Organic Chemistry 8: Carboxylic Acids (9-Carboxylic Acid Derivatives)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
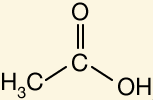
[...] functional groups contain a carbonyl and a hydroxyl group connected to the same carbon
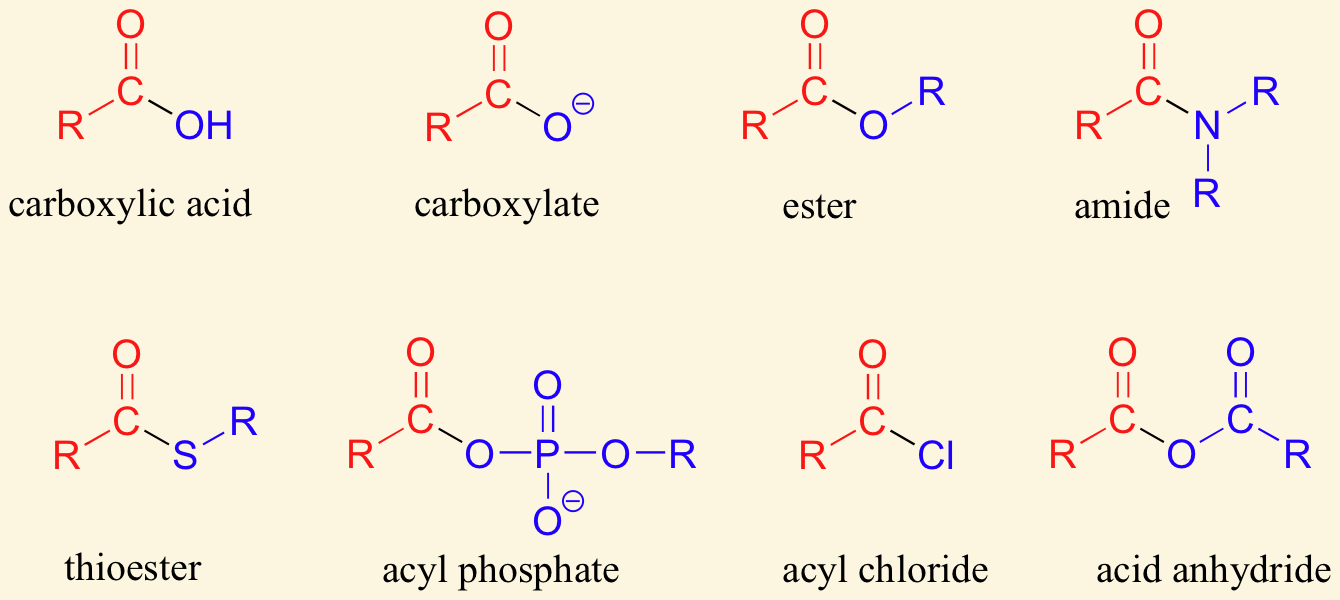
carboxylic acid
they are always terminal groups
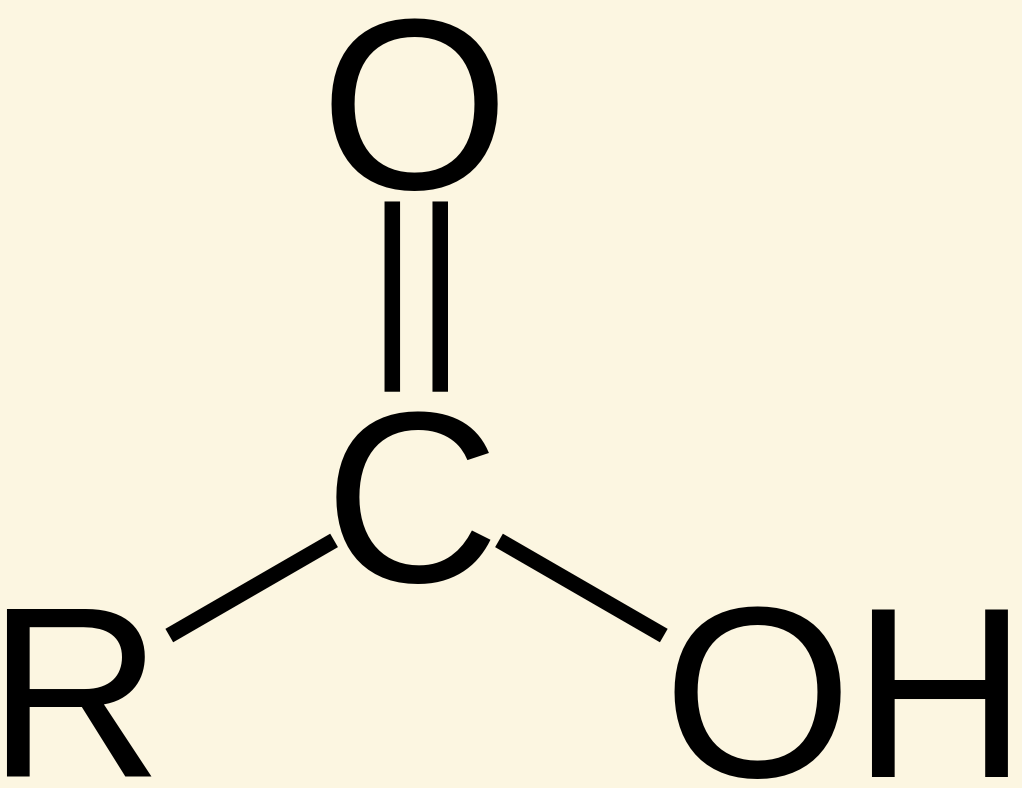
Carboxylic acids use the suffix [...]
-oic acid
salts are named with the suffix -oate
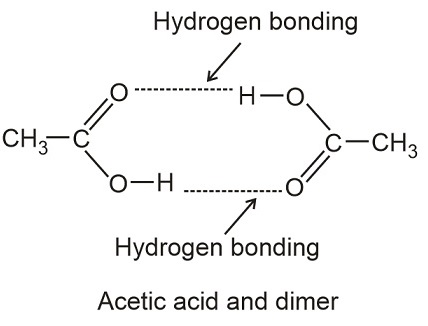
Carboxylic acids have a high boiling point due to [...]
hydrogen bonding
they often as dimers in solution due to the hydrogen bonding
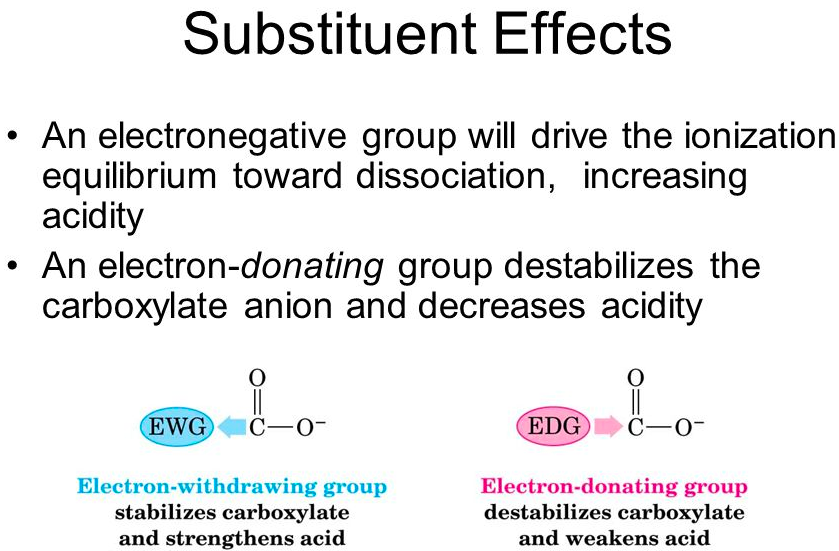
the acidity of a carboxylic acid can be enhanced by substituents that are electron-[withdrawing or donating]
withdrawing
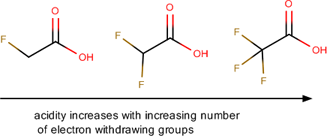
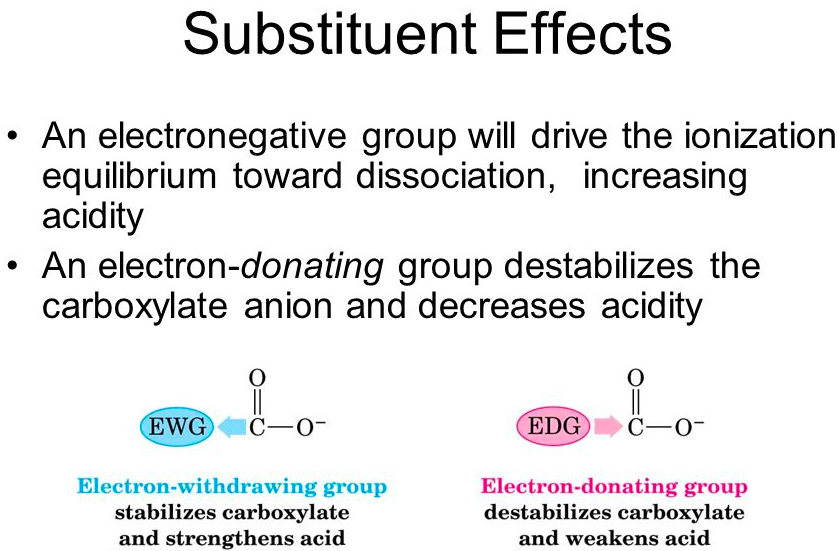
The acidity of a carboxylic acid can be decreased by substituents that are electron-[withdrawing or donating]
donating
Identify the acidic proton
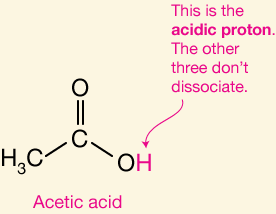
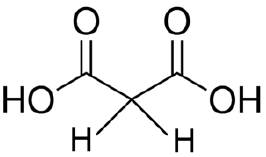
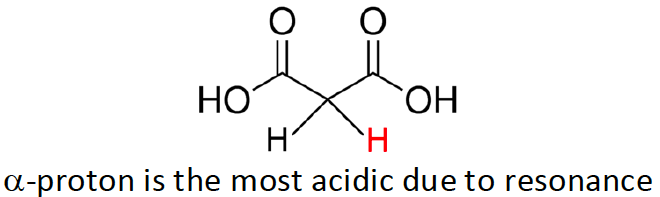
Identify the most acidic proton
this is a β-dicarboxylic acid
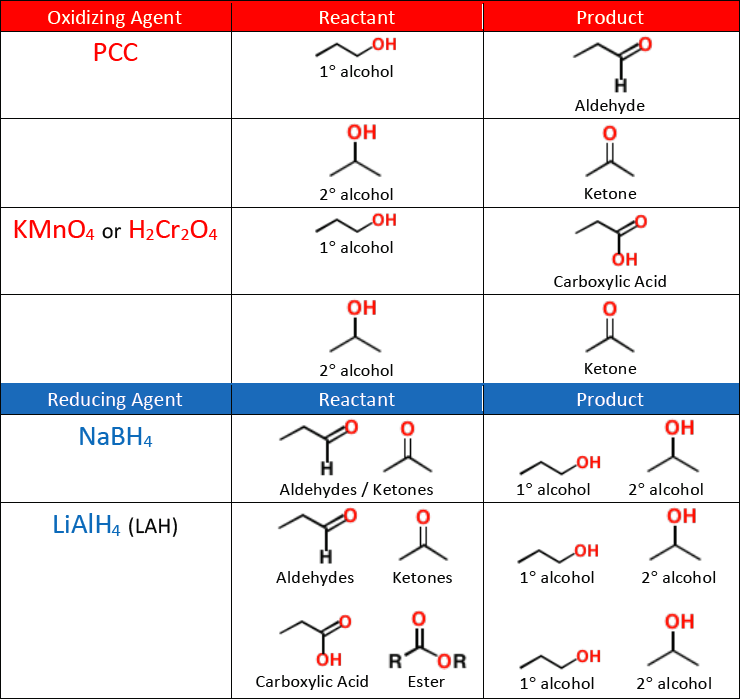
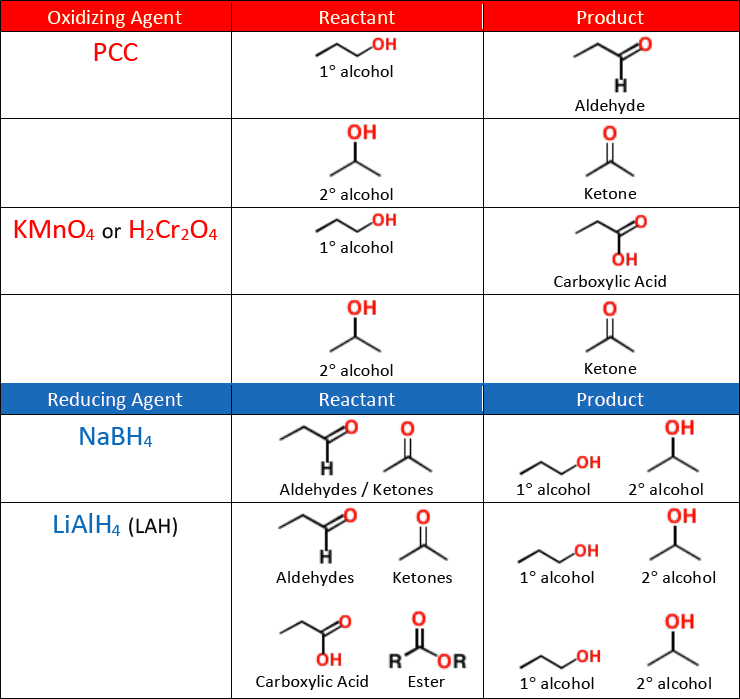
Carboxylic acids can be made by the [...] of 1° alcohols or aldehydes
oxidation
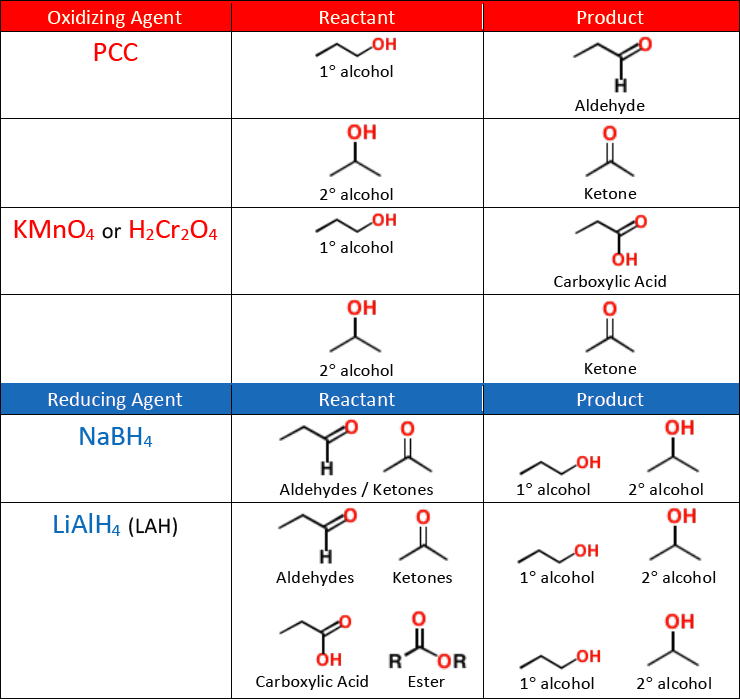
KMnO4
Na2Cr2O7
K2Cr2O7
CrO3
The above list shows [oxidizing or reducing] agents that can form [...]
oxidizing agents that can form carboxylic acid
PCC is weak and stops oxidizing at he aldehyde
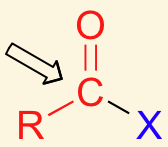
Identify the functional group in red
acyl groups are derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups form an oxyacid (acid that contains oxygen)
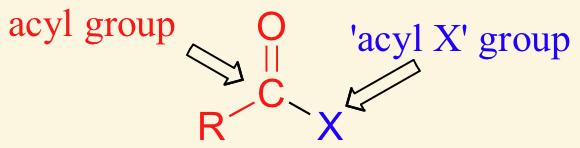
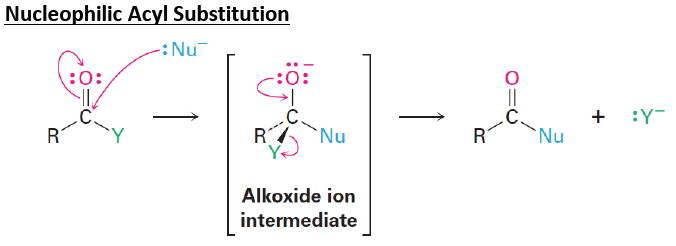
In nucleophilic acyl substitution a [...] displaces the [...]
nucleophile displaces the leaving group
the nucleophile attacks the electrophile carbonyl carbon, opening the carbonyl and forming a tetrahedral intermediate
the carbonyl reforms kicking off the leaving group
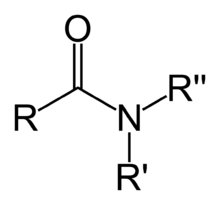
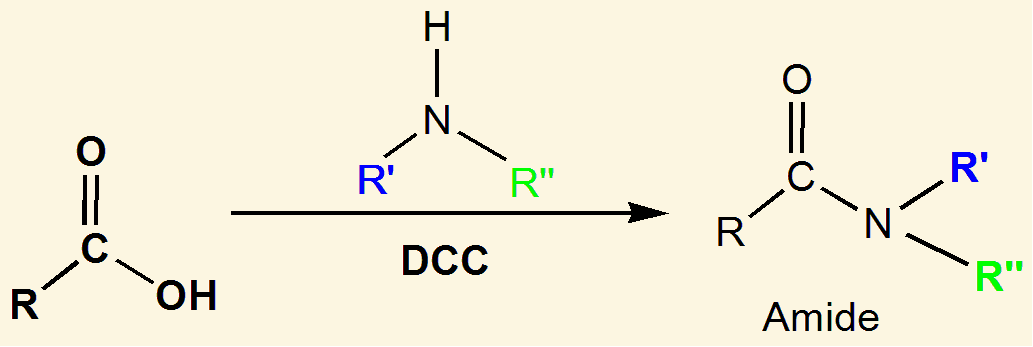
The nitrogen containing functional group shown above is called a/an …
amide
amides are synthesized from a carboxylic acid by replacing the -OH group with amino group that may or may not be substituted
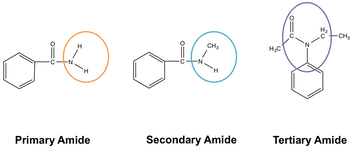
Amides are given the suffix [...]
-amide
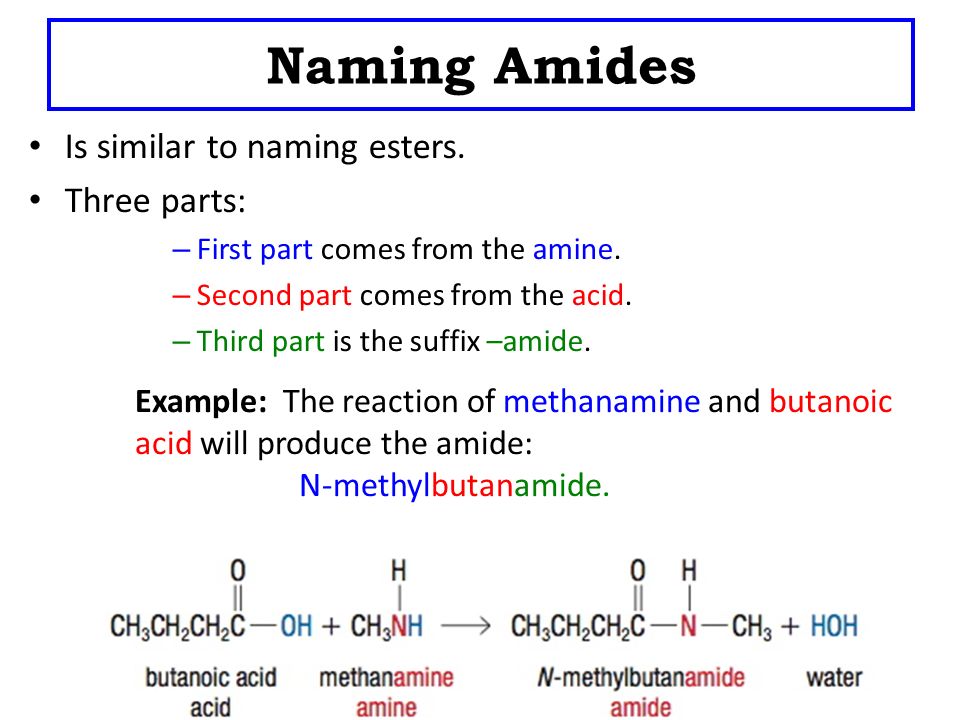
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acids in which the [...] group has been replaced by a/an [...]
amine or ammonia
A/an [...] is a carboxylic acid derivative where –OH is replaced with -OR
ester
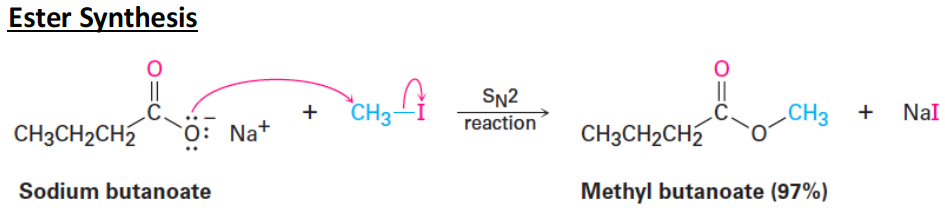
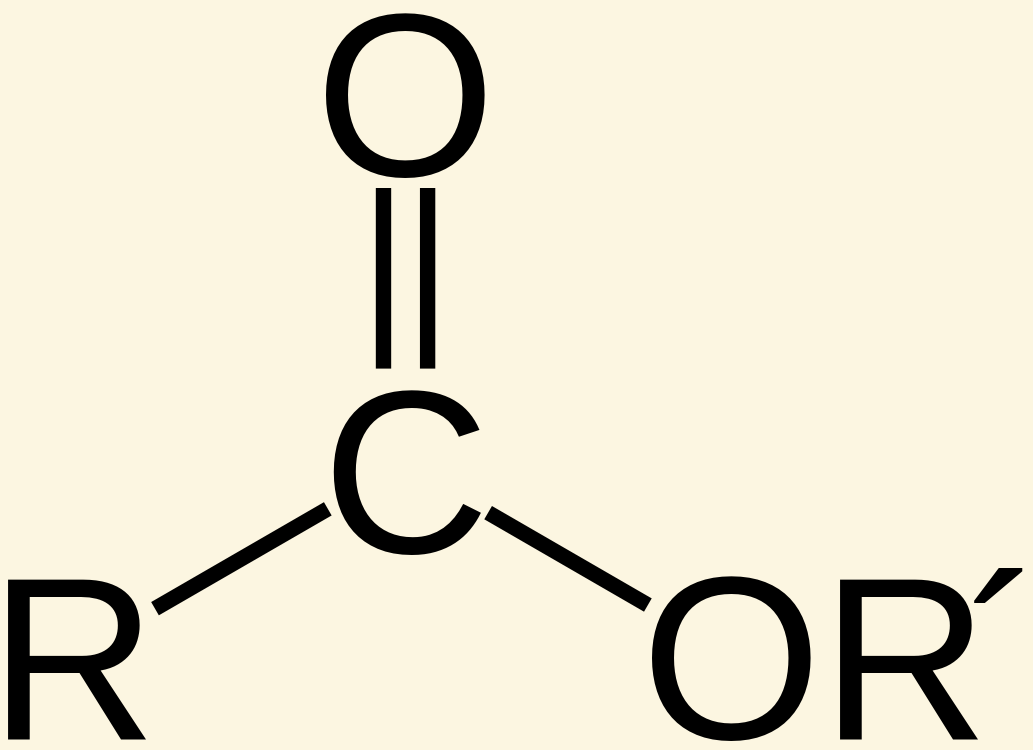
Esters are given the suffix [...]
-oate
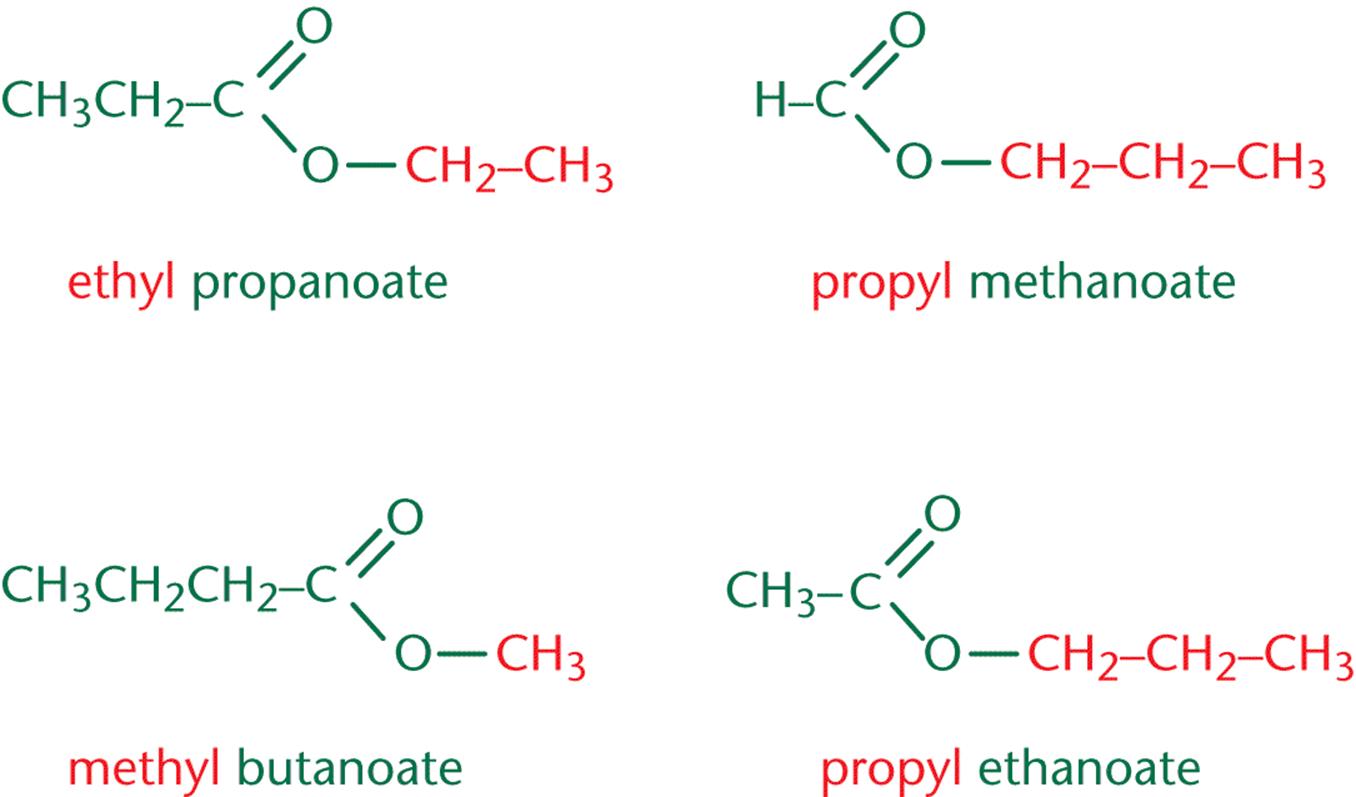
Carboxylic acid can act as a nucleophile and attack a second carboxylic acid to form a/an [...]
anhydride
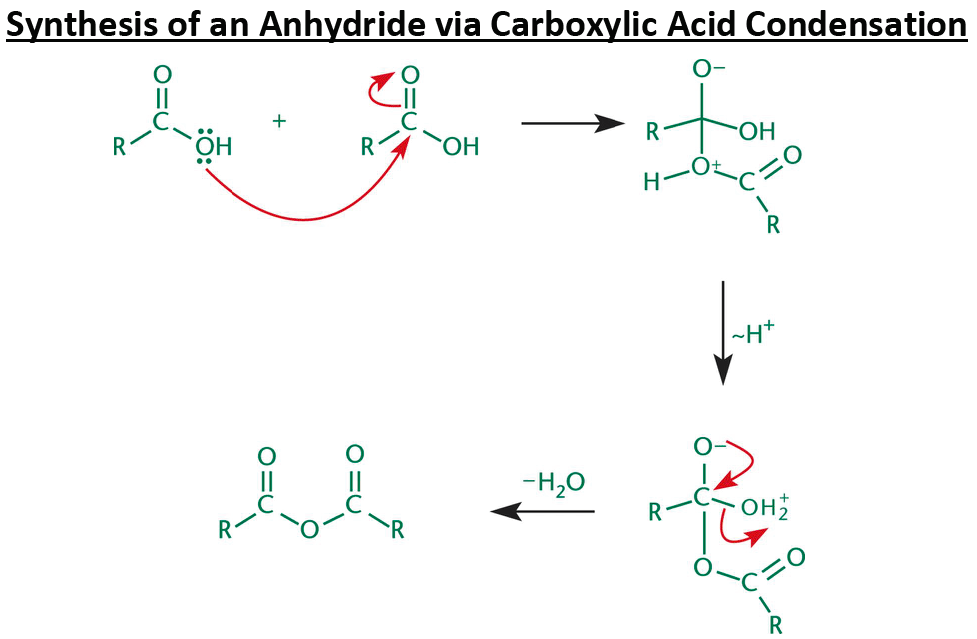
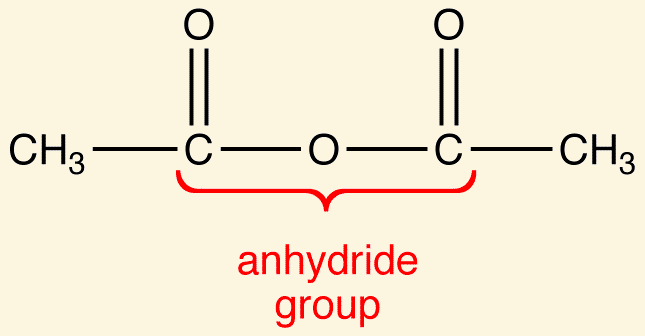
Both linear and cyclic anhydrides are given the suffix [...]
anhydride
A carboxylic acid can be reduced to a 1° alcohol with a strong reducing agent like [...]
LiAlH4
NaBH4 is not strong enough to reduce a carboxylic acid
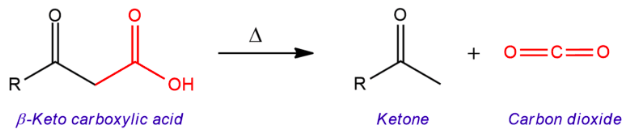
[...] is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2)
decarboxylation
the reaction proceeds spontaneously when heated
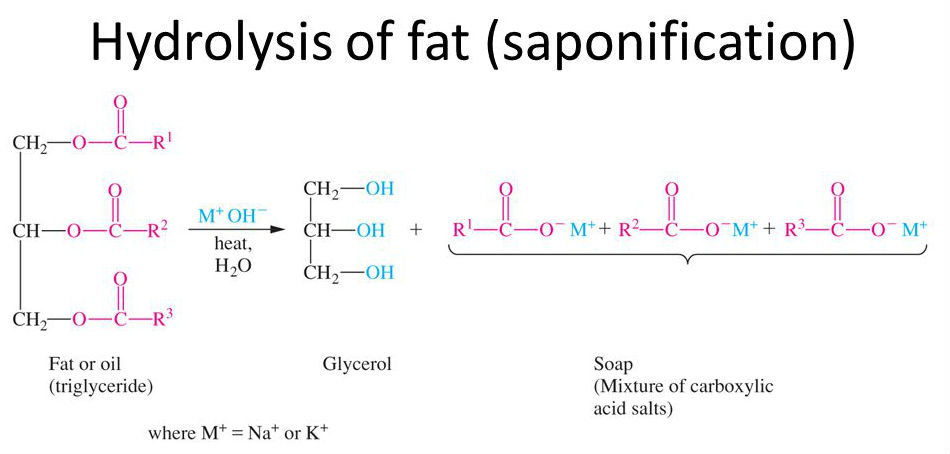
[...] is an ester hydrolysis of triacylglycerols using a strong base like sodium or KOH
saponification
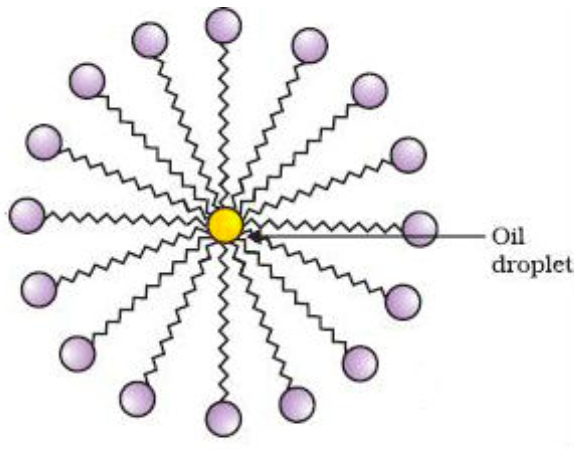
they organize in water to form micelles
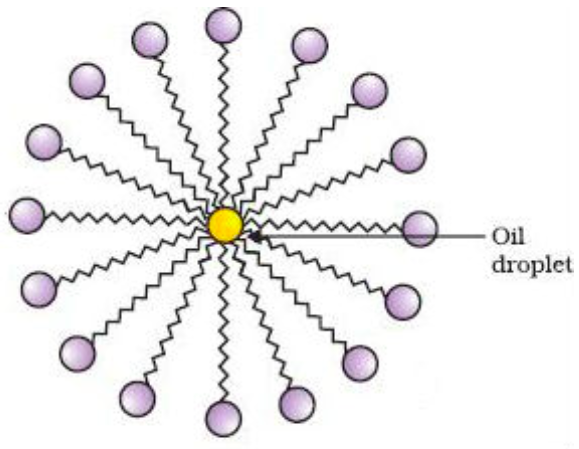
A/an [...] dissolves nonpolar organic molecules in its interior, and can be solvated with water due to its exterior shell of hydrophilic groups
micelle
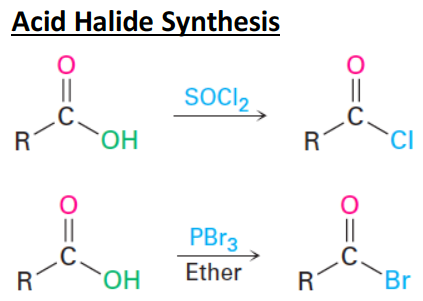
![<p><span>The reagents used in </span><strong><u>acid halide synthesis</u></strong><span> are </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> and </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/021b1d34-f1b6-498c-8b2d-18dc122d5e8f.png)
The reagents used in acid halide synthesis are [...] and [...]
SOcl2 and PBr3
example of
-fischer esterification
treatment of a carboxylic acid with an alcoholic in the presence of an acid catalyst leads to the formation of ester, along with the elimination H2O
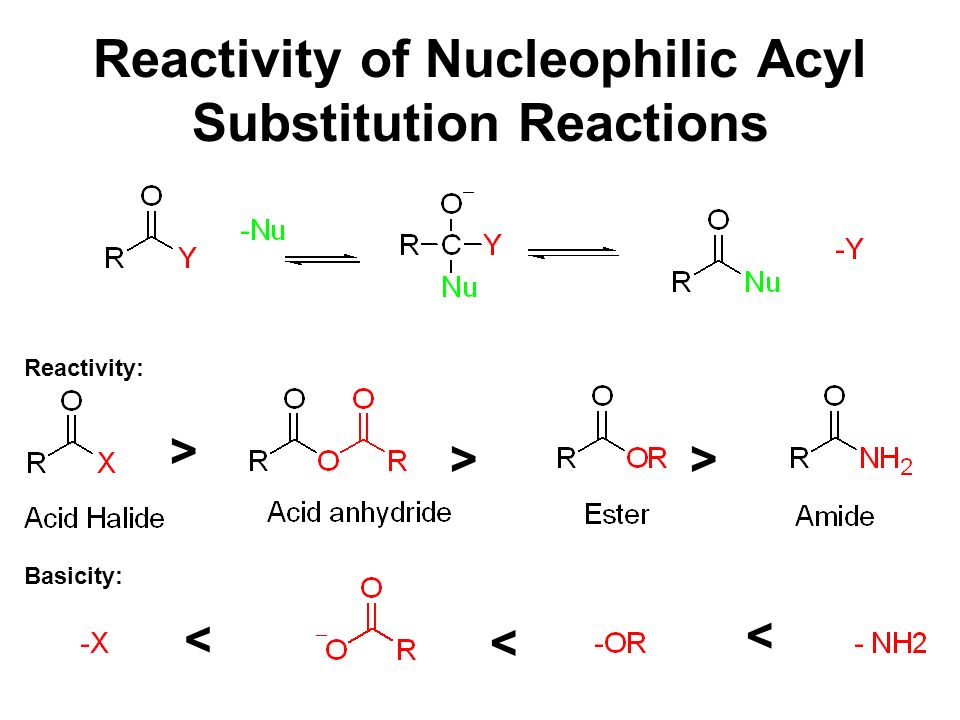
Acid chloride
Amides
Anhydrides
Carboxylate
Esters
Place the above molecules in order from most reactive to least reactive in nucleophilic substitution reactions
Acid chloride > Anhydrides > Esters > Amides > Carboxylate
...] describes when a reaction cannot proceed (or significantly slows) because substituents crowd the reactive site
steric hindrance
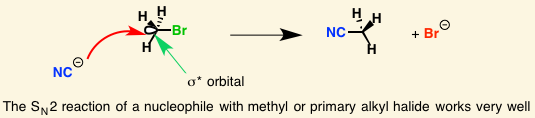
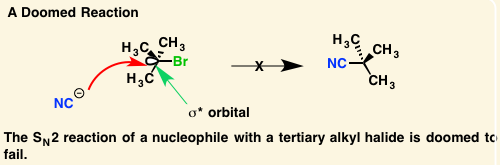
[...] refers to uneven distribution of charge across a σ bond because of differences in electronegativity
induction
the more electronegative group a carbonyl-containing compound has, the greater its reactivity
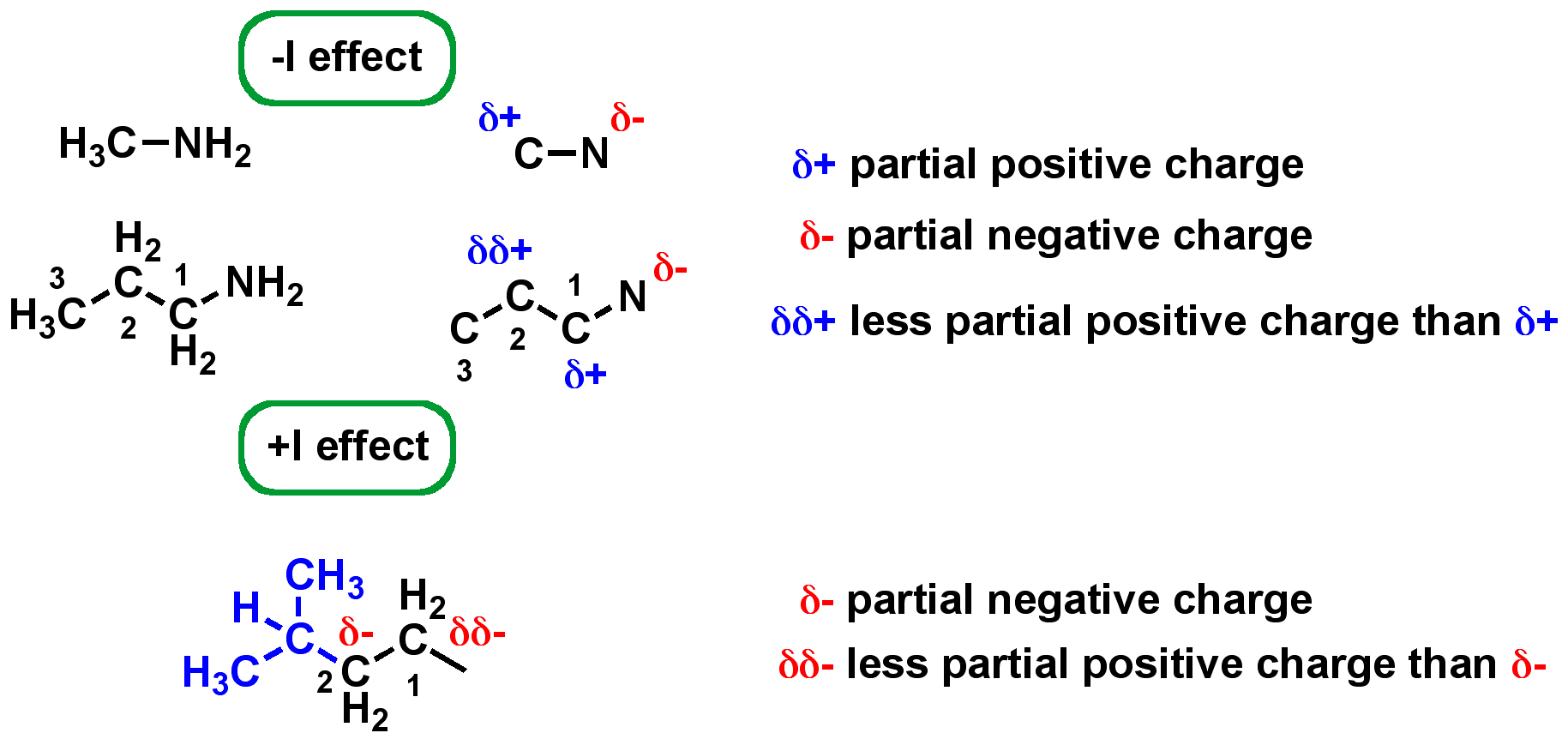
Increased ring strain in a molecule can make it [more or less] reactive
ring strain
more
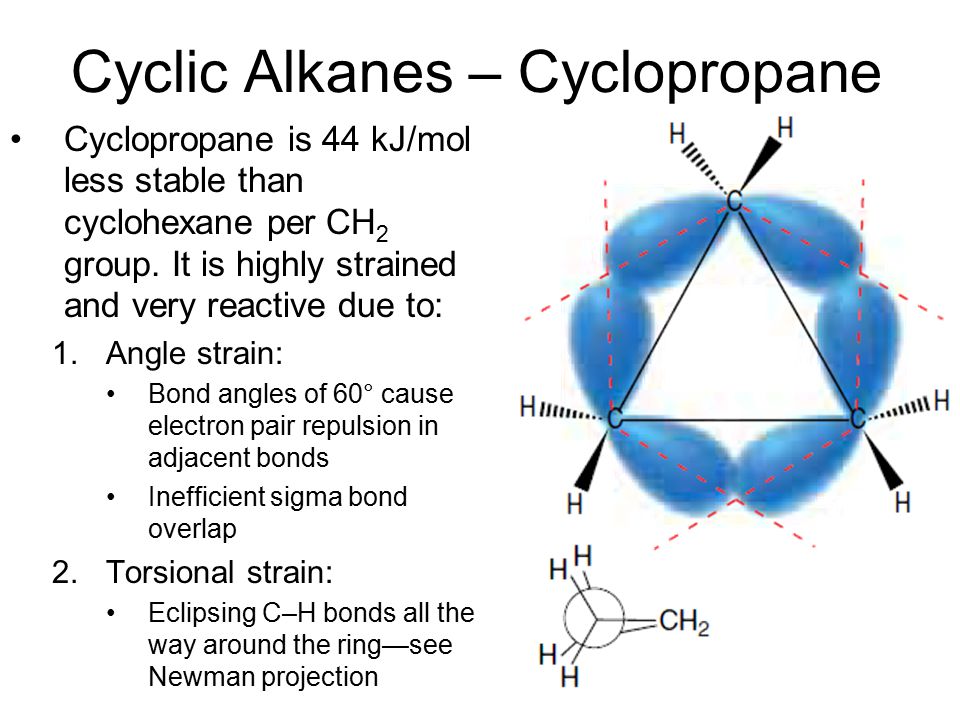
[...] is the process of exchanging the R″ group of an ester with the R′ group of an alcohol
transesterification
transformation of an ester
alcohol is the attacking nucleophile
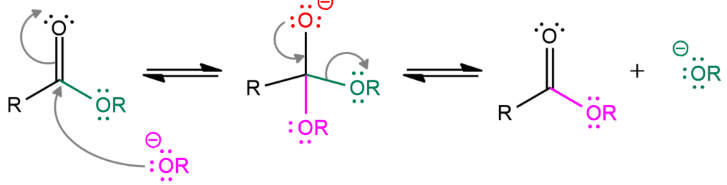
When a phosphodiester bond is formed, a/an [...] is released
pyrophosphate (ppi)
the pyrophosphate can then be hydrolyzed into two inorganic phosphates (Pi)
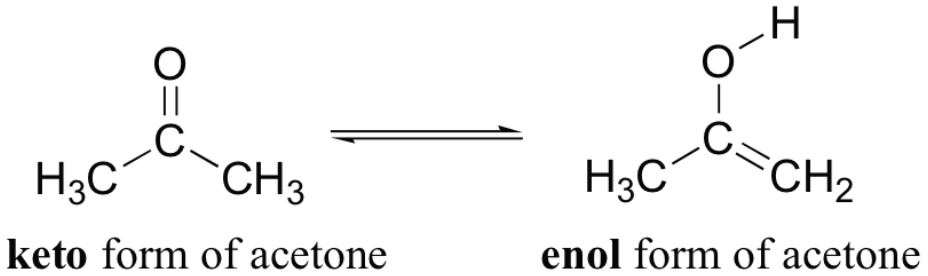
![<p><span>This is the </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[keto or enol]</strong></span><span> form of acetone</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/908b9f9a-bdf9-4656-b468-87387bfad0fa.png)
This is the [keto or enol] form of acetone
enol
enol form contains an alcohol
keto form has a regular ketone or an aldehyde