Ch 13 & 16. Bacterial Genome and Genetic Variation
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
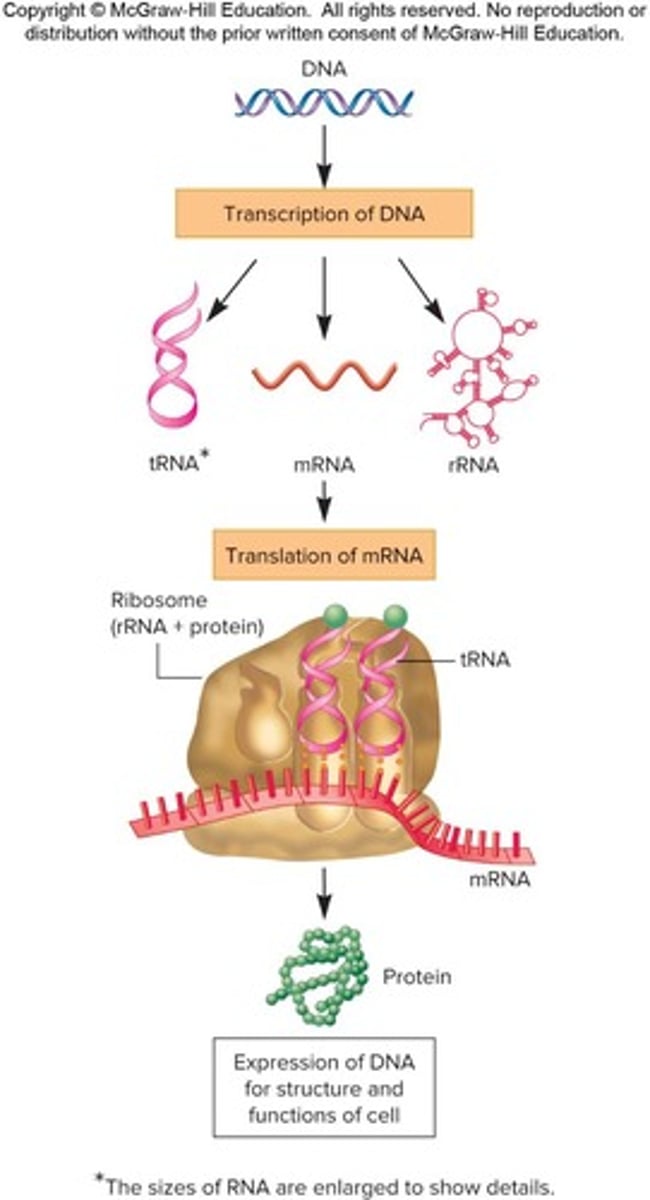
Central Dogma
Process of DNA to RNA to protein synthesis.
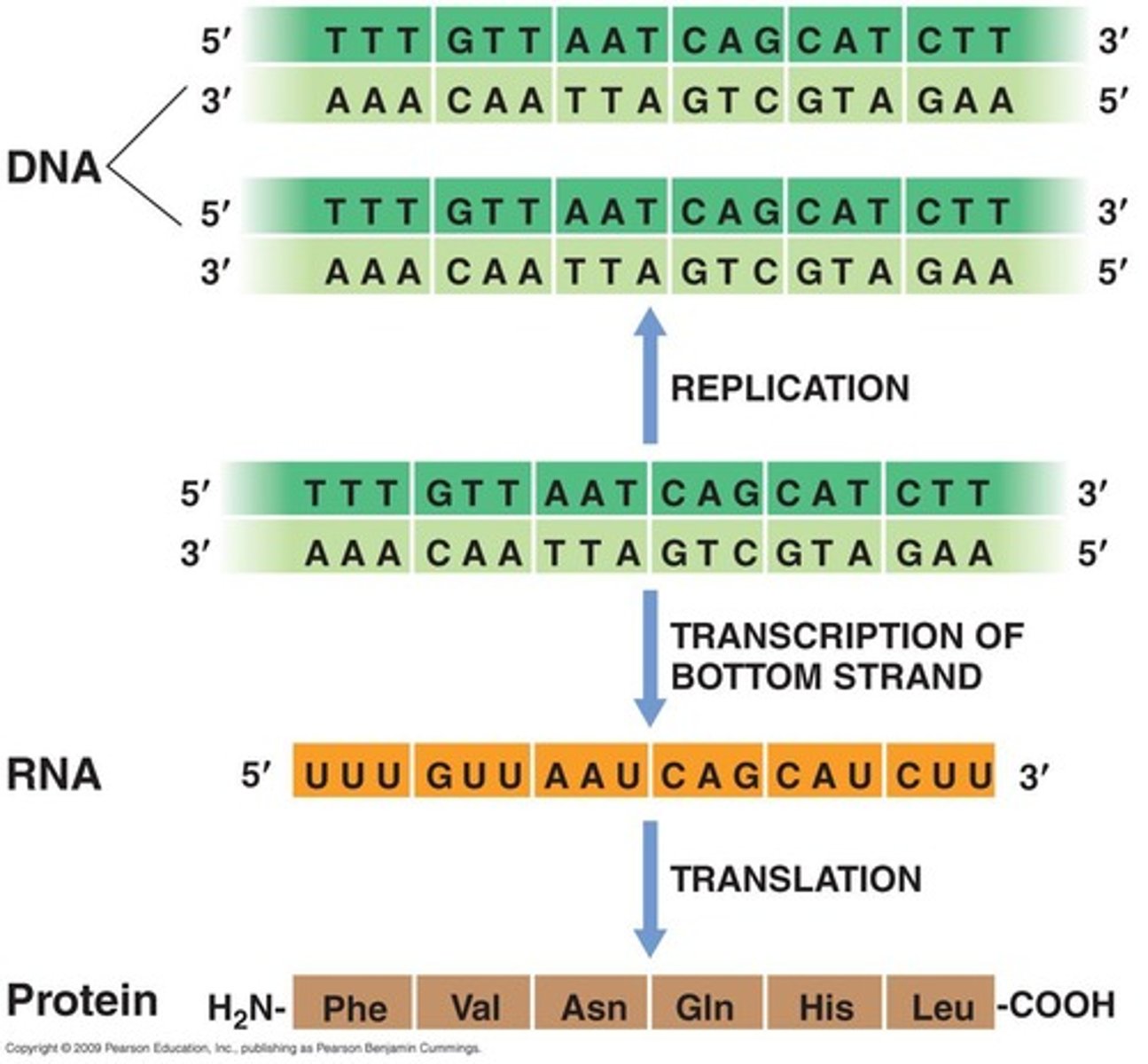
DNA Replication
Copying DNA using DNA polymerase enzyme.
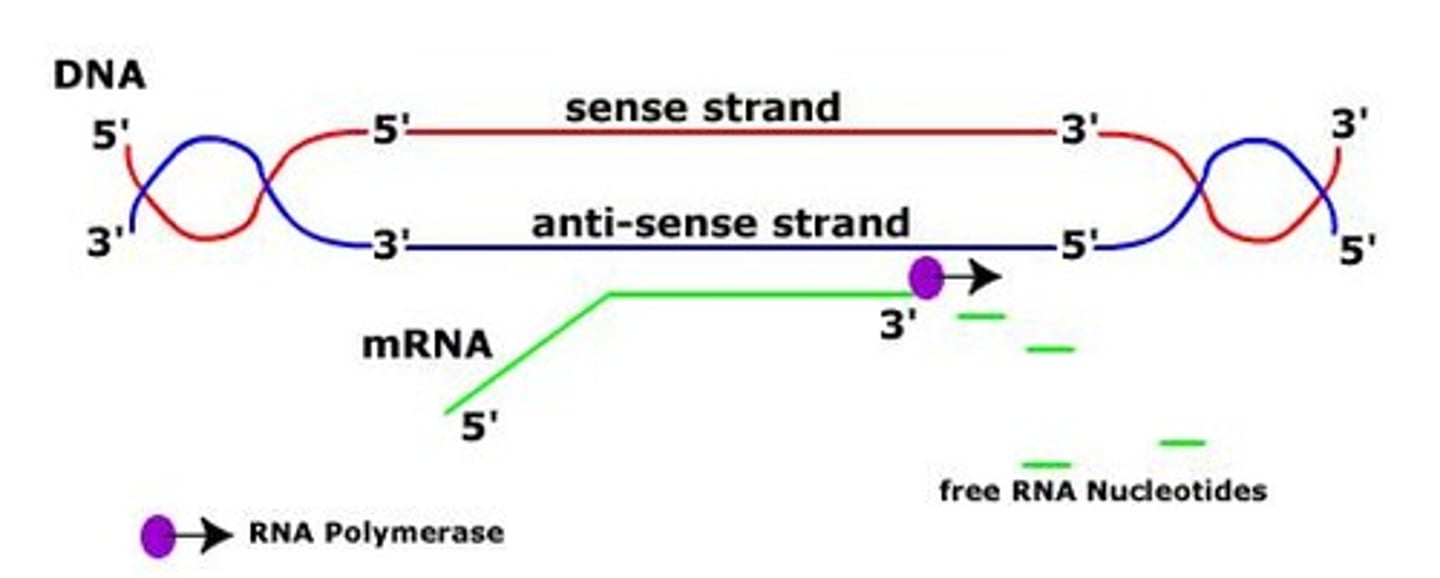
Transcription
Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA template.
Translation
Synthesis of proteins from mRNA by ribosomes.
Transformation Test
Griffith's experiment showing genetic material transfer.
Avery-MacLeod-McCarty Experiment
Showed DNA is the transforming principle.
Hershey-Chase Experiment
Demonstrated DNA as genetic material using bacteriophages.
Bacteriophage T2
Virus used to study DNA and protein roles.
Nucleic acids
Polymers of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds.
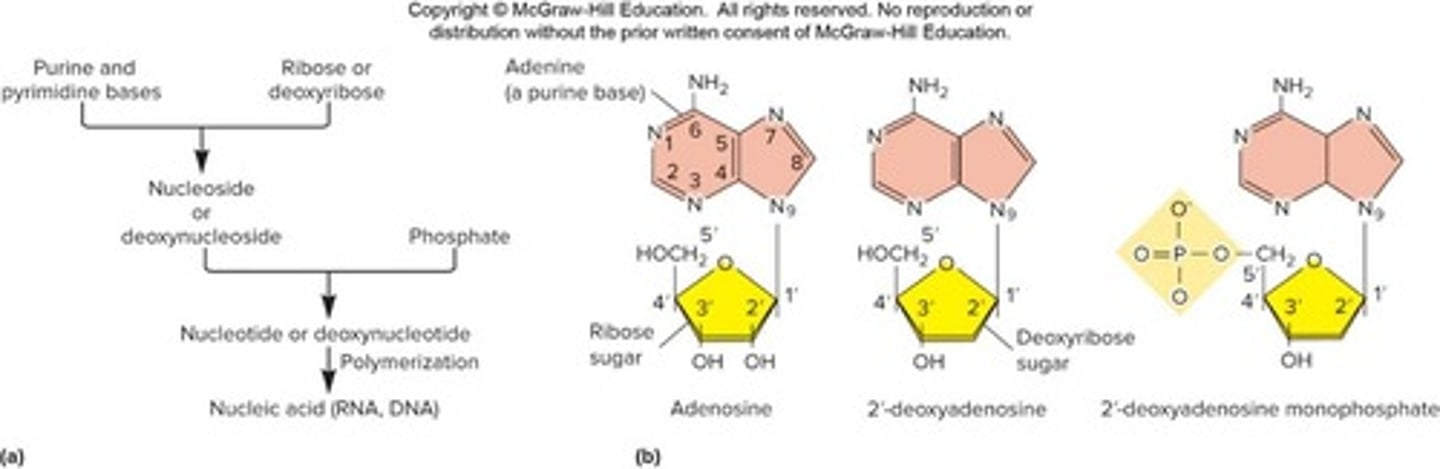
Nucleotides
Building blocks of nucleic acids, containing a base.
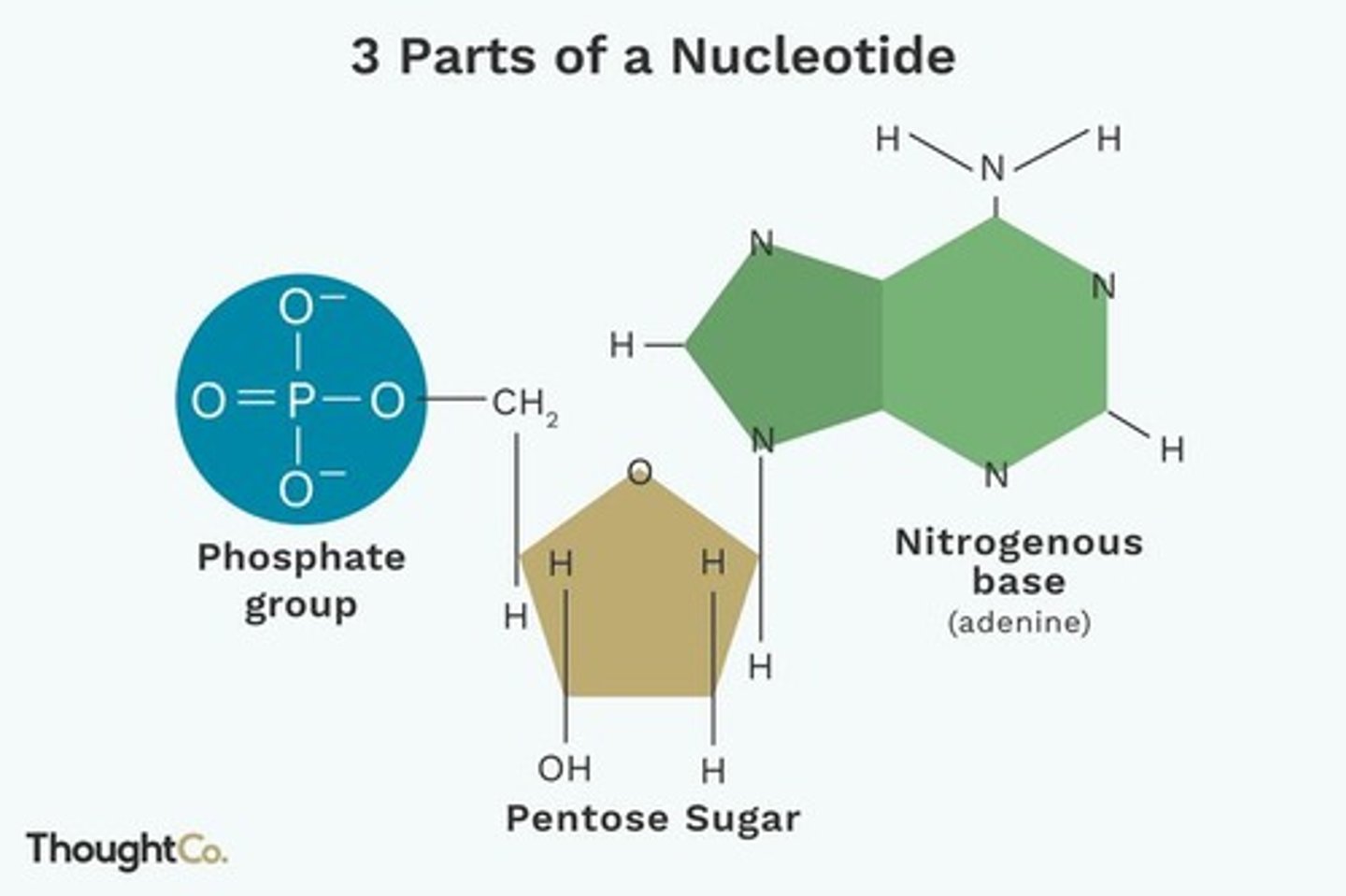
Nitrogenous bases
Components of nucleotides; include purines and pyrimidines.
Nucleoside
Base plus sugar, without phosphate group.
Nucleotide
Nucleoside with one or more phosphate groups.
Purines
Two-ring nitrogenous bases: adenine and guanine.
Pyrimidines
Single-ring nitrogenous bases: cytosine, uracil, thymine.
RNA
Single-stranded nucleic acid with ribose sugar.
DNA
Double-stranded nucleic acid with deoxyribose sugar.
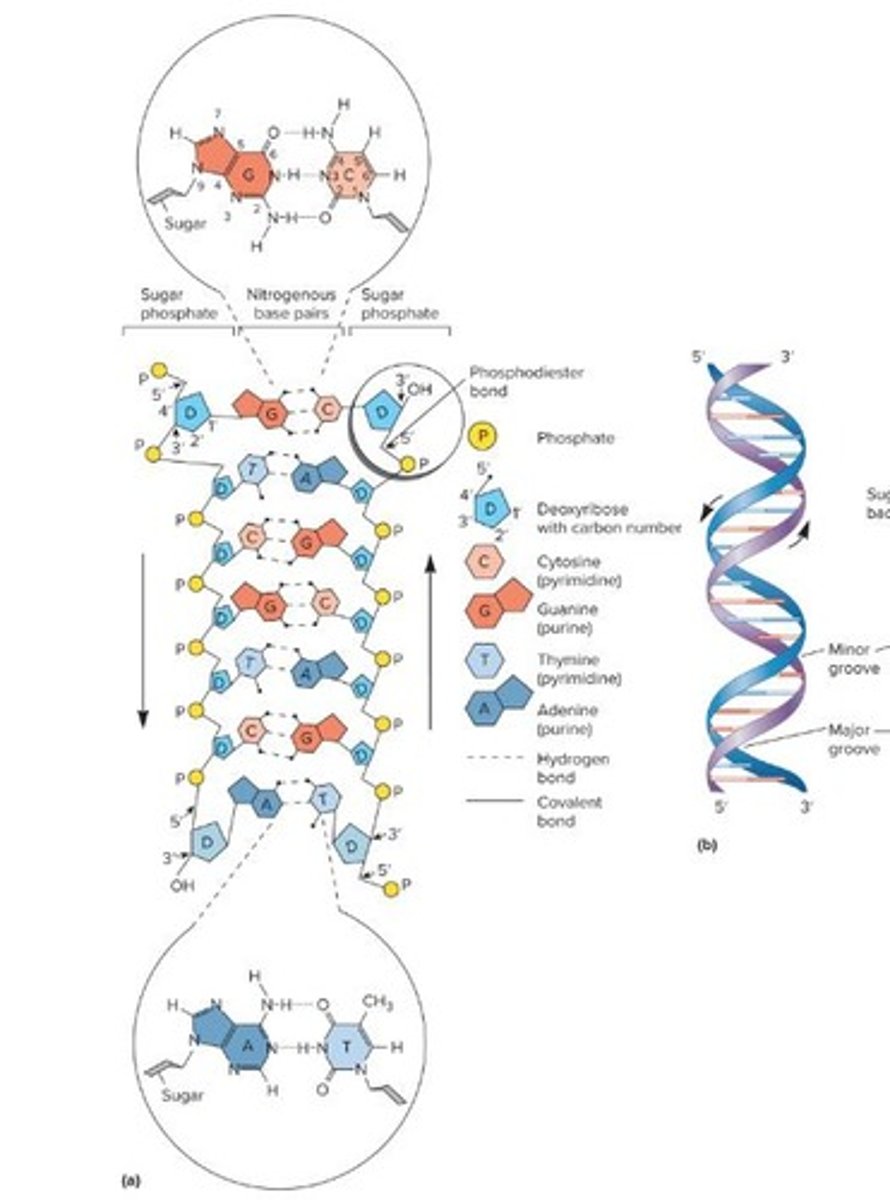
Base pairing
Specific pairing of nitrogenous bases: A-T, G-C.
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds holding base pairs together in DNA.
RNA types
Includes rRNA, tRNA, mRNA, and others.
Polypeptides
Chains of amino acids forming proteins.
Peptide bond
Covalent bond linking amino acids in proteins.
Amino acids
Monomers of proteins, containing amino and carboxyl groups.
Primary structure
Sequence of amino acids in a protein.
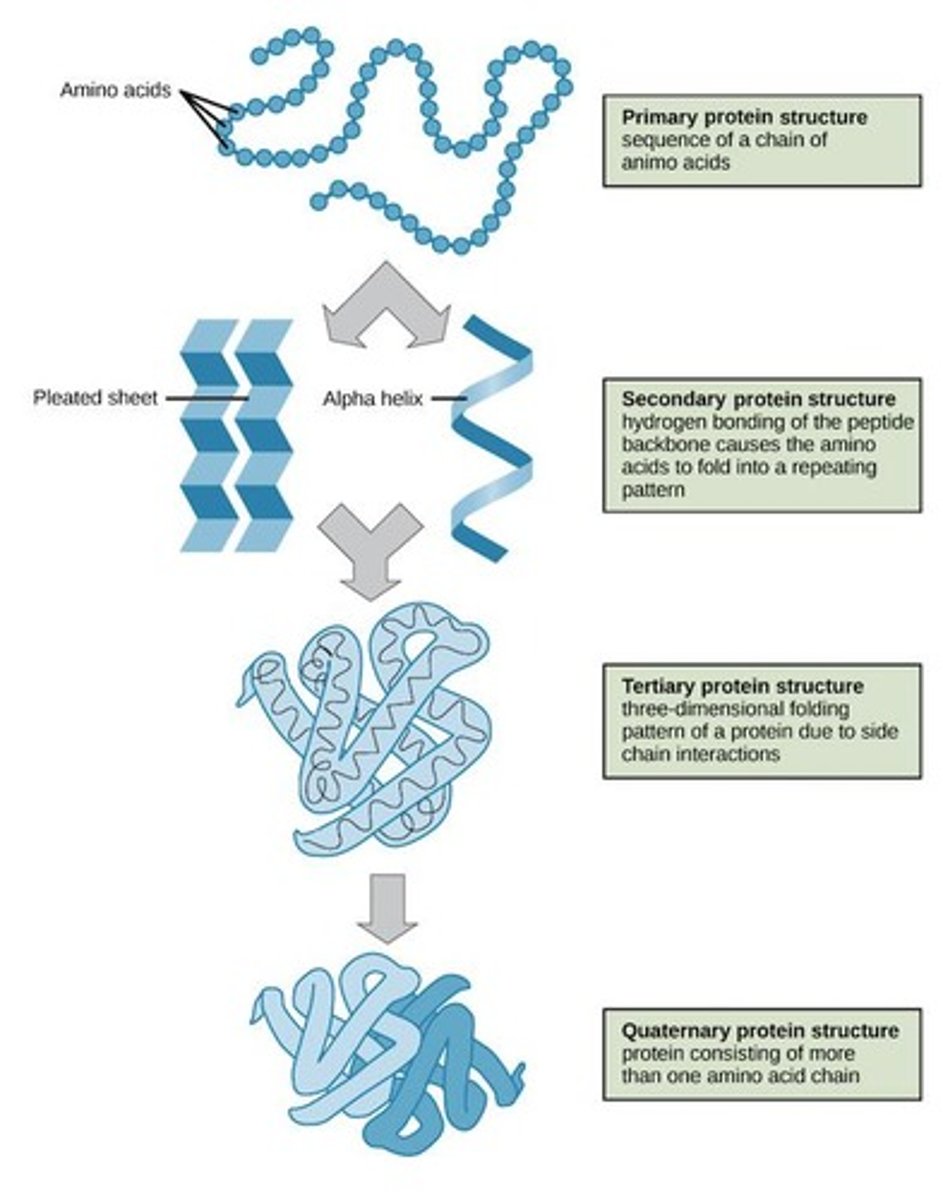
Secondary structure
Local folding patterns, like alpha helices and beta sheets.
Tertiary structure
Overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide.
Quaternary structure
Assembly of multiple polypeptide chains in a protein.
Bacterial DNA replication
Circular DNA replication, bidirectional from oriC.
Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence on mRNA specifying an amino acid.
Start codon
AUG; signals the beginning of translation.
Stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA; signal termination of translation.
Genetic code
Rules for translating mRNA codons into amino acids.
Molecular chaperones
Proteins assisting in the proper folding of other proteins.
Protein secretion
Movement of proteins from the cytoplasm to the outside.
Twin Arginine Translocation
System for moving folded proteins across membranes.
Type III secretion system
Injects proteins into host cells, aiding bacterial virulence.
Type IV Secretion System
Translocates proteins, mediates DNA transfer.
EHEC
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli, causes severe diarrhea.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Opportunistic pathogen, resistant to many antibiotics.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Marine bacterium, causes gastroenteritis.
Mutations
Stable changes in DNA base sequences.
Point mutations
Alterations in a single DNA base.
Larger mutations
Include insertions, deletions, inversions, duplications.
Spontaneous Mutations
Errors during DNA replication, random changes.
Induced Mutations
Caused by external agents damaging DNA.
Ames Test
Assesses mutagenicity using bacteria and His media.
Auxotroph
Mutant requiring additional nutrients for growth.
Forward mutation
Changes in DNA leading to altered phenotype.
Reversion mutation
Restores original phenotype from mutant form.
SOS Response
Inducible repair system activated by DNA damage.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Transfer of genes between organisms, not by reproduction.
Bacterial transformation
Uptake of free DNA by competent bacteria.
Bacterial transduction
Gene transfer via bacteriophages, general or specialized.
Bacterial conjugation
Direct transfer of DNA between bacteria via contact.
Bacterial Plasmids
Small, self-replicating DNA molecules in bacteria.
Hfr Conjugation
Transfer of chromosomal genes from Hfr cells.
Drug Resistance Genes
Genes conferring resistance to antibiotics, found on plasmids.
DNA Repair Mechanisms
Processes maintaining genome stability, including proofreading.