Chapter 23 Localization techniques, Chapter 8 Digital Imaging, Chapter 27 Three-dimensional digital imaging
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
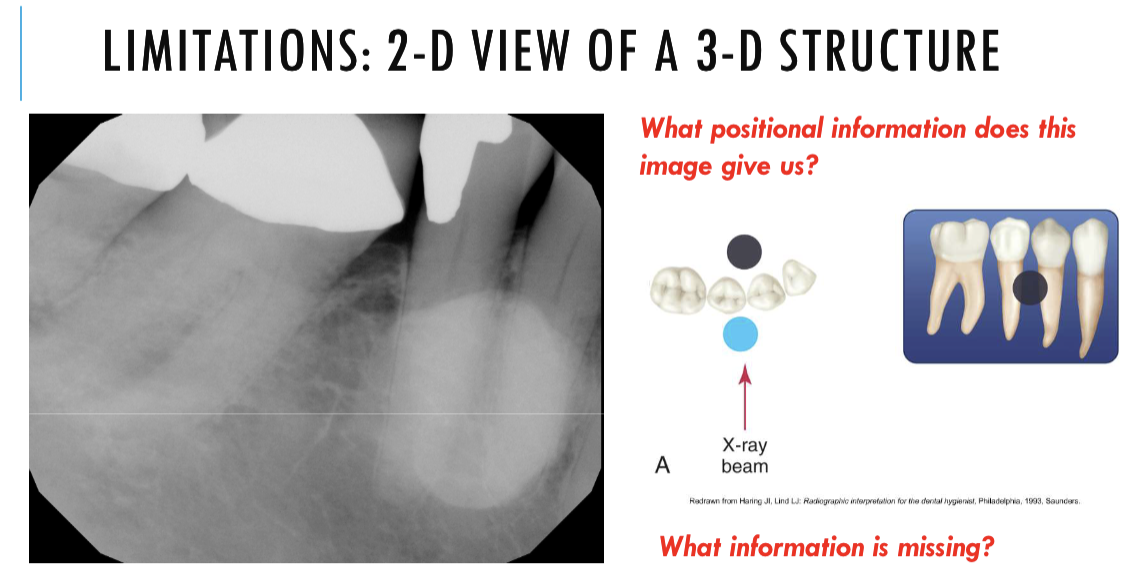
can tell us how forward how far back or how inferior or superior
can tell us anterior or posterior
but cant like us inferior or superior
Purpose of localization
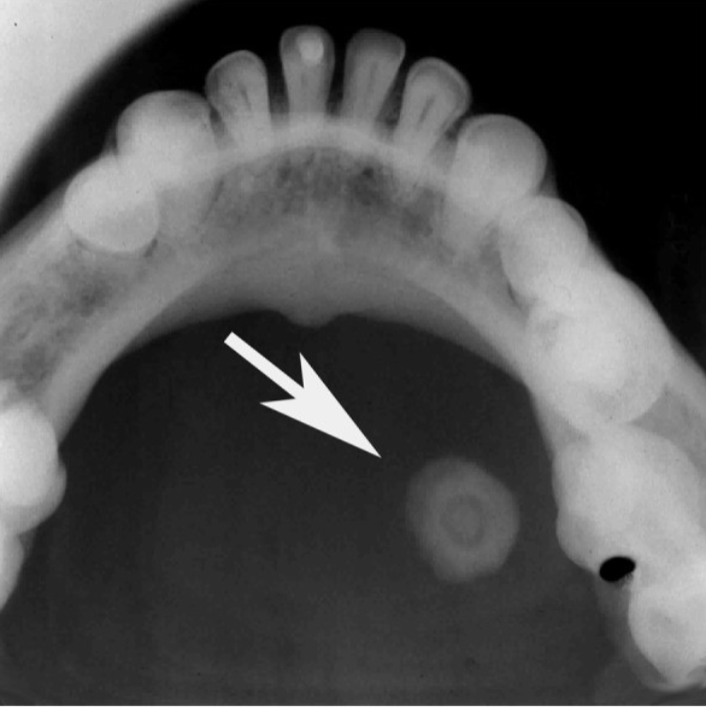
foreign bodies, impacted, unerupted teeth, retained roots, root positions, salivary stones, jaw fractures, broken needles and instruments, restorative materials
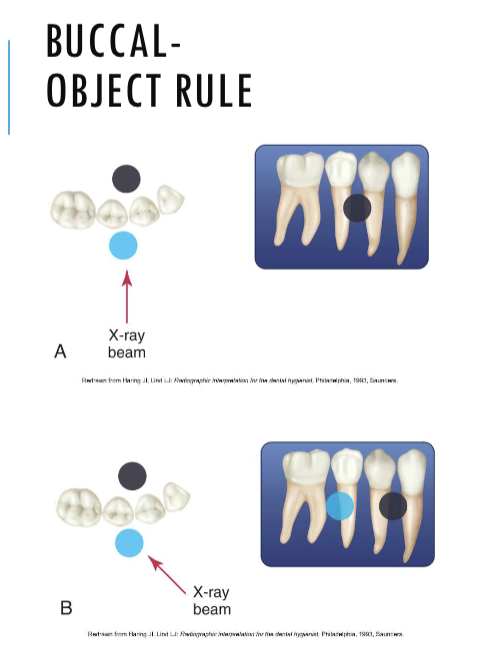
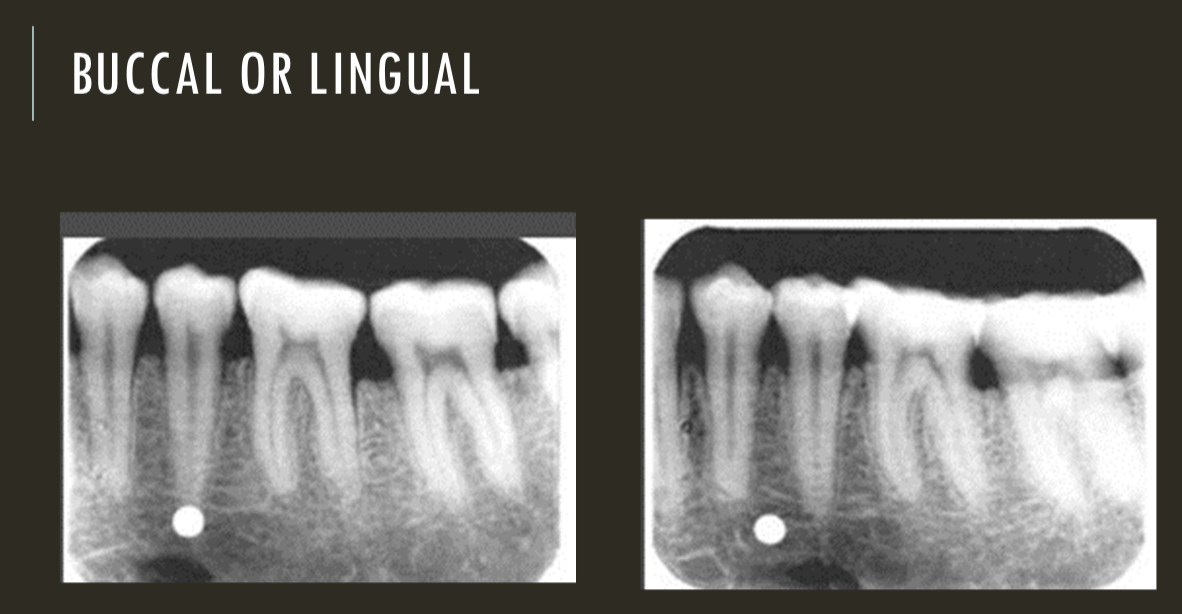
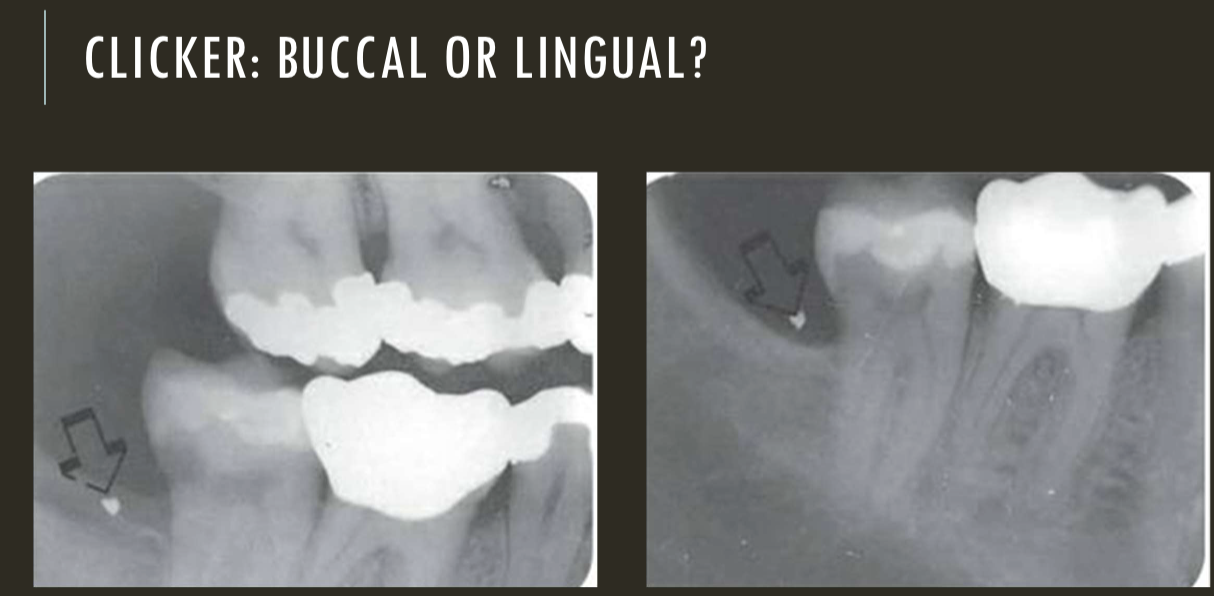
buccal object rule
expose 1st image (PA or bw)
take a second image with a different H or V angulation aka same area different angle
compare images to see how the object shifted in the image
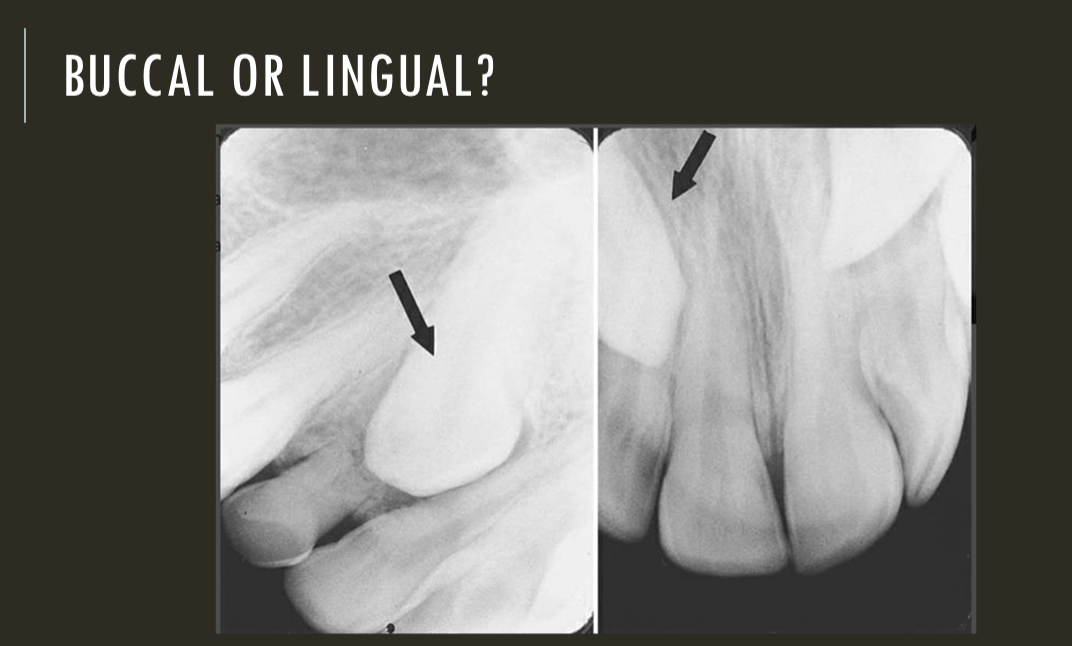
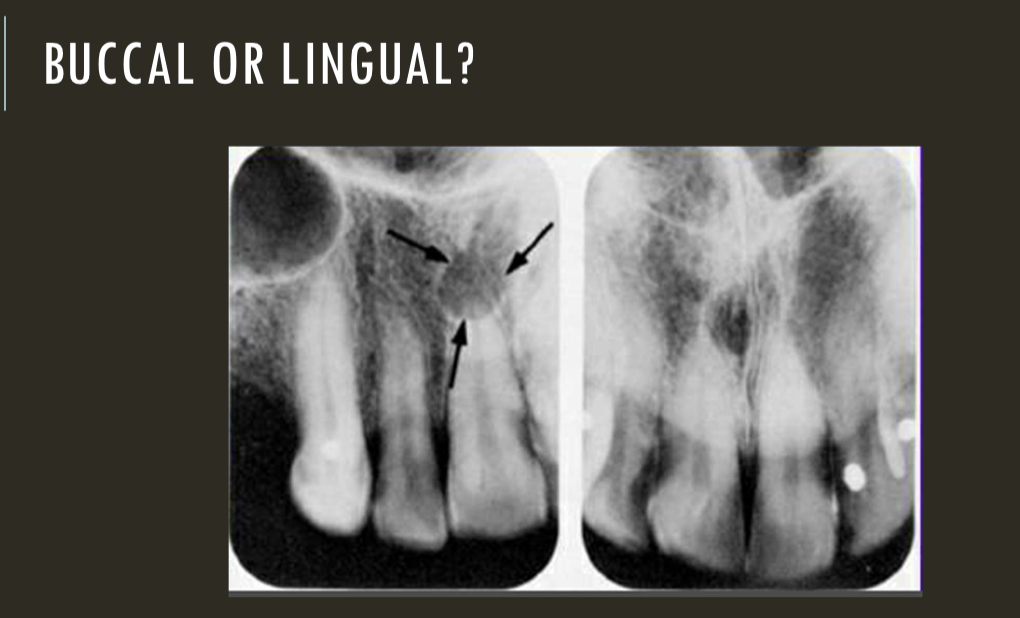
SLOB
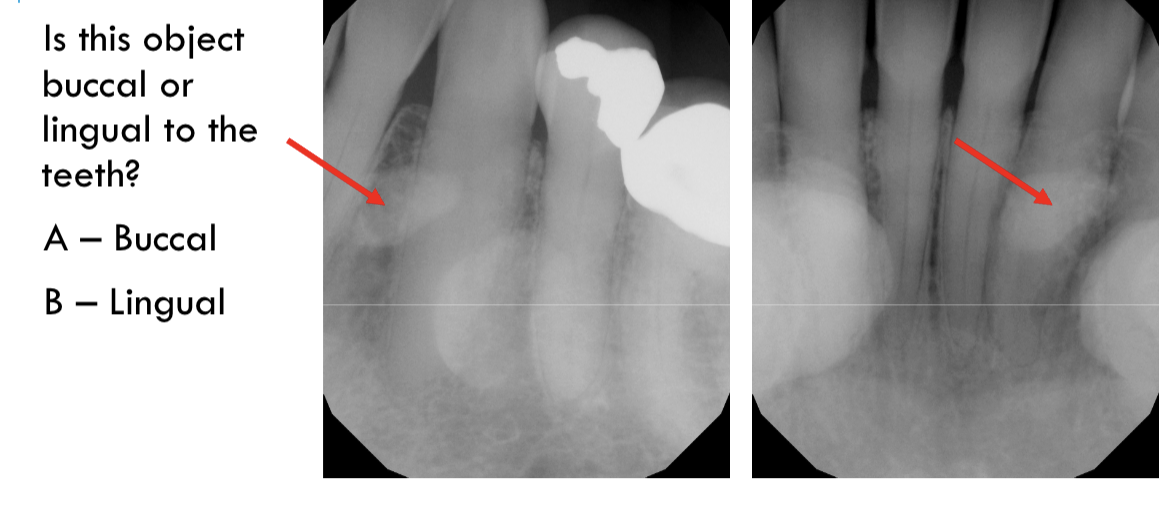
lingual
right angle technique
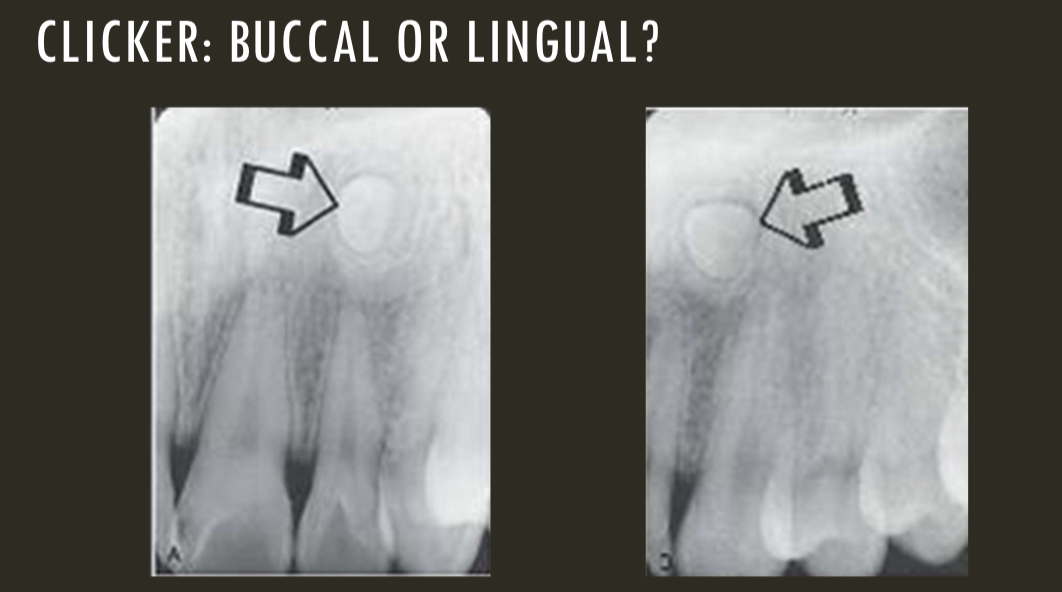
buccal
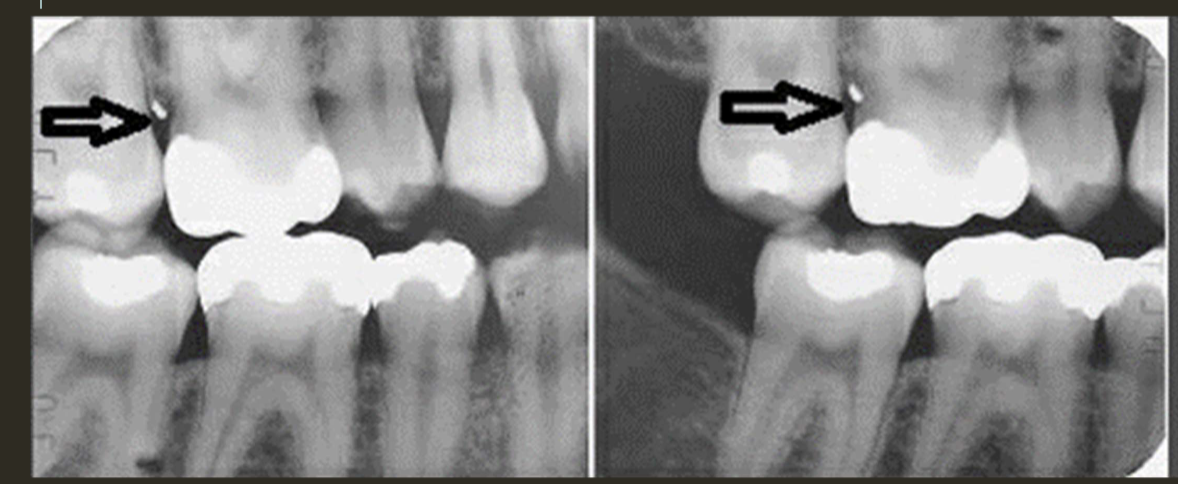
lingual
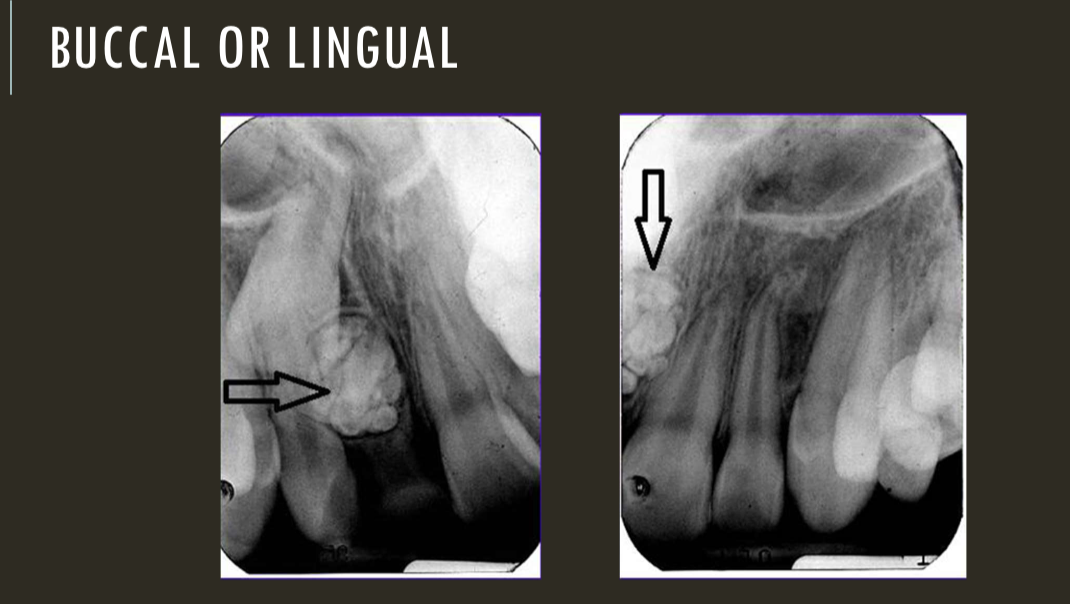
lingual
buccal

Digital
Scintillating layer
stars sparkling glowing
converts x-ray photons to light photons
Charge-coupled device
pixels abut each other
complementary metal oxide semiconductor/ active pixel sensor (CMOS/APS)
each pixel surrounded by amplifiers
contrast resolution (range of grays)
8- bit (2^8) is 256 shades
superior to human eye
spatial resolution (line pairs/ millimeter)
digital - 6-22 lp/mm
film - 20 lp/mm
human eye 6-8 lp/mm w/out mag
Types of digital imaging
direct digital imaging (CCD, CMOS)
or
indirect digital imaging ( Digitizing tradition film images, photostimulable phosphor imaging)
3-D imaging
CBCT scan - cone beam, computed tomography
cone-shaped x-ray beam, rotates around the patients head
scan time 7-30 seconds
contrast res > bit depth
spatial res - voxels 3-dimensional pixels
2D vs 3D
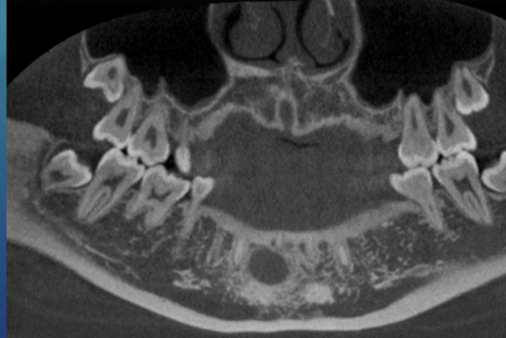
unable to assess from this single image the objects buccal-lingual position relative to the teeth
traditional medical CT
computed tomography
fan shaped x-ray beam rotates around pt
rotations move down the section of anatomy of interest
layers/ slices of images are stacked with software during image reconstruction
Coronal plane
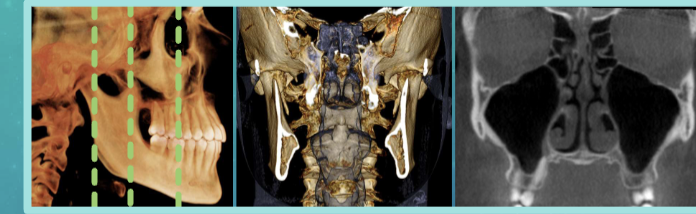
axial plane
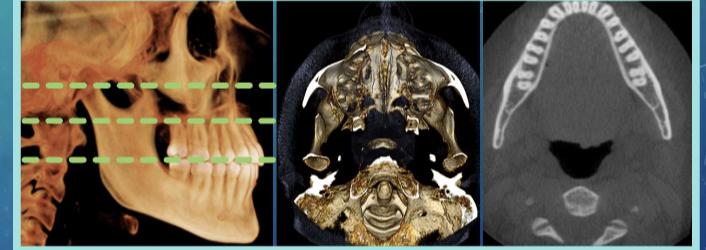
sagittal plane
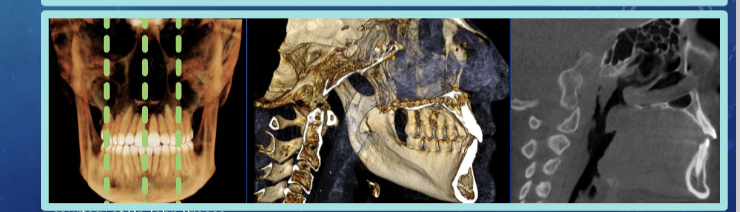
anatomical/ orthogonal projections
multiplanar reconstruction/ reformation
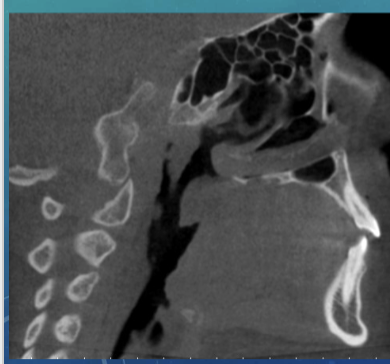
volumetric rendering
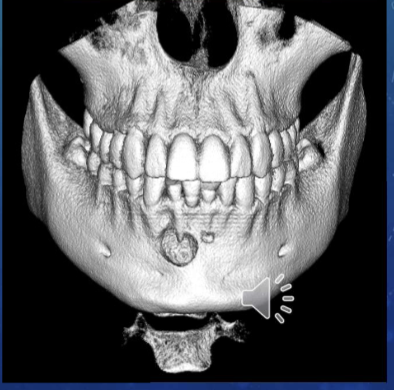
commons uses of 3D imaging
improved interpretation diagnosis and treatment planning of dental care
implant placement
extraction or exposure of impacted teeth
definition of anatomic structures
endo assessment
airway and sinus analysis
eval of TMJ disorders
ortho eval
eval of lesions/ abnormalities
trauma eval
Training for CBCT
American academy of oral and maxillofacial radiology - CBCT interpreted by board certified oral and maxillofacial radiologist
intersocietal accreditation commission -min standards when using dental cbct
patient preparation
explain to pt
ensure glasses, jewelry, appliances etc, are removed
chin/ head support for pt comfort and stability
use lasers to align pt
advantages of CBCT
lower radiation dose than CT
easy to save and share date
brief scanning tim e
accurate anatomical images
disadvantages of CBCT
patient movement, small FOV could limit view, cost, training, exposure