Hardware and software
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Rer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Logical unit
Sections in which computers are technically divided into:
Input unit
Storages (Primary & secondary)
Output unit
Control unit
Arithmetic logic unit
Input unit
Receiving section, it can receive anything from external devices, scanning images or secondary storage devices as well.
Output unit
Transfers the taken information onto output devices, mostly screens, but applies to many devices.
Memory unit
Rapid access, lower capacity “warehouse” that stores information from input unit or processed info ready for output. Also called primary memory or RAM, volatile and disappears when computer is turned off.
Arithmetic and logic unit
Manufacturing section that performs calculations, also compares and decides whether two items in memory are equal.
CPU Central Processing unit
Coordinates and supervises actions of the other sections. Tells when input should go to memory, when memory should be processed by ALU, etc.
Multicore processors
Computers have more than one processors to multitask directions. Some have dual-core processors, and others quad-core processors.
Secondary storage unit
Long term high capacity warehouse section. Stores programs and data not actively used. Information is persistent, takes longer to access, but its cost per unit is lesser.
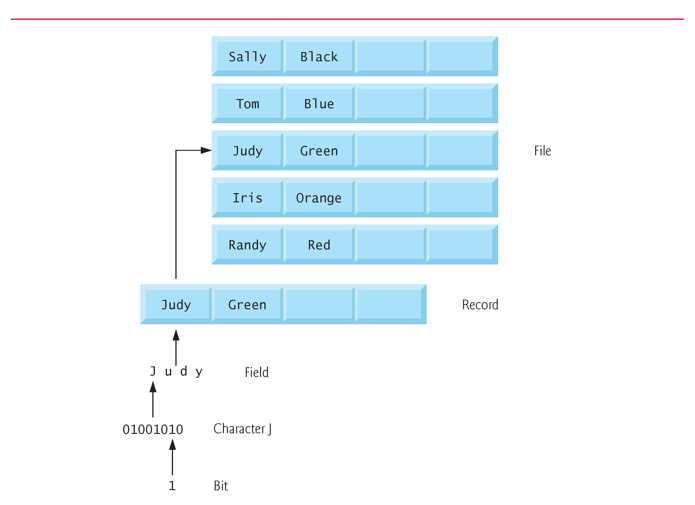
Data Hierarchy
File
Record
Field
Character/Byte
Bit
Machine language
Understandable by computers, generally consists of numbers reduced to 1s and 0s.
Assembly languages
Made with english abbreviations for programmers to understand and work with better.
Translator programs/Assemblers
Developed to convert assembly language to machine language.
High-level language
Substantial tasks are accomplished in a single statement.
Use everyday English and common math expressions.
Compilers
Translator programs for high-level languages to machine languages.
Interpreter
Program that executes high-level language programs directly, although slower than compiler programs.
Scripting languages
Interpreted from source code directly, no need for compiling, can execute directly. Control applications and used in automation. They are processed by interpreters.
Examples: JavaScript, Python and PHP
C facts
Evolved from B by Dennis Ritchie
Implemented in 1972
Development language of UNIX operating system
Is mostly hardware independent
C programs are portable to most computers usually.
C standard library
C programs consist of pieces called functions, programmers take advantage of a rich collection of existing functions names the standard library.
Parts of C systems
Program development environment
Language
C Standard Library
C program phases
Edit, process, compile, link, load, execute
Linker
During the linking phase, holes are created in the code due to functions being defined/referenced elsewhere such as standard libraries. A linker links the object code with code from missing functions to create an executable image.
gcc
Command to compile and link a program in linux system (GNU compiler)
Execute command
./a.out
Editing
Creating code in the editing program, also where you make corrections, then store it.
Preprocessing a C program
Compiler translates the c program into machine language code.
In C, preprocessor executes automatically before compiler translation, includes other files in file and text replacements.
Compiling a C program
Where the compiler does its job of translating, you may get a syntax/compile error when something is written wrong.
Linking
Linker creates an executable image when there are “holes” in program created by references to functions defined elsewhere (other libraries).
Loading
Program, and other additional components from library are placed in memory before being executed.
Done by loader, which takes executable image from disk to memory.
Execution
Actually running the program.