ecology sixth lab
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Are ponds freshwater or saltwater? Are they shallow?
small freshwater ecosystems that support diverse communities of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
they are shallow which means sunlight can often reach the bottom, which strongly influences temperature, dissolved oxygen, and the distribution of organisms.
Ponds vs Lakes
Ponds are smaller and usually shallow enough for light to penetrate to the bottom.
What ae 4 Abiotic Factors:
Temperature – Affects oxygen levels and metabolic activity.
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) – Essential for aquatic organisms; higher in cooler water and lower in warm water.
Turbidity – Cloudiness of water, influenced by sediment, algae, and organic matter; higher turbidity leads to lower light penetration.
Nutrients (Nitrogen & Phosphorus) – In lower concentrations, these elements are essential for a healthy ecosystem, but high concentrations can cause algal blooms, lower dissolved oxygen, and increase turbidity.
What are the 4 Zones in Ponds:
Littoral Zone: Near shore, lots of light and plant life.
Photic Zone (Limnetic Zone—> open surface waters away from shore): Depth where light penetrates (~1% of surface light).
Aphotic Zone (Profundal Zone—> deep): Deep area with little/no light.
Benthic Zone: Bottom of the pond.
Stratification
Epilimnion?
Warm surface water.
Stratification
Thermocline?
Rapid temperature change with depth.
Stratification
Hypolimnion?
Cold, nutrient-rich deeper water.
What are the 4 Organisms Found in Ponds?
Phytoplankton: Microscopic algae (primary producers).
Zooplankton: Small animals or protists that consume phytoplankton (e.g., rotifers, copepods, Daphnia).
Macroorganisms: Crayfish, snails, worms, and fish.
Protists: Single-celled eukaryotes with diverse feeding strategies (some photosynthetic, some predatory).
What are 6 Pond equipment tools?
YSI DO/Temp Meter – Measures dissolved oxygen and temperature.
Turbidometer – Measures turbidity (water clarity).
Plankton Net – Used to filter water and collect plankton.
Collection Bottles & Tubes – For storing water samples.
Calorimeter – Used in the lab to test nitrate and phosphate concentrations.
Microscope – For identifying plankton species.
What are 5 Pond Procedures?
Field Measurements: Record turbidity, temperature, and dissolved oxygen in the field.
Water Collection: Collect samples to analyze nitrate and phosphate in the lab.
Plankton Sampling: Use a plankton net to concentrate plankton, then prepare microscope slides.
Microscopy: Identify and quantify plankton species from your sample.
Data Analysis: Calculate Shannon Diversity Index (H′) to quantify biodiversity.
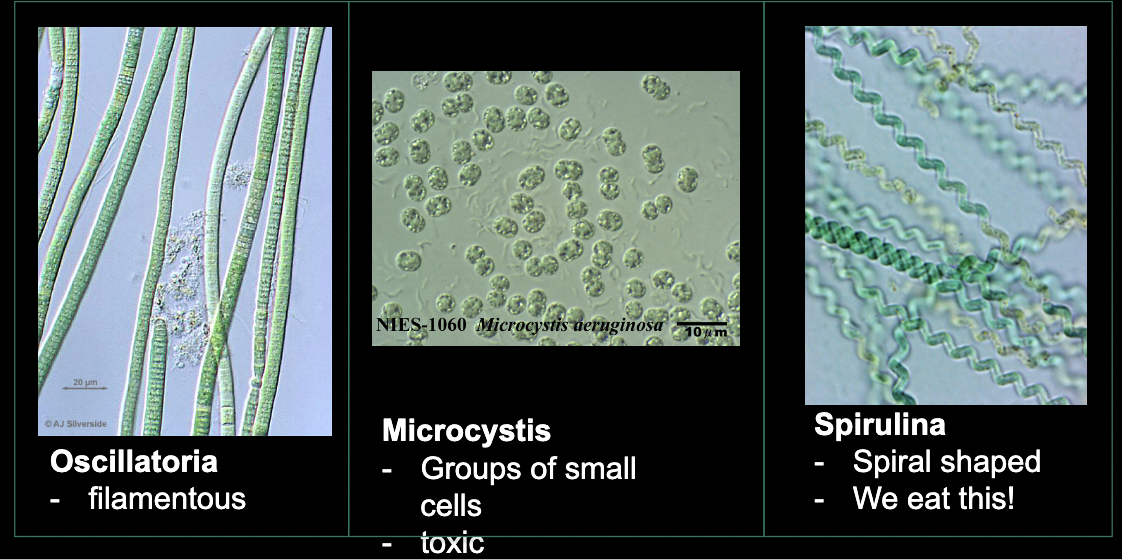
What bacteria is this?
Cyanobacteria
• “blue-green algae”
• origin of oxygen photosynthesis
• ancestor to chloroplasts
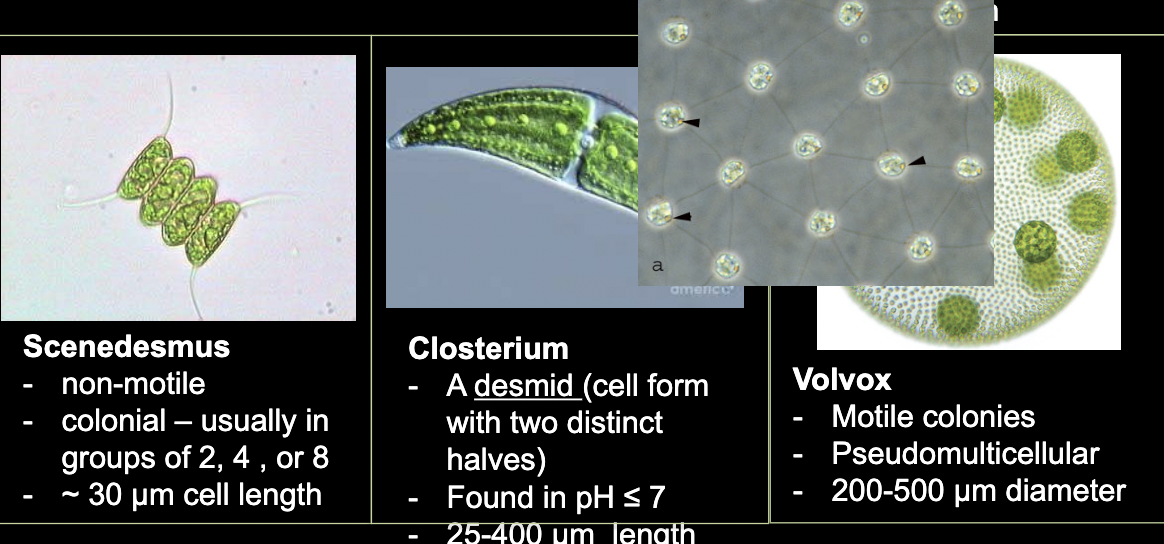
What bacteria is this?
Green Algae
• Filamentous, colonial, unicellular forms
• Green colored photosynthetic pigment
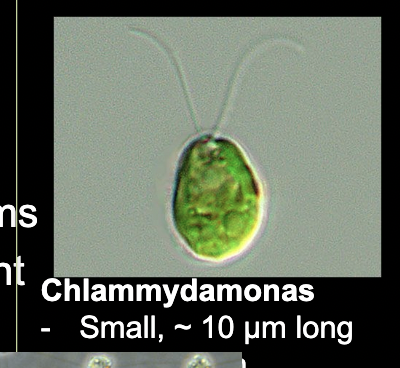
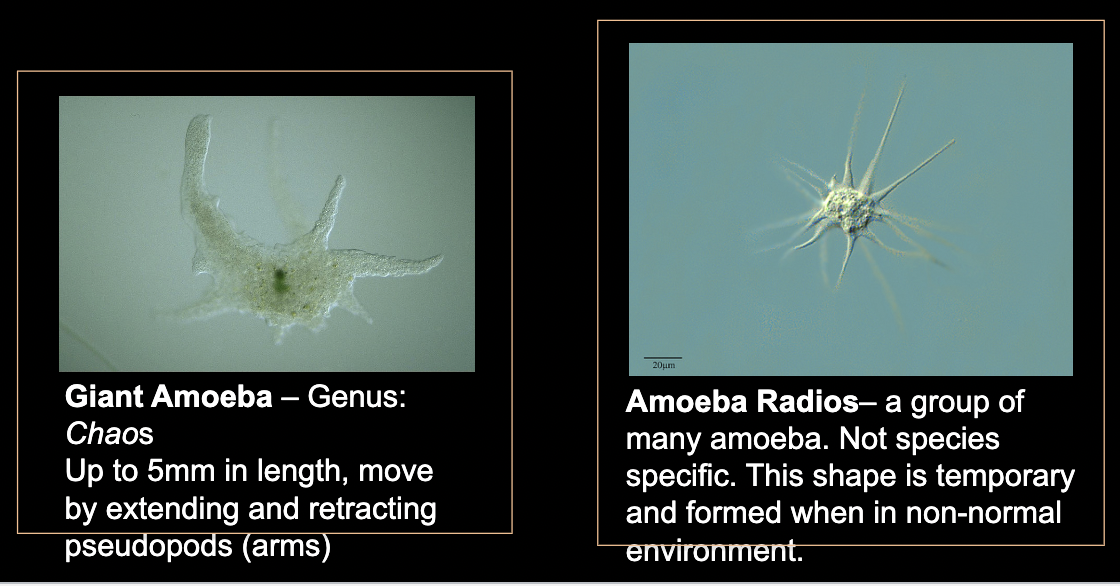
What bacteria is this?
Amoeba
• Amoebas do not form a specific taxonomic group, they are found in many Eukaryotic lineages
• Look for blob-shape or floating pointy blob-shape
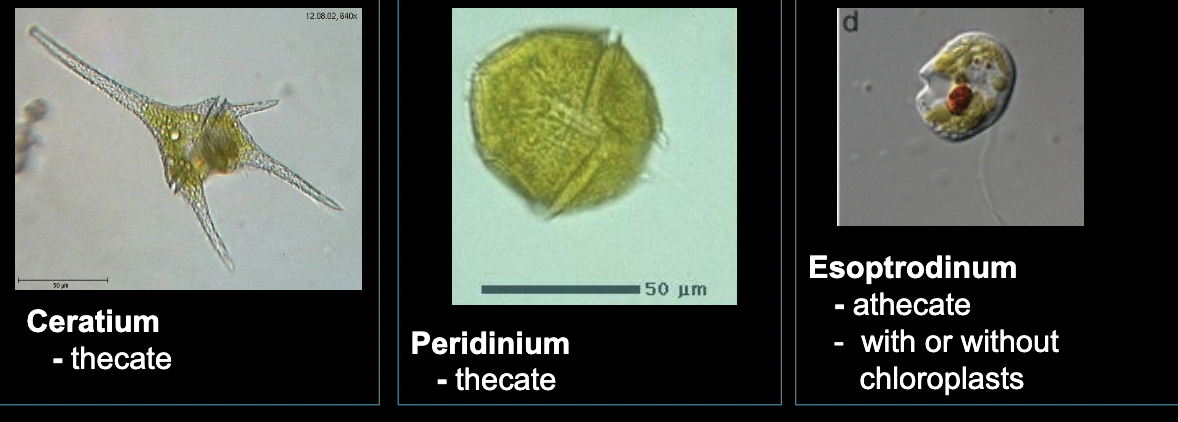
What bacteria is this?
Dinoflagellates
• bi-flagellate, motile
• thecate or athecate
• ½ are photosynthesizes and most are heterotrophic
Envornomental significance: harmful algal blooms (red tide), carbon fixation (top 3 marine carbon fixator), symbiotic relationship with corals (symbiodinium, zooxanthella)
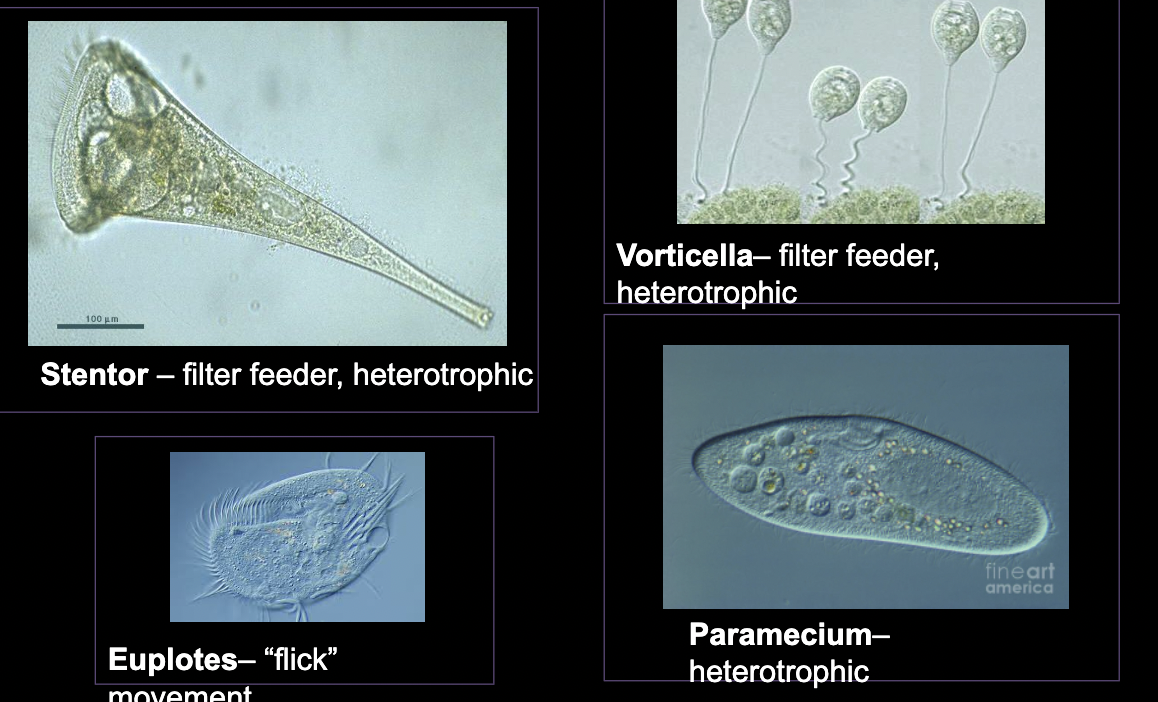
What bacteria is this?
Cilliates
• Motile, unicellular
• Have cilia!
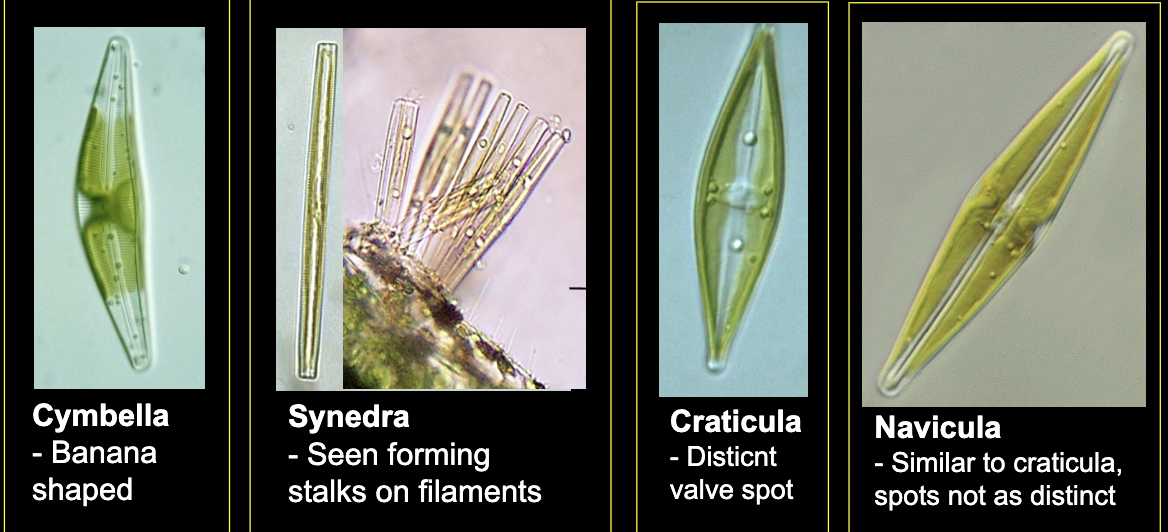
What bacteria is this?
Diatoms
• Silica walls
• Halved cell form, generally symmetrical
• Photosynthesizers (mostly)
• most are motile, little to no personality
• Environmental significance: responsible for majority of carbon fixation in
marine systems
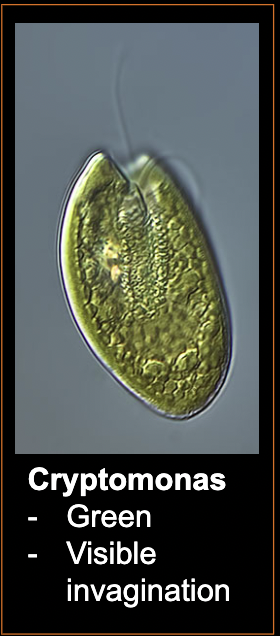
What bacteria is this?
Cryptomonads
• bi-flagellate, asymmetrical, flattened
• Spin along longitudinal axis when swimming
• Photosynthesizers (can thrive in low light)
• Food source (and chloroplast sometimes!) for many dinoflagellates
• 10 -50 μm cell length

What bacteria is this?
Euglenoids
• Generally green photosynthesizers
• distinct red eye spot
• 1-3 flagella
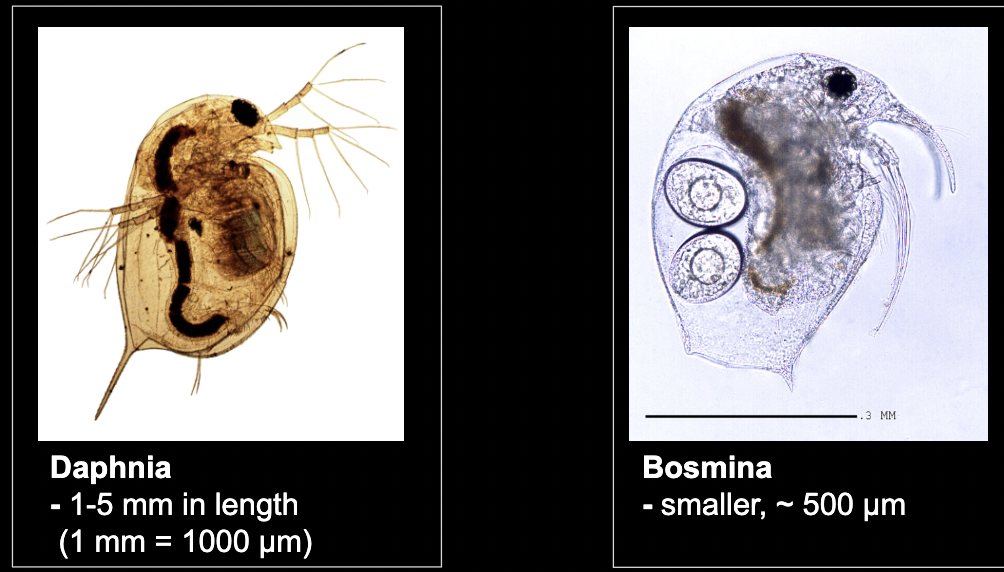
What bacteria is this?
Cladocera
• Crustaceans
• Filter feeders
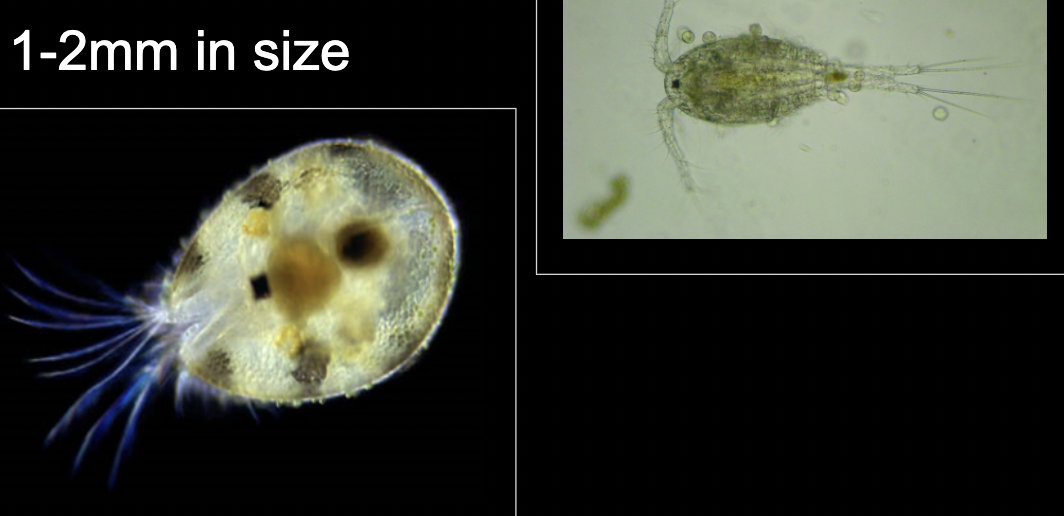
What bacteria is this?
Copepods
• Filter feeders
• Crustaceans
• 1-2mm in size
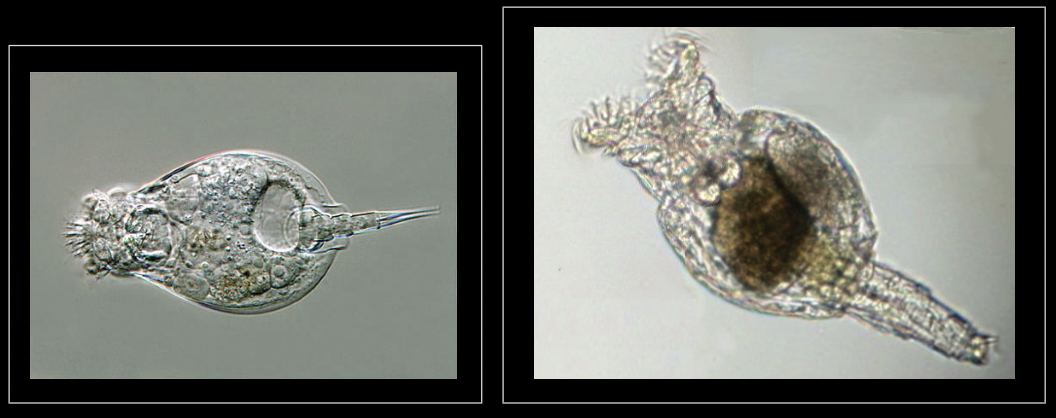
What bacteria is this?
Rotifers
• Major food source in freshwater systems
• instrumental in decomposition & nutrient cycling
• Directly compete with other micro-animals
• 50μm- 2mm siz