HBS Final Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Last updated 11:18 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
Lateral
Away from the midline
2
New cards
Medial
Closer to the midline
3
New cards
Proximal
Nearest point of attachment
4
New cards
Anterior
Front
5
New cards
Distal
Farthest point of attachment
6
New cards
Superior
Above
7
New cards
Inferior
Below
8
New cards
Posterior
Back
9
New cards
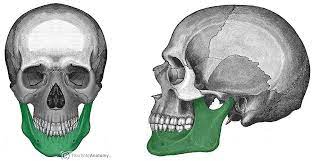
Mandible
10
New cards
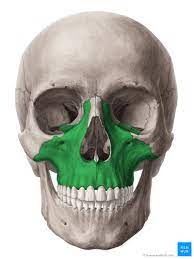
Maxilla
11
New cards
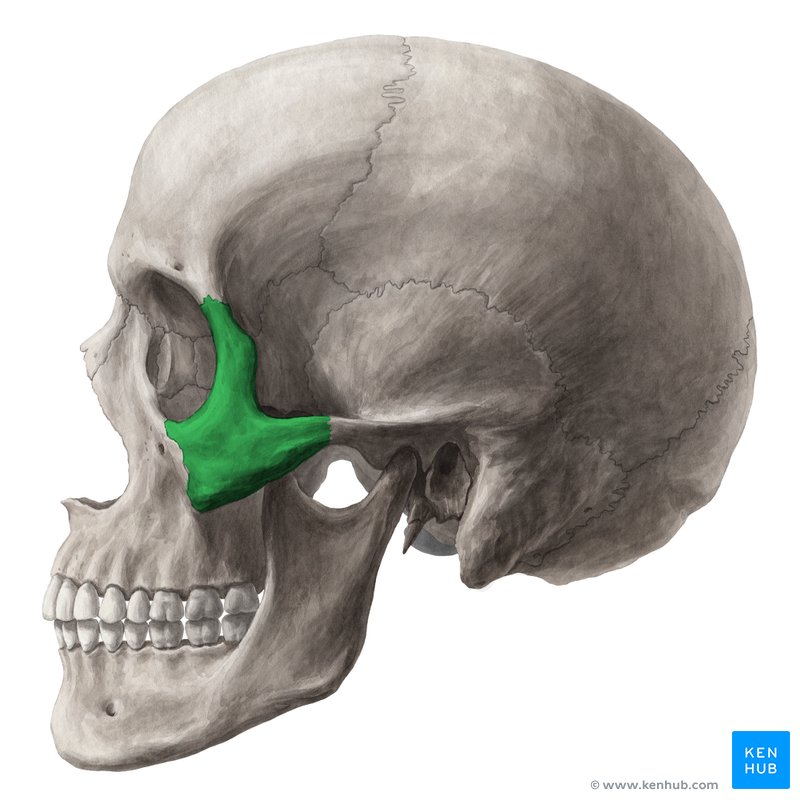
Zygomatic Process
12
New cards
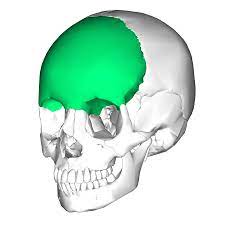
Frontal Bone
13
New cards
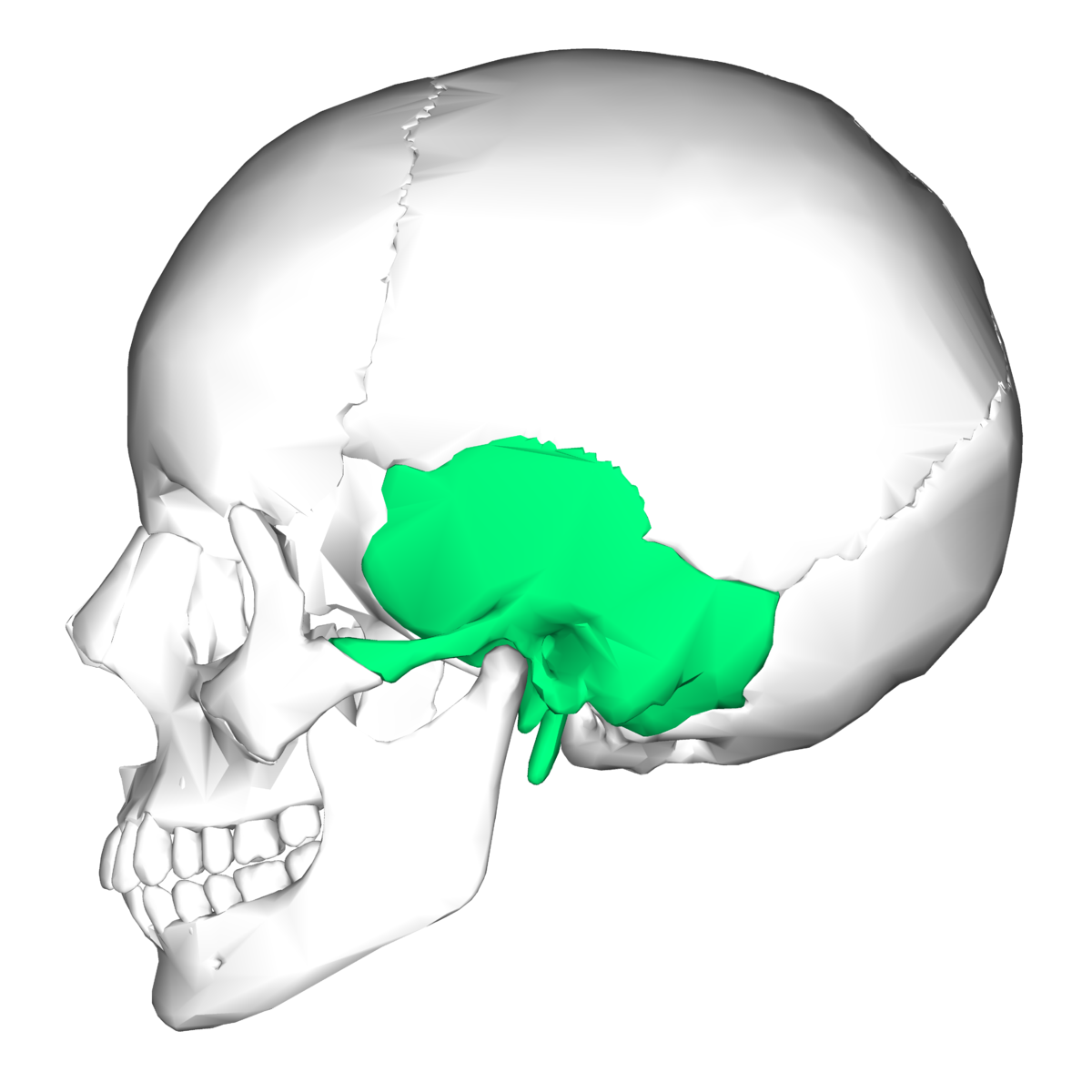
Temporal Bone
14
New cards
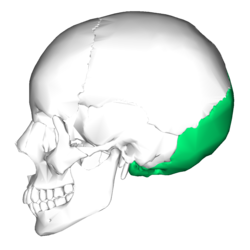
Occiptal Bone
15
New cards
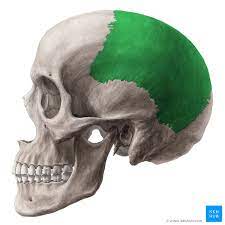
Parietal Bone
16
New cards
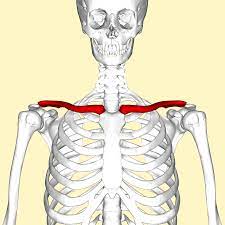
Clavicle
17
New cards
Humerus
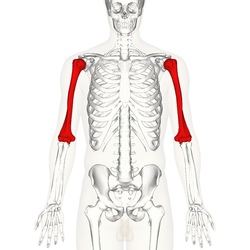
18
New cards
Ulna
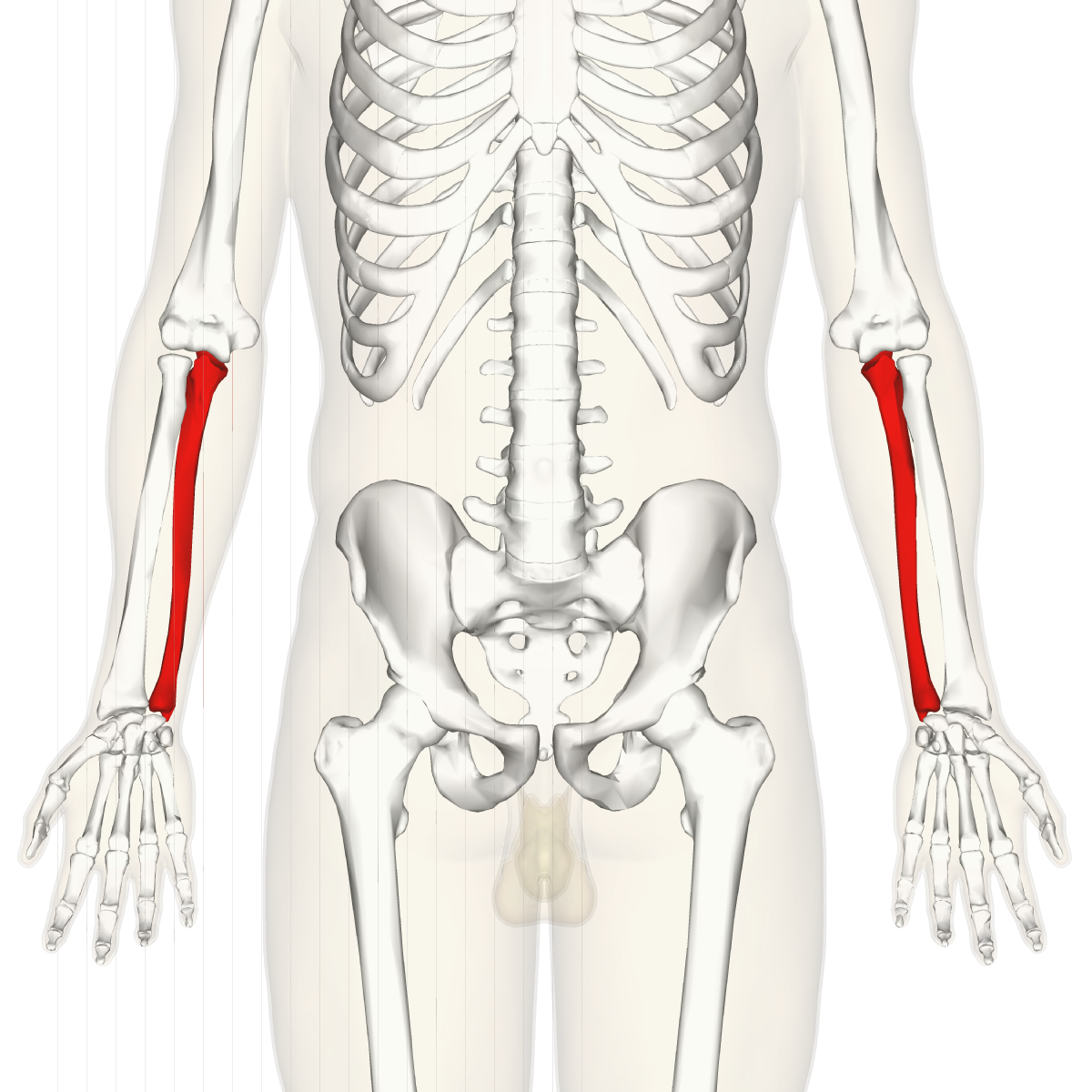
19
New cards
Temporalis
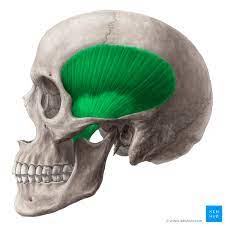
20
New cards
Orbicularis Oculi
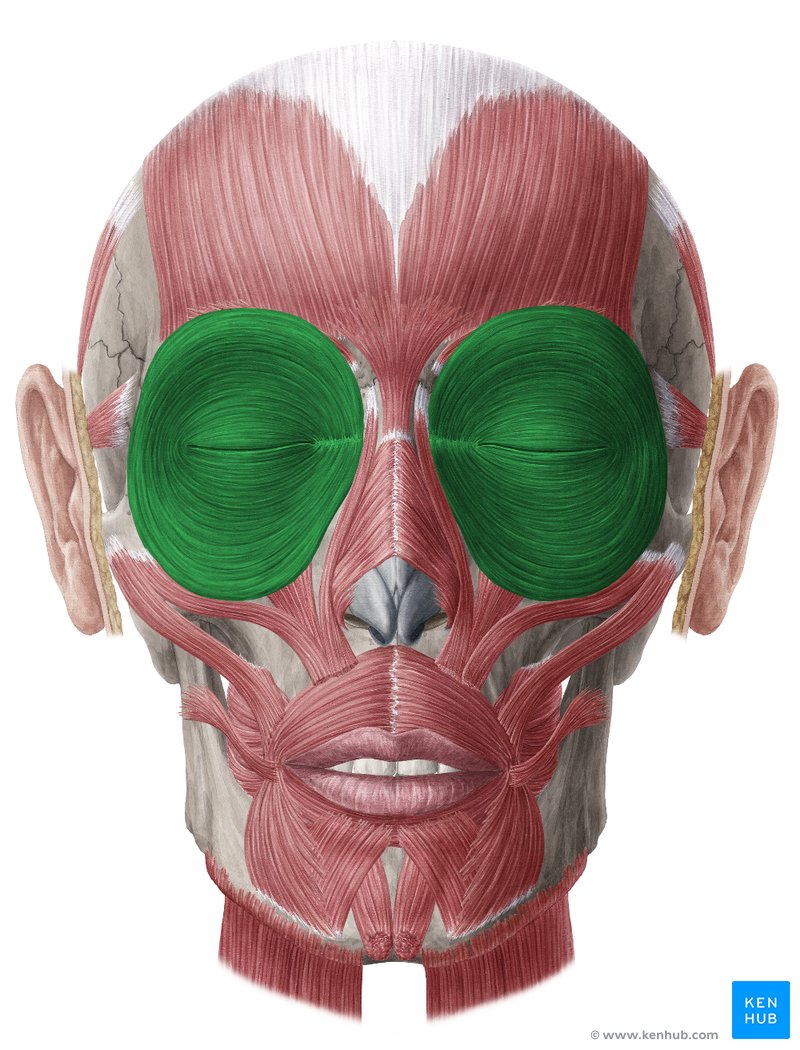
21
New cards
Orbicularis Oris
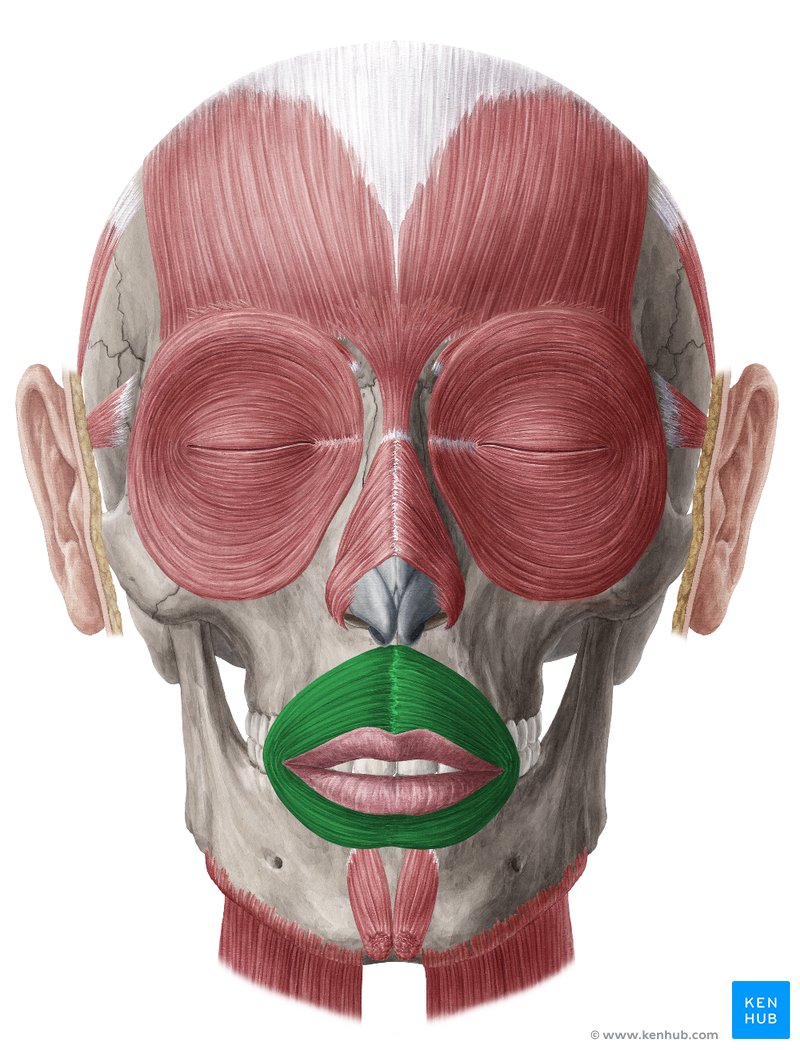
22
New cards
Radius
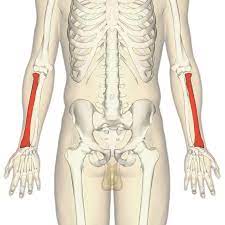
23
New cards
Action of the Temporalis
Move the lower jaw
24
New cards
Action of the Orbicular Oculi
Blink, Wink
25
New cards
Action of the Orbicular Oris
Move the lips
26
New cards
How can differences in our skeleton contribute to our identity?
Differences in our skeleton contribute to our outside appearance, which relates to the size of our body and muscles.
27
New cards
How do the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system work together to control the body?
The nerves of the PNS allows the brain and spinal cord to send and receive information.
28
New cards
Why is the story of Phineas Gage considered so extraordinary? What does his story teach us about the brain?
The story is extraordinary because Phineas Gage survived his injury and lived on after the fact, and this story taught us that the brain has different regions that control our characteristics.
29
New cards
The path of electrical impulses through the brain
Impulses are sent down a neuron starting in the dendrites, and moves down the axon. The myelin sheath speeds up the nerve impulses, and the nodes of ranvier speed up the action potential. At the axon terminal the impulse goes through the synapse to the neurotransmitters.
30
New cards
How do neurons convey information using both electrical and chemical signals?
Chemical and electrical signals are conveyed across the cell membrane. Electrical signals are converted into chemical signals from neurotransmitters.
31
New cards
Which parts of the eye are most important when it comes to focusing light so we can see a perfect image?
The cornea allows for the eye to bend light and focus on an image. The lens focus the light on the retina.
32
New cards
The relationship between “seeing” with the eye and “perceiving” with the brain
When the eye sees an image in front of it, the brain quickly assumes it is that of a past image seen.
33
New cards
Nasal
Nose
34
New cards
Oral
Mouth
35
New cards
Cervical
Neck
36
New cards
Acromial
Collarbone
37
New cards
Thoracic
Chest
38
New cards
Brachial
Bicep
39
New cards
Anticubital
Below the Bicep
40
New cards
Abdominal
Abs
41
New cards
Umbilical
Belly Button
42
New cards
Carpal
Wrist
43
New cards
Digits
Fingertips
44
New cards
Pubic
Genital Region
45
New cards
Patellar
knee
46
New cards
Crural
Front Shin
47
New cards
Tarsal
Feet
48
New cards
Orbital
Eyes
49
New cards
Buccal
Cheek
50
New cards
\
Sternal
Sternal
Sternum
51
New cards
Axillary
Armpit
52
New cards
Pelvic
Above Pelvis
53
New cards
Coxal
Hips
54
New cards
Inguinal
Above Pubic Region
55
New cards
Femoral
Femur
56
New cards
Fibular
Side of the shin
57
New cards
Cephalic
Whole Head
58
New cards
Occipital
Back of the Head
59
New cards
Deltoid
Shoulder
60
New cards
Scapular
Scapula
61
New cards
Vertebral
Vertebrae
62
New cards
Olecranal
Back of the Elbow
63
New cards
Lumbar
Low Back
64
New cards
Sacral
Above Glutes
65
New cards
Gluteal
Glutes
66
New cards
Popliteal
Back of the Knee
67
New cards
Sural
Calf
68
New cards
Calcneal
Heel
69
New cards
Metatarsal
Bottom of the Foot
70
New cards
\
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that lines the cavities of organs to provide protection (Ex. skin)
71
New cards
Connective Tissue
Tissue that binds tissue and organs together. (Ex. blood)
72
New cards
Muscle Tissue
Tissue that allows movement (Ex. skeletal muscle)
73
New cards
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that controls body activities (Ex. neurons)
74
New cards
Bones used to identify height
Femur, Tibia, and Radius
75
New cards
Bone used to identify sex
Pelvis
76
New cards
Bone used to identify race
Skull
77
New cards
Biometrics
Body measurements related to human characteristics (Ex. fingerprints)
78
New cards
Pituitary Gland
Controls the functions of other endocrine glands
79
New cards
Thyroid Gland
Releases hormones that control metabolism
80
New cards
Thymus
Makes and trains special white blood cells (t-cells)
81
New cards
Pancreas
Produces enzymes that break down sugars, fats, and starches
82
New cards
Adrenal Gland
Makes steroids hormones and adrenaline
83
New cards
Dendrites
appendages that are designed to receive communications from other cells. They resemble a tree-like structure, forming projections that become stimulated by other neurons and conduct the electrochemical charge to the cell body
84
New cards
Axon
where electrical impulses from the neuron travel away to be received by other neurons
85
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
function as repeaters to regenerate the action potential as it propagates in a saltatory manner along the axon to the nerve terminal
86
New cards
Myelin Sheath
an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty substances. This allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells
87
New cards
Synapse
the site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two nerve cells
88
New cards
Neurotransmitters
a chemical substance that is released at the end of a nerve fiber by the arrival of a nerve impulse and, by diffusing across the synapse or junction, causes the transfer of the impulse to another nerve fiber, a muscle fiber, or some other structure.
89
New cards
Frontal Lobe
voluntary movement, expressive language and for managing higher level executive functions
90
New cards
Parietal Lobe
processes sensory information it receives from the outside world, mainly relating to touch, taste, and temperature
91
New cards
Temporal Lobe
Memory and Hearing
92
New cards
Occipital Lobe
Vision
93
New cards
Spinal Cord
Carry’s messages and sends sensory information
94
New cards
Cerebellum
Helps maintain balance and posture
95
New cards
Depolarization
the gated sodium ion channels on the neuron's membrane suddenly open and allow sodium ions (Na+) present outside the membrane to rush into the cell. As the sodium ions quickly enter the cell, the internal charge of the nerve changes from -70 mV to -55 mV
96
New cards
Repolarization
a stage of an action potential in which the cell experiences a decrease of voltage due to the efflux of potassium (K+) ions along its electrochemical gradient.
97
New cards
Hyperpolarization
when the membrane potential becomes more negative at a particular spot on the neuron's membrane
98
New cards
Endocrine Gland
A gland that secretes hormones directly into the blood (pituitary gland)
99
New cards
Exocrine Gland
Substances are produced and released on the body’s surface (sweat)
100
New cards
How do hormones interact with target cells?
They cause cellular changes by binding to receptors on target cells