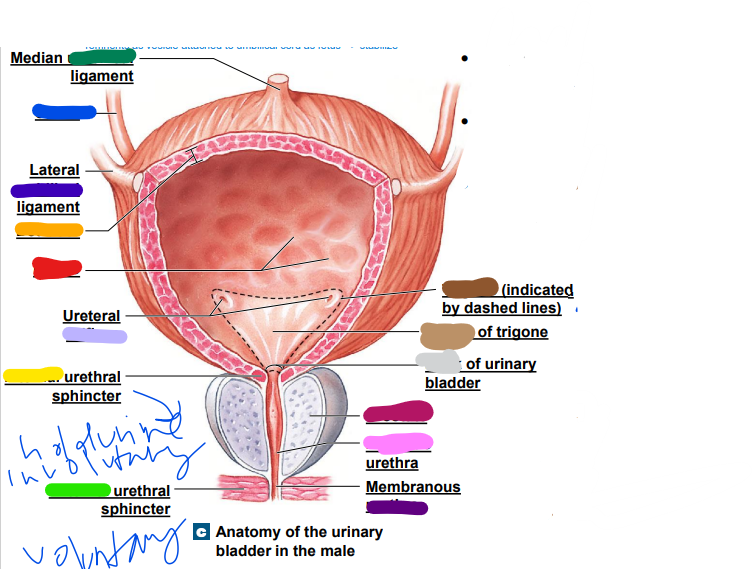
31
New cards
detrusor
smooth muscle walls (orange)
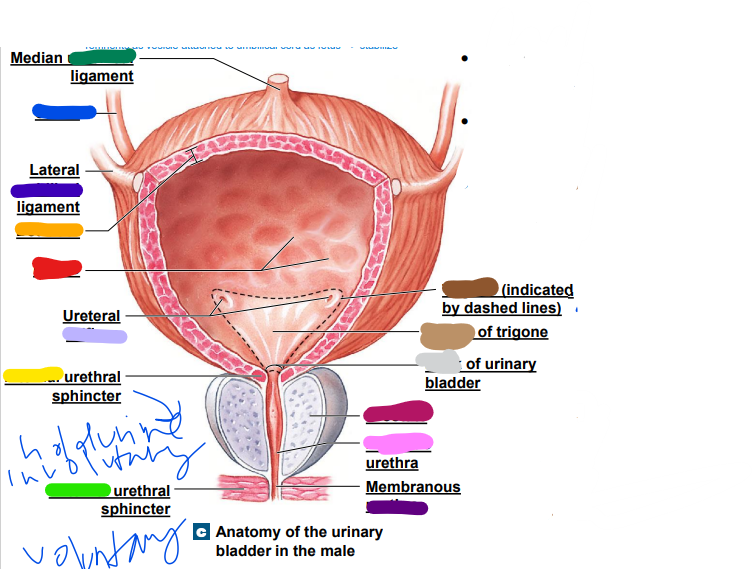
32
New cards
internal
______ urethral sphincter: automatic (involuntary) control, smooth muscle (yellow)
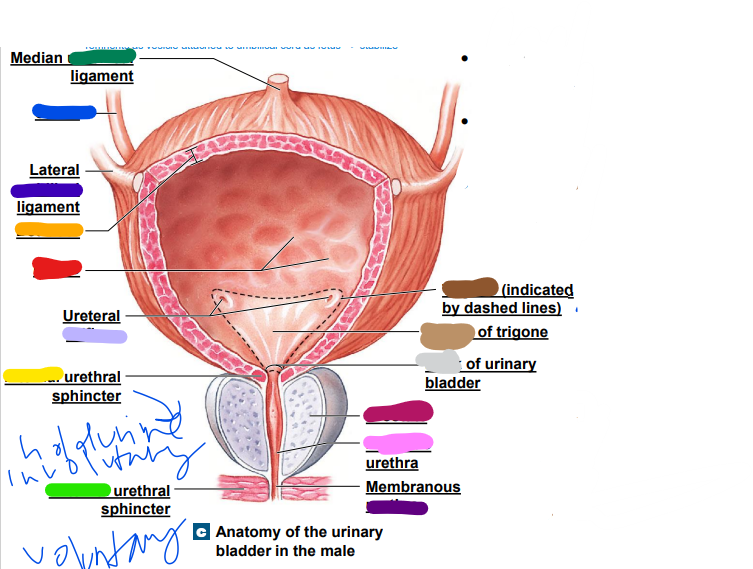
33
New cards
skeletal
external urethral sphincter: conscious control, ________ muscle (green)
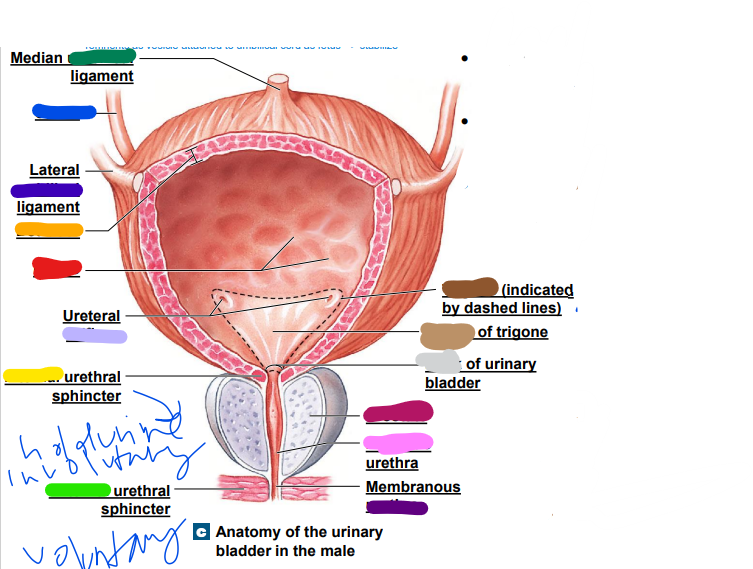
34
New cards
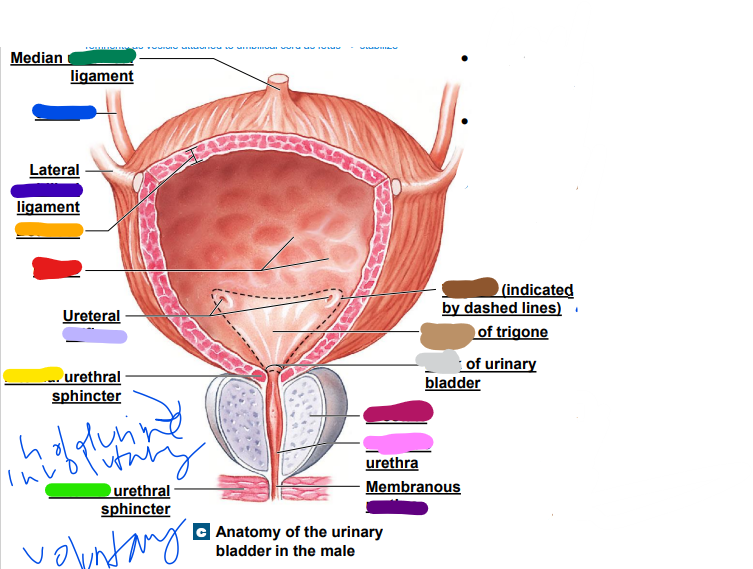
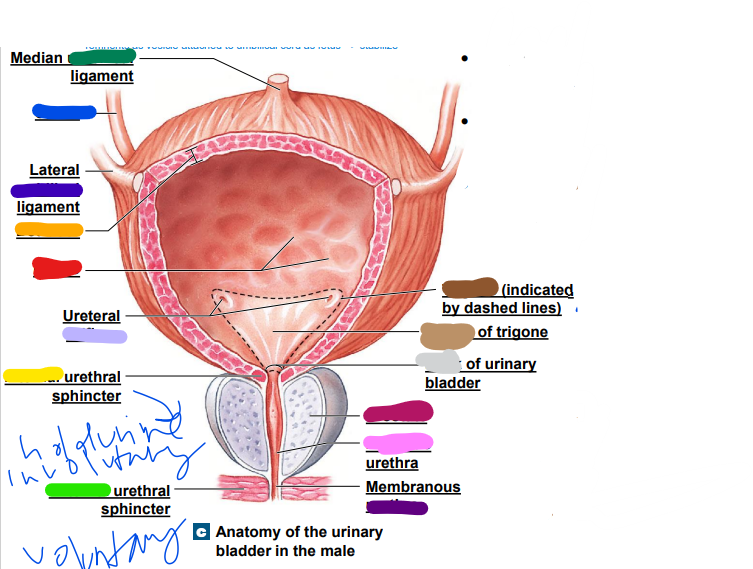
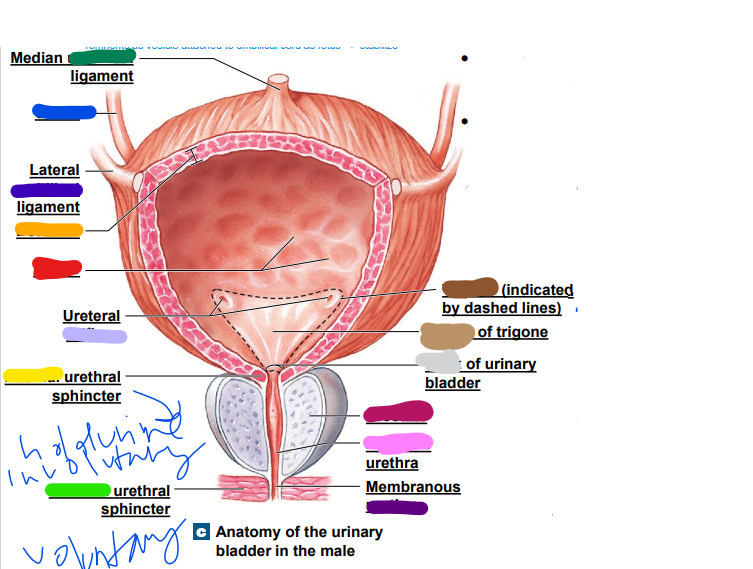
umbilical
median __________ ligament (dark green)
-remnants as vesicle attached to umbilical cord as fetus... stabilize
-remnants as vesicle attached to umbilical cord as fetus... stabilize
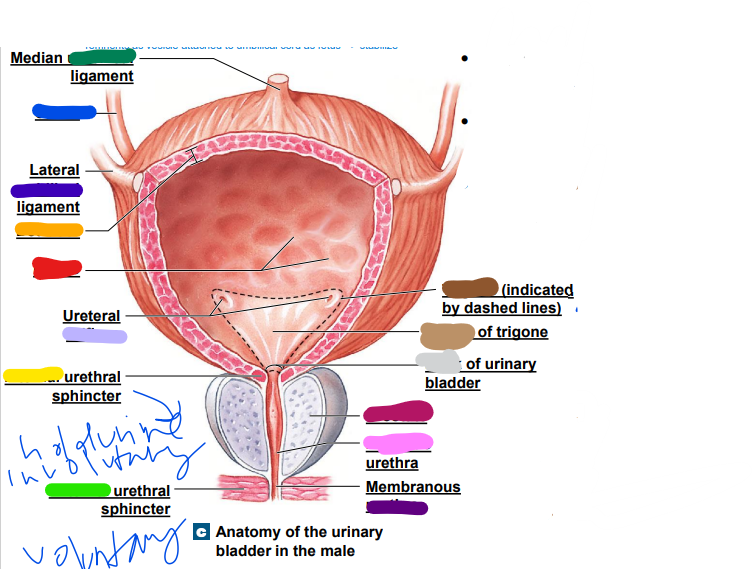
35
New cards
ureter
light blue ______
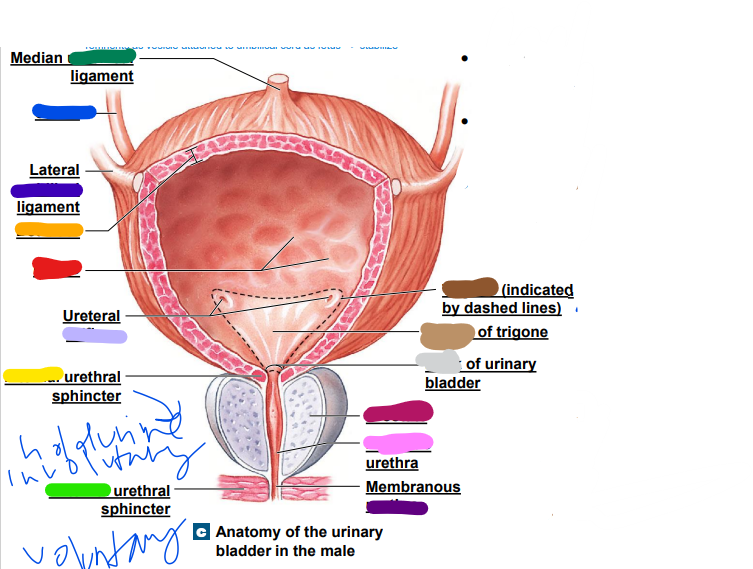
36
New cards
umbilical
later ______ ligament (dark blue)
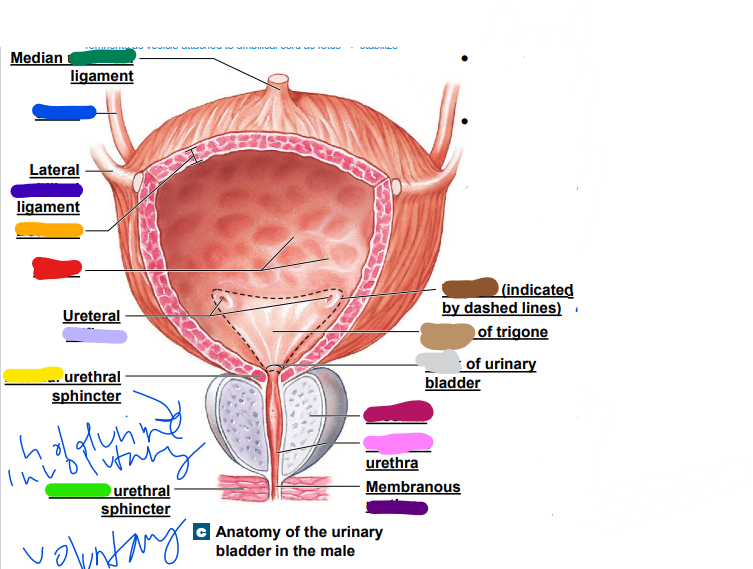
37
New cards
orifices
light purple: ureteral _________
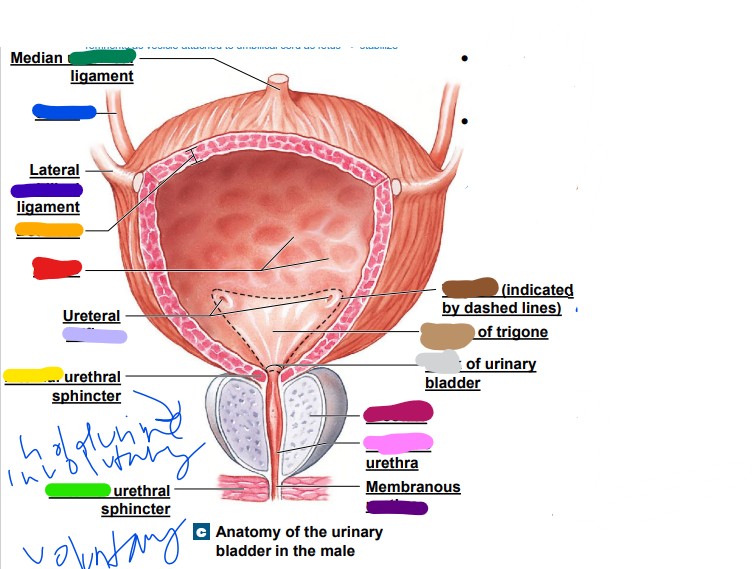
38
New cards
urethra
dark purple: membranous _______
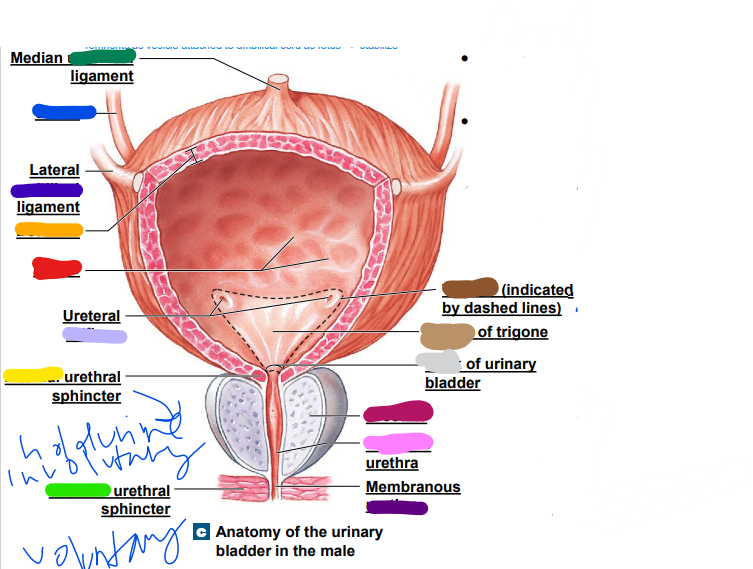
39
New cards
prostate
magenta: _______
40
New cards
prostatic
pink: _________ urethra
41
New cards
neck
light grey: _______ of urinary bladder
42
New cards
trigone
dark brown: ________
openings
openings
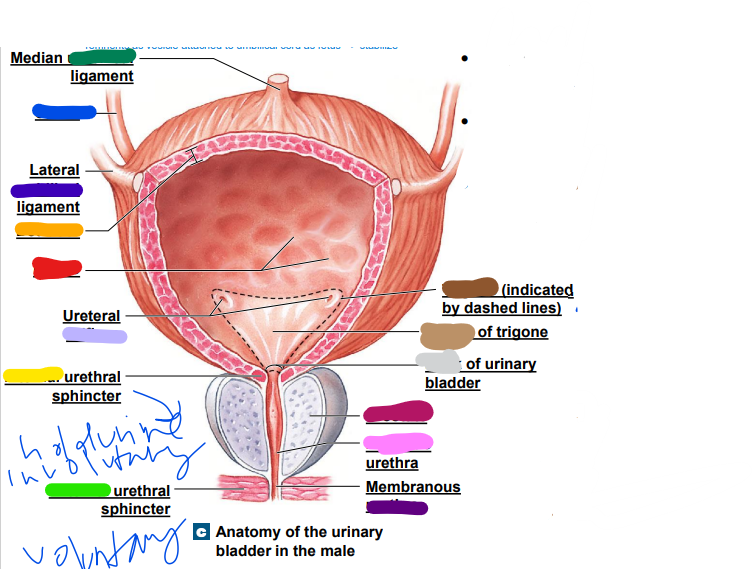
43
New cards
trigone
light brown: center of _____
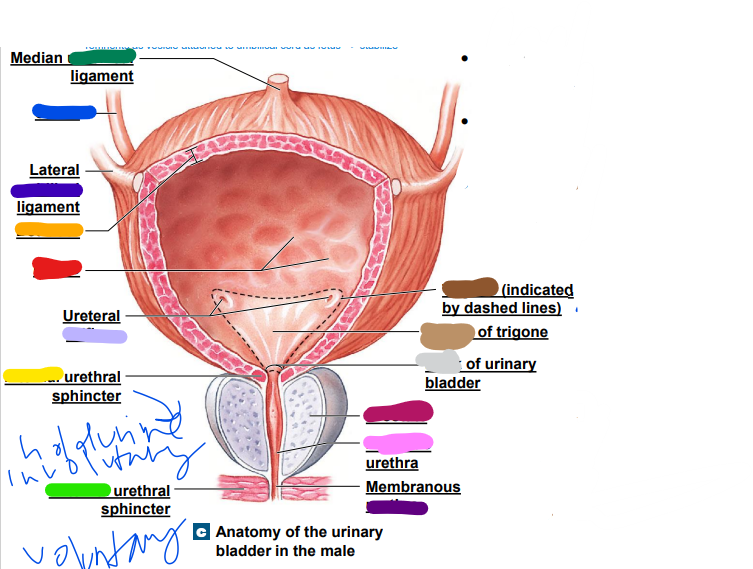
44
New cards
detrusor
______- contracts to push urine
-2 longitudinal
-1 circular
(submucosa right?)
-2 longitudinal
-1 circular
(submucosa right?)
45
New cards
visceral
in this, the serosa is equivalent to ________ peritoneum
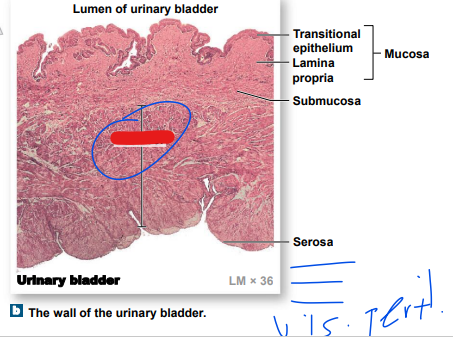
46
New cards
smooth, mucous
Urethra
• Circular _____ muscle
• _______- producing cells
in epithelium
• Circular _____ muscle
• _______- producing cells
in epithelium
47
New cards
female urethra... memorize pls
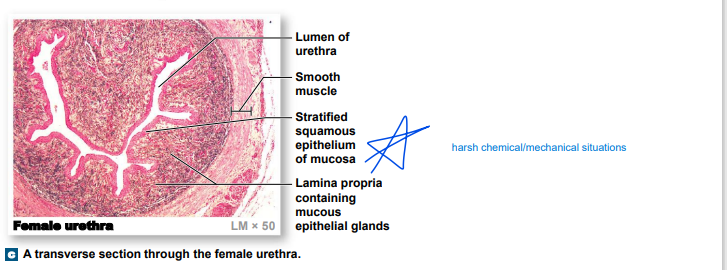
48
New cards
stratified
______ squamous epithelium of mucosa- harsh chemical/mechanical situations
49
New cards
prostatic
Males
________
urethra: through
prostate gland (orange)
________
urethra: through
prostate gland (orange)
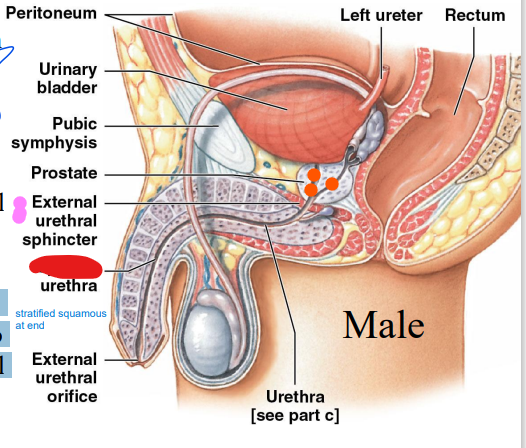
50
New cards
membranous
Males
________
urethra: Short
segment
through external
urethral
sphincter (pink)
________
urethra: Short
segment
through external
urethral
sphincter (pink)
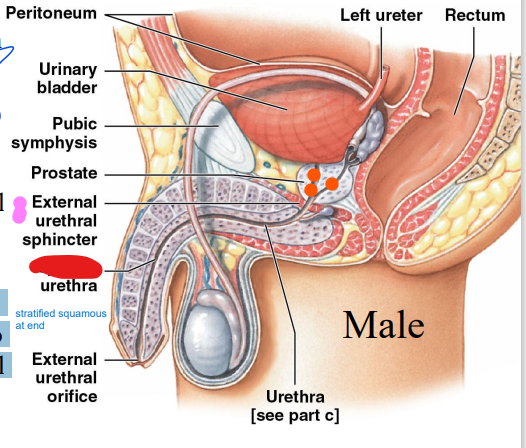
51
New cards
Spongy
Males
_____ urethra:
through penis to
external urethral
orifice; can
expand (red)
_____ urethra:
through penis to
external urethral
orifice; can
expand (red)
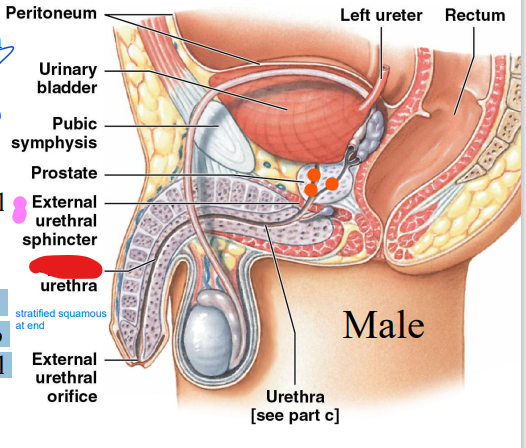
52
New cards
shorter
Females
External urethral orifice near anterior wall of vagina
• Much _____ urethra
External urethral orifice near anterior wall of vagina
• Much _____ urethra
53
New cards
pontine
Urine Storage & Voiding Reflexes: involve spinal
cord & ______centers of brain (in pons)
cord & ______centers of brain (in pons)
54
New cards
sympathetic
Urine Storage Reflex (continence)
– Urine storage increases __________ activity (fight or flight)
– Urine storage increases __________ activity (fight or flight)
55
New cards
detrusor
Urine Storage Reflex (continence)
• Stretch receptors in bladder signals
sympathetic reflex
• Inhibits ________muscle
• Stimulates contraction of internal &
external urethral sphincters
• Stretch receptors in bladder signals
sympathetic reflex
• Inhibits ________muscle
• Stimulates contraction of internal &
external urethral sphincters
56
New cards
parasympathetic
Urine Voiding Reflex (micturition)
– first urge when bladder fills to ~ 200 mL
– High frequency stretch-activated spinal reflexes stimulate
_________ activity
• Detrusor contracts; smooth muscle wall of bladder
• Internal urethral sphincter relaxes; smooth muscle
– first urge when bladder fills to ~ 200 mL
– High frequency stretch-activated spinal reflexes stimulate
_________ activity
• Detrusor contracts; smooth muscle wall of bladder
• Internal urethral sphincter relaxes; smooth muscle
57
New cards
internal
Urine Voiding Reflex (micturition)
– High frequency stretch signals also decreases sympathetic
activity
• _______ urethral sphincter relaxes
– High frequency stretch signals also decreases sympathetic
activity
• _______ urethral sphincter relaxes
58
New cards
10
– Voluntary effort is needed to relax (therefore open) external
urethral sphincter; skeletal muscle
– Upon “complete void,” ~ __ mL of urine still remains
– When urinary bladder nears capacity, both urethral sphincters
will open based on pressure
urethral sphincter; skeletal muscle
– Upon “complete void,” ~ __ mL of urine still remains
– When urinary bladder nears capacity, both urethral sphincters
will open based on pressure
59
New cards
smooth, skeletal
again
1. internal urethral sphincter: ________ muscle
2. external urethral sphincter ______ muscle
1. internal urethral sphincter: ________ muscle
2. external urethral sphincter ______ muscle
60
New cards
homeostatic
Reproductive system
No major ___________ role; yet perpetuates our species
• Produces, stores, nourishes, & transports gametes
• Testes produce sperm
• Ovaries produce oocytes
No major ___________ role; yet perpetuates our species
• Produces, stores, nourishes, & transports gametes
• Testes produce sperm
• Ovaries produce oocytes
61
New cards
gonads
____: Testes/Ovaries that produce gametes & hormones
62
New cards
tract
Reproductive ___: Ducts that receive, store, & transport
gametes
gametes
63
New cards
accessory
______ glands: Secrete fluids
males- seminal, prostate, bulbo-urethral
males- seminal, prostate, bulbo-urethral
64
New cards
External
_________ genitalia: Perineal structures
65
New cards
scrotum
____
– Testis
– Epididymis
(red)
– Testis
– Epididymis
(red)
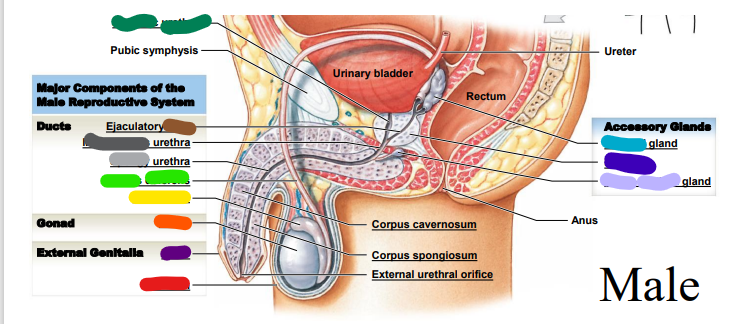
66
New cards
Testis
orange
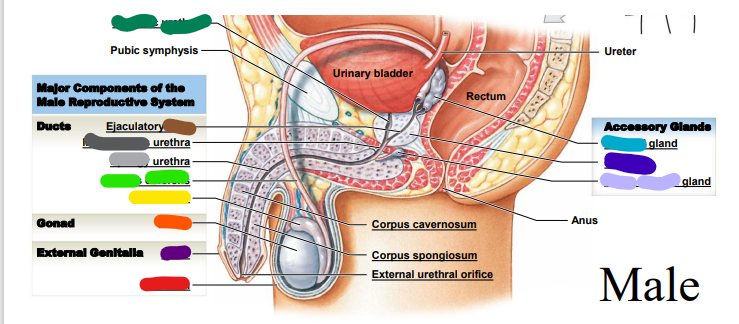
67
New cards
Epididymis
yellow
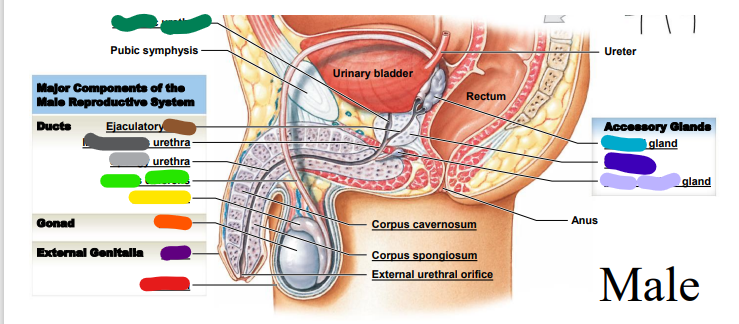
68
New cards
Ductus deferens
light green: _______ deferens
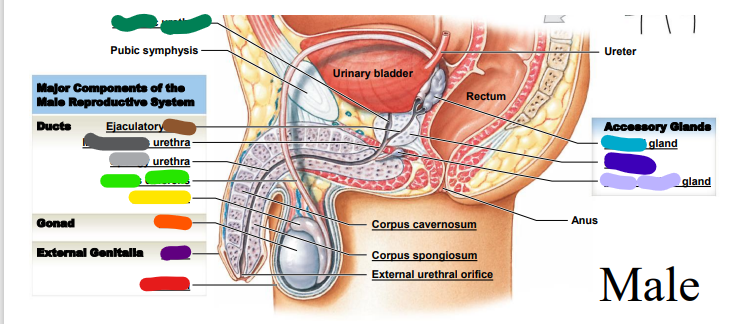
69
New cards
Urethra
dark green: prostatic___________
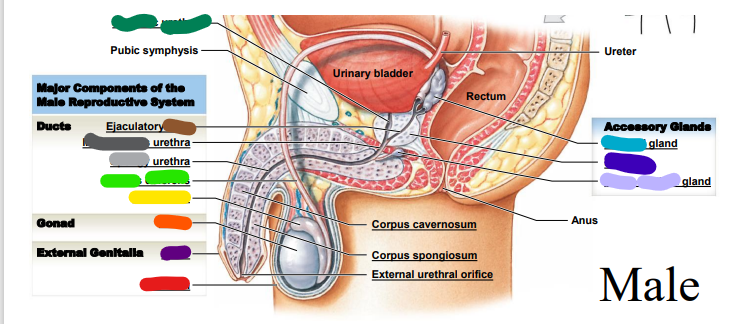
70
New cards
seminal
light blue: _______ gland
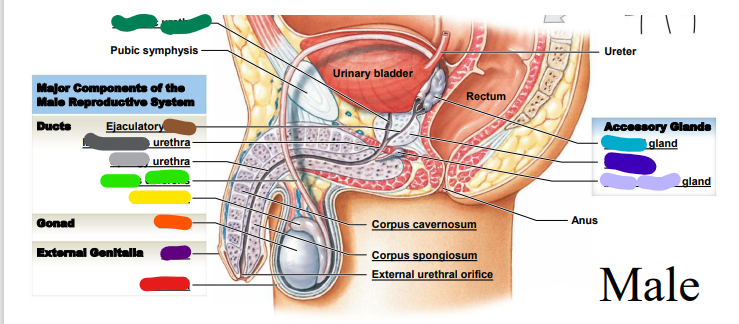
71
New cards
prostate
dark blue: _______
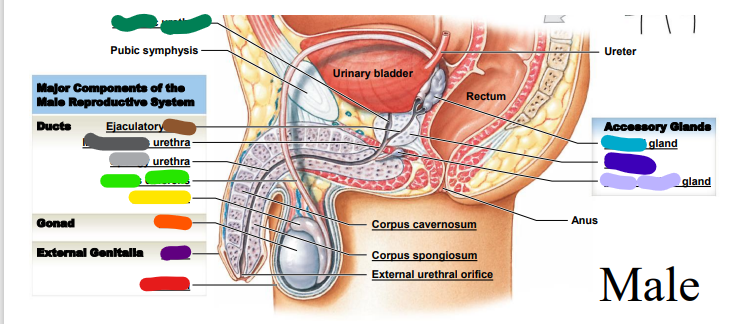
72
New cards
bulbo-urethral
light purple: _______-_______ gland
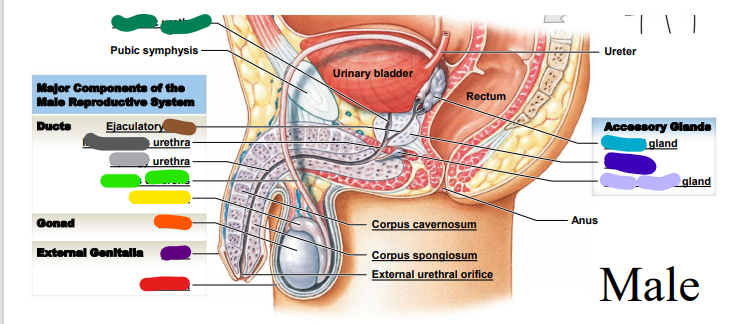
73
New cards
penis
dark purple
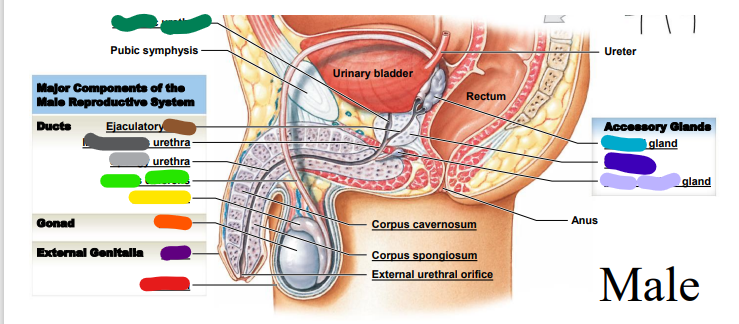
74
New cards
spongy
________ urethra (repeat, light grey)
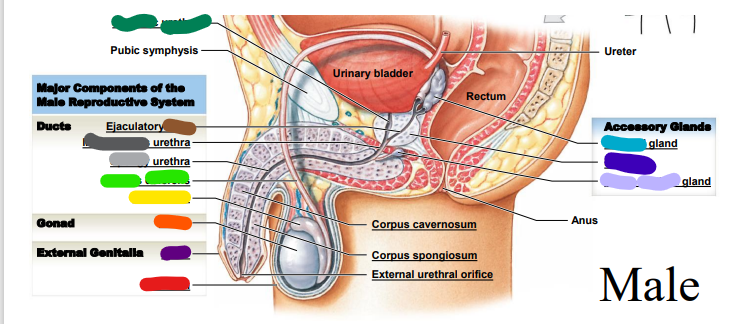
75
New cards
membranous
dark grey: ______ urethra (repeat)
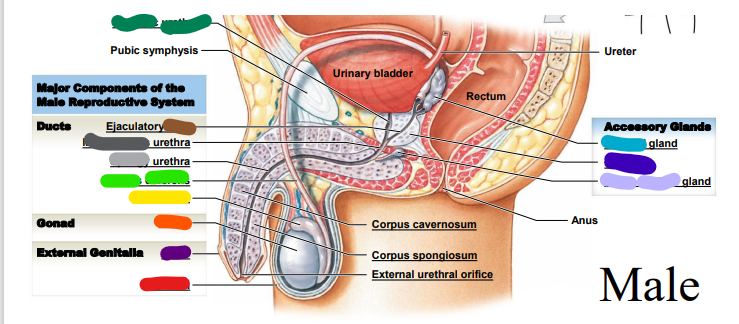
76
New cards
duct
dark brown: __________ duct
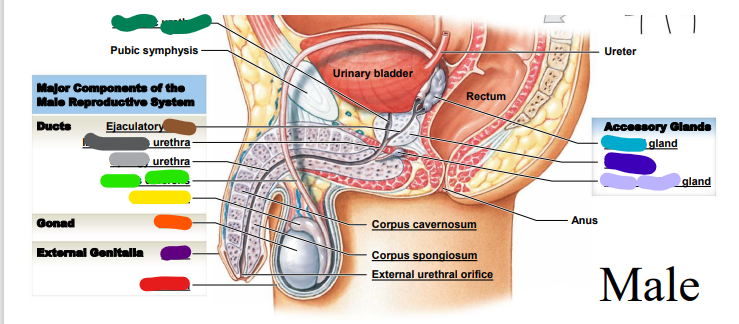
77
New cards
cavernosum
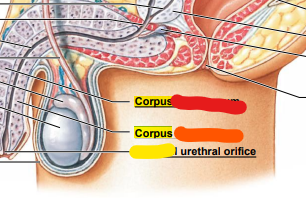
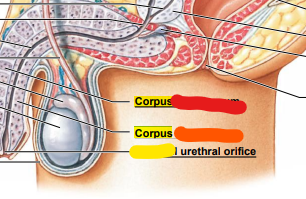
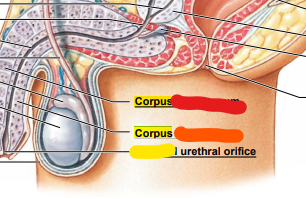
red: corpus _______
78
New cards
spongiosum
orange: corpus ______
79
New cards
external
yellow: _________ urethral orifice
80
New cards
testes
Scrotum: dual chambers that
house ______
house ______
81
New cards
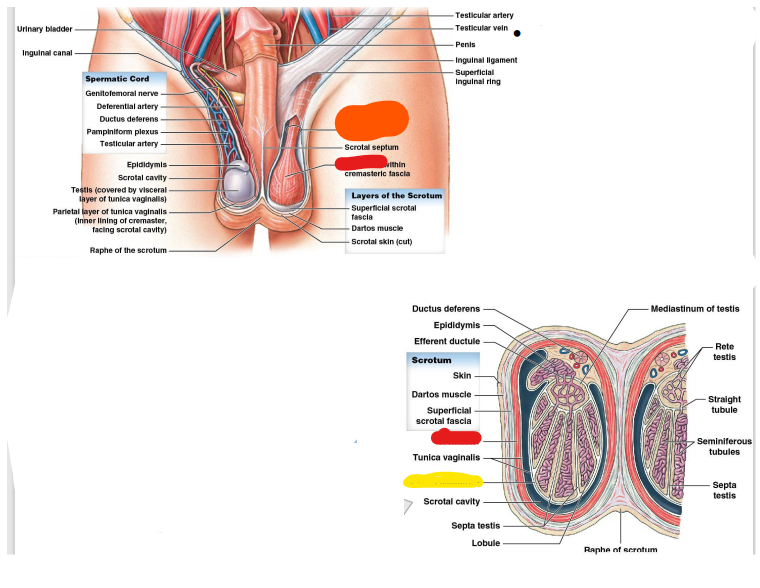
Tunica albuginea
______ _________:
connective tissue;
surrounds testes
(yellow)
connective tissue;
surrounds testes
(yellow)
82
New cards
Spermatic cord
• ______ _______ : all
testes associated
connections; pass
via inguinal canal
to peritoneal cavity
(Ductus deferens
• Nerves
• Lymphatic tissue
• Cremaster muscles)
(orange)
testes associated
connections; pass
via inguinal canal
to peritoneal cavity
(Ductus deferens
• Nerves
• Lymphatic tissue
• Cremaster muscles)
(orange)
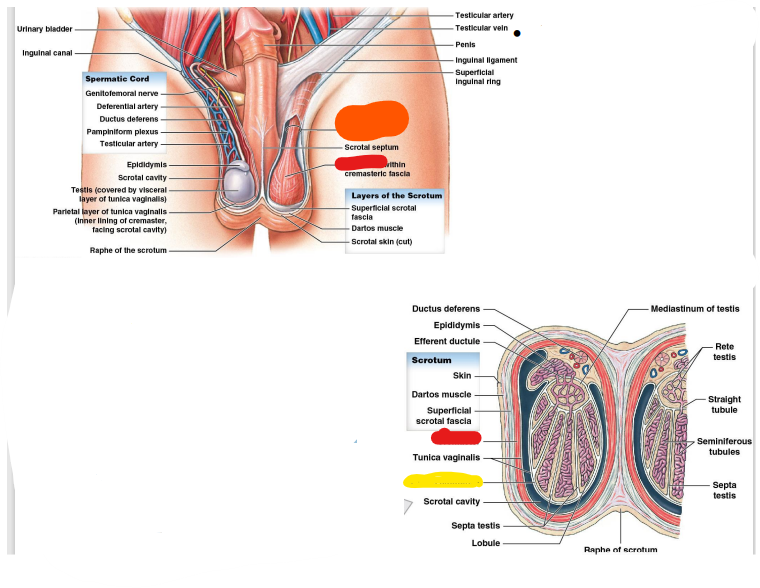
83
New cards
Ductus deferens
red
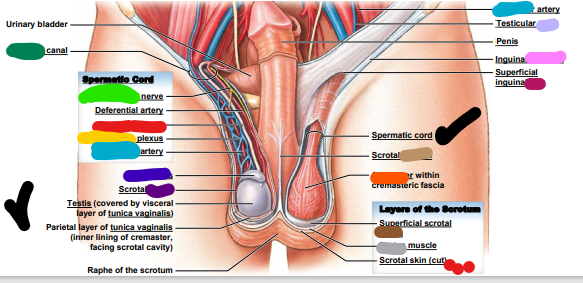
84
New cards
Cremaster
_______ muscle: skeletal
muscle
Contraction tenses scrotal
sac & pulls it closer to
body
– thermoregulation of testes
(orange)
muscle
Contraction tenses scrotal
sac & pulls it closer to
body
– thermoregulation of testes
(orange)
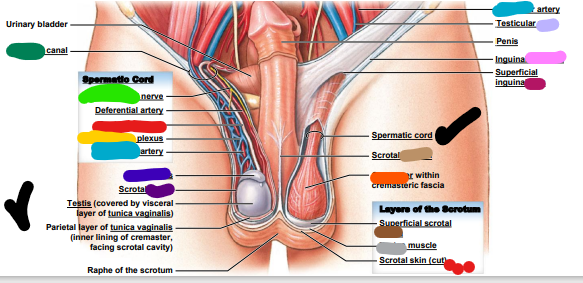
85
New cards
pampiniform
blood vessels:
__________ plexus cools
blood in arteries heading to
testes via countercurrent
heat exchange (yellow)
__________ plexus cools
blood in arteries heading to
testes via countercurrent
heat exchange (yellow)
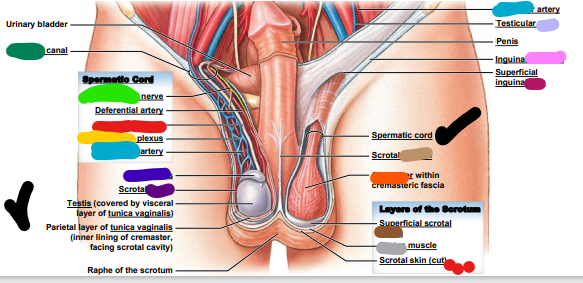
86
New cards
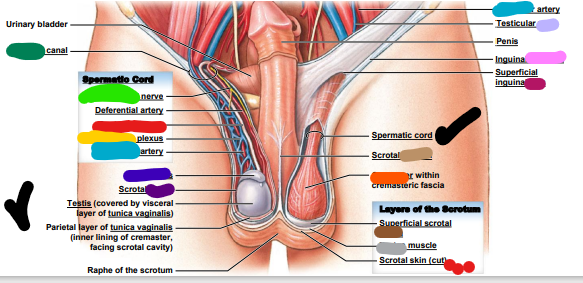
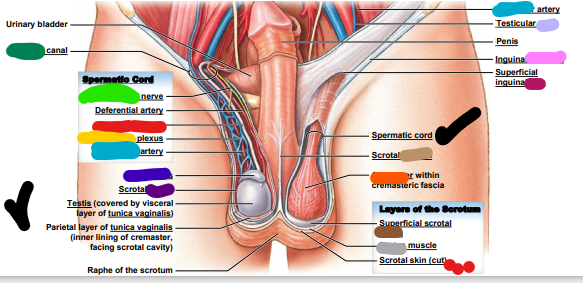
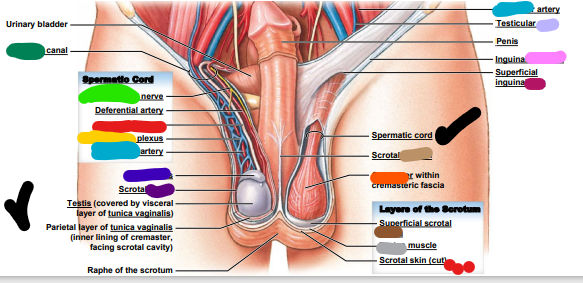
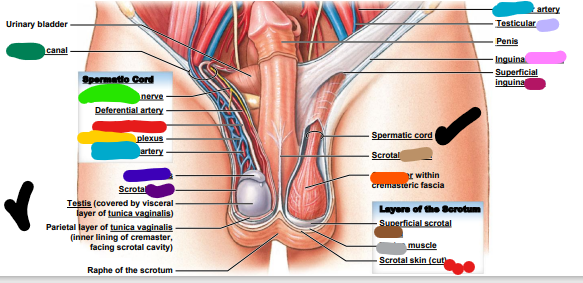
genitofemoral
___________ nerve (light green)
87
New cards
inguinal
dark green: _________ canal
88
New cards
testicular
light blue: ________ artery
89
New cards
epididymis
dark blue: ________
90
New cards
cavity
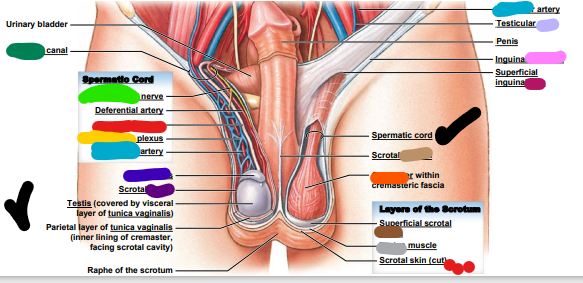
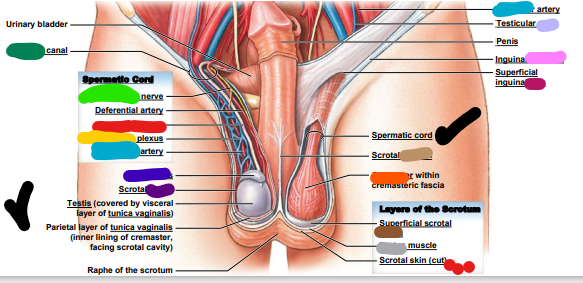
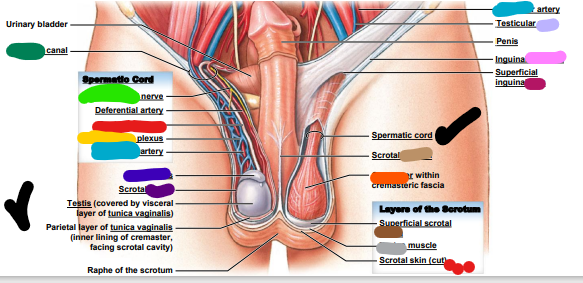
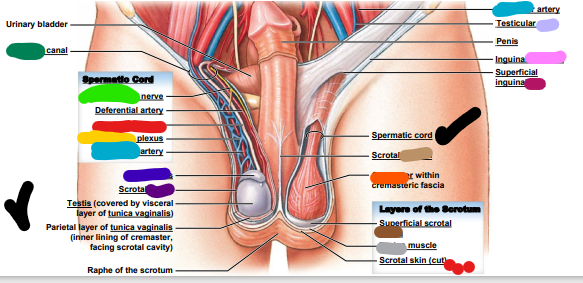
dark purple: scrotal _______
91
New cards
vein
light purple: testicular ____
92
New cards
ligament
pink: ______ ligament
93
New cards
ring
magenta: superficial inguinal ______
94
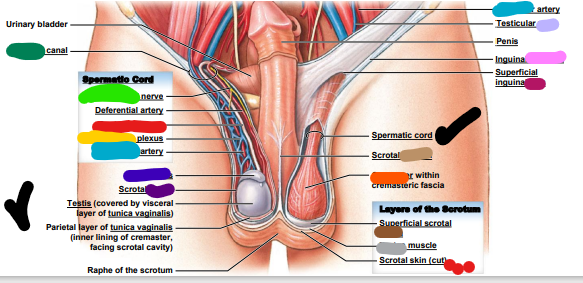
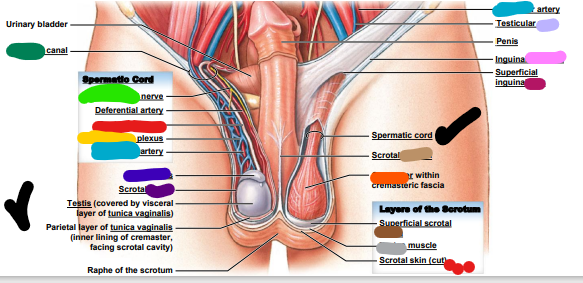
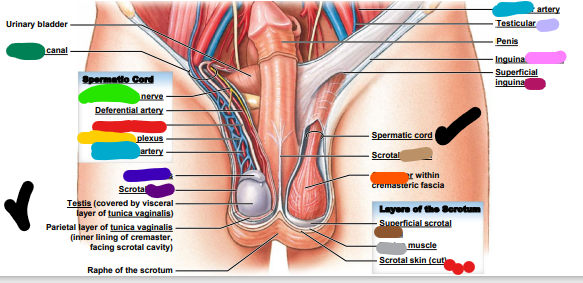
New cards
septum
light brown: scrotal ______
95
New cards
fascia
dark brown: superficial scrotal _______
96
New cards
dartos
light grey: _______ muscle
97
New cards
spermatic cord
red: ________ ______
98
New cards
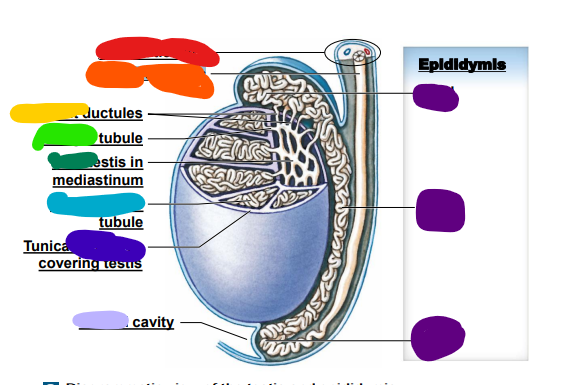
ductus deferens
orange: _____ _______
-THIS IS CUT IN VASECTOMY
-THIS IS CUT IN VASECTOMY
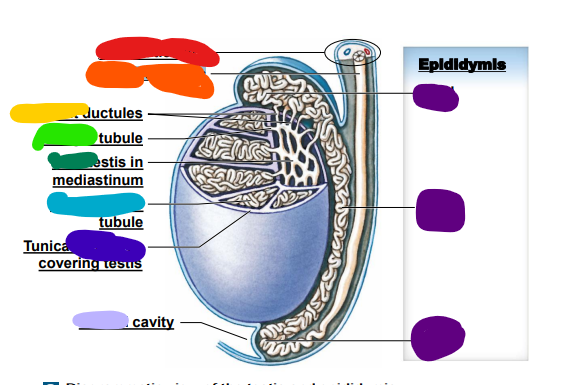
99
New cards
efferent
yellow: _______ ductules
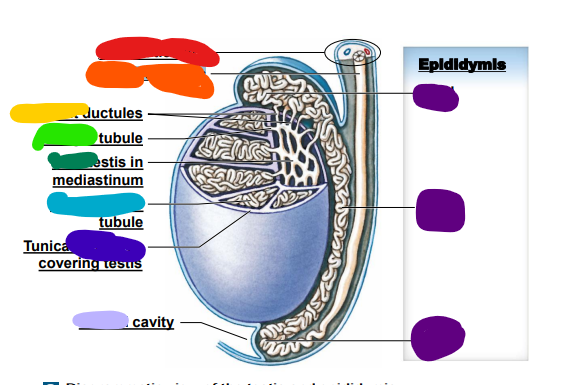
100
New cards
straight
light green: ______ tubule