Exam 4
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
lack of ascorbic acid (vitamin c) will result in reduced stability of
Collagen
Which method would be most useful for solving the structure of a small soluble protein that does not form a repeating structure
NMR
Which disease is not on characterized or associated with unfolded protein aggregate
Scurvy
When oxygen binds to a heme containing protein the two open coodination bonds of Fe are occupied by":
One O2 molecule and one amino acid atom
Which statement about protein ligand binding is correct
The larger the Ka the smaller the Kd
In hemoglobin the transition from T to R state is triggered by
Oxygen binding
Which statement is not correct concerning 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
It increases the affinity of Hemoglobin for oxygen
carbon monoxide is toxic to humans becase it
Binds to the Fe in hemoglobin and prevents the binding of O2
two proteins bind to the same ligand and protein a has half of its binding sites occupied when the ligand concentration is 0.5mM, while protein B has half of its binding sites occupied when the ligand concentration is 0.3 mM. Which protein binds to the ligand more strongly and what is the dissociation constant for that protein ligand interaction
B binds more strongly with a Kd of 0.3mM
Muscle fibers are made of which protein(s)
Actin and myosin
what pair of amino acids can be used to measure the concentration of proteins based on absorbtion
tyrosine and tryptophan
the following data was obtained and follows Michaelis Menten kinetics, what is the Km of this enzyme
2mM
When oxygen binds to a heme containing protein, the two open coordination bonds of Fe2+ are occupied by
One O2 atom and one amino acid atom
The fundamental cause of sickle cell disease is a change in the structure of
Hemoglobin
The formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids is an example of a
condensation
At the isoelectric pH of an amino acid
the amino acid has no net charge
In a conjugated protein, a prosthetic group is
part of the protein that is not composed of amino acids
Which of the following best represents the backbone of two peptide bonds
Ca-C-N-Ca-C-N-Ca-C-N
Amino acids commonly found in the beta turns
include proline and glycine, which help facilitate the tight turns in protein structures.
How to determine the Ka for a protein and ligand
Make an experiment where the protein of defined structure and known quality is combined with different amounts of ligand. The ratio of protein molecules that are bound with a ligand can be determined for each concentration of ligand and plotted. The bound ligand concentration = .5 would be equal to 1/Ka.
Why is michaelis menton kinetics refered to as saturation kinetics
When the concentration of a solution is brought to its very limits to create a Vmax. The Vmax is the backbone of the menton kinetics becase the Km is based off of it and the concentration curve stops increasing at the Vmax. This Vmax would not be obtained unless saturating the protein with its substrate, hence the saturation kinetics, which at full saturation the protein is working at its Vmax.
An enzyme catalyzes a reaction at a velocity of 20 μmol/min when the concentration of substrate (S) is 0.01 M. The Km for this substrate is 1 X10-5 M. Assuming that Michaelis-Menten kinetics are followed, what will the reaction velocity be when the concentration of S is 1 x 10-5 M?
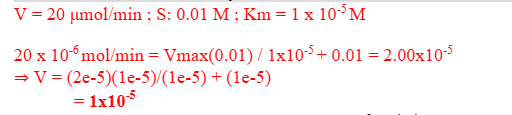
Enzymes with a kcat / Km ratio of about 108 M-1s-1are considered to show optimal catalytic efficiency. Fumarase, which catalyzes the reversible-dehydration reaction {fumarate + H2O → malate} has a ratio of turnover number to the Michaelis-Menten constant, (kcat / Km) of 1.6 x108for the substrate fumarate and 3.x107for the substrate malate. Because the turnover number for both substrates is nearly identical, what
factors might be involved that explain the different ratio for the two substrates?
The Km value for malate has to be greater than fumarate since the turnover rate is closely similar between the two substrates. This could be one possible case because the enzyme may have a higher affinity for fumarate than malate but this is only one factor in the catalysis rate
what is the affect of pH on the binding of hemoglobin (the Bohr effect) and describe this affect
The affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen decreases when the pH is more acidic or basic. The mechanism is when the pH is low the surrounding protein residues are protonated which stabilized them. The protonated proteins in their adjusted conformations have a lower affinity for oxygen than before protonation and then are stabilized.
Name four factors (bonds or other forces) that contribute to stabilizing the native structure of a protein and describe one reagent that interferes with each type of stabilizing force.
Hydrogen bonds: any extreme pH envionment which would change the protonation states of the residues.
Disulfide bonds: any reducing agent or nucleophile to disrupt the disulfide bonds
Van der waals forces: any condition stronger than these forces which is the weakest of the IMF’s
Hydrophobic interactions: any detergents that the protein may come in contact with
Why are glycine and proline often found in a beta turn?
They are found because glycine does not have a side chain, this promotes flexibility when it comes to the angles and geometry needed to form the turn. Proline is found becase its side chain attaches to the protein backbone two times instead of once, which makes it stable to introduce to loops but not common structure.
Describe the five major groups of amino acids
Non polar: hydrophobic and the more hydrocarbons the more hydrophobic they are
Polar: side chains are able to form hydrogen bonds and are usually hydrophilic
Aromatic: usually non polar and absorb UV light, all have at least one COOH group
Acidic : contains an additional acid on side chain
Basic: contains an amine functional group
A biochemist obtains the following set of data for an enzyme that is known to follow michaelis menten kinetics what is the Vmax? How did you determine the Km is 8?
Vmax is the the value that the initial velocity approaches but never reaches. By finding the concentration that half of the Vmax is at you can find the Km which is 8uM
RNA polymerase can synth RNA chains without a primer
True
The sigma factor of E.Coli RNA polymerase combines with the core enzyme to start signals in DNA
False - recognizes a promoter
Termination of transcription is a known function of TFIIH
False- DNA helicase activity, Hydrolysis of ATP, formation of an open complex, nucleotide excision repair (any of the following works
Processing of a primary mRNA transcript in a eukaryotic cell normally involve conversion of normal bases to modified bases, such as inosine and pseudouridine
False- 5’ cap, 3’ polyA tail and splice out intron
5’ terminal cap structure is a 7-methylguanosine joined to the mRNA via 5’ to 5’ triphosphate linkage
True
Compared with DNA polymerase, reverse transcriptase makes more errors because it lacks the 3’ to 5’ proofreading exonuclease activity
True
Several different codons may encode the same amino acid
True
The largest subunit of ribosome contains rRna molecules and the small subunit does not
False both have rRNA
aminoacyl tRNA synthetases “recognize” any tRNA molecules and specific amino acids
False- recognize specific tRNA and specific amino acids
Since introns are genetic “junk” they do not have to be removed precisely from the primary transcript during RNA splicing
False they must otherwise you get wrong coding sequences
All eukaryotic cells use one type of RNA polymerase to transcribe all classes of RNA
False Eukaryotic cells have three types of RNA polymerases