The Living World - Introduction to Ecosystems: Tropical Rainforest
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Ecosystem
A natural system that comprises a community of plants and animals that interact with each other and their physical environment
Nutirent cycling
A set if processes whereby organisms extract minerals necessary for growth from soil or water, before passing them on through the food chain- and ultimately back to the soil and water
Producer
An organism or plant that is able to absorb energy from the sun through photosynthesis.
Abiotic
Non-living things, e.g soil,rocks,water
Food chain
The connections between different organisms(plants and animals) that rely upon one another as their source of food
Biome
Large areas on the earth’s surface with fauna and flora adapting to their environment
Consumer
Creature that eats herbivores and/or plant matter.
Biomass
Reneweable organic materials, that comes from living or recently living organisms, such as wood, agricultural crops or wastes. Can be used to generate electricity.
Biotic
Living things
Decomposer
An organism such as bacterium or fungus, that breaks down dead tissue, which is then recycled to the environment
Biodiversity
The variety of life in an ecosystem
Food web
A complex hierarchy of plants and animals relying on each other for food.
Epping Forest’s location
Located East of London
Characteristics of Epping Forest,UK
High Biodiversity
A large number of native tree species including oak,elm,ash and beech.
177 species of moss and lichen grow here
Many insects,mammals and bird consumer species are supported,including nine amphibian and reptile species and 38 bird species.
Epping’s Forest food web
Fox,Ow
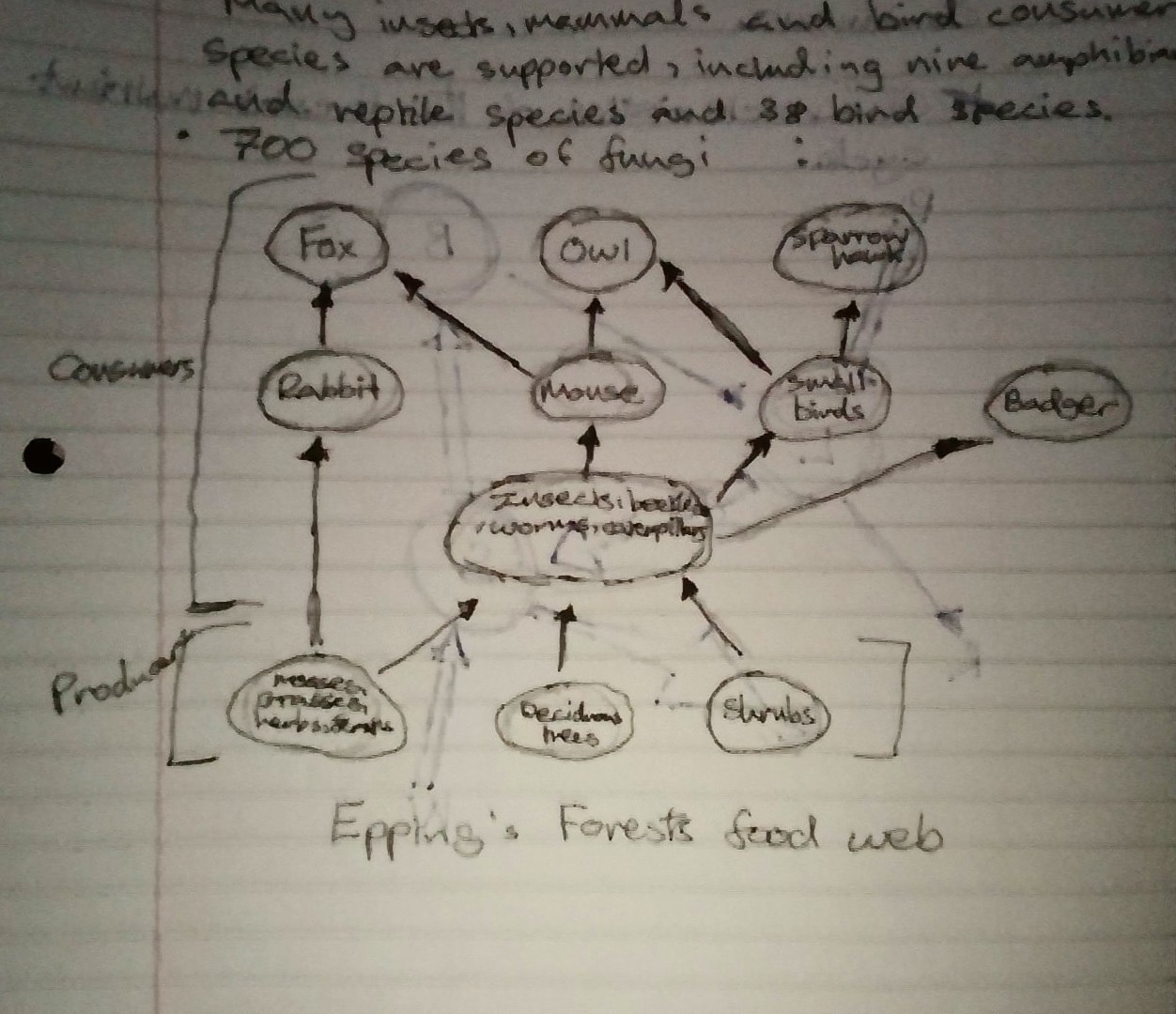
How the forest is interdependent
In autumn, the trees shed their leaves to conserve energy. The decomposers and detritivores convert the nutrients in leaves to humus in the soil which supports the new season’s plant growth, in turn it will support the primary consumers.
Epping Forest Interdepence: People and Animals
People maintain the forest and ponds the habitats of the animals and so they don’t become endangered or extinct, e.g herd of fallow deer
Animals provides an income for people working in tourism, such as bird watching, e.g Wood Pecker
Epping Forest Interdepence: People and Plants
People - Coppicing encourages growth
Pollarding deciduous trees such as Oak.
Plants have their seeds spread by people, such as berry picking
Epping Forest Interdepence: People and soil
Litter and fertilisers from people contributes the soil growth
Management of maintaining fertile soils
Epping Forest Interdepence: Animals and Plants
Plants provide shelter and food for the animals, e.g Fox.
Grazing from animals maintains the grassland, flora and fauna associated
Epping Forest Interdepence: Animals and Soils
Earthworms, mix up the nutrients for fertile soil.
Dead bodies and faeces contribute to the soil
Epping Forest Interdepence: Climate and Plants
Climate provides the optimum temperatures and condition for growth, e.g 30 inches of rainfall and it’s rarely below 5 degrees Celsius
Epping Forest Interdepence: Climate and Soil
Mid autumn seasons leads to detritivores converting the nutrients in the leaves to humus for the soil.
Epping Forest Interdepence: Soil and Plants
Brown earth - fertile soil for plant growth
What is Pollarding
Cutting off trees at about shoulder height to encourage growth
What is Coppicing
Cutting trees to ground level just above the roots to stimulate growth.
How is the Epping forest used by people
Used for recreation, a designated a site of special scientific interest and a European Special Area of Conversation.
How is the Epping forest sustainably managed
Managing recreation by providing appropiate car parks,toilets and refreshment facilities and by maintaining footpath
Providing three easy-access park to allow access for people with disabilities
Allowing old trees to die and collapse naturally unless they’re dangerous.
Characteristic of Tropical Rainforests
Have a warm and wet climate, found 0-20 degrees north or south the equator.
Typically receive over 200mm of rainfall per year.
Temperatures are very even averaging 26-27 degrees every day, allowing for a very lust amount of vegetation
Soil in Tropical Rainforests
Several meters thick but often very nutrient poor and often red in colour since they’re rich in iron.
This because the rainwater washes out or leeches the nutrients and minerals out of the soil. This means that the lower layers of the soils lack the nutrients and minerals needed.
Huge and rapid system of nutrient cycling that allows vegetation grow
Interdependence of Tropical Rainforests
Because nutrients from the forest floor are leached into the soil which then in turn is taken up to trees and understory plants by roots. The trees produce fruit that people harvest as well as animals that eat the plants.
Adaptations of vegetation in a tropical rainforest: Mimosa Plant
-adapted to rainfall as it wilts as a defence mechanism against heavy rain and climate. Overcoming the over 200mm of rainfall the Rainforest.
As well as herbivores as it makes the plant look unhealthy to eat.
Adaptations of vegetation in a tropicaal rainforest: Pitcher Plant
Traps insects inside with nectar and digest the body of its prey, this overcomes the challenge of the nutrient-poor soil by getting nutrients from its prey
Adaptations of vegetation in a tropicaal rainforest:Emerald tree boa
Being able to camouflage with trees for prey and hides from predators
Adaptations of vegetation in a tropicaal rainforest: Hummingbird
Has a long bill to get deep into the flower to have nectar, getting its nutrients.
Case Study: Brazil
The Brazilian rainforest occupies the huge lowland basin drained by the Amazon and its tributaries,covering 9 countries: 60% in Brazil, and the rest shared between Colombia,Bolivia,Ecuador,Guyana and others.
Indigenous tribes in the amazon harvest fruits and nuts,cut wood for fuel as well as use timber for building their dwellings.Human use of the rainforest doesn’t lead to deforestation, rather leads to forest degradation where the forest ecosystem is changed in a negative way and its resources decline
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation: Subsistence
Poor farmers occupy plots of the forest to grow food for themselves and their families, many indigenous people are subsistence farmers. The soil is used until it’s exhausted and they clear areas of the forest and then burn it.
The Brazilian region of Mato Grosso has been affected by deforestation in the 1980s and 1990s. 43% of rainforest losses were in this region.
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation: Commercial Farming
The forest is cleared to make space for cattle grazing or for huge plantations, cattle ranching is the main cause of deforestation in the amazon- in Brazil there are 200 million cattle on about 450 000 km^2 of pasture. Cattle grazing accounts for 70% of deforestation in the Amazon.
Rice, corn, soy and sugarcane are also grown
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation: Logging
The amazon is full of valuable hardwood trees such as mahogany, which makes logging extremely tempting to legal and illegal businesses. This involves cutting down trees for sale as timber or pulp. The timber is used to build homes, furniture, etc. and the pulp is used to make paper and paper products. Logging can be either selective or clear cutting.This accounts for around 10% of deforestation in the Amazon.
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation: Road Building
Unless paved, many roads are unusable during the wettest periods of the year. The Trans Amazonian Highway has already opened up large parts of the forest and now a new road is going to be paved, the BR163 is a road that runs 1700 km from Cuiaba to Santarem. The government planned to tarmac it making it a superhighway. This would make the untouched forest along the route more accessible and under threat from development.
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation: Mineral Extraction
Some of the minerals needed by developed countries are found beneath Tropical Rainforests. In the Amazon, gold mining is prominent, over 50,000 hectares. Rainforest suffers badly as it is clear-felled for mining to occur. The same applies to the extraction of other minerals.
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation:Energy development
An unlimited supply of water and ideal river conditions encouraged the development of dams to generate hydroelectric power. This involves flooding vast areas of rainforest the submerged forest gradually rots, making water very acidic. This then corrodes the HEP turbines and then dams also become blocked with soil, washed down deforested slopes by heavy rain. The huge Belo Monte dam started operating in April 2016 and will generate over 11,000 Mw of power.
Case Study: Brazil - Causes of deforestation: Settlement, population growth
Population growth and migration to the area is putting pressure on the amazon rainforest, especially as the brazilian government offers land in the rainforest to poor people from overcrowded cities. The Brazilian Amazon’s population grew by a massive 23% between 2000 and 2010, 11% above the national average.
Case Study: Brazil - Impacts of deforestation: Economic development
Brazil faces losses of $317 billion per year if deforestation continues
The amazon rainforest contributes to about 10% of the GDP
Jeopardises the jobs of 86 million people as well as their livelihoods, setting back the economy..
Brazil has huge foreign debt and lots of poor people to feed, so developing the forest is key however many brazilians view deforestation as a way to help develop their country
Case Study: Brazil - Impacts of deforestation: Soil erosion
As soon as any part of the forest is cleared the thin topsoil is quickly removed by heavy rainfall which is the only part of the soil with nutrients for plants to grow, once removed it's hard for plants to grow again.
In 2022, the world lost more than 16 million acres of forest.
Farmers in the amazon now artificially fertilise the soil due to the infertile soil however in the past the nutrient cycle would have done this naturally.
Case Study: Brazil - Impacts of deforestation: Contribution to climate change
Tree canopies absorb carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which is stopped when trees are felled so more CO2 remains in the air. The trees reduce annual global greenhouse emissions by 30%.
Fire is often used in clearing rainforests so carbon stored in wood returns to atmosphere, therefore deforestation is the main contributor to the greenhouse effect
Local climate becomes dried,this dry hot climate isn't good for people or activities like agriculture that follow the forest clearance.
Why is the rainforest valuable
Goods: Things that can be obtained directly from the rainforest
Services: Benefits that the rainforest can offer to both people and the environment
Example of goods
Fruits and Nuts
Wood/Timber
Gold
Water
Palm oil
Example of services
Natural carbon sink
Provides habitats for animals
Land for farming - cattle farming
Nutrient cycling
Water-hydroelectric power
Example of Sustainable Management Strategies: Borneo
Ecotourism in Borneo provides financial compensation for the locals, without destroying the forest. It encourages sustainability and educates locals.Tourists see animals in their nature state and habitat and stay with the locals.
Example of Sustainable Management Strategies: Costa Rica
Draws over 3 million visitors annually with its ecotourism, it encourages hotels to be sustainable. It minimises the mass affect of tourism. Over 25% of land is protected by national park status and generates 90% of its energy via hydroelectric power.
strategies for managing tropical rainforests: Selective logging and replanting
In 1977 Malaysia introduced a completely sustainable approach to logging called selective logging,a cycle lasting between 30-40 years which protects soil from erosion and prevents ecosystems from being destroyed.
Only fully grown trees are cut down while younger trees are left to mature. After 30-40 years the cycle starts again
strategies for managing tropical rainforests: Conservation and education
Non governmental organisations (NGO) such as WWF, Fauna and Flora International, Birdlife International and the world land trust operate anywhere in the world where they think the ecosystem is seriously under threat.Recently large businesses have also supported conservation projects in exchange for carrying out scientific research or the provision of raw materials.
They promote the conservation message in schools and colleges. They provide practical help to make the programme more sustainable
strategies for managing tropical rainforests: Ecotourism
Countries such as Costa Rica,Belize and Malaysia have promoted their forest for ecotourism. Ecotourism aims to introduce and educate people of the natural world and local cultures. It is controlled by local people, protecting the future of the environment. Income generated from ecotourism benefits locals and governments from logging and protects their rainforests. It minimises the consumption of nonrenewable resources and the ecological impacts
strategies for managing tropical rainforests: Tropical Hardwood
The Forest Stewardship Council(FSC) is an international organisation that promotes sustainable forestry. The fsc tries to educate manufacturers and consumers about the need to buy sustainable hardwood like mahogany. It aims to reduce demand for rare and valuable hardwood.
The international tropical timber agreement(2006) which restricts the trade in hardwoods taken from tropical rainforests. It also restricts the trade in hardwood timber to timber that has been felled in sustainably managed forests.
strategies for managing tropical rainforests: Debt Reduction
High-income countries agree to write off the debts of some LIC countries. In 2010, USA signed an agreement to convert a Brazilian debt of £13.5 million into a fund to protect large areas of tropical rainforest.