Astronomy Midterm - Russo's Class
Lines of latitude begin at the equator and run _____ around the circumference of the Earth.
East and West
Eratosthenes took two measurements, one in Alexandria and the other one in Syene to measure the Earth's _____.
Circumference
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Lines of latitude begin at the equator and run _____ around the circumference of the Earth.
East and West
Eratosthenes took two measurements, one in Alexandria and the other one in Syene to measure the Earth's _____.
Circumference
The Earth travels around the sun in an _____ orbit.
Elliptical
Our Sun began its life as a molecular cloud of ______.
Hydrogen (+ Helium)
A light year is ______ miles.
About 5.88 Trillion
____ is the fourth planet from the Sun.
Mars
____ literally means 'round stone'.
Lithosphere
____ is the Babylonian goddess of fertility.
Ishtar
____ is when a fertilized cell splits into 2 equal parts.
Cleavage
The Earth is surrounded by an invisible grid used to help plot the coordinates of the surrounding universe known as the _____.
Celestial sphere
With regard to temperature, a sun spot is ____ than the Sun.
Cooler
Know the steps involved in creating heavier elements inside the heart of stars.
Nucleosysthesis - the fusion of nuclei deep within the cores of stars that began creating heavier and heavier elements.
How old is our Sun if it is at half life, and what does that mean?
4.6 Billion years old; It means it has completed half of its solar life.
What are Silicates?
Minerals composed of silicon and oxygen, common in Earth's crust.
The North star is also known as _____.
Polaris
How many degrees = one hour?
15 degrees
What is the significance of Heliocentric?
Sun-centred solar system.
What is the significance of 'A hollow ball of cells during gestation'?
Blastocyst - develops into an embryo attached to a placenta, surrounded by fluid-filled membranes.
What is the significance of 'Fluctions or calcalus'?
Developed by Isaac Newton; Fluctions is an early term for calculus, a branch of mathematics that studies change and motion.
What is the significance of 'String Theory'?
A theoretical framework in which particles are described as one-dimensional strings rather than points, aiming to unify all fundamental forces.
What is the significance of 'Cepheus' and 'Draco'?
They are constellations. Cepheus is shaped as a house, Draco is shaped as a dragon. They are both northern circumpolar.
What is the significance of 'Observed sun spots'?
Originally observed by Galileo Galilei, sun spots are temporary phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that signal an increase in solar flares, resulting in higher volatile geomagnetic storm activity.
What is the significance of 'Laws of planetary motion?'
Formulated by Johannes Kepler, describing orbits of the planets around the Sun.
1. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun as a focus
2. A planet covers the same area of space and time no matter the stage of its orbit
3. A planet's orbital period is proportional to the size of its orbit
What is the significance of 'Orbital paths of comets'?
Studied by Edmond Halley, who predicted the return of the Halley's Comet. Comets orbit the Sun in the same direction as the planets, but with a more elliptical shape.
What is the significance of 'Cells begin to change or differentiate after ten weeks into a...'?
After ten weeks, cells begin to differentiate into more specialised cells, forming tissues and/or organs during embryonic development.
What is the significance of 'A fertilized egg is a...'?
It is a zygote.
What is the significance of 'Galaxies are moving away from us'?
Supports and proves that the Universe is always expanding.
What is the significance of 'Warned Roosevelt of danger of atomic energy'?
Albert Einstein warned President Roosevelt about the potential of atomic energy leading to the development of nuclear weapons.
What is the significance of 'An object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon'?
Newton's First Law of Motion - an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
What is the significance of 'Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis'?
A neurodegenerative disease affecting motor neurons; Stephen Hawking was diagnosed with ALS at age 21.
What is the significance of 'The Earth's distance from the centre of the Milky Way'?
The centre of the Milky Way is approximately 27,000 light years from Earth.
What is the significance of 'Stars that are visible all year long'?
Characterised as 'Circumpolar Stars', they never settle below the horizon.
What is the significance of 'Distance from the Earth to the Sun'?
Earth is approximately 93 million miles, or 1 astronomical unit (AU) from the Sun.
How did astronomy aid early cultures during their change from a nomadic lifestyle to an agricultural one? Give specific examples.
Certain constellations set/rise during certain seasons, marking the turn of weather and indicating ideal times for crop-growth and farming. The Egyptians' focus on Sirius predicted the flooding of the Nile, necessary for their agricultural needs.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative science and what is the impact of the latter on the scientific community?
Qualitative = quality; Quantitative = quantity. Quantitative science is essential in experimentation, testing hypotheses, collecting data, and can be used over a range of scientific fields.
Why did the gas giants form before the terrestrial planets during our solar genes?
The closer to the Sun, the hotter the compounds, so as they were further away, the compounds in the colder region of the solar nebula moved to create gas giants.
Nicholas Copernicus was responsible for today's accepted theory of a heliocentric solar system. Yet during his time he published axioms to the contrary. One such axiom says, "The centre of the universe is near the sun." Why would Copernicus publish something different than his research?
During his time, the Catholic Church heavily endorsed the geocentric model (Earth being the centre of the universe), so Copernicus published contradictory opinions to his own research as to avoid conflict and persecution by the church.
Arrange in order:
Homo Erectus; Australopithecus; Homo Habilis; Homo Sapiens; Homo Neanderthals; Cro Magnon; Ardipithicus.
Correct order:
Ardipithicus; Australopithecus; Homo Habilis; Homo Erectus; Homo Neanderthal; Cro Magnon; Homo Sapiens.
List ten phases within a star's formation.
1. Molecular Cloud of Hydrogen
2. Dark Star
3. Fuse; Photon Effect
4. Protostar
5. Angular Momentum
6. Solar Nebula
7. T-Tauri Phase
8. Post T-Tauri Phase
9. Main Sequence
10. Stable Star
Know the facts about Stone Henge.
1. Prehistoric megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England.
2. Constructed around 3000 BC to 1600 BC.
3. Speculated to have been used for ceremonial/religious purposes, possibly related to astronomy.
4. Its stones align with the Summer Solstice sunrise.
5. 83 stones at Stone Henge currently.
Know the facts about the Babylonians.
1. Created the great empire of Babylon, first to cover nearly all of Mesopotamia.
2. Babylonians thought the planets and stars were Gods.
3. First civilization to map the constellations.
4. Calendar based on the phases of the moon and thus, also the sun.
What is the difference between Aphelion and Perihelion with regard to the Earth's orbit around the Sun and total distance traveled?
Aphelion - the point in Earth's orbit furthest from the Sun; Furthest away around July 4th; about 94.5 Million miles away.
Perihelion - the point in Earth's orbit closest to the Sun; closest around January 4th; about 91.4 Million miles away.
Total distance traveled by Earth's orbit is consistent, although the speed of Earth's travel changes - becoming faster at Perihelion and slower at Aphelion.
What are the 11 body systems?
1. Integumentary System
2. Circulatory System
3. Respiratory System
4. Digestive System
5. Urinary System
6. Muscular System
7. Skeletal System
8. Nervous System
9. Endocrine System
10. Reproductive System
11. Lymphatic System
Explain agglomeration with regard to the formation of celestial objects.
Agglomeration is the process by which small particles/fragments collide and stick together to form larger bodies/fragments/objects.
What happened (in detail) during the first three seconds in the beginning of the Universe?
1st. The Universe underwent rapid sudden expansion and cooling, a period known as cosmic inflation (Big Bang).
2nd. The Universe was shaped and set to continually expand.
3rd. Basic particles then elements began to form, forming protons and neutrons.
Explain the photon effect with regard to a star's stabilization.
Photon Effect refers to the balance between gravitational collapse and radioactive pressure. As a star forms, nuclear fusion in its core produces photons that exert outward pressure, balancing the inward pull of gravity and stabilizing the star.
What happens to an objects rotation as it becomes denser?
As an object becomes denser, its rotation can increase due to the conversation of angular momentum. An object's mass distribution becomes more compact the faster it rotates.
What happens to a protoplanet as its size increases?
As its gravitational pull strengthens, it attracts more surrounding material (leading to rapid growth). Heavier elements sink to the centre as lighter elements rise to the surface.
What are the 4 atmospheric layers and give an example of what can take place in each.
1. Troposphere - Lowest layer, where weather occurs. Snow storms can happen here.
2. Stratosphere - Above the Troposphere; Contains the Ozone Layer. Weather balloons can reach this layer.
3. Mesosphere - Third layer. Meteors burn up in Earth's atmosphere.
4. Thermosphere - The outermost layer, very high temperatures. Auroras occur here and the International Space Station orbits.
Please know both orbital speed, and rotation (around the axis) speed.
Orbital Speed - Speed at which Earth travels along its orbit around the Sun. Average orbital speed of Earth is about 29.78 km/s (Round to 30 km/s).
Rotation Speed - Speed at which Earth rotates on its axis. Average rotational speed of Earth is about 1670 km/her (1037 mph) at the equator.
Gemini (Season and Mythology)
Winter; Twins Castor and Pollux, sons of Queen Leda and Zeus.
Scorpio (Season and Mythology)
Summer; Scorpion that killed Orion.
Leo (Season and Mythology)
Spring; Lion that terrorized town of Nemea, was killed by Hercules.
Sagittarius (Season and Mythology)
Summer; Represents Satyr, son of Pan who invented archery and hunting on horseback.
Pegasus (Season and Mythology)
Autumn; Winged Horse, born from Medusa after she was killed by Perseus.
Cassiopeia (Season and Mythology)
Northern Circumpolar; Autumn; Vain queen Cassiopeia, wife to king Cepheus and mother of Andromeda.
Canis Major (Season and Mythology)
Winter; Laelaps, a dog so swift no prey could escape it except for the Teumessian Fox - they went on an unending chase.
Cepheus (Season and Mythology)
Northern Circumpolar; Autumn; King Cepheus of Ethiopia, husband to Cassiopeia and father of Andromeda.
Draco (Season and Mythology)
Northern Circumpolar; Summer; Dragon that guarded the golden apples on Mount Atlas in the Garden of Hera. Hercules killed him.
Cygnus (Season and Mythology)
Summer; The swan that Zeus disguised himself as to have an affair with Queen Leda of Sparta.
Ophiuchus (Season and Mythology)
Summer; Represents a man coiled up/wrestling a snake.
Ursa Major (Season and Mythology)
Northern Circumpolar; Spring; One of the two nymphs that cared for Zeus after hiding him from Cronus, depicted as a bear.
Ursa Minor (Season and Mythology)
Northern Circumpolar; Summer; One of the two nymphs that cared for Zeus after hiding him from Cronus, depicted as a little bear.
Orion (Season and Mythology)
Winter; Son of Poseidon, skilled hunter, killed by a scorpion (Scorpio) for being too boastful.
Taurus (Season and Mythology)
Winter; Represents a bull, one of Zeus' disguises.
Lyra (Season and Mythology)
Summer; Represents Orpheus' lyre when he went to the Underworld to retrieve Eurydice.
Aquila (Season and Mythology)
Summer; Represents the eagle Zeus used to carry thunderbolts.
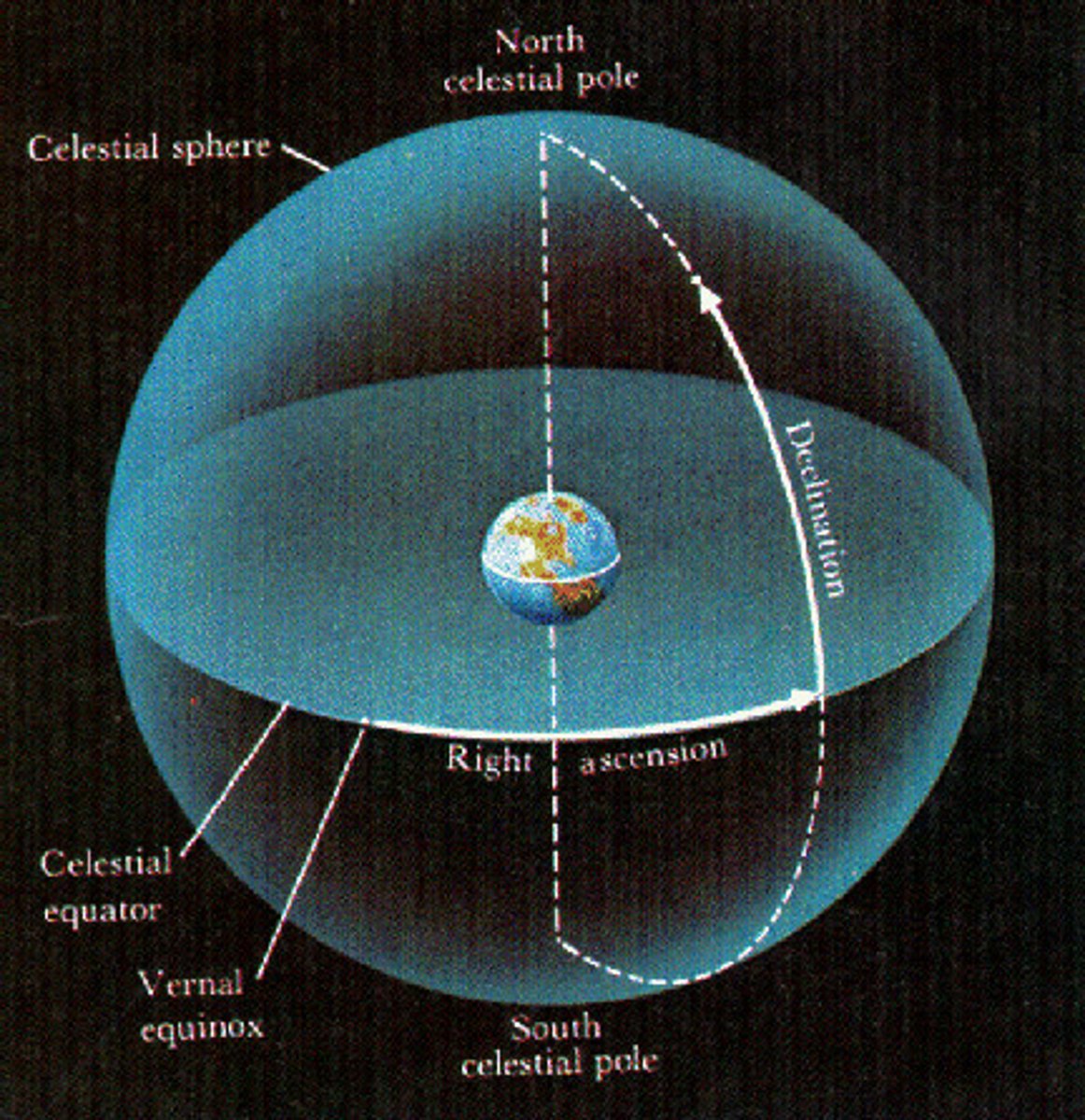
The Celestial Sphere
Focus on terms such as: Zenith, Line of Ascension, Line of Declination, Vernal equinox, Celestial Equator, Ecliptic, etc.
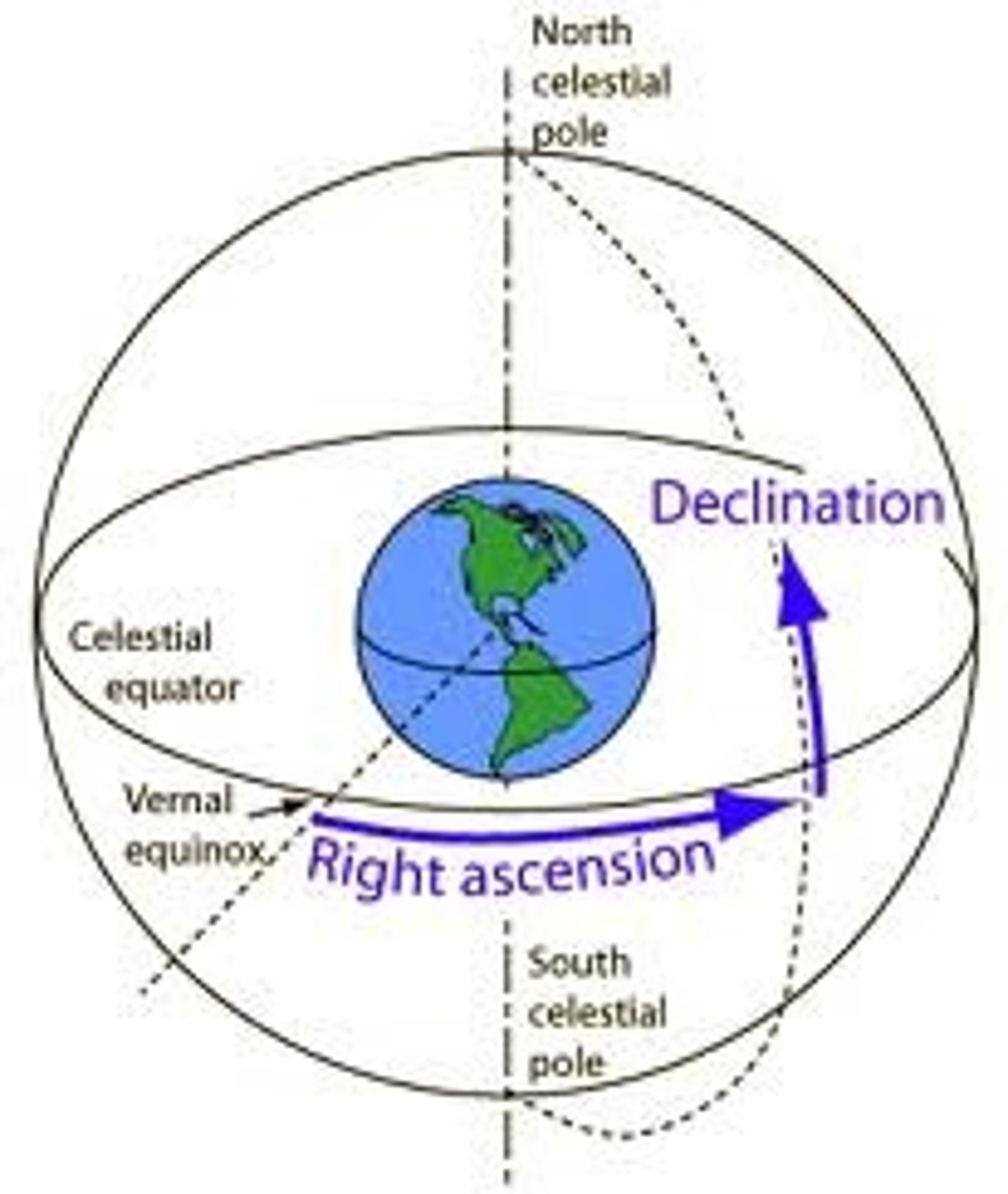
The Celestial Sphere (Different Diagram)
Focus on terms such as: Zenith, Line of Ascension, Line of Declination, Vernal equinox, Celestial Equator, Ecliptic, etc.
What is the significance of Mother Farmer with regard to the evolution of man?
The "Mother Farmer" concept symbolizes the shift from hunter-gatherer societies to agriculture, fostering permanent settlements, population growth, and the development of civilizations.
What are some negatives associated with the creation of agriculture?
Environmental degradation (soil depletion, deforestation), reliance on monoculture crops leading to vulnerability to famine, and health issues from reduced dietary diversity.
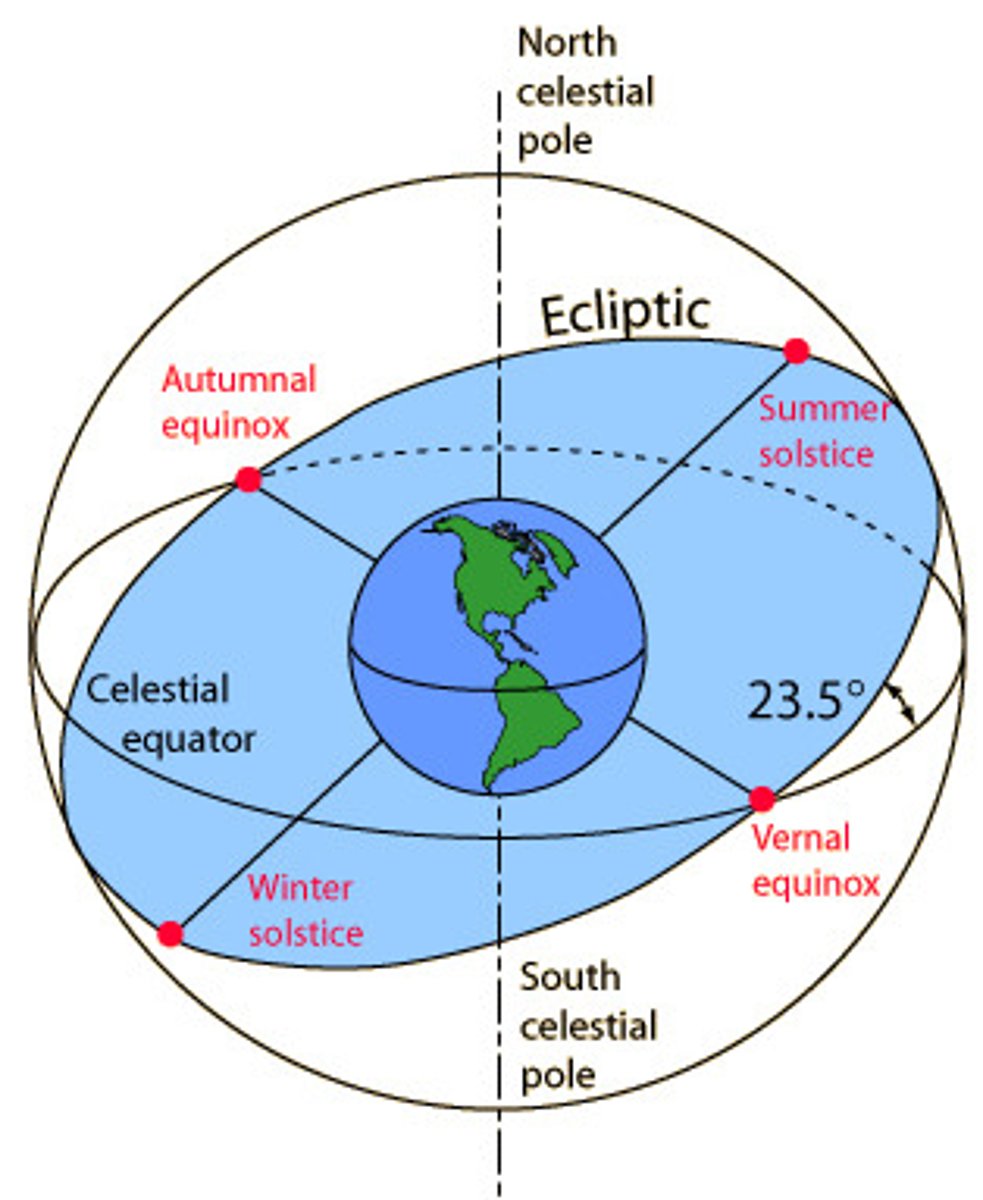
Identify the seasons and the position of the Earth during each season.
Spring: March Equinox; Sun above the equator.
Summer: June Solstice; Sun above the Tropic of Cancer (23.5 Degrees North).
Autumn: September Equinox; Sun above the equator.
Winter: December Solstice; Sun above the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 Degrees South).
Nova Sun Video - He will choose four of the most 'stand-out' questions from the document.
I suggest we focus on CME (Coronal Mass Ejection) and its definition, as well as the SDO (Solar Dynamics Observatory) and what it does, photons and plasma regarding the Sun, and the Sun's magnetic fields (as well as Solar Maximum and Solar Minimum) - just a suggestion.
History of the World in 2 Hours - He will choose 10 questions from the document.
He mentioned choosing questions regarding the shift from mammals on four legs to mammals on two (how we evolved from the trees), as well as questions regarding the steam-engine - so this is assuming he means most of the later evolutionary periods. However, I suggest focusing on questions such as Number 17 in the document, as well as 22, 27, 30, 33, 41. - Just a suggestion.
Text Task 1:
Number 5. Define a Nebula.
NEBULA - A cloud of gas and dust that is usually brighter/more prominent than other phenomenon.
Text Task 1:
Number 6. Stars form energy through...
Nuclear fusion in their cores.
Text Task 1:
Number 12. List the 5 Galaxy shapes.
1. Spiral, 2. Barred Spiral, 3. Elliptical, 4. Lenticular, 5. Irregular
Text Task 1:
Number 13. Explain what is meant by "black holes can only be detected by the material around them".
Because the gravitational pull is so strong and light cannot escape, the behaviour of surrounding material is the only thing that can be used to detect a black hole.
Text Task 1:
Number 14. What is the difference between Super-massive and stellar black holes?
-Supermassive: Typically exist in the centres of most galaxies; may be a biproduct of galaxy formation.
-Stellar: Form from collapsed remains of exploded supergiants; may be very common in all galaxies.
Text Task 1:
Number 19. What did Niels Bohr propose?
Proposed that electrons in an atom move within discrete 'orbits'. He suggested the orbits have fixed energy levels and that atoms emit/absorb energy in fixed amounts. They're called orbitals.
Text Task 1:
Number 20. What constitutes a plasma?
When a gas becomes so hot that collisions start to knock electrons out of their atoms; consists of ions and electrons; stars are made of plasma.
Text Task 2:
Number 9. Explain "Life on earth is so ubiquitous... There is a very good chance life also exists elsewhere."
The universe is so vast and life on earth is found everywhere - who is to say it does not exist in other parts of the known world/galaxy?
Text Task 2:
Number 10. The living requirement/s to be an organism is/are...
Bare minimum: Living entity must be able to replicate itself and eventually evolve. Preferably exist as cells or possess own biochemical machinery.
Text Task 2:
Number 12. What role did scientist Stanley Millar play in the primordial theory?
He recreated what he thought was Earth's primordial atmosphere in a flask. The results of his experiment were many amino acids.
Text Task 2:
Number 16. Explain the motion of the sky at the POLES, MID-LATITUDE, EQUATOR:
-Poles: All celestial objects seem to circle the pole overhead. Counter-clockwise at the North, clockwise at the South.
-Mid-latitude: Stars rise in the East, cross the sky obliquely, and set in the West. Some only circle.
-Equator: Stars and other objects appear to rise vertically in the East, move overhead, and fall vertically in the West.
Text Task 2:
Number 19. What is the difference between astrology and astronomy?
Number 20. Is there a significance to their relationship, if so what is it?
19. -Astrology is the study of the positions/movements of the sun, moon, constellations, and planets in the belief that these behaviours influence humanity.
-Astronomy is the study of celestial objects, space, and the universe within itself - in relation to all things, not only humanity.
20. They both study the placement of certain celestial objects.
Text Task 2:
Number 23. What is PRECESSION and what causes it?
Precession: The Earth's wobble that alters the direction of its axis over a 25,800 year cycle. It is caused by the gravity of the sun and moon.
Text Task 3:
Number 2. What is responsible for the phases of the moon?
The changing angles that happen during each lunar orbit.
Text Task 3:
Number 4. Explain the difference between a lunar and solar eclipse.
Lunar Eclipse: When the moon orbits Earth and moves into Earth's shadow.
Solar Eclipse: When the moon orbits Earth and blocks sunlight from reaching the Earth's surface
Text Task 3:
Number 5. What are Keplers 3 Laws?
1. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun as a focus
2. A planet covers the same area of space and time no matter the stage of its orbit
3. A planet's orbital period is proportional to the size of its orbit
Text Task 3:
Number 7. What is a planetary conjunction?
When the planets are in the sky at roughly the same time, usually in a line.
Text Task 3:
Number 8. What happens when a planet is in transit?
It means the planet has passed between the Earth and sun, crossing over the sun's disk.
Text Task 3:
Number 12. How many sections is the sky divided into, what is found within each section?
88 sections; Contains at least one constellation.
Text Task 3:
Number 13. Who is Charles Messier, and what is he known for?
-Was a French comet-hunter; most famous for his 'Catalogue of Non-comets' but also discovered M3, a globular star cluster in Canes Venatici.
Text Task 3:
Number 14. What is the NGC?
The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters.
Text Task 3:
Number 15. What are the 2 Aurorae, and what causes them?
Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis - Caused when charged particles from the sun, carried to Earth in the solar wind, become trapped by Earth's magnetic field.
Text Task 3:
Number 20. Measuring the night sky with your hand. Sketch the finger widths, joints, hand spans, and add measurements.
finger tip = 1 degree, a bent finger = distal tip 3 deg, medial finger = 4 deg, proximal finger = 6 deg, Spread hand thumb to pinky = 20 degrees
Anemella
is a diagram showing the position of the Sun in the sky as seen from a fixed location on Earth at the same mean solar time, as that position varies over the course of a year. The diagram resembles a figure eight.
Azimuth
The angle between North, measured clockwise around the observer's horizon, and a celestial body (sun, moon).
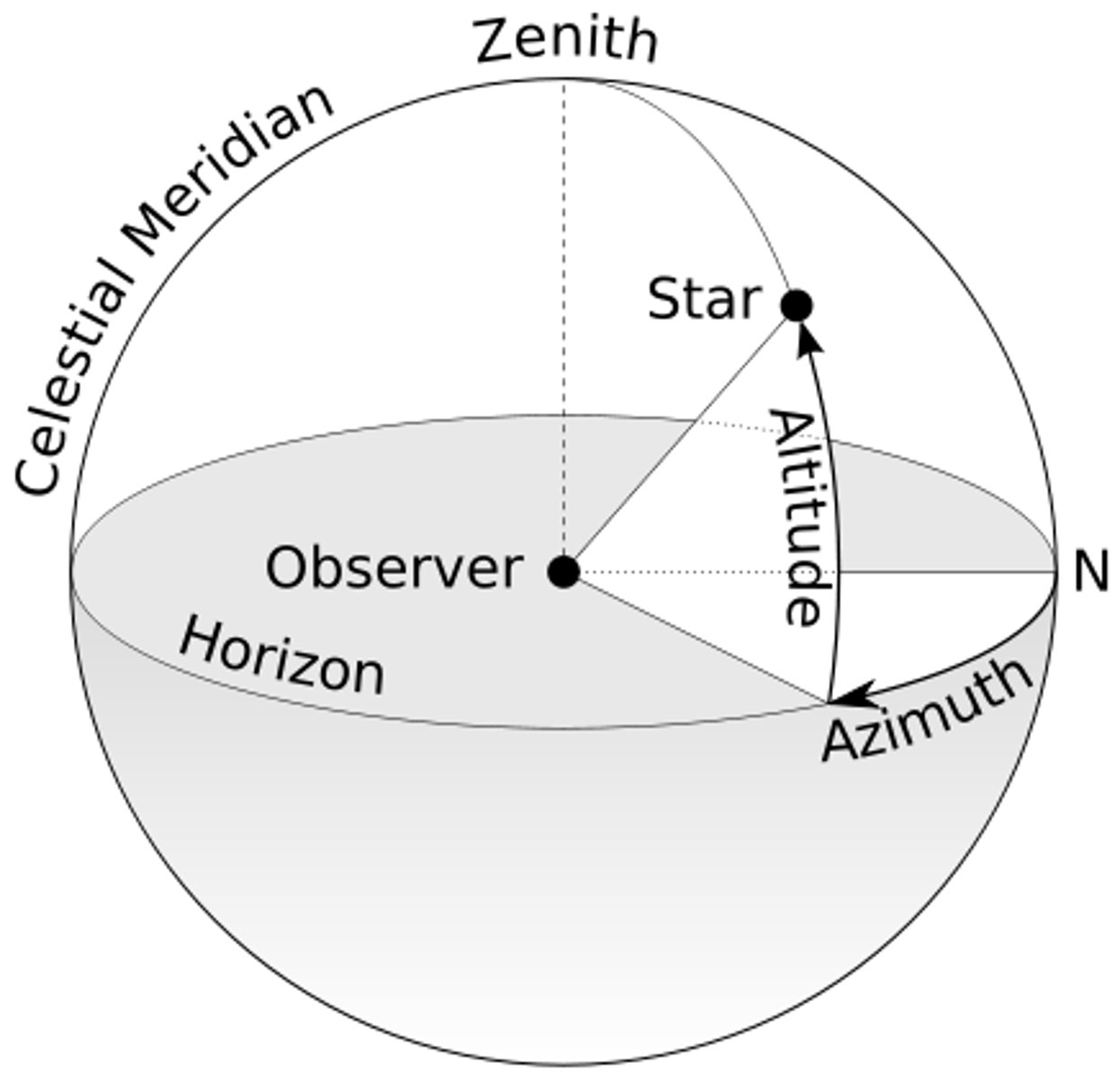
Azimuth (Different Diagram)
The angle between North, measured clockwise around the observer's horizon, and a celestial body (sun, moon).