Mood disorders: Unipolar and bipolar
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
MDD was first described by hippocrates as what
Melancholia
melancholia arose from a presence of too much __ __
black bile
Emile Kraepelin and classification
believed the chied origin of psych is biological/genetic in nature
grouped diseases based on class of syndromes not symptoms
Kraepelin and theory of psychosis
refined the concept of psychosis into
1) dmentia praecox: cog disiintegration
2) Manic-depressive illness, mood disturbance, disrupt in affect
Dementia praecox was eventually re labeled into
schizophrenic
who first distinguished uni and bi polar depression
Karl leonhard
MDD introduced in what DSM
3
DSM 5: chnages to MDD
addition of disruptive mood disregulation disorder
persistent depresive disorder (dysthymia)
PRE menstrual dysphoric disorder
bereavement clase removed
if you have any hiostory of mania can you be diagnosed with MDD
no
DSM criteria: MDD all __symptoms must be present simultaneously over a __ week period
5, 2
MDD DSM criteria: two cardinal symptoms
dysphoric mood (sad, empty. tearful)
Anhedonia: diminished intereast in almost all activities
DSM criteria: non cardinal symptoms 7
weight loss or gain
insomnia/hypersomnia
psychomotor aggitation or retardation (jiggle or slow)
fatigue
worthelessnes/guilt
diminished ability to concentrate or indecissiveness
thoughts of death
Prevalence distinction between uni and bi polar
MDD is 10-20x more common
uni is 2F:M
which mood disorder has an earlier onset
bipolar
forms of unipolar depression 4
recurrent depression
Melancholia
atypical
Chronic MDD
Forms of Unipolar: Melancholia
more biological?
dosesnt respond to anti depressants as much
respond to psychotherapy
no difference in family history
not stable across episodes
Forms of Unipolar: Atypical
15% of patients
early onset
more comorbidity
strongly associated with treatments (MAOIs and less effective SSRI)
which form of unipolar dep does not respond to tricyclics
atypical
Forms of Unipolar: chronic
2+ year episodes
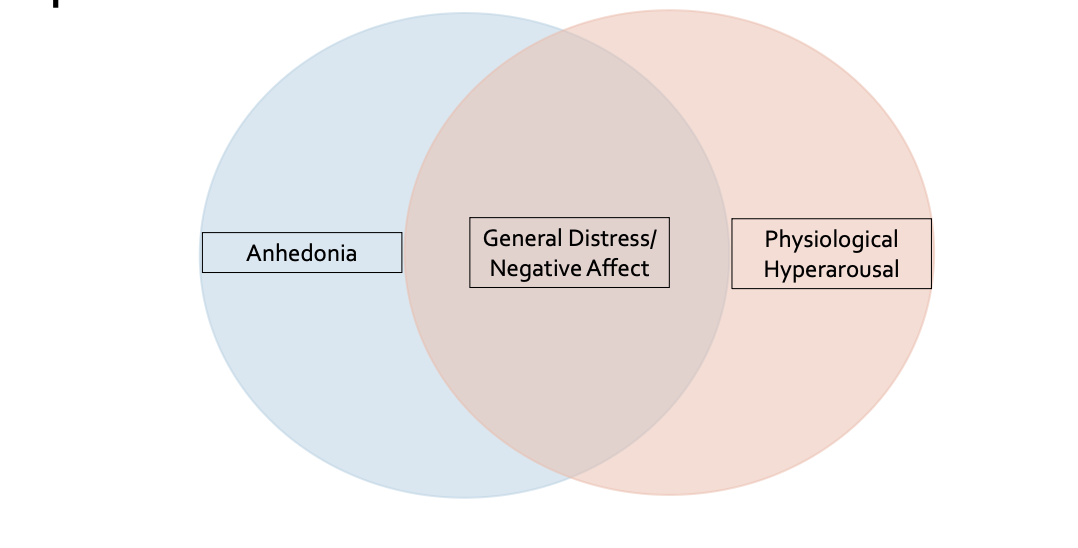
Tripartite model of MDD and GAD
Epidemiology: unipolar
Lifetime prev 16-17%
20-25% for F and 9-12 for M
prevalence of Persistent depressive disorder is higher or lower than other unipolar disorders
lower
cross culture prevalence within North america of unipolar
suggests lower for black americans lower than white
in asian/latin american and north african countries depressions has more ___ presentations
somatic, headache, loss of energy, sleeplessness
Course iof MDD
-onset, mid teens-20s
25% preceded by low grade chronic PDD
predictors of loinger episodes unipolar
personailty dis
non mood comorbid disorders
at least ___ of people iwth one depressive episode will have another
1/2
suicide is most common in what period of a mood disorder
6 months after recovery
etiology: familial
higehr rates of mood disorders in family where proband has mood disorder
gigher rates of MDD in family of proband with MDD
PBI Parker study of stress and adversity in mood disorders
Two dimensions of caregiving: care and overprotection
depressed patients report parents lower in care, some higehr in overprotection
interaction poses heightened risk for depression
Stress and Depression: prior to onset of MDD what percentage of women experienced a stressful event
75%
Causality of stress and adversity
depressed people more sensitiuve to effects of stress
but also generate more stress in their lives
important to distinguish between dependent and independent stressors
Behavioural models of depressions: reward and positive reinforcement
depression is related to a reduction in behaviours that are positively reinforced
treatment would be to increase the amount of positive behaviours in the world
Behavioural models of depressions: Beck
Cognitive triad
focused on cognitions that contribute to lack of motivation
Negative views of world, negative views of future, negative niews of oneself
Behavioural models of depressions: learned helplessness
Puppy study, shocks and gate no gate
essentially puppy stops trying to get out
Behavioural models of depressions: revised learned helplessness
3 dimensions of attributions to stressor
external vs internal
global vs specific (eg. if you arenst the favourite than No ONE likes you)
stable vs unstable (forver vs now)
what attributional styles are mpost associated with depression
internal, global and stable
Cognitive biases associated with MDD
memory and attentional
stroop task tests what?
colour/word task and MDD patients find it harder to avoid negative words
Bipolar DSM criteria A: 3
manic episode at least one week
manic episode can consitist of elevated expansive mood or irritability
persistent goal directed activity
Bipolar DSM criteria: B
need 3 or 4 (if only irritability in criteria A)
grandiosity
decreased need for sleep
more talkative (pressured speech)
distractability (jumping thoughts)
goal directed activity
increased libido
more agitated
excessive pleasurable activities
Bipolar has a large overlap with what
unipolar, ADHD and psychosis
To diagnose with Bipolar you need __ impairment
marked
Bipolar 1 vs 2
mania plus an episode of MDD
Hypomania and depression, milder
no hospotalization
less interference
cyclothymia
a form of bipolar
hypomania and shity depressive episodes
chronic but less severe
lots of highs and lowsat increased risk for bipolar 1
what form of bipolar can antidepressant meds trigger
cyclothymia
Forms of bipolar: Rapid cycler
a specifier
4+ episodes within a year
can be either type of episode
to be a rapid cycler you need how many episdoes per year
4+
Bipolar: Psychotic Symptoms
loss of contact with reality
in bipolar its usually mood related not thought
if they occur during manic episode then they are considered a mood disorder w psychosis
Bipolar Psychotic Symptoms: Mood congruent vs incongruent
congruent: align with affective state
in mania: grandiose delusions
in dep: sad low delusions of sin/disease
incongruent:
mania: thought insertion mind control
dep: anythings happy
an example of mood incongruent psychosis in mania
though insertion or mind control
an example of mood congruent psychosis in mania
delisoons of grandeur
Epidemiology of Bipolar: LT prev and F vs M
2-4% for bip 1 amd 2
prev is not affected by sex
takes __ years for individual with bipolar disorder to receive corect diagnosis
6-10 years
treatments for bipolar
mood stabilizers and anticonvulscents
you are more likely to begin bipolar with a depressive episode T or F
no, its ½
Suicide and bipolar
15X higher than general population
death by suicide is __X more likely in Bipolar patinets than MDD
4
Etiology of Bipolar: Environmental stress and adversity
stress increases 6 months prior to episode
frequent relapse following stressful experiences
class of stressors that are important to triggering mania
goal attainment events
when achieve goal, become very happy, disregulation of mood
How does stress get into the brain? Goddard
kindling:
stimulated brain repeatedly with electricty to develop seizures
over time requirelower doses to provoke
eventually seizures occur spontaneously
kindling and bipolar
idea that each episode of mania requires less stress to trigger
exposure to bright lights can trigger manuic episode how
can change circaidan rhythms
Neurobiology of Bipolar
Striatum
larger in bipolar patients
Reward activity in VS is abnormally elevated in patients
there is a failure of pre frontal regions to __ __ VS responses
down regulate
reward consumption related activation is more prominent in what type of Bipolar
1
lithium does what
interrupts dopa signalling in Brian, glutatmate antagonist