PNF for strengthening
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is the motor unit?
Functional unit: single alpha motor neuron and all muscle fibres it innervates. Together they work as a unit to produce muscle contraction
What is Henneman's Principle?
Motor units are recruited from smallest to largest according to force demand; helps minimize fatigue, allows graded force.
Small motor units = Fewer muscle fibres - precise/fine motor control
Large motor units = Many muscle fibres - generates greater force but less precsision
What is Sherrington's Law of Reciprocal Innervation?
When an agonist contracts, the antagonist relaxes, enabling smooth, coordinated movement. Key to PNF facilitation principles
What is the primary aim of PNF?
For strengthening
To stimulate the maximum number of motor units into activity
What are proprioceptors key for in PNF?
The facilitation of muscle contractions
What does exercise at maximal resistance lead to?
Hypertrophy and increased muscle strengthW

What are the basic movement diagonals for the shoulder (beegees)?
Start: Extension/adduction/medial rotation
End: Flexion/abduction/lateral rotation
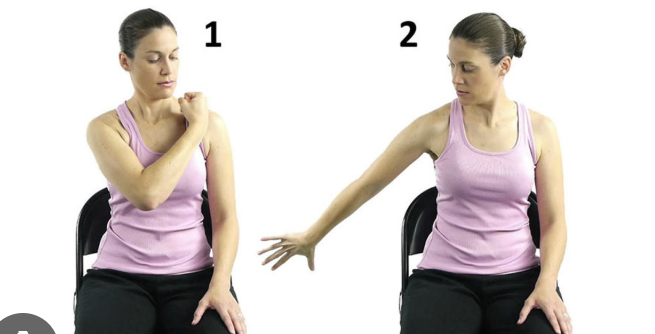
What are the basic movement diagonals for the shoulder (upper cut)?
Start: Flexion/adduction/lateral rotation
End: Extension/abduction/medial rotation
What is cutaneous stimulation?
Stimulation of skin enhances proprioceptive input; encourages optimal motor responses
What is the initial stretch?
Muscle should be fully lengthened at start of PNF; quick stretch activates stretch reflex for increased activity.
What does traction do?
Separates joint surfaces
What does approximation do?
Compresses joint surfaces; maximizes proprioceptive stimulation.
What is maximal resistance?
Use highest resistance maintaining smooth movement through range; matches patient strength, varies with reps and patterns.
Repeated contractions is the basic method
What is Auditory & Visual Stimulus?
Crisp commands and having patient watch movement increase effort and facilitate natural movement
What is Overflow/Irradiation?
Maximal CNS excitation causes stronger muscles to assist weaker ones. The brain recognises groups of muscles working together:
- normal timing can be adjusted to facilitate this (Timing for Emphasis).
What are the PNF Modalities for strengthening?
Repeated Contractions
Slow Reversals: Sherrington’s Reciprocal Innervation
Timing for Emphasis: Irradiation/Overflow.