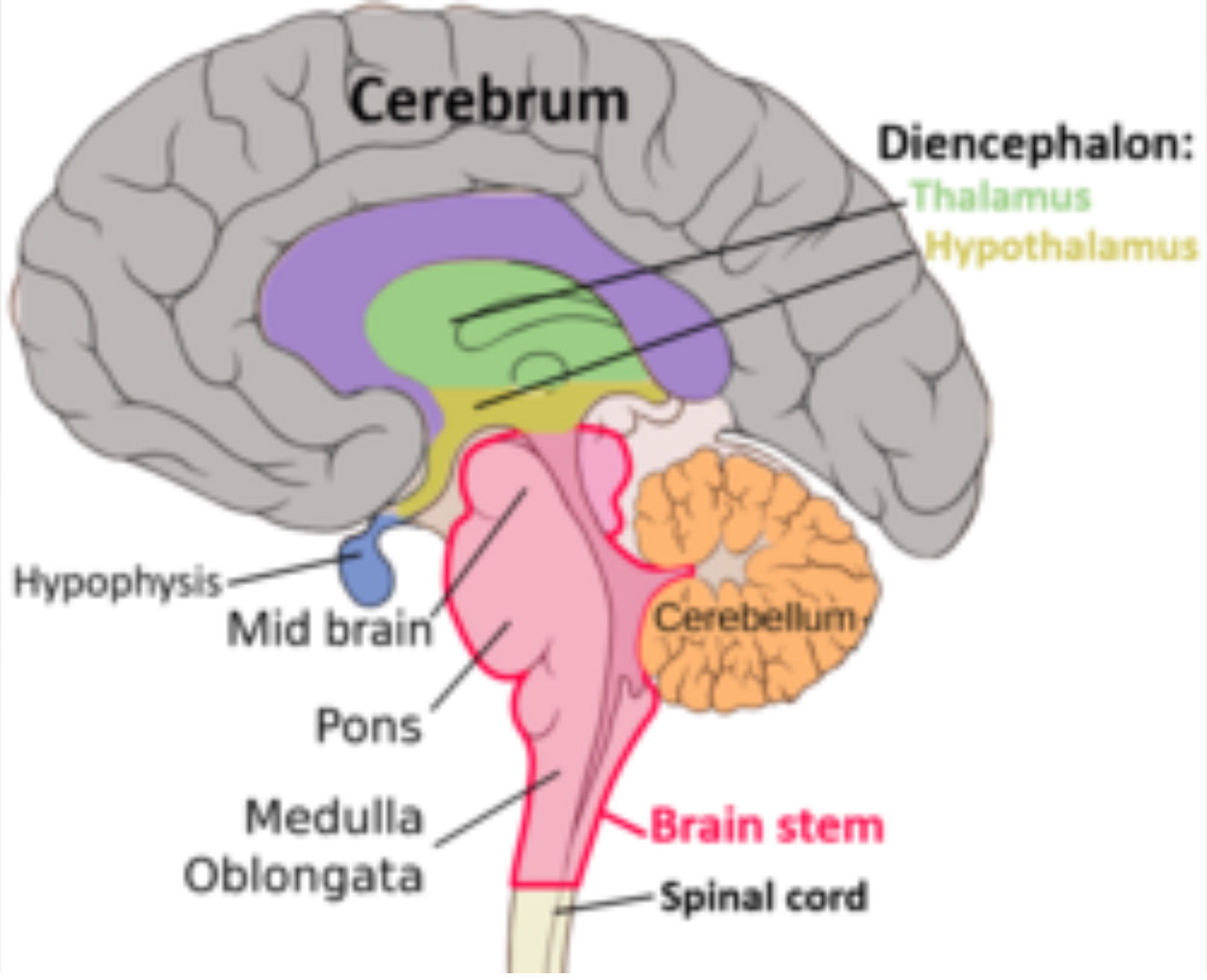
8 Major Regions of Brain
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based on Slideshow from Prof. Munoz Neuroanatomy class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Cortex (Cerebrum)
▪ Conscious thought processes and intellectual functions
▪ Memory storage and processing
▪ Conscious and subconscious regulation of skeletal muscle contractions
▪ Largest Part of brain
▪ Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres
Limbic System
A functional grouping that
▪ Establishes emotional states
▪ Links conscious functions of cerebral cortex with autonomic functions of brain stem
▪ Facilitates memory storage and retrieval
Thalamus
▪ One half of Diencephalon
▪ Filters ascending sensory information for primary sensory cortex
▪ Relays information between basal nuclei and cerebral cortex
▪ Plays a role in regulating sleep, alertness, and consciousness.
Hypothalamus
▪ One half of Diencephalon
▪ Regulates body temperature, hunger and thirst
▪ Controls circadian rhythms via. suprachiasmatic nucleus
▪ Centers controlling emotions, autonomic functions, and hormone production
Cerebellum
▪ Second largest part of brain
▪ Coordinates repetitive body movements
▪ Two hemispheres
▪ Covered with cerebellar cortex
▪ Adjusts postural muscles
▪ Fine-tunes conscious and subconscious movements
▪ The pons and the cerebellum act in synchrony to regulate the movements of the limbs.
▪ Compares motor commands with actual execution to detect errors (versus basal nuclei).
Overseeing the postural muscles of the body and making rapid adjustments to maintain balance and equilibrium are functions of the _____
Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
Processes sight, sound, and associated reflexes
Maintains consciousness
Contains Tectum, aka Superior and Inferior Colliculus
Also contains Tegmentum, Red nucleus and Substantia Nigra
Alsooo contains Cerebral peduncles
Pons
Part of Brainstem
Connects cerebellum to brain stem
Links to mesencephalon, diencephalon, cerebrum and spinal cord
Is involved in somatic and visceral motor control
Damage to the cerebellum or pons may result in poor coordination of limb movement
Nuclei involved with respiration
middle cerebellar peduncles - links cerebellum with pons
Medulla Oblongata
Part of Brain Stem
Allows brain and spinal cord to communicate
Coordinates complex autonomic reflexes
Controls visceral functions
Nuclei in the Medulla: Autonomic nuclei, Sensory and motor nuclei, Relay stations
- Affects cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities
The medulla oblongata regulates Blood pressure and Respiration .
8 Major Brain regions in order
Eight Major Regions of the Brain
▪ Cortex (Cerebrum)
▪ Limbic System
▪ Thalamus
▪ Hypothalamus
▪ Cerebellum
▪ Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
▪ Pons
▪ Medulla oblongata