bmb 460 final - paper 1 pptx
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
tophat and pptx questions
Last updated 3:43 PM on 4/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
what is transdifferentiation?
conversion of one cell type to another
2
New cards
what is determination?
cell undergoing a self-perpetuating change of internal character that distinguishes it and its’ progeny from other cells, and commits it to a specialized course of development
3
New cards
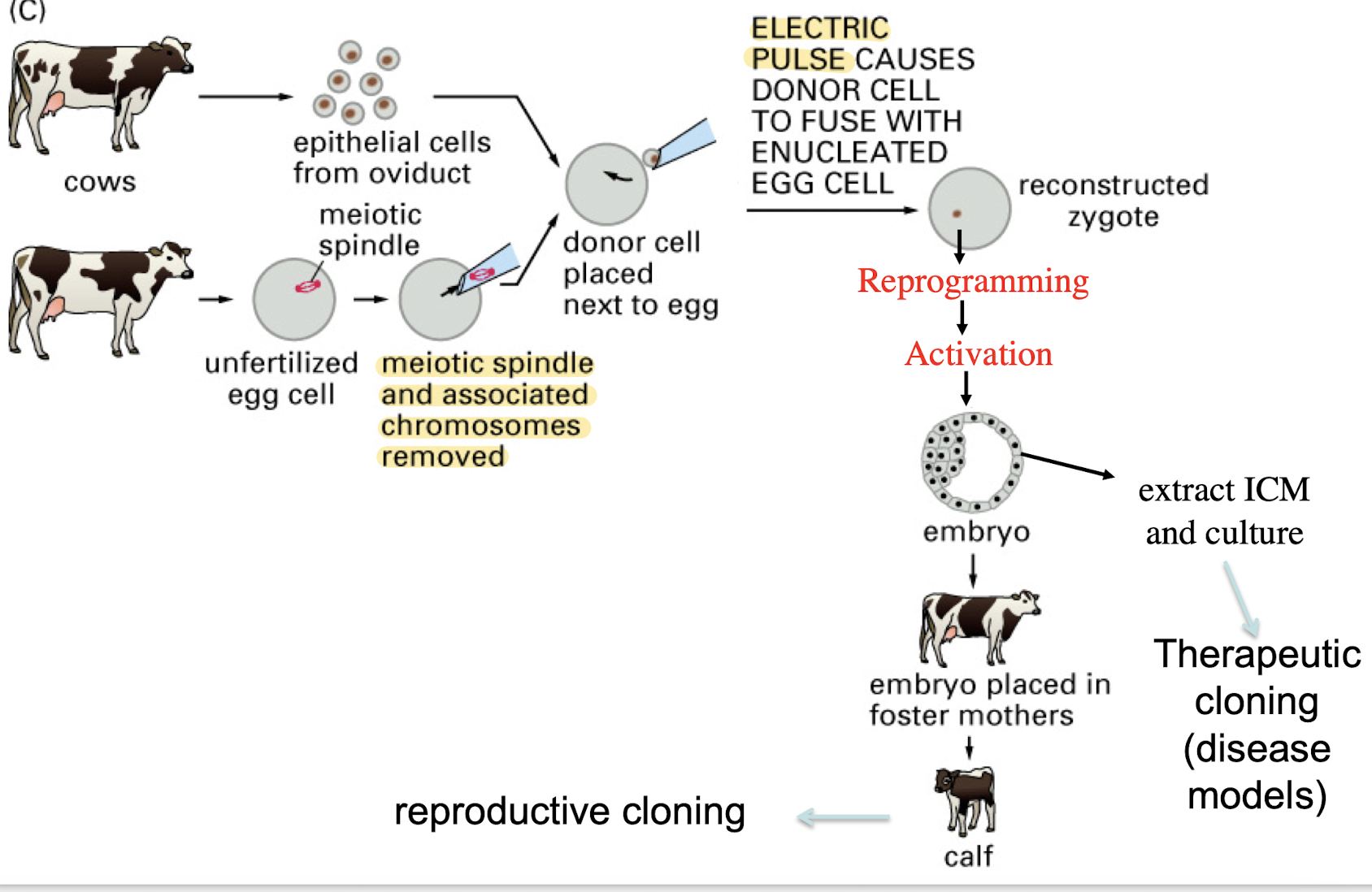
what can somatic cell nuclear transfer do for a cell?
provide evidence that terminally differentiated chromatin from an adult can be reprogrammed to allow for transdifferentiation
4
New cards
________ is the conversion from one cell type to another
transdifferentiation
5
New cards
hypothesis for paper
can ES cells “reprogram” other adult stem cells into a pluripotent state, to then differentiate into other cell types?
6
New cards
select which statements are correct
\
A. Hematopoetic stem cells are found in the peripheral blood and bone marrow
B. ES cells are pluripotent cells derived from the inner mass of the blastocyst
C. skin cells (fibroblasts) or blood cells from adults are converted into iPSCs via transdifferentiation
D. Yamanaka factors are a group of TFs that play a vital role in the creation of iPSCs
E. Electric pulses cause the donor cell to split into equal halves during the process of SCNT
\
A. Hematopoetic stem cells are found in the peripheral blood and bone marrow
B. ES cells are pluripotent cells derived from the inner mass of the blastocyst
C. skin cells (fibroblasts) or blood cells from adults are converted into iPSCs via transdifferentiation
D. Yamanaka factors are a group of TFs that play a vital role in the creation of iPSCs
E. Electric pulses cause the donor cell to split into equal halves during the process of SCNT
A. B. and D.
7
New cards
what three substances need to be added to the isolated bone marrow cells from GFP+ female mice?
1. Puromycin
2. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF)
3. IL3
8
New cards
What does puromycin do for the cells?
enables the resistant cells to be selected for
9
New cards
what does LIF do for the cells?
allows growth of mouse ES cells without a feeder cell layer (feeder cells consist in a lower of cells unable to divide, which provides extracellular secretions to help another cell proliferate)
10
New cards
what does IL3 do for the cells
supports growth of hematopoietic cells
11
New cards
which of the three factors must be maintained throughout the entire experiment to sustain ES cell life?
LIF
12
New cards
how does puromycin work?
antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis, blocks further extension of protein via incorporation of ribosomes onto C-terminus, causes premature termination of translation
13
New cards
what is LIF?
leukemia inhibiting factor; secreted cytokine that suppresses leukemia proliferation. it’s necessary to maintain ES cells in their undifferentiated state (maintains pluripotency), regulates ESC self-renewal.
\
without it, ES lose their SC character
\
without it, ES lose their SC character
14
New cards
what is IL3?
interleukin-3; potent growth promoting cytokine
15
New cards
what is the purpose of LIF in the culture?
\
A. LIF is required for promoting cell proliferation
B. regulates puromycin sensitivity
C. LIF is necessary to maintain the ES cells in an undifferentiated state
D. LIF is necessary to maintain GFP expression
\
A. LIF is required for promoting cell proliferation
B. regulates puromycin sensitivity
C. LIF is necessary to maintain the ES cells in an undifferentiated state
D. LIF is necessary to maintain GFP expression
C. LIF is necessary to maintain the ES cells in an undifferentiated state
16
New cards
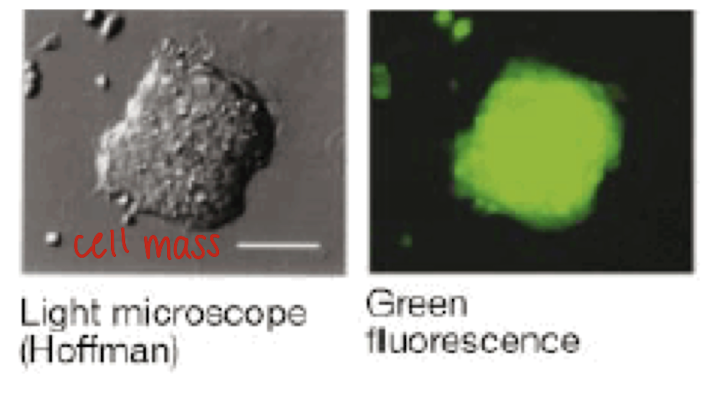
within three weeks of isolation, what to the colonies look like?
GFP+ colonies grow (indicates cells are derived from bone marrow), look like ES colonies (looks like a cell mass - flattened colonies with tight cell-cell junctions), and proliferate at a rate similar to ES cells for >6mo
17
New cards
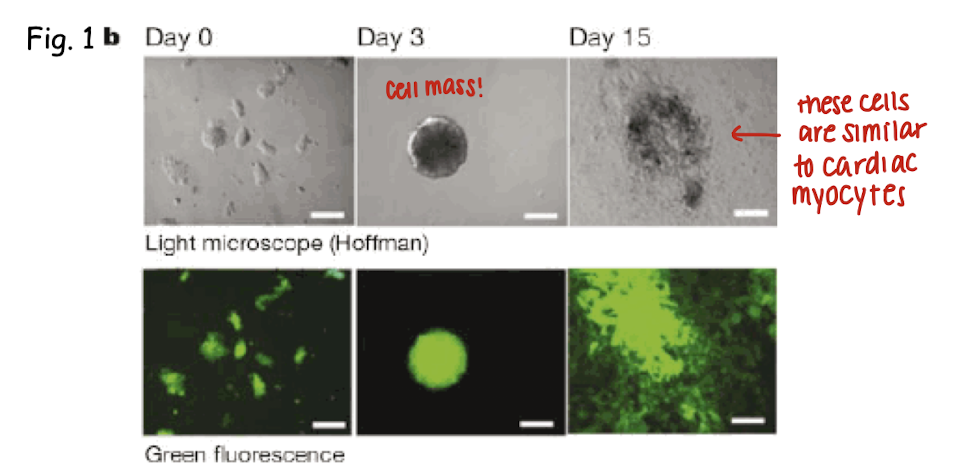
what happens when LIF is withdrawn from the cultured ES cells?
they differentiate into a variety of cell types (BM-derived, embryonic stem like); a sphere of aggregated cells of various morphologies forms (embryoid bodies)
\
basically, removal of LIF causes differentiation
\
basically, removal of LIF causes differentiation
18
New cards
how did authors induce differentiation in the embryonic stem-like (BMESL) cells in vitro?
\
A. by adding LIF at day 0
B. by removing LIF
\
A. by adding LIF at day 0
B. by removing LIF
B. by removing LIF
19
New cards
what are yamanaka factors Oct3/4 and UTF1 markers for?
undifferentiated pluripotent ES cells
20
New cards
what happens to Oct3/4 and UTF1 during differentiation?
their expression levels go down, while expression of differentiation genes goes up (ex: mesodermal differentiation gene collagen II, endodermal differentiation gene albumin, and ectodermal differentiation gene PTX3)
21
New cards
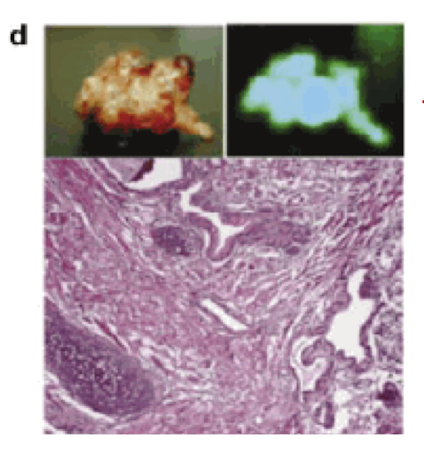
what was an additional piece of evidence for pluripotent in the BMESL cells?
when ES cells are injected into immune-compromised mice, they form teratocarcinomas that express GFP+ activity
22
New cards
what other than GFP+ expression indicated that the BMESL cells injected into immunocompromised mice were pluripotent?
the tumor formed contained a variety of cell types, including chondrocytes, striated muscle cells, and gland-like structures
23
New cards
the presence of these mRNA transcripts indicated that differentiation was taking place in BMESL cells 15 days after removing LIF. Select all that applies!
\
A. actin
B. UTF1
C. Collagen
D. PTX3
E. Oct 3/4
\
A. actin
B. UTF1
C. Collagen
D. PTX3
E. Oct 3/4
C. and D.
24
New cards
how were ES-like pluripotent cells verified ?
via genetic analysis
25
New cards
what technology is used to see the number of DNA copies?
FACS - fluorescence-activated cell sorting
26
New cards
what are ES cells stained with during FACS?
propidium iodide - fluorescent molecule that stains the nuclei by intercalating into the major groove of DNA
27
New cards
how does propidium iodide stan nuclei?
via binding to the major groove of DNA and emitting fluorescence
28
New cards
why is FACS necessary for ES cell analysis?
to determine ploidy, as ES cells are unstable (tend to gain or lose chromosomes)
29
New cards
how will you verify the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells using flow cytometry?
\
A. using propidium iodide
B. using fluorescent labelled pluripotency markers such as Oct3/4 and UTF1
\
A. using propidium iodide
B. using fluorescent labelled pluripotency markers such as Oct3/4 and UTF1
B.
30
New cards
if BMESL cells arose by cell fusion, how many of each chromosome pair do you expect to see?
\
A. 8
B. 6
C. 2
D. 4
\
A. 8
B. 6
C. 2
D. 4
C. 2