Microbiology Exam 1
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
Microbiology
The study of microscopic organisms
What determines if an organism is a microorganism
size
Microorganism
an organism whose size is measured in microns
can be seen in detail only through a microscope
include Bacteria, Archaea (prokaryotes), eukaryotes (and most parasites and viruses)
Characteristics of living organisms
Metabolism - ALL
Reproduction - ALL
Differentiation - SOME
Movement - SOME
Communication - ALL
Evolution - ALL
Metabolism
Done by all living organisms; uptake of nutrients from the environment, their transformation with in the cell, and elimination of wastes into the environment
Reproduction
Done by all living organisms; new cells from preexisting cells; growth
Differentiation
Done by some; some kind of change that can be detected as they grow; formation of a new cell structure
Movement
Done by some; motility; movement by self-propulsion
Communication
Done by all living organisms; interact primarily by means of chemicals that are released or taken up
Evolution
Done by all living organisms; all things evolve
Population
All organisms of the same species
Microbial ecology
The study of microorganisms in their natural environment and their relationships with one another
Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek
first person to describe bacteria as individual cells
developed the first high magnification lenses
first person to view and report on bacteria
developed the first simple microscope
Louis Pasteur
pasteurization
established the “germ theory of disease”: showed that infectious agents were living things for the first time
Disproved “spontaneous generation” with swan neck experiment
Spontaneous Generation
People believed that if you had some sort of corrupted meat that flies just magically appeared
Swan neck experiment
disproved spontaneous generation
Contaminated flask neck does not contaminate the sterile liquid until the flask is tipped and the liquid mixes with the contaminated particles causing it to putrefy
Robert Koch
first to demonstrate the role of bacteria in causing disease
Germ theory of disease
established four postulates
1st Kochs Postulates
The suspected pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease and absent from the healthy animals
2nd Kochs Postulates
The suspected pathogenic microorganism should be grown in pure culture - must be isolated
3rd Kochs Postulates
Cells of the pure culture of the suspected pathogen must cause disease in healthy animal; must have the same symptoms as animal with the original disease
4th Kochs postulate
The microorganism should be re-isolated and shown to be the same as the original in the culture
Elements of cell structure
cell wall - In most bacteria, plants, archaea, and fungi
Outer membrane
Means no engulfment
Rigid structure outside cytoplasmic membrane
Provides support and protection from osmotic lysis (the cell bursting)
Cytoplasmic membrane - in all cells
critical permeability barrier → separates inside from outside
Macromolecules
Proteins - amino acids
Nucleic acids - nucleocides
Lipids - fatty acids + glycerol
Polysaccharides - carbohydrates (a polymer of sugar)
Small organic molecules
Amino acids
Nucleotides
Fatty acids
Sugars
Communication molecules
Not typically found in high abundance inside the cell
Prokaryotes
No nucleus
smaller and less complex than eukaryotes but bigger and more complex than viruses
Eukaryotes
Have a nucleus
Larger and more complex than viruses and prokaryotes
all multicellular life forms
Arrangement of DNA in Prokaryotes
nucleoid - DNA just loosely in the cytoplasm; no real structure
Single chromosome
singular circular DNA molecule that is usually a single protein
Circular
Haploid (one copy of each gene)
Extra-chromosomal DNA - plasmid fission
aprox. 1000 bases = 1 gene = 1 peptide = 300 amino acids
Arrangement of DNA in Eukaryotes
nucleus
linear
diploid/haploid
multiple chromosomes
mitosis and meiosis
Viruses
Not cellular
obligate “parasites”: only way they can survive is by hijacking a cell
Cannot reproduce themselves; synthesis is carried out by the host cell
No growth (fixed size)
Particles: bits and pieces of other cells
Small
Unable to carry out independent metabolism
Three domains of life
Archaea
Bacteria
Eukarya
Most genetic diversity
Bacteria
Least genetic diversity
Eukarya
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor
Evolutionary Chronometer
evolutionary distance measured by differences in nucleotide or amino acid sequences
bacteria rRNA: 16s
Eukaryote rRNA: 18s
Three sources of energy
organic chemicals (or carbon)
inorganic chemicals
light
Chemoorganotrophs
Get energy from organic chemicals
bacteria, archaea, eukarya
Chemolithotrophs
Get energy from inorganic chemicals; strips electrons off of inorganic compounds
Bacteria, Archaea
Phototrophs
Get energy from light; have chlorophyll that contains electrons that get excited from the sun
Heterotrophs
derive carbon from organic carbon
Autorophs
Derive carbon from inorganic carbon
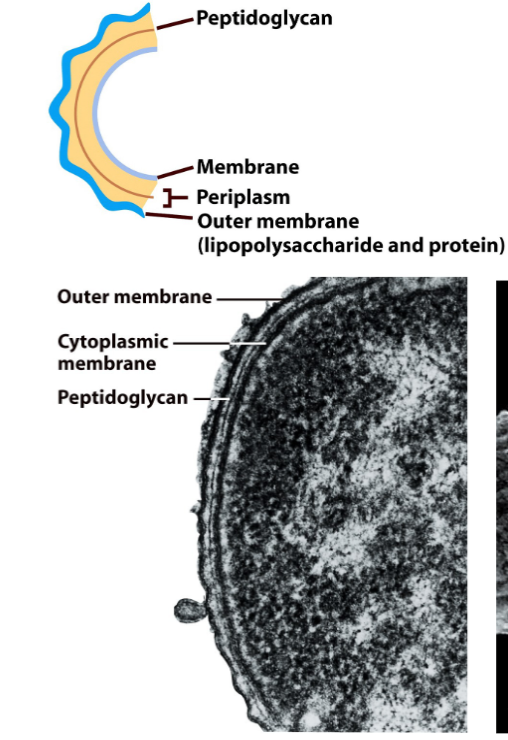
Gram Negative
Have a cytoplasmic membrane, periplasmic space, peptidoglycan, and lipopolysaccharides - essential difference is that it has an outermembrane
proteobacteria (largest phylum)
extreme metabolic diversity
red to pink stain
have lipopolysachharides
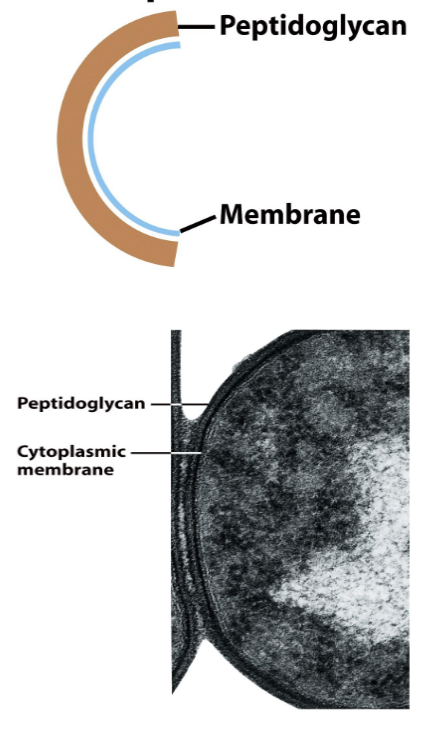
Gram-positive bacteria
Have a cytoplasmic membrane and peptidoglycan (which is thick and heavily crossed making it hard to remove stain)
second largest phylum
has a purple stain
Mycoplasma
relate to gram-positive but lack a cell wall; still cannot engulf
Cyanobacteria
first to carry out oxygenic photosynthesis
Methanogens
Unique metabolism; responsible for production of all natural gas
Total weight of bacteria
aprox. 1.0 × 10^12 grams
Cells are made up of mostly…
macromolecules - most of which are proteins
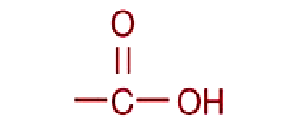
Carboxylic acid
functional group
Source: organic, amino, and fatty acids; lipids; proteins
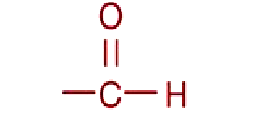
Aldehyde
functional group
Source: functional groups of reducing sugars such as glucose; polysaccharides
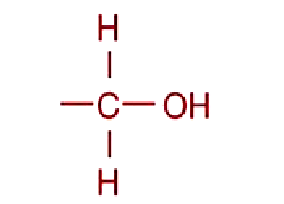
Alcohol
functional group
Source: lipids; carbohydrates
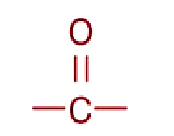
Keto
functional group
Source: pyruvate, citric acid cycle intermediates
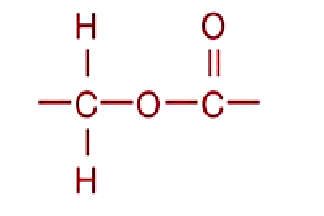
Ester
functional group
Source: lipids of bacteria and eukarya; amino acid attachment to tRNAs
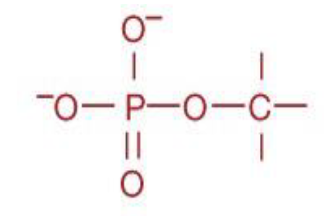
Phosphate ester
functional group
Source: nucleic acids, DNA and RNA
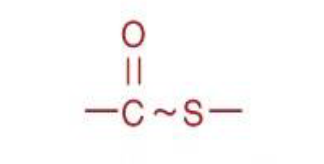
Thioester
functional group
Source: energy metabolism; biosynthesis of fatty acids
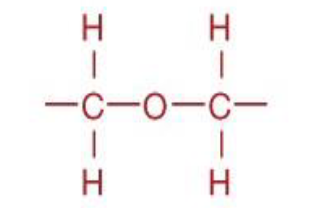
Ether
functional group
Source: lipids of Archaea, sphingolipids
Acid anhydride
functional group
Source: energy metabolism; ex: acetylphosphate
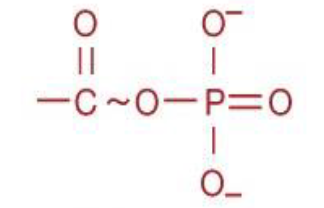
Phosphoanhydride
functional group
Source: energy metabolism; ex: ATP
Proteins are measured in
kilodalton
DNA is measured in
megadalton
Covalent bonds
Strong bonds
Hydrogen bonds
easily broken and easily formed
In strands of DNA:
Guanine and cytosine - triple H bond
Adenine and thymine - double H bond
Nucleotide
phosphate at the base
Nucleocide
No phosphate at the base
Polysachharides
Carbohydrate polymers
organic compounds containing carbon hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1
Most are D-form sugars
D-form sugar
“dextrorotary” → means if you shine a light through it bends right
OH on the right means D form
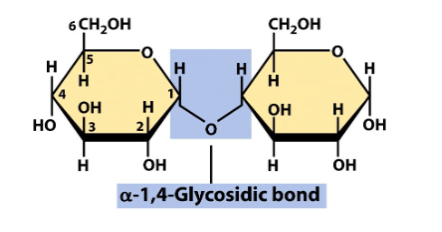
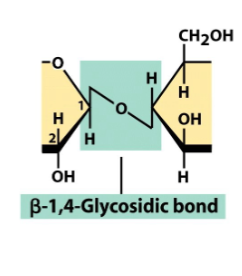
Alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond
will NOT give you a branch
Both down
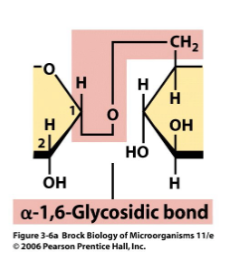
alpha-1,6-glycosidic bond
will give you a branch
left up
beta-glycosidic bond
left down
Lipids - fats
fatty acids bound to glycerol
eukarya and bacteria: fats are esther linked
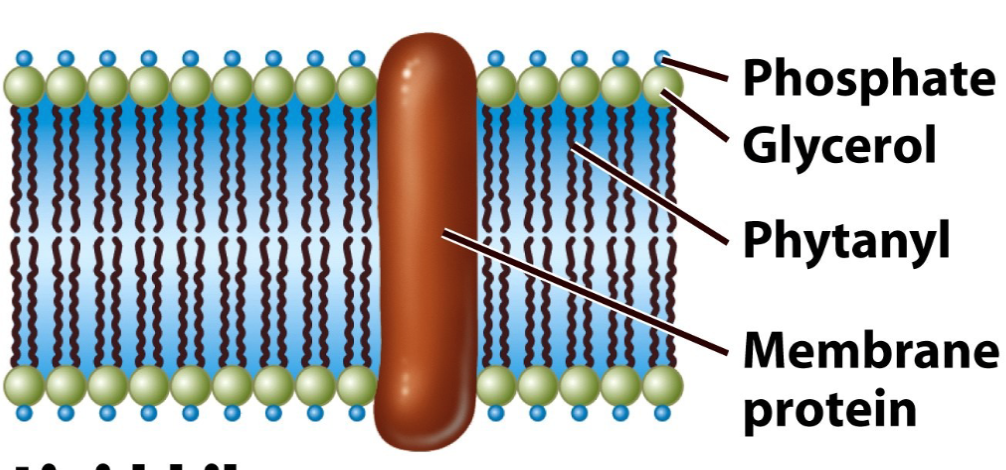
Archaea: fats are ether linked
Contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components
principle component of membranes
Nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
can only be polymerized if there is an existing free 3’ hydroxy → polynucleotides are linked together in a 3’ to 5’ configuration → polymerize happens backwards so 5’ comes first
Bases of nucleic acids are either purines or pyrimidines
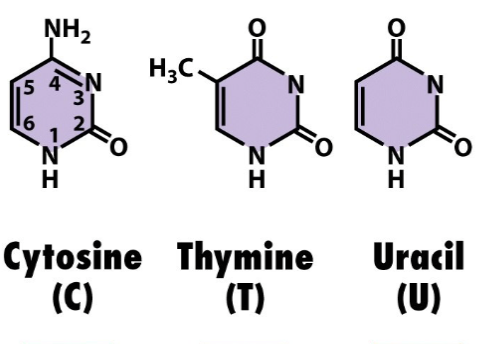
Pyrimidine
base of nucleic acids
have one ring
cytosine, thymine and uracil
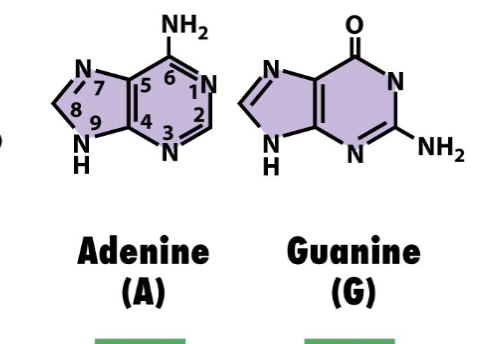
Purine
have two rings
longer
adenine and guanine
Three rules of biochemistry
biochem is backwards
biochem does not exist in the absence of water
biochem is stupid
Amino Acids
monomeric units of proteins and polypeptides
joined together by peptide linkage
Has 4 groups
Ionizable acidic amino acid
one of four groups of amino acids
aspartate
glutamate
Ionizable basic amino acid
one of four groups of amino acids
lysine
arginine
Histidine
Nonionizable polar amino acid
one of four groups of amino acids
serine
cysteine
theoronine
asparagine
Glutamine
selenocysteine
tyrosine
Nonpolar (hydrophobic) amino acid
one of four groups of amino acids
alanine
valine
leucine
isoleucine
methionine
phenylaline
tryptophan
proline
L-form
in amino acids - commonly used in biology
Primary structure
the juxtaposition of alpha-carbon R groups dictates the primary structure of a protein (the amino acid sequence)
Secondary Structure
determined by intramolecular hydrogen bonds
alpha - helix
beta - pleated sheets
Both in all proteins
Tertiary structure
folding of the secondary structure and is “cemented” by the covalent bridging (which takes a lot to break) by Disulfide Linkages
Quaternary structure
when one or more peptide chains interact via strong or weak molecular bonds
separate peptide chains bonding together
Denaturation
cannot be (in most cases) fixed
occurs when secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structures are broken chemically or by heat or radiation
Parts of a microscope
ocular (lense)
objective (lense)
stage
condenser
focusing knobs
light

Limit of resolution
0.2 micrometers
anything smaller, you wont be able to see
wavelength determines if you can see something → to increase resolution decrease amplitude
Staining
increases contrast for bright-field microscopy
Gram-staining
shows phylogenic differences
gram negative are all genetically related to each other and gram positive are all genetically related to each other
Gram-positive → purple
Gram-negative → pink to red
Ribosomes
responsible for synthesis of proteins
composed of protein and ribonucleic acids
Inclusions
NOT universal
aggregates of storage compounds containing carbon (eg. starch), nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus
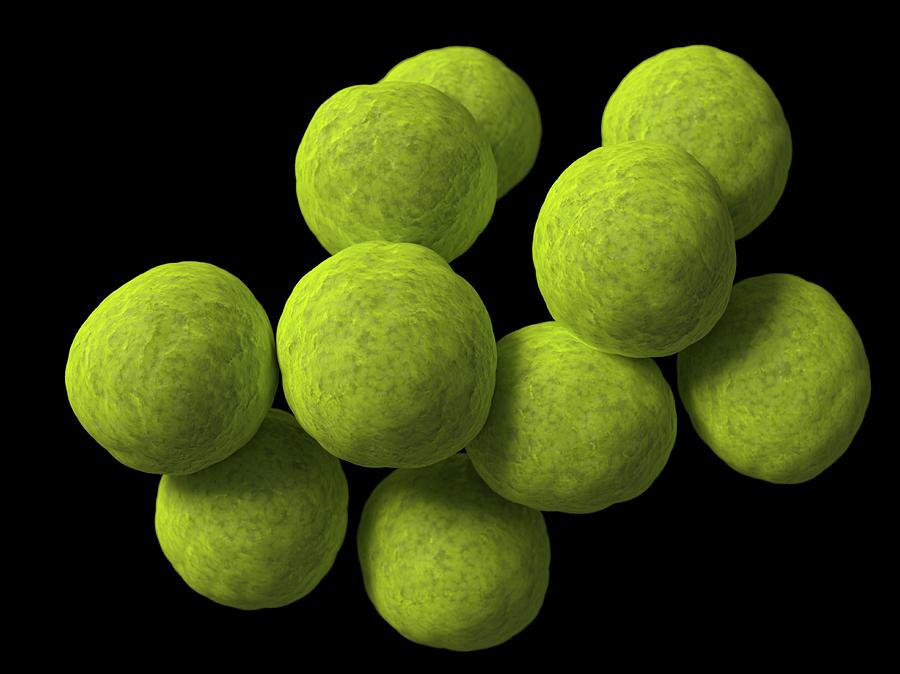
Coccus
1 of the 6 basic morphological structures of bacteria
round
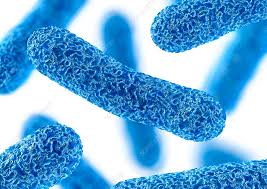
Rod (bacillus)
1 of the 6 basic morphological structures of bacteria
Staff - long shaped
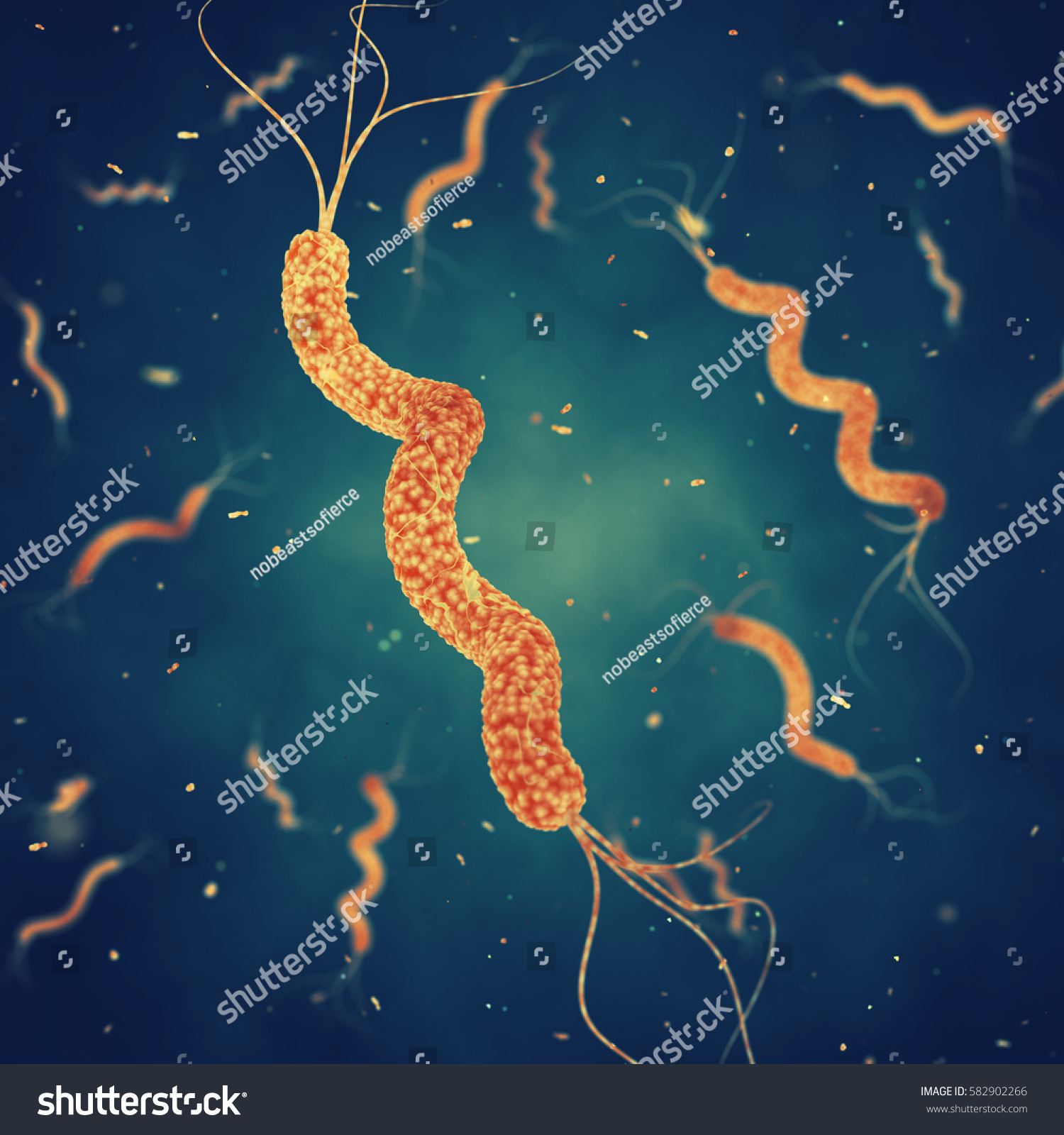
Spirillum
1 of the 6 basic morphological structures of bacteria
Corkscrew
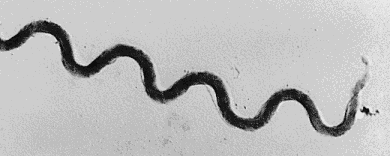
Spirochete
1 of the 6 basic morphological structures of bacteria
wave
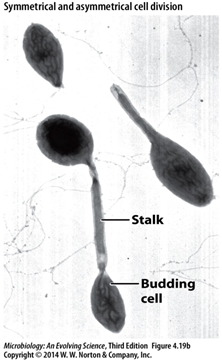
Appendaged
1 of the 6 basic morphological structures of bacteria
has a thing sticking out
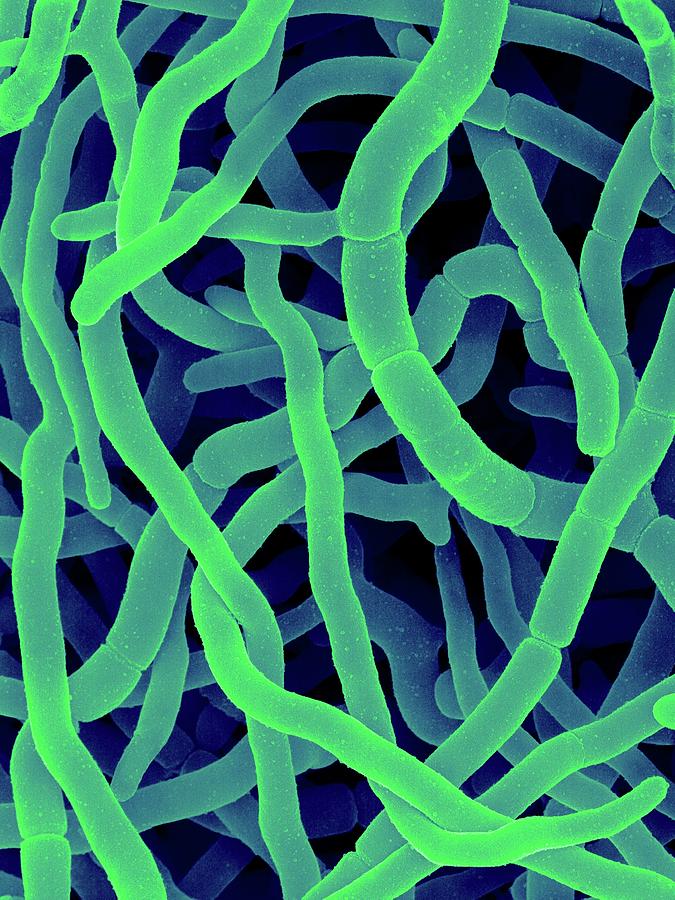
Filamentous
1 of the 6 basic morphological structures of bacteria
long rod
Importance of smallness
transport is a function of size
sa/v ration decreases as size increases
want a bigger sa/v ratio (meaning being smaller)
being small means more nutrients it can take in and less to feed - less surface area to bring nutrients throughout the cell and get waste out
Size of bacteria in based on environment
nutrient poor - get smaller
nutrient rich (theres food for them) - get bigger
Reductive cell division
divide in half without growing
parent is larger than daughter cells
Structure of cytoplasmic membrane in eubacteria
phospholipid bilayer: fatty acid, glycerol, phosphate
integral membrane proteins: anchored proteins in the membrane;
membrane strengthening proteins
eukaryotes and methanotrophs: use sterols (cholesterol)
bacteria: use hopanoids
phospholipid bilayer formed from glycerol components esther linked to fatty acids