Topic 9- Forces and their effects
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
force
a push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object
can cause an object to change direction, speed or shape
non-contact forces are caused by
fields
examples of non-contact forces
gravitational force
caused by gravitational attraction between two masses
increased by increasing mass
electrostatic force
caused by charged objects repelling or attracting each other
increased by increasing strength of electrical field, bringing charges closer together
magnetic force
caused by a force exerted on a magnetic material in a magnetic field, two magnetic poles
increased by increasing strength of field, bringing objects closer together
contact forces
friction
opposes motion
occurs when objects rub against each other
air resistance
type of friction
occurs when air particles hit and push against an object travelling in air
tension
pulls two objects connected by a length (e.g. string)
occurs when a force is applied to both ends of a length
normal contact/reaction force
perpendicular to the surface of contact due to the push of one object on another (pushes touching objects apart)
occurs when objects are supported by a surface
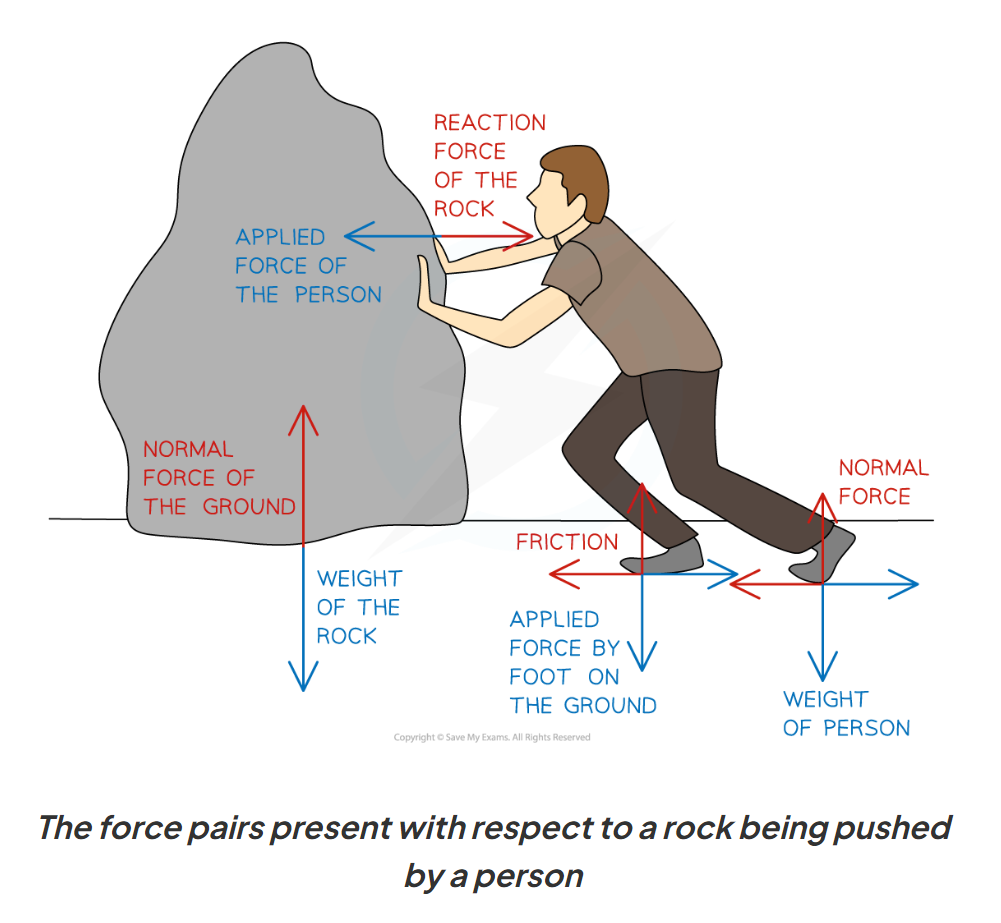
force pairs (why and characteristics)
when there is an interaction between two objects, force is exerted on both objects (different objects)
same type of force
acting on different bodies
in opposite directions
in a line
Newton’s third law
when two forces interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other
how to find the resultant force of non-aligned forces (scale drawings)
connect the arrows tip to tail
in free body force diagrams, should the arrows be to scale? what should happen if they are balanced?
yes; they should form a closed triangle when put tip-to-tail
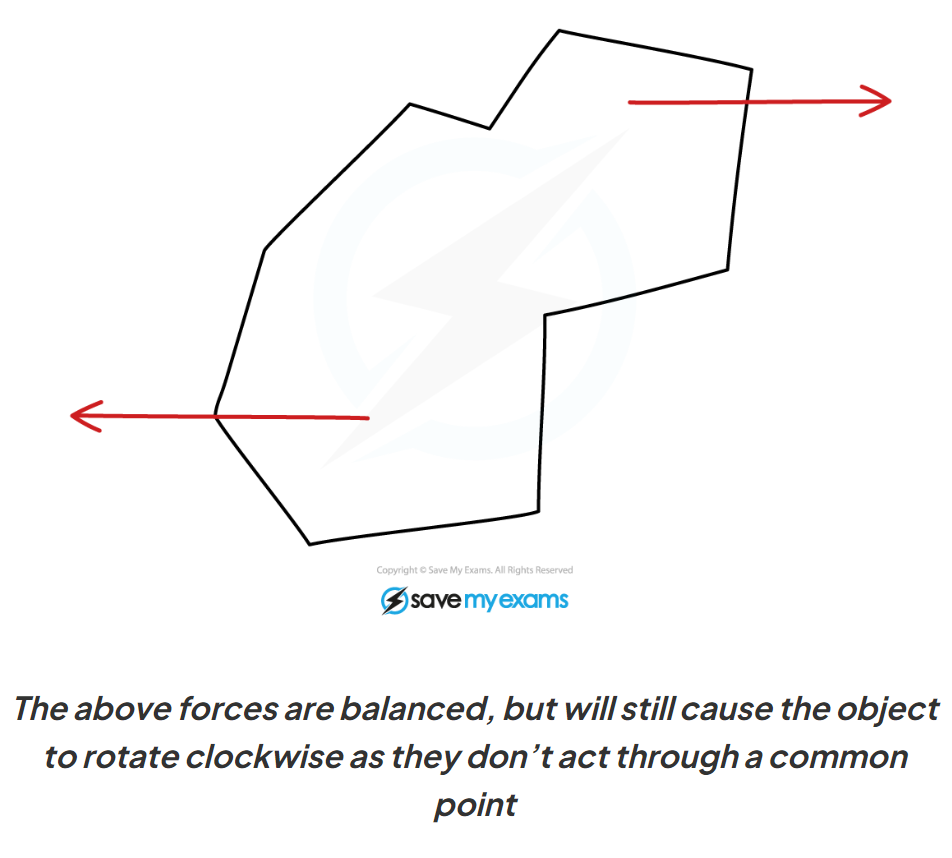
when can forces cause an object to rotate? (2 things)
a force on one side of a fixed pivot
two forces act on an object but DON’T pass through the same point (even if they are balanced)
moment
turning effect of a force about a pivot
moment equation
m = F x d (perpendicular distance from pivot)
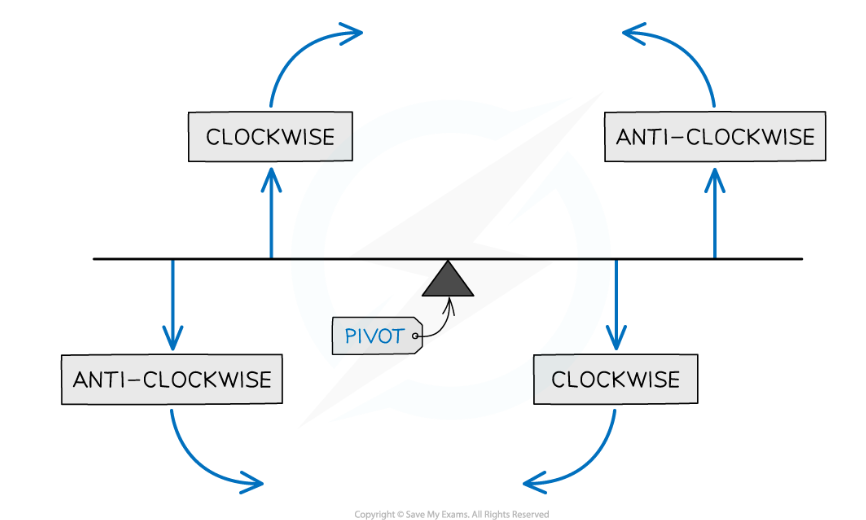
principle of moments
if an object is balanced, the total clockwise moment about a pivot equals the total anticlockwise moment about that pivot
levers and gears can be used to
transmit and amplify the rotational effects of forces
how do levers transmit and amplify the rotational effect of a force?
smaller force applied to end of lever (further away from the pivot than where the force is needed)
greater distance increases moment, therefore the force exerted will be greater at the end with the smaller distance from pivot
how do gears transmit and amplify the rotational effect of a force?
turning force applied to one wheel
interlocking teeth turn adjacent wheel in opposite direction
moment = turning force x wheel radius
a larger gear can turn a smaller gear faster with a smaller moment
a smaller gear can turn a larger gear slower but with a greater moment
what is the relationship between the ratio of teeth, moments, and radii between 2 gears?
ratio of moments = ratio of teeth no. = ratio of radii