Micro Lab
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Lab PPE
1) lab coat
2) hair tied (long)
3) get rid of jewelry
4) closed toe shoe
5) gloves
Sanitation desk & handwashing & microscope (when & how)
Handwash
before/after lab wash hands
a) cold & hot faucet on
b) rinse hands in water
c) lather soap under nails and hands
d) rinse
e) paper towel & wipe
f) use paper towel to turn off sink
g) dispose paper towel
Desk
before/after labs clean desk
a) drench lab table in bleach; leave a film
b) wipe
Microscope
before/after use is ideal
a) wipe lens w kim tech wipes & cleaning sol → get rid of oils & stuff on screen
b) lower stage after ALWAYS
Personal safety FOOD & storage
1) Do not eat, chew gum or drink in lab
2) electronics & class work material (lab, workbooks) must be stored at safe area w/ little contamination
Disposal
hazardous material
glass
test tubes
contaminated waste w/body fluids
nonbiohazard
Disposal
no HAZARDOUS & infectious material in sink (like: MATCH & PAPER)
GLASS disposal in hazardous container
test tubes→ remove label→ dispose in proper container
contaminated waste w/body fluids→in proper container
non biohazard→ in designated containers
Spill (keep in mind glass and spill)
Pour disinfectant
Inform professor and students
Let 10 mins pass
Use paper towels to soak
do NOT use bare hands (gloved) to get towels if glass SWEEP w broom
Aseptic technique & quadrant
Sterilize WHOLE inoculating loop w flame
let it rest on metal
open test tube (pinky method) & heat lip
grab loop put it in once all the way
flame lip & seal tube w cap (pinky method)
but loop in medium ( agar or liquid)
1st quadrant
strelize loop
DRAG FROM FIRST to 2nd quadrant
sterilize
DRAGE FROM SECOND to 3rd quadrant
sterilize
DRAG FROM THIRD to 4th quadrant
sterilize
seal medium
Fire alarm
fire extinguisher
eye wash
shower
first aid kit location
door of entry
near door of inner office
near door of inner office
near door of inner office
on shower & wash station wood
If fire starts or fire alarm sounds ( 3 things)
unplug electrical apparatus & turn off burner
press button at door of inner office to shut off gas
evacuate in orderly manner
if you have contact lenses and something gets into ur eye should you take it off?
no, lenses can melt onto eye and don’t want to peel it and ruin eye
Holds the objective lens and can be rotated to change the magnification.
Rotating/Revolving Nosepiece
Eyepiece which contains a lens to magnify an image 10x that projected by the objective lens.
Ocular Lens
Connects the Ocular Lens to the Objective Lenses and provides alignment to direct the light from the specimen into the viewer's eye.
Body Tube
Connects the body tube to the base. One hand should be around this when carrying a microscope.
Arm
First knob you should use and always under low power, makes large adjustments to the focus. Should never be used in high power.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
The second knob you should use under higher power for exact focusing.
Fine Adjustment
Adjustable lens system that permits the use of a low power lens, a medium lens, or a high power lens
Objective Lenses
This objective lens provides the lowest magnification, 4 x
Scanning Power
This objective lens provides a medium magnification, or power, 10x
Low power
This objective lens provides the abt the highest magnification, 40x
high power
Objective used w/ oil 100x
Oil-immersion
Where you place the slide containing the specimen; It contains a hole that allows light to pass through the stage and onto the specimen.
Stage
Holds the slides in place on the stage for viewing.
Stage Clips
It contains a dial that rotates to adjust the amount of light that reaches the specimen and is passed upwards towards the eyepiece. Change it w what?
iris diaphragm
change w obj lense power
Supports the weight of the microscope. Contains the electronics and the light source.
Base
An electric source of illumination or a mirror used to direct light upward.
Light Source/ illuminator
The lens under the stage that focuses light from the illuminator through to the hole in the stage
Condenser Lens
Total Magnification =
Ocular Lens Magnification x Objective Lens Magnification
As obj lense mag (+)
FOV decreases
microscope inverts
image vertically and laterally
Why do we use oil only with the 100× objective?
oil = light control (bends and travels) for high power only.
Why do we calibrate the ocular ruler at different total magnifications bc each lense has what and allows which conversion?
ensures accurate measurement of microorganisms bc→
a) each objective lens has a different µm-per-ocular-unit value
b) allowing conversion of ocular units into real metric units.
Know ur values
Objective | Total Magnification | Millimeters (mm)/ space | Micrometer (Mm)/space |
4x | |||
10x | |||
40x | |||
100x |
Objective | Total Magnification | Millimeters (mm)/ space | Micrometer (Mm)/space |
4x | 40x | 0.025 | 25 |
10x | 100x | 0.01 | 10 |
40x | 400x | 0.0025 | 2.5 |
100x | 1000x | 0.001 | 1 |
does cell shape change with objective lense changing
No, ONLY lenses CHANGE
Of a cell is 20 ocular spaces in 40x total mag what is micro or milimeter?
0.5mm
500 micrometer
when is plate properly streaked?
describe the amount of growth in FIRST area
describe growth in later quandrants
where should isolated colonies be
Heavy growth in the first streak area
Progressively lighter growth in each subsequent streak
Well-isolated colonies in the final streak area
A plate is not properly streaked if you see:
growth where?
isolated or no isolated___?
which kind of streaks?
overlapping?
Growth covering the entire plate (no dilution)
No isolated colonies
Thick, continuous streak lines
Colonies overlapping or merging together
How does chromogenesis help distinguish microorganisms?
allows microorganisms to produce different colored colonies on chromogenic media →making it easy to visually differentiate species in mixed cultures.
when is something a pure culture?
size, shape, texture, & color are consistent throughout
can you isolate a single microbe from a mixed culture?
Yes→streak method→separate individual cells→isolated colonies

6 forms known as what?
Circular
Spindle (diagonal oval)
concentric (target)
irregular
filamentous (filament like)
Rhizoid (like filamentous but less complex)

6 Margins look like what?
Entire (circle)
undulate (slightly spiky)
scalloped (looks like scallop w ridges)
erose (pom pom)
lobate (nickelodeon drop)
filamentous (same)
6 elevations
flat
raised
subsurface (underneath)
convex (contact lenses)
pulvinate (lid on globe)
umbonate (bottle cap)
4 Appearance terms
dull
glistening
shiny
wet-looking
4 optical properties (TIOO)
opaque
opalescent
iridescent
translucent
Pigmentation 2 types & know what they mean
pigmented
nonpigmented
5 surface texture types?
Smooth
wrinkled
rough
powdery
dry
Microbe HUNT→How were nitrogen-fixing microbes enriched from soil?
By culturing soil in a nitrogen-free medium, so only microbes that can fix atmospheric nitrogen grow.
MICROBE HUNT→Thermoduric treatment
heat treatment killed NON-heat-resistant bacteria while allowing heat-resistant or spore-forming bacteria survive & grow
Microbe HUNT→How were benzoate-using microbes enriched from soil?
By using a medium where benzoate is the sole carbon source, selecting for microbes that can metabolize benzoate.
MicrobeHUNT→Why use enrichment instead of streaking soil directly onto nutrient agar?
Enrichment selectively favors target microbes and prevents fast-growing, non-target organisms from dominating growth.
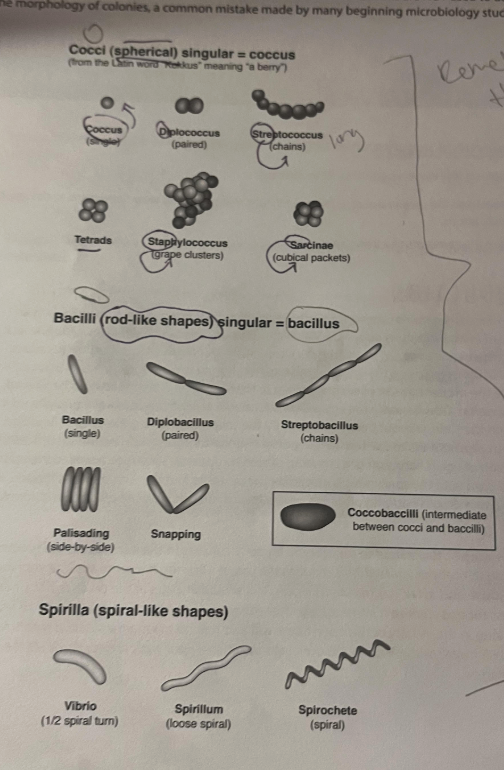
Bacteria (NOT EUKARYOTES→Yeast, Paramecium, & Mold)
A) 3 shapes known as what?
B) Within those shapes, which has 6? Which has 5? Which has 3? All of them known as what?
C) which one is grape shape? which one is rice shaped? which one is spaghetti shaped?
D) which one is in between cocci and bacillus?
A) Coccus (circle)
coccus (one grape)
diplococcus (two sets of grapes)
streptococcus (string of grapes)
tetrads (one cube layer of grapes)
staphylococcus (cluster of grapes)
sarcinae (layered cube of grapes)
B) Bacilli (rod-shaped)
Bacillus (one rice grain)
diplobacillus (2 rice grain lined)
streptobacillus (4 rice grain lined)
palisading (4 rice grain cube)
snapping (2 rice grain V shape)
C) Spirlia (spiral)
vibrio→ short pasta
spirillum→ soft curly spaghetti
spirochete→corkscrew spaghetti
D) coccobaccilli
1st step Crystal Violet (Primary stain)
what color?
# stain applied?
Colors all bacteria purple
First stain applied
2nd step Gram’s Iodine (Mordant)
forms what type of complex is it
helps what
Forms crystal violet–iodine complex
Helps the dye stick inside gram-positive cells
3rd step Ethanol or Acetone (Decolorizer)
Which step?
Removes dye from which bacteria?
Which retains color?
Differential step
Removes dye from gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria retain purple color
4th step Safranin (Counterstain)
what color stain for which type of cells?
which type of cell remains which purple?
Stains gram-negative bacteria pink
Gram-positive bacteria remain purple
Why does gram (+) retain dye versus gram (-)? Because of this difference what color do they remain?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer
Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane
because of this…
Gram-positive bacteria retain crystal violet → purple
Gram-negative bacteria lose crystal violet and take up safranin → pink
simple v.s. negative v.s. differential stain
Simple stain: one dye, all cells the same color
Negative stain: stains the background, not the cells
Differential stain: uses multiple dyes to distinguish cell types
If the Gram’s iodine step was skipped, what color would the cells likely be?
Most cells would appear red/pink.
Why:
Gram’s iodine forms the crystal violet–iodine complex.
If iodine is skipped:
Crystal violet is not fixed in the cell
Ethanol removes it from both types
Safranin stains most cells pink
what stain for flagella?
flagella stain is required.
Introducing a sample into a nutrient medium is called:
Inoculation = placing microorganisms into a growth medium.
Transferring a sample to a separate medium to obtain a single microbe (pure culture) is called:
Isolation separates individual microbes so a pure colony can grow.
Macroscopically observed colony characteristics include all EXCEPT:
Cell shape requires a microscope
What is the most universal diagnostic staining technique for bacterial identification and classification? & what type?
Gram stain
Differential stain
Why:
It uses multiple dyes and produces different colors depending on bacterial structure.
In addition to liquid, which are physical types of media?
know what each is used for or what they contain
Solid (convertible to liquid) → contains agar
Solid (not convertible to liquid) → egg-based media
Semisolid → used to test motility or oxygen requirements
5 i’s
Inoculation – placing the specimen into a growth medium
Incubation – storing the culture under proper conditions so microbes grow
Isolation – separating individual microbes to obtain pure colonies
Inspection – observing colony morphology and microscopic features
Identification – determining the exact microorganism (stains, tests, etc.)
The Gram stain follows a specific sequence (four) :
Crystal violet (primary stain)
Gram’s iodine (mordant)
Alcohol or acetone (decolorizer)
Safranin (counterstain)
Why use heat with certain stains and not with other ones?
Use heat for structures that are tough and impermeable (endospores, acid-fast walls).
Avoid heat for fragile structures (capsules, some glycocalyx or flagella stains).
Why use basic dye? Why fix cells? And why rinse with water?
Use basic dye | Positively charged → binds negatively charged cells |
Fix cells | Kill, stick to slide, preserve structure |
Rinse with water | Remove unbound dye, improve contrast |
3 reasons why is it a bad idea to throw out shards of glass and paper towel in normal trash?
glass could injure custodial staff or others
glass is most likely contaminated with microorganisms
biohazard material like the towel needs to be specifcally disposed to prevent infection and exposure
why should 4x and or 10x be used to intially focus on specimen
large FOV→easy to focus & find specimen→doesn’t hit glass slide
What is chromogenesis, and how can it be used to define the purity of culture? What if contaminated?
bacteria→pigment→clarity of morphology
size, texture, shape, elevation, and color will not resemble one another
Can a pure culture containing a single type of microbe be prepared from a culture with a mixture of cells explain?
Isolation on solid media + colony selection → pure culture from a mixed culture.
Eukaryotic cells are distinguished from prokaryotic cells by the presence of internal membranebound structures called organelles. In which eukaryotic cell can you find internal structures? What do you think these structures are?
(bacillus, anabaena (green), saccharomyces/yeast (yellow), aspergilus niger/mold (yellow green))
eukaryotic cells (Saccharomyces (yeast) & Aspergillus (mold) ) have internal membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotes rely on cytoplasmic structures, not true organelles
We add immersion oil to view bacterial slides.Why is the oil NOT used with the Paramecium slide?
Use oil immersion: for very small specimens (bacteria, fine structures) under 100× objective.
Do NOT use oil: for large eukaryotic microbes (Paramecium, amoeba, yeast) viewed at 10× or 40×.
What happens if you accidentally flip your slide upside-down so the specimen is on the bottom? Can you still see it clearly with different objective lenses?
Specimen may be visible but blurry; low/medium power might work with refocusing, high-power/oil won’t focus properly.
Why are thick or dense smears less likely to produce a good smear preparation for microscopic evaluation?
Too many cells overlap → hard to see individual cells and their shapes.
Why is it essential that smears be air-dried rather than gently heated over a flame to speed up the drying process?
Heat can distort or burst cells; air-drying preserves shape for staining.
Why is fixing important during the direct staining process?
Fixing kills cells, sticks them to the slide, and preserves their shape.
Which part of the cell is a basic stain actually staining
The negatively charged cell surface (membrane, wall, cytoplasm).
Think about what these biological stains are doing, and how they "stick" to the cells even when rinsed with water.
Do you think that coffee would be considered a good biological stain?
After all ifyou spill it on a white shirt, the shirt will have a coffee stain. (HINT: A coffee stain that is still wet will rinse out with just water.)
No. Coffee rinses away with water → it doesn’t bind to cells like a proper dye.
When doing 5 I’s with colony v.s. culture what is different, exceptic ASEPTIC technique
1) colony→ water on slide→inoculate & mix → fix→stain→rinse
2) culture→inoculate driectly on slide→fix→ stain→rinse
How does a basic dye differ from an acidic dye? (HINT: Think about differences in the chemicals and what they can Interact with).
1) basic dye (+)→(-) of a cell like cell wall & DNA
2) acidic dye(-)→(-) of a cell=repelling→ doesn’t stick to cell but background
When you perform a negative stain, why does the specimen appear light, while the background is stained dark?
(-) indirect dye repels (-) part of cell→stains background
When you perform a simple stain on cells, why does the direct stain (with a basic dye) require rinsing with water, while an indirect stain (with nigrosin) does not?
direct stain (+)→ sticks (-) of cell→rinsing is NEEDED to get rid of extra dye→aid in visibility of cells
indirect stain (-)→ repels cell→ sticks but not as tight as direct→ rinsing would wash the stain off→ which is a NO→ since we need it to see shape of cells (CAN’t see inside though)
Which method, direct or indirect staining, do you think would give you a better estimate of the true size of a microorganism? Explain your reasoning. HINT: Bacteria cells can have structures outside of the cell wall layer.
indirect (-)→ doesn’t stick or need heat fixation→ which will alter cell’s shape & will visualize all structures outside → for accurate size determination this method is recommended