10.1= low unemployment
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
unemployment
refers to people of working age who are actively looking for a job but who are not employed
underemployment
people of working age with part-time jobs when they would rather work full time, or with jobs that do not make full use of their skills and education
what does underemployment and unemployment lead to?
wastage of scarce resources by not using them fully
labour force
number of people who are employed (working) plus the number of working age who are unemployed (not working but seeking work)
fraction of the total population as children, retired old people, adult students and many more aren’t included
also those who don’t wish to work
unemployment can be measured in 2 ways which are
as a number, total number of unemployed people in the economy
as a percentage, unemployment is called the unemployment rate, defined as
= (number of unemployed)/(labour force) X 100
difficulties in measuring unemployment
official stats underestimate true unemployment because of hidden employment
official stats might overstate true unemployment
national unemployment rate (for whole nation) is an average and doesn't account for unemployment among individuals and different groups in a society.
official stats underestimate true unemployment because of hidden employment
only includes people actively looking for a job so discouraged workers who are unemployed workers who gave up looking a for a job because after trying they were unsuccessful
doesnt differentiate between parttime and fulltime jobs so people who are undereployed cant be counted
doesn’t inlude pople on retraining programmes who lost their job, also people who retire early although they would rather be working
no distinctions on the type of work done, a highly trained individual can be a waitress and thats still under employed
official stats overestimate true unemployment
dont include people working in the underground or informal economy
people registered as unemplyed may be working in an unreported (underground) activity
national unemployment rate (for whole nation) is an average and doesn't account for unemployment among individuals and different groups in a society.
regions with declining unemplyment might have higher than others
gender- women face higher unemployment rates than men
ethnic group- disadvantages due to discrimination and low levels of education and training
age- youth employment is hard due to low experience
occupation and educational attainment- people with lesser skills may have higher unemployment rates (in some countries higher skills set people have higher unemployment people
economics costs of unemployment (1-5) of 8 total
loss of real output (real GDP)= fewer people work than are available to work, the amount of output produced is less than the level the economy is capable or producing
loss of income for unemployed workers= worse off financially compared to if they were working even with unemployment benefits
loss of tax revenue for govt= unemployed people dont have an income so dont pay tax thus lesser tax revenue
costs to govt for unemployment benefits= more the unemployment more the tax revenue is used for paying unemployment benefits (revenue that was left over to pay for other govt provided goods and services)
costs of govt for dealing with social probs arising with unemployment= need funds
economics costs of unemployment (3-8) of 8 total
larger budget deficit, smaller budget surplus= budget deficit is when tax revenue is less than govt expenditure (budget surplus is opposite) unemployment decreases tax revenue (less payers) and increases expenditure (dealing with social probs, paying unemployment benefits)
more unequal distribution of income= gap in income disparity increases and communities facing disadvantages face more poverty. high unemployment for long periods of time leads to increased social tensions and social unrest
unemployed people have difficulty in finding work- unemployed workers lose their skills over time or a new skill is required that the workers can’t keep up with, or because firms have found ways to work with less people
hysteresis
high unemployment rates in the present mean high unemployment rates in the future, even economic conditions become more favourable
personal and social costs of unemployment
personal problems: loss of income, higher indebtedness as people borrow to survive, loss of self esteem —> immense psychological stress leading to lowers levels of health, family tensions and even suicide
greater social probs: especially due to unequal distirbution lead to increase in social probs including increased crime, violence, drug use and poverty increasing
structural unemployment
occurs as a result of changes in the demand for particular types of labour skills, changes in the geographical location of industries and therefore jobs, and labour market rigidities
changes in demand for particular labour skills
technological change- increase demand for a skills but increase for a previously exisiting one
ex- ATMs increased need for workers with computer literacy and reduced need for bank tellers, typists and telephone operators
automation will lead to more job losses
changes in demand for labour skills may occur because of changes in the strucuture of the economy
workers who lose their job in the declining industries and become strucuturally unemployed as they dont have the skills set for the growing economy
these are the mismatches between labour skills demanded by employers and labour skills supplied by workers
changes in geographical location
if companies move from one location to another they are changing the demand of labour in where its moving from (decrease) and increase in where it moves
if people cannot move to economically expanding regions they may become structurally unemployed
again showing mismatch in labour demanded and labour supplied
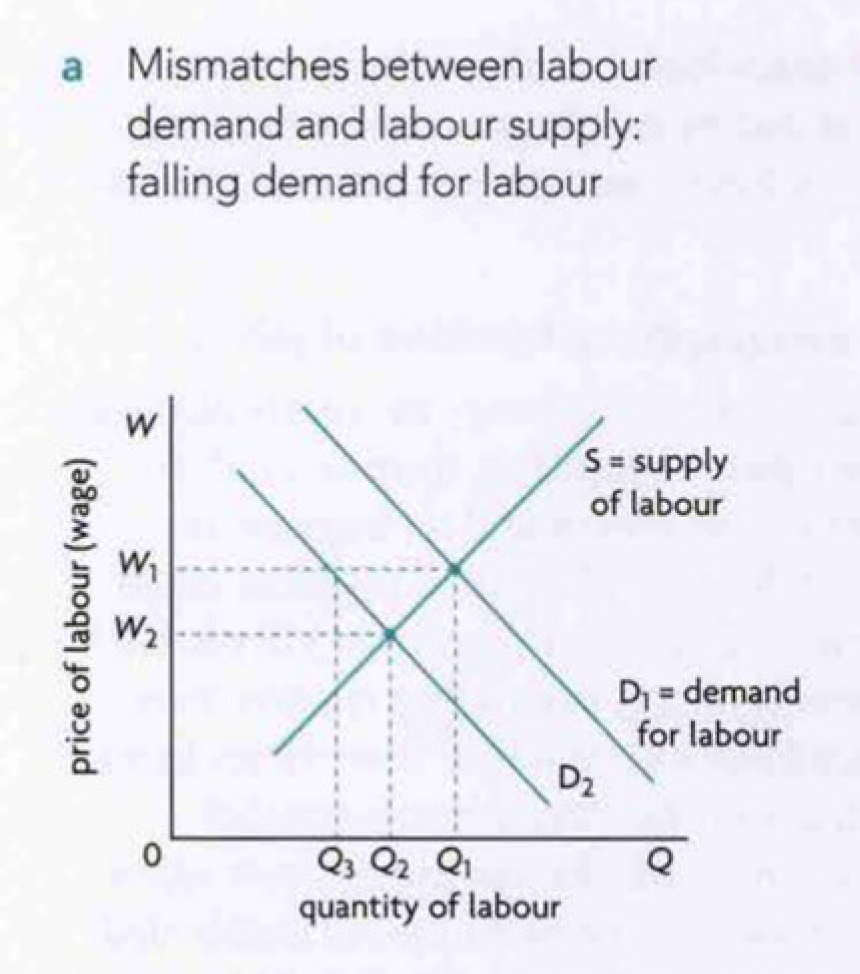
diagram- structural unemployment due to mismatches between labour demand and labour supply
demand curve= quantity of labour firms willing and able to hire at each wage
supply curve= quantity of labour workers supply at each wage
assume due to tech, geogrpahical or structure of economy demand has reduced
shown by D1 to D2
if market forces worked perfectly, problem of structural unemployment would be resolved
at lower wage W2 only Q2 workers would work and no excess of supply would be there
however irl wages don’t easily fall in the short term period
wage would remain at W1, in the foreseeable future and excess supply of labour that corresponds ot structural unemployment created by the demand in the fall for labour
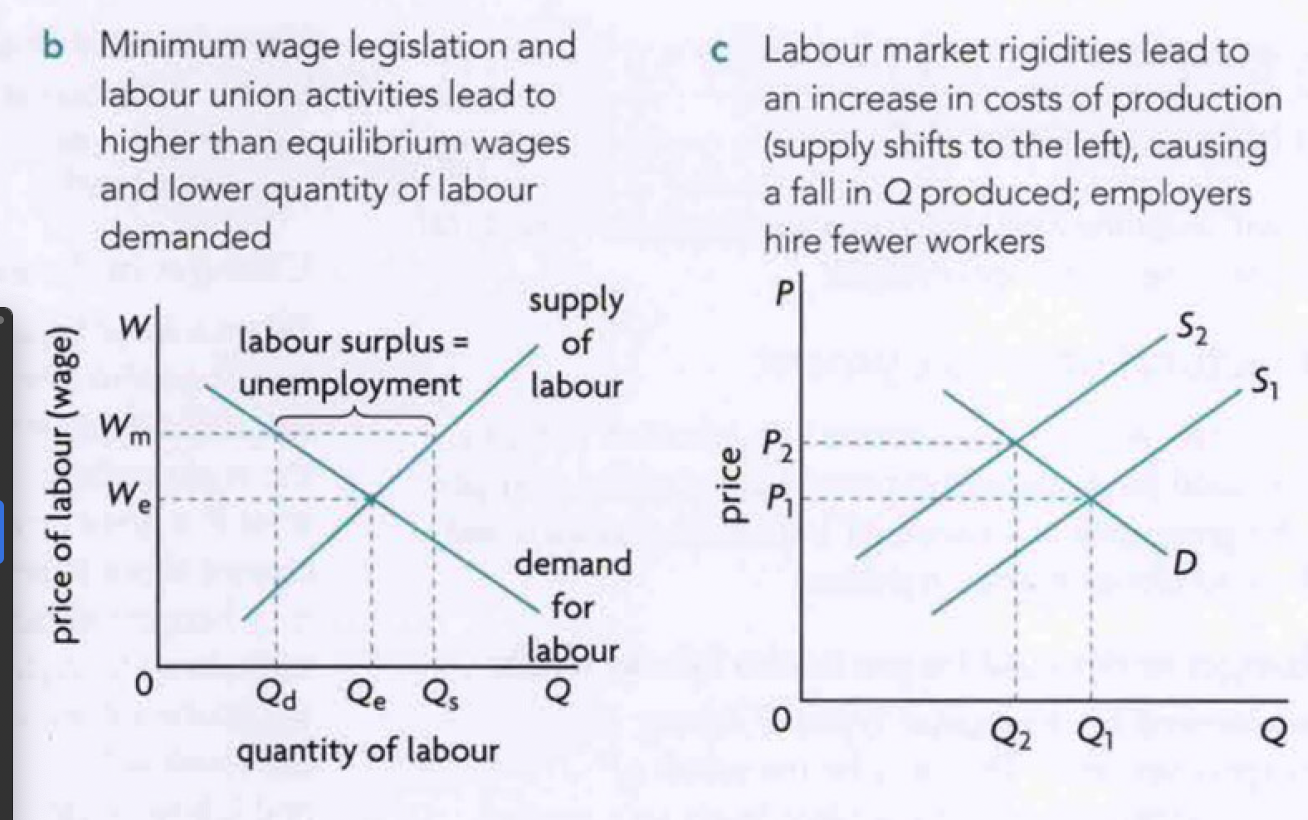
labour market rigidities
factors preventing the forces of supply and demand from operating in the labour market
minimum wage legislation- higher than equilibrium prices
labour union activities and wage bargaining- higher than equilibrium prices
employment protection laws- makes it costly for firms to fire workers (they are paid compensation) makes firms more cautious about hiring
generous unemployment benefits- increases attractiveness of being unemployed and reduces incentives to work
diagram to show structural unemployment arising from labour market rigidities
in 10.c…
labour market rigidities lead to higher costs of production causing supply curve to shift left
smaller q produced, hence firms hire less labour
certain amount of structural employment persists and is unavoidable in any dynamic, growing economy and is therefore considered to be a part of natural employment. it can also be lowered
how can structural employment be reduced?
policies by govt
measures to encourage workers to retrain and obtain new skills
relocate to areas with greater employment opps
providing incentives to firms to hire structurally unemployed workers
Frictional unemployment
occurs when workers are between jobs. workers may leave their job because they have been fired or because they are in the search of a better job, or waiting to start a new job
characteristics of frictional unemployment
short term
does not involve a lack of skills that are in demand
less serious than structural
certain amount if inevitable in any growing changing economy
some firms grow faster and workers seek to advance icnome and professional positions
importance cause is incomplete information between employers and workers regarding job vacancies and job qualifications
finds time to find the right person and hence also a part of natural unemployment
seasonal unemployment
occurs when the demand for labour in certain industries changes on a seasonal basis because of variations in needs. farm workers experience seasonal unemployment because they are hired during peak harvesting season and laid off rest of the year
part of natural unemployment as there will always be some industries with seasonal variation in labour demand
natural rate of unemployment
when the economy produced at full employment output or potential output, it has unemployment equal to natural rate of unemployment
natural rate of unemployment is the sum of structural, frictional plus seasonal
at full employment, unemployment is sum of of structural, frictional plus seasonal
cyclical (demand- deficient) unemployment
additional unemployment when the economy produced less than its potential output
occurs during the downturns of the business cycle when the economy is in a deflationary/recessionary gap
dowturns is seen as arising from declining or low aggregate demand aka demand deficient unemployment
how cyclical unemployment works

cyclical unemployment in graphs
initially producing at Yp with zero cyclical unemployment
fall in AD causing AD to shift leftward creates a deflationary/recessionary gap as real output fall to Yrec.
the new new unemployment at Y rec is the cyclical unemployment
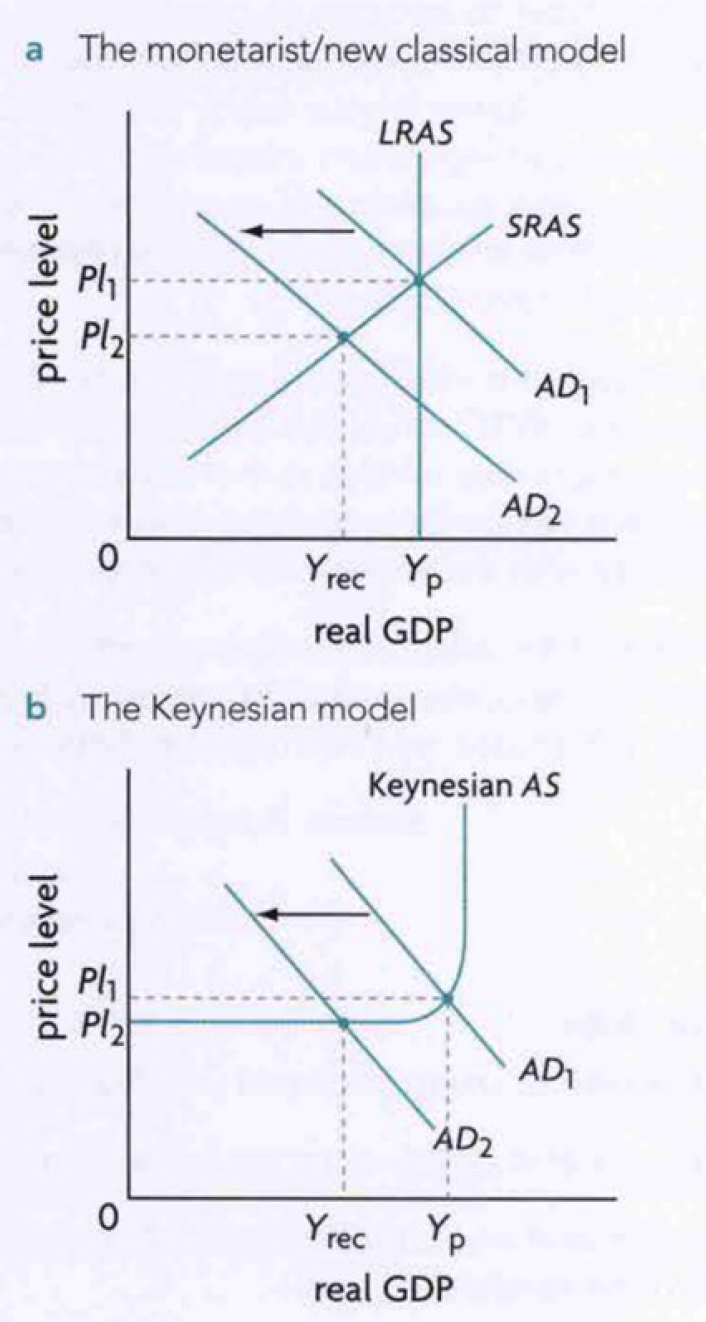
measures to reduce cyclical unemployment
arises from deficiency in AD
reduce by use of govt policies to increase AD and eliminate the recessionary gap
AD-AS model for all 4 unemployments- deflationary/ recessionary gap
unemployment> natural rate
there is cyclical unemployment in addition to structural + frictional + seasonal unemployment
current GDP< potential GDP
AD-AS model for all 4 unemployments- inflationary gap
unemployment falls below natural rate of unemployment
unemployment < natural rate
0 cyclical unemployment
portion of workers who were structurally, frictionally or seasonly unemployed now find jobs in the short term duration
AD-AS model for all 4 unemployments- potential GDP
unemployment = natural rate (seasonal+ frictional + structural)
0 cyclical unemployment