IB biology C3.1.2 Cells, tissues, organs and body systems as a hierarchy of subsystems that are integrated in a multicellular living organism; C2.2.16 Consciousness as a property that emerges from the interaction of individual neurons in the brain; A2.2.7— Processes of life in unicellular organisms.
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
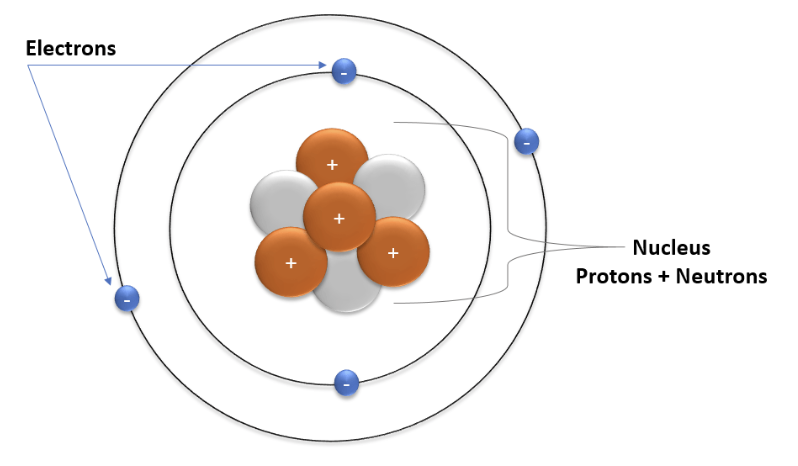
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that forms a chemical element.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of atoms.
Simple molecules
Different atoms bonded together to form small molecules. (ex: Water, Amino acid, Fatty acid, Glucose)
Macromolecules
Large molecules, often the results of the polymerization of smaller molecules. (ex: Proteins, Phospholipids, Nucleic Acids, Polysaccharides)
Subcellular Structures
Structures that are specialized for a specific function within the cell. (ex: Nucleus, Cell membrane, Ribosome, Mitochondria)
Cells
The smallest unit that is capable of carrying out all the life processes. (ex: Bacteria, Neuron, Plant cell, Sperm cell)
Tissues
A group of cells, not necessarily of the same kind, that work together to perform a specific task. (ex:Connective tissue, Epithelial tissue, Nervous tissue, Muscle tissue)
Organs
A group of different tissues that form a singular unit and perform a similar function. (ex: Heart, Lung, Stomach, Root, Stem)
Organ system
A group of organs that interact to perform a similar function (ex: Plant shoot system, Plant root system, Digestive system, Respiratory system)
Organisms
An single living organism (unicellular or multicellular).
The unit of natural selection (survival and reproduction).
(ex: Amoeba,Human, Cat, Oak tree, Bacteria)
Population
A group of organisms belonging to the same species that live in the same area at the same time.
Used to study genetic diversity and evolution.
(ex: All the fir trees in a forest, All the elephants on the savanna, All the bacteria in the Petri dish)
Communities
All of the populations of different species that live in the same area and at the same time.
Used to study biodiversity.
Ex: Bee and flowers in a meadow, Different types of bacteria living on human skin
Ecosystems
Includes the the biotic and abiotic factors in an area.
Used to study energy flow and nutrient cycling.
ex: A forest, A stream, A reef
Biomes
Large geographic regions of with similar abiotic factors and with organisms adapted to that climate.
Groups of similar ecosystems make up individual biomes.
Ex: Tundra, Grassland, Desert, Temperate forest
Biosphere
The regions of the planet where life exists, includes below the surface and into the atmosphere.
The zone for life on Earth is limited by:
Temperature,
Light,
Humidity,
Radiation,
Pressure.
Earth has the only known biosphere.
Biotic factors
The living, once living or materials made by an organism
Abiotic factors
The non-living physical and chemical features
Emergent properties
At each level of biological organization, new properties or behaviors develop that are not present in the lower levels.
Constiousness
Is a state of being awake and aware.
neuroscientists argue that…
…consciousness emerges from the collective interactions of neurons in a brain
Homeostasis
Living organisms keep their internal environments within a stable internal condition, despite changes in their external environment.
Metabolism
Is the sum of all the chemical reactions in a cell.
Nutrition
The process of obtaining energy and matter.
Autotrophs use external energy sources (usually the the sun) to synthesize carbon compounds from simple inorganic substances
Heterotrophs use carbon compounds obtained from other organisms to synthesize the carbon compounds that they require
Movement
Sessile organisms stay in one place, whereas motile organisms are mobile.
Excretion
The process in which metabolic waste is eliminated from an organism.
Growth
The process in which an organism increases in size and mass.
Response to stimuli
All life can recognize and respond to changes in environmental conditions
Reproduction
All life has the capability for *term*; life will create more life. Sexual & asexual.
Species
a group of organisms/ living things with shared traits, and recognizably distinct from all others by their shared characteristics.