Chapter 4
1/114
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What are the fundamental units of Life?
Cells
What are cells?
The building Blocks of all organisms
What are cells in single celled organisms?
Everything
What is the multicellular organisms in hierarchy ?
Cells
Tissues
Organ
Organ system
Organism
What are tissues made of?
Interconnected cells with a common function
What are organs made of?
Several tissues
What is a organ system made of?
Organs that work together
What makes up an entire organism?
Multiple organ systems functioning together
How are cells seen?
Through Microscopes
What is Magnification?
The process of enlarging an object in appearance
What is Resolution?
The ability of a microscope to distinguish two adjacent structures as separated; the higher the better clarity
Compound light microscopes
Bends visible light to provide magnification ( transparent objects must be treated with chemical statins to make out the different parts.
Electron Microscope
Uses beams of electrons to achieve a higher magnification and resolution
Transmission electron Microscopes
Shows fine detail within cells (internal)
Scanning Electron Microscopes
Provide 3-D exterior views ( external)
What is the cell theory?
Cells are basic units of life
All living Organisms made of cells
All cells come from preexisting cells
All cells have what four common componets?
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
What are Prokaryotes?
Cells that lack membrane- enclosed internal compartments (e.g. nucleus)
Most prokaryotes’ cell walls have ______
Peptodoglycan
What are believed to be much like the first cells?
Prokaryotes
What organisms are in the Prokaryotes domain?
Archaea and Bacteria
What is the generalized Structure of a prokaryotic cell?
Chromosomal DNA is localized in the Nucleoid
Ribosomes are in the cytoplasm
The cell membrane is surrounded by a cell wall
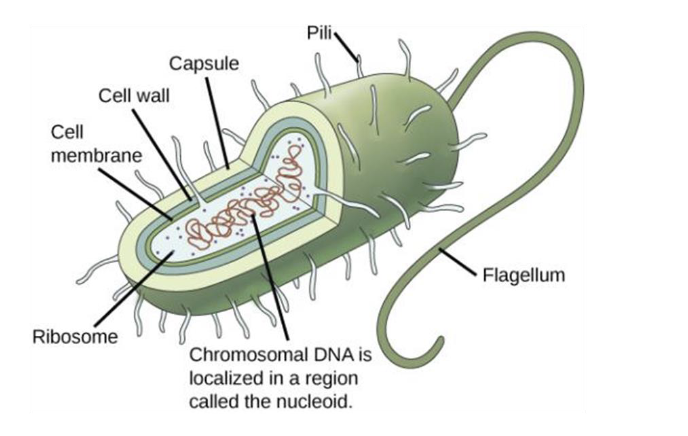
What is this Photo?
Prokaryotic cell
Which are smaller, Prokaryotic cells or Eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells
What are prokaryotic cells small?
The surface area to volume ration is more favorable for moving material in and out of the cell
They lack modifications found in eukaryotes that aid internal transport
What is the Surface area-to-volume ratio?
As cells get bigger, the colume increase faster than surface area
What are eukaryotes?
Cells with membrane bound organelles ( eg Nucleus)
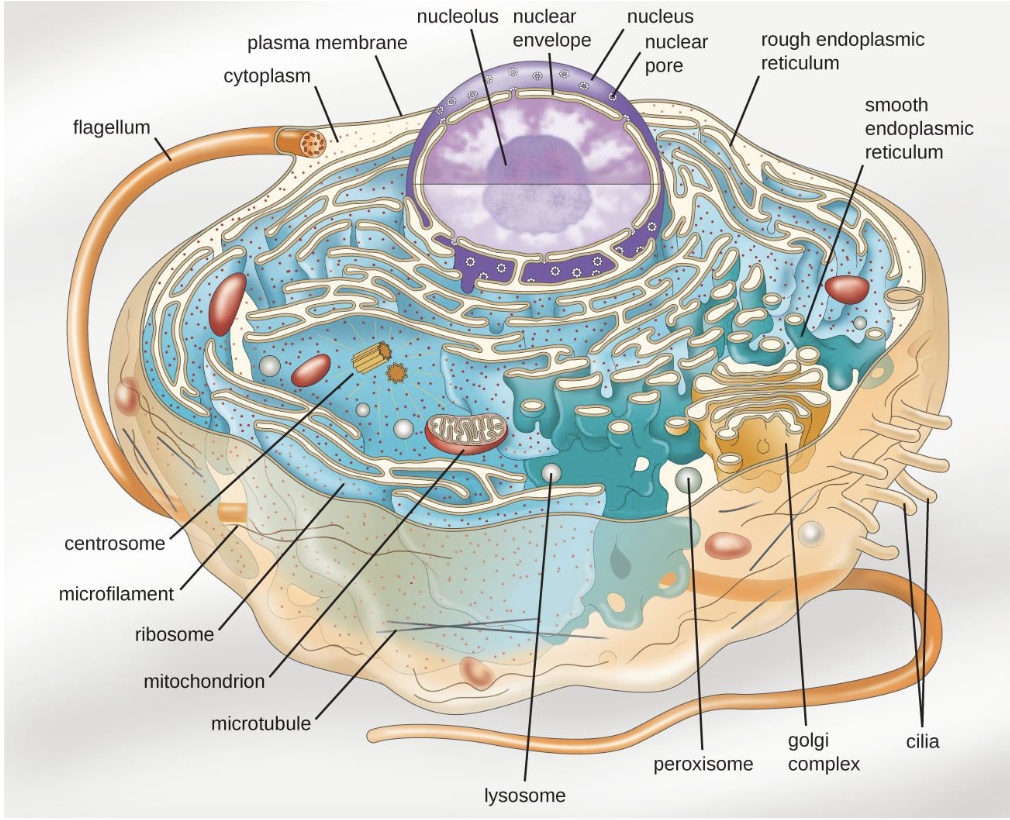
What type of cell is this?
Eukaryote
What is the eukaryotic plasma membrane made out of?
A Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
What is the Cytoplasm?
The region between the plasma membrane and nuclear envelope
What does the cytoplasm consist of?
Organelles suspended in gel-like cytosol plus the cytoskeleton.
What is the Cytoplasm made of?
70-80% water; it is semi-solid due to the proteins in it.
How many Nucleus per cell?
One
What is the largest Organelle? (Hint* it is bigger that most prokaryotic cells)
Nucleus
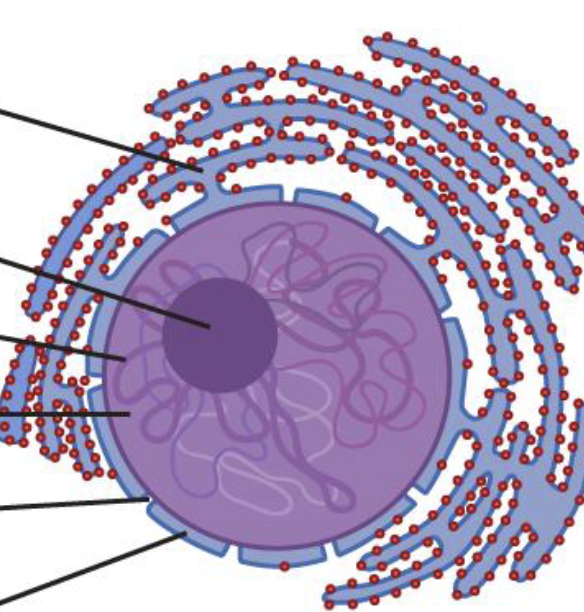
What is this Organelle?
Nucleus
What is the Nuclear Envelope?
A double membrane
What is the nuclear envelope made of?
Two phospholipid bilayers
What does the Nuclear Envelop edo?
Separates DNA from Cytoplasm
Nuclear pores perforate the nuclear envelope. What does it do?
Connect Nucleoplasm to cytoplasm
Regulate flow of molecules back and forth
Large Molecules require nuclear localization signal (NLS) to pass
What does this represent?
The nuclear Envelope
Where is the Nucleolus located?
A region inside the nucleus
What happens in the Nucleolus
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized and ribosome are assembled from rRNA and Proteins
What does Ribosomes consist of?
Two different-sized subunits
Are ribosome bigger in Eukaryotes or Prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes
What are Ribosomes made of?
Special rRNA and Proteins
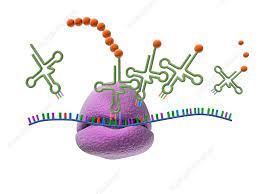
What is this organelle?
Ribosome
During Protein Synthesis, what do Ribosomes do?
They assemble amino acids into proteins
What is the site for conversion of stored energy ( macromolecule molecular bonds) to more useful form ( ATP)
Mitchondrion
What does the Mitochondrion do?
Convert Glucose into Carbon Dioxide and ATP
What does the Mitochindrion look like?
The inner membrane is folded
What are the folds in the mitochondrion called?
Cristae
What is the enclosed area in the mitochondrion?
The Mitochondrial Matrix
Both Plants and Animals cells have microtubule organizing centers (MTOC). T or F
T; Although animal class also have centrioles associated with the MTOC
Plant cells have a centrosome and lysosomes. T or F
F; Only Animal cells have centrosomes and lysosomes
Animal cells have a cell wall, chloroplast, and other specialized plastid and a large central Vacuole. T or F
F; Plants cells have all them things, not Animal cells
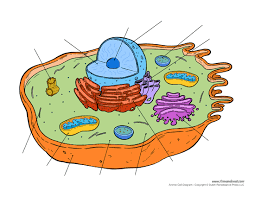
What type of cell is this?
Animal
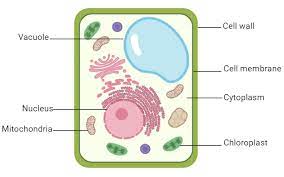
What type of cell is this?
Plant
What do Centrosomes consist of?
Two Centrioles that lie at right angles to each other
What is centriole cylinder made up of?
Nine triplets of microtubules
What holds the microtubule triplets together?
Non-tubulin proteins

What is this?
Centrosome
What are Plant Cell Walls?
a rigid protective structure external to the plasma membrane
How do plant cell walls differ from prokaryotes?
They are made up of cellulose rather than peptidoglycan.
What are chloroplasts?
Double-membrane organelles; they have their own ribosomee and DNA like mitochondria
What does the chloroplast inner membrane enclose?
An aqueous fluid ( Stroma); it contains a set of interconnected and stacked fluid-filled membrane sacs.
What are thylakoids?
Interconnected and stacked fluid-filled membrane sacs in the chloroplasts
What is a stack of Thylakoids called?
a Granum ( plural= grana)

What is this?
A chloroplast
What does the central Vacuole do?
Helps regulate water concentrations under changing environmental conditions, and contributes to cell expansion.
What does the Central Vacuole look like in a plant cell?
It is large and occupies most of the area in the cell.
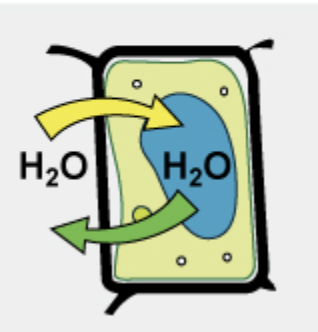
What condition is this?
Isotonic Condition
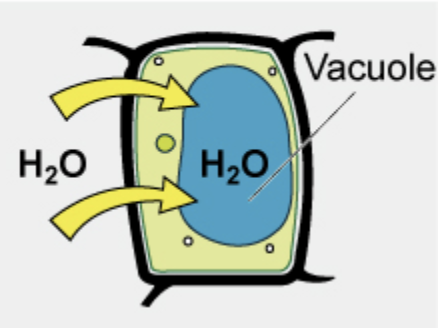
What condition is this?
Hypotonic Condition
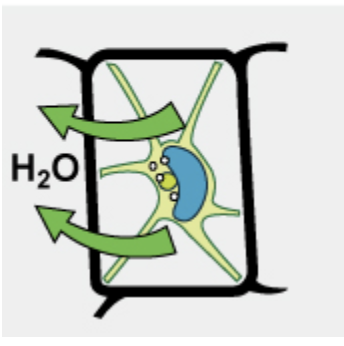
What condition is this?
Hypertonic Condition
What organelles are hypothesized to have originated as independent prokaryotic organisms?
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
What becomes endosymbionts of the prokaryotic ancestors of the eukaryotes?
Chloroplast and mitochondria
What organelles have their own DNA and Ribosomes?
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
What does the endomembrane system consist of?
internal membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
What organelles are included in the endomembrane system?
Nuclear Envelope, Lysosomes, and vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi Apparatus plus the plasma membrane.
What type of cells contsin lysosomes?
Animal Cells
What does lysosomes contain?
Digestive Enzymes
What do lysosomes do?
Break down large biomolecules and even worn-out organelles.
What does Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) look like?
Interconnected membranoues sacs and tubules
What does the ER do?
Modifies Proteins and Synthesizes lipids
What is the hollow portion of the ER tubules called?
Lumen or cisternal space
What is continuous with the nuclear envelope?
The membrane of the ER
Why is it called the rough ER
Because Ribosomes are attached
What do the ribosomes on the rough ER do?
They manufacture proteins
How and where are new proteins modified?
In the lumen of the RER and by folding or the acquisition of side chains
What happens to proteins after they are modified?
They are either incorporated into cellular membrane or secreted from the cell ( protein hormones, enzymes, etc)
Other than modifying proteins, what is something else that the RER do?
Makes phospholipids for cellular membranes.
If phospholipids or modified proteins are not destined to stay in the RER, what happens to them?
They reach their destinations via transport vesicles theh bud from the RER’s membrane.
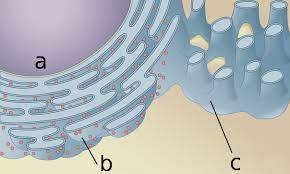
What is this Organelle (b)?
Rough ER
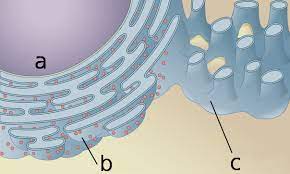
What is this organelle (C)?
Smooth ER
Is the SER continuous or noncontinuous with the RER?
Continuous
How is the Smooth ER different from the Rough ER?
It has few to none ribosomes
What does the SER sythesis
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Steroid Hormones
What are some other functions rather that synthesis of the SER?
Detoxification of medications and poisons
Storage of Ca^++
What is Sarcoplasmic reticulum and what does it do?
It is a specialized SER that stores Ca^++ needed for contractions of the muscle cells.

What is this Organelle?
Golgi Apparatus
What is the Golgi Apparatus made of?
A series of flatten membranes