Embryology and Neuroanatomy Overview
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
CNS (central) structures
Brain
Spinal cord
PNS (peripheral) structures
Cranial nerves
Spinal nerves
ANS (autonomic)
Embryologic germ layers
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
CNS derived from which germ layer
Ectoderm
Neural plate/tube development
Neural plate folds to form neural tube
Rostral (cephalic) tube forms brain
Caudal tube forms spinal cord
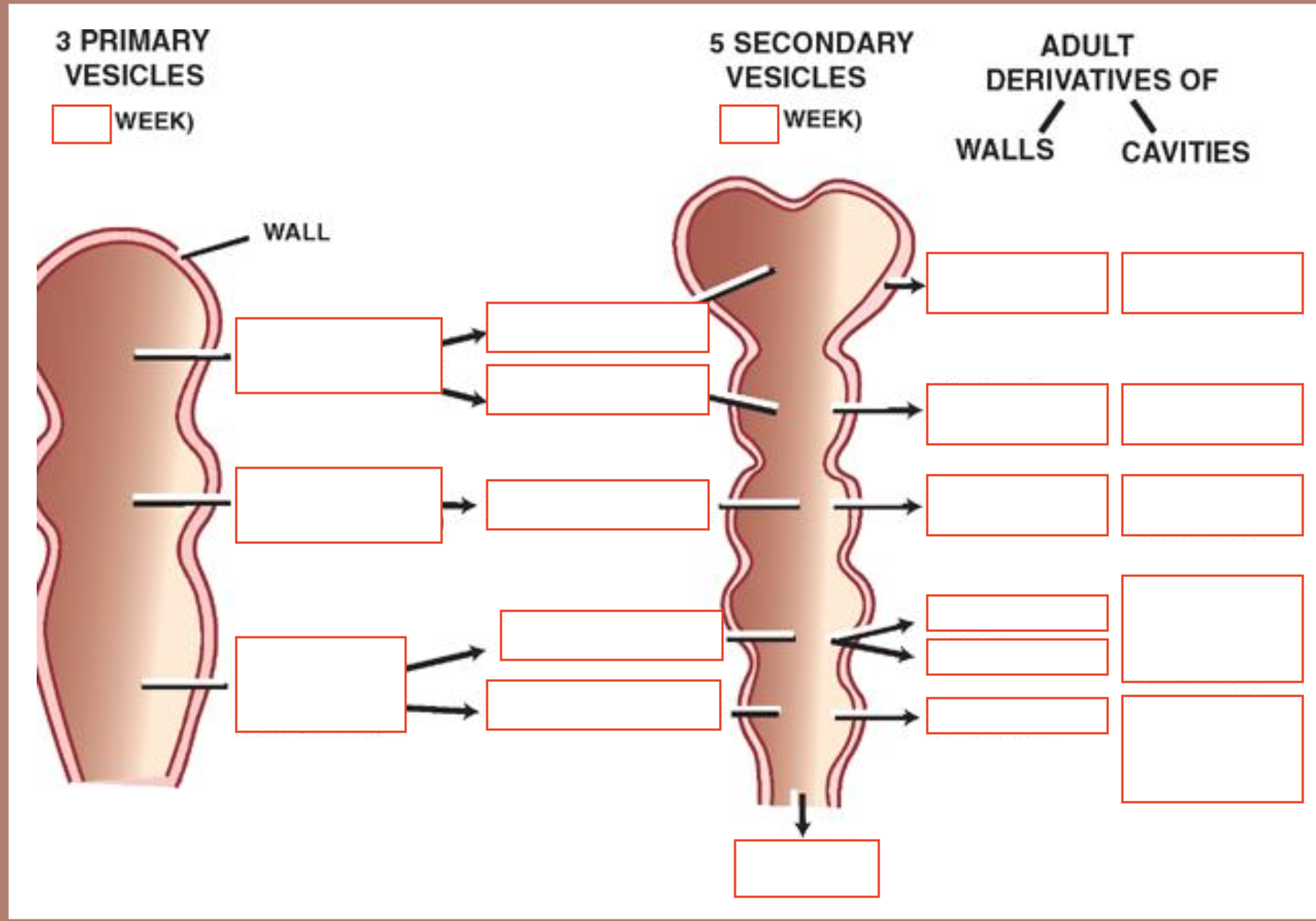
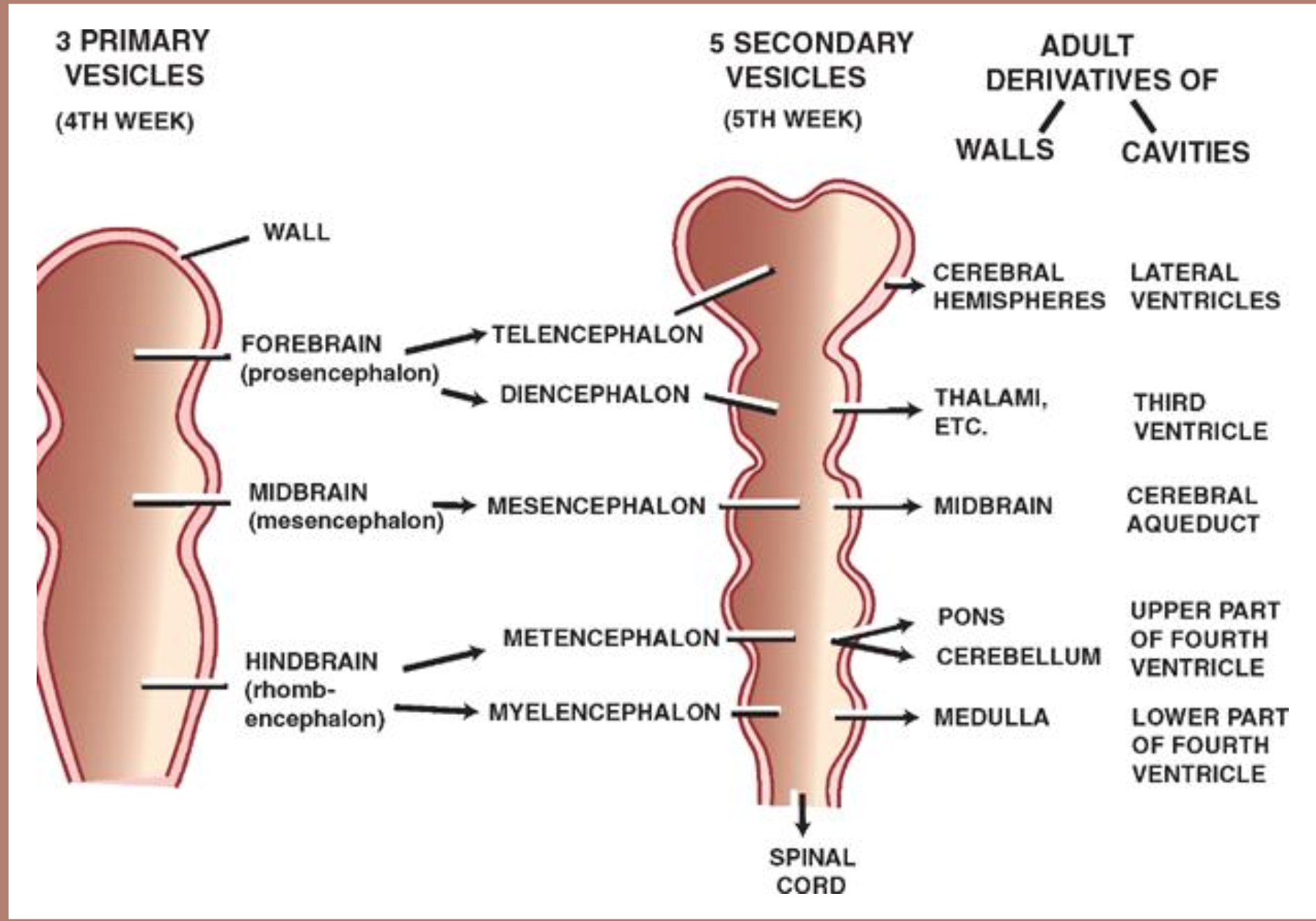
Ventricular system arises from neural tube lumen
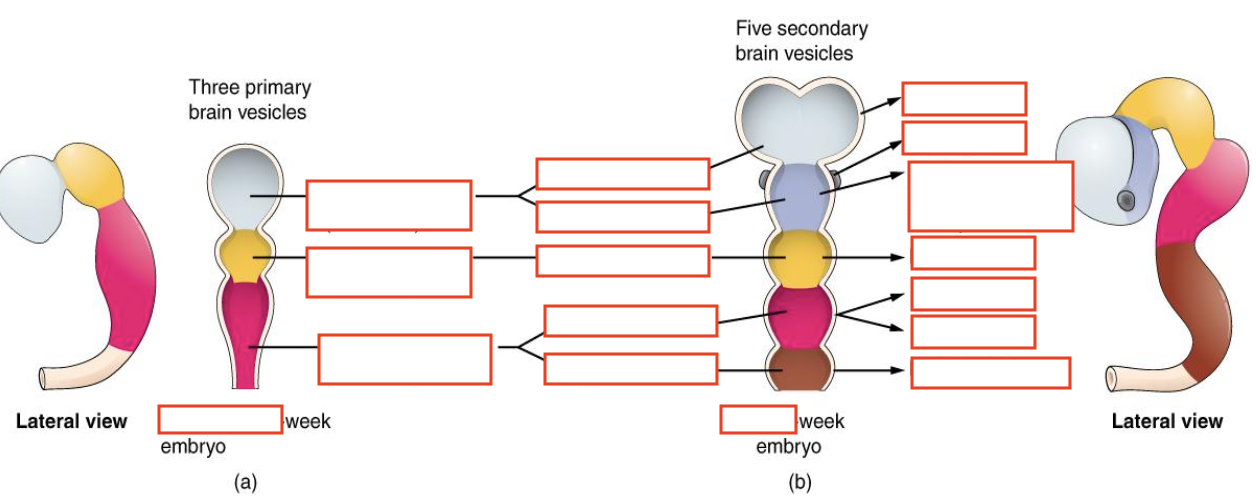
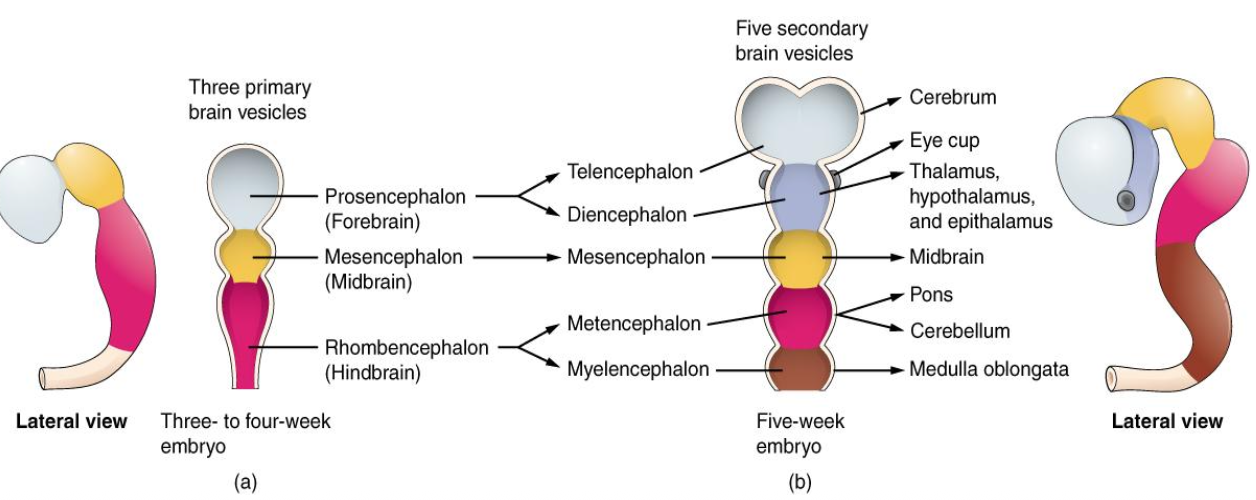
Primary brain vesicles
PMR
Prosencephalon - forebrain
Mesencephalon - midbrain
Rhombencephalon - hindbrain
Prosencephalon secondary brain vesicles
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Prosencephalon structures
Cerebral hemispheres - telencephalon
Basal ganglia
Thalami - diencephalon
Limbic system
Prosencephalon functions
Motor planning and voluntary movement
Cognition, attention, memory
Behavior and executive function
Prosencephalon disorders
Cerebral palsy (cortical involvement)
Cognitive and perceptual impairments
Prosencephalon disorder implications
Impaired motor learning and task sequencing
Altered postural control due to cortical processing deficits
Need for task-specific, repetition-based neuroplastic interventions
Mesencephalon secondary brain vesicles
Mesencephalon
Mesencephalon structures
Midbrain
Superior and inferior colliculi
Cerebral peduncles
Red nucleus
Substantia nigra
Mesencephalon functions
Postural reflexes
Visual and auditory integration
Motor control and tone regulation
Mesencephalon disorders
Abnormal muscle tone
Impaired righting reactions
Gait and balance dysfunction
Mesencephalon disorder implications
Postural alignment
Balance training
Sensory integration strategies
Rhombencephalon secondary brain vesicles
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Rhombencephalon structures
Pons - metencephalon
Cerebellum - metencephalon
Medulla oblongata - myelencephalon
Rhombencephalon functions
Coordination and motor timing (cerebellum)
Autonomic and vital functions (medulla)
Cranial nerve nuclei (pons and medulla)
Rhombencephalon disorders
Ataxia
Dysmetria - poor distance, speed, power judgement
Poor motor coordination
Abnormal breathing patterns or endurance limitations
Rhombencephalon disorder implications
Gait training
Coordination exercises
Vestibular and balance rehabilitation
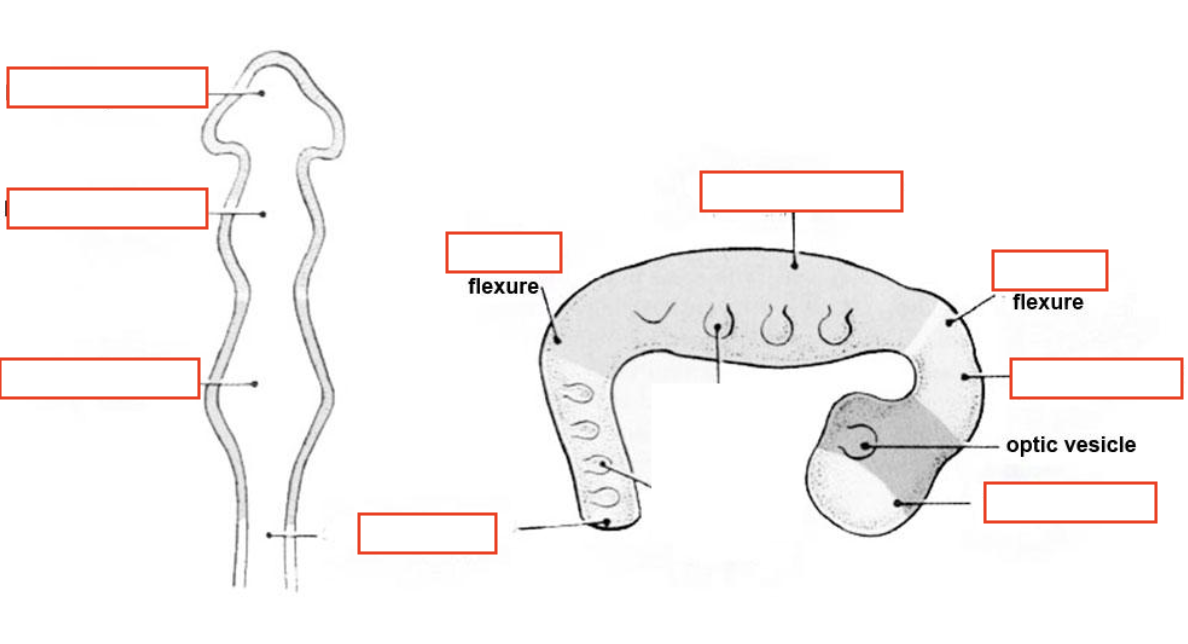
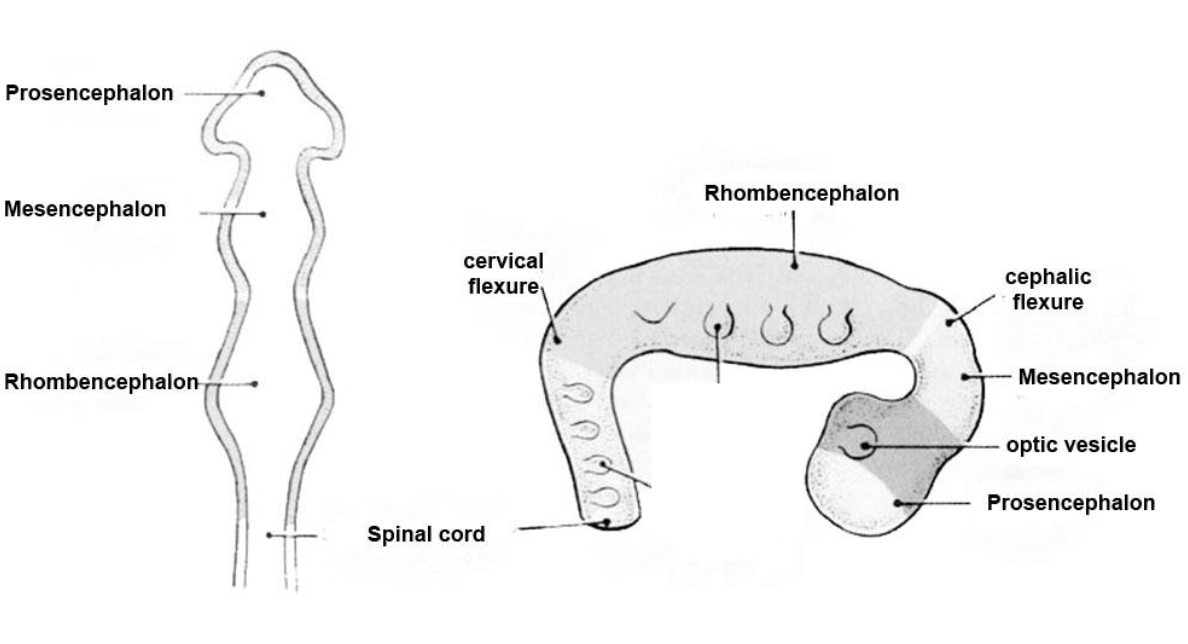
Importance of cervical flexure
Establishes brain–spinal cord orientation - vertical alignment of CNS
Separates brainstem from spinal cord - anatomically defines medulla oblongata (above) and cervical spinal cord (below)
Supports brainstem organization - cranial nerve and motor/sensory tract positioning
Foundation for adult neuroanatomy - vertical alignment of CNS, motor/sensory tract organization
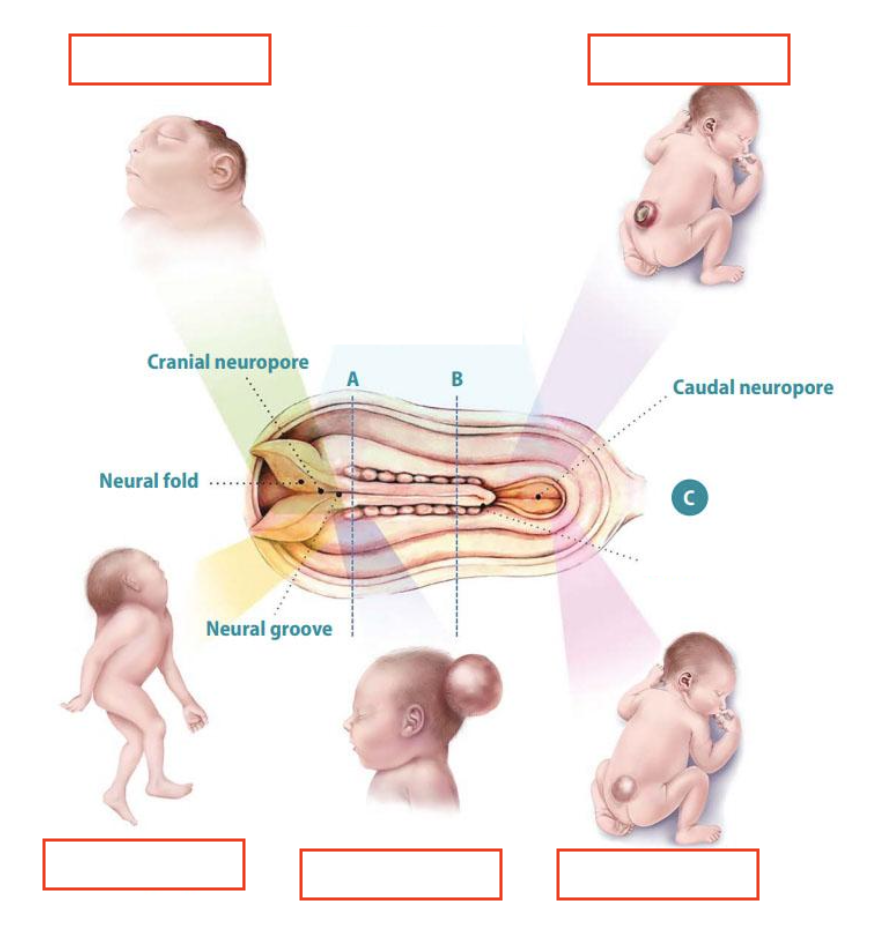
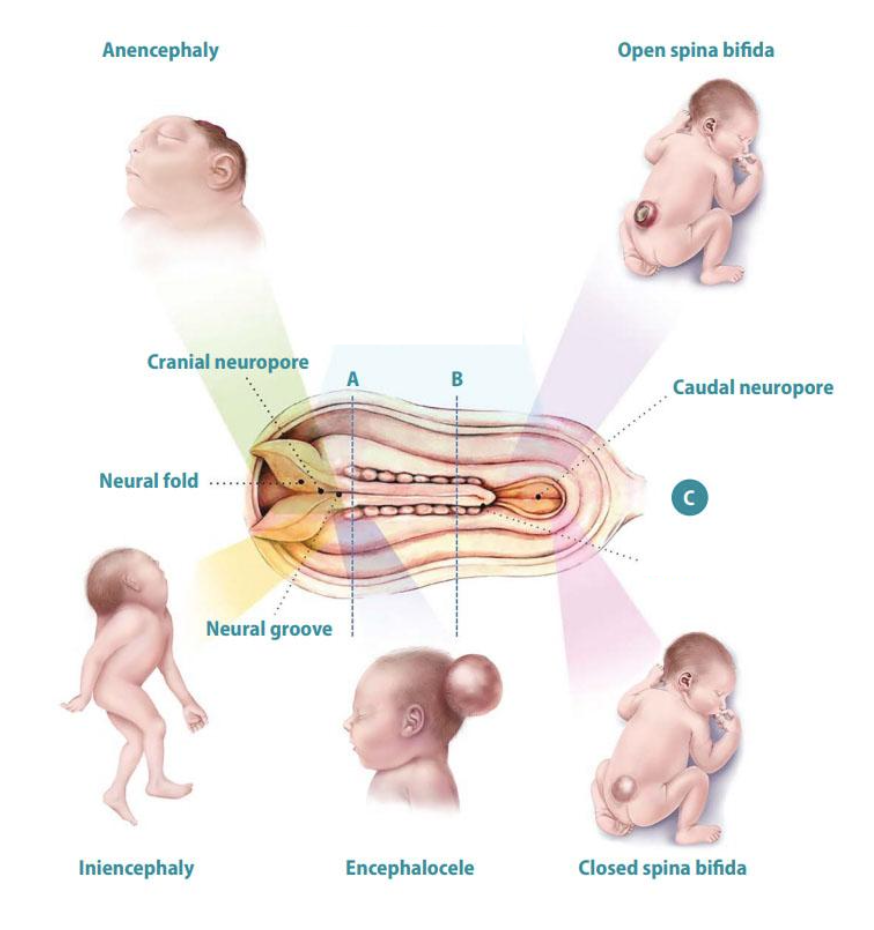
Neural tube defects
Anencephaly
Iniencephaly
Encephalocele
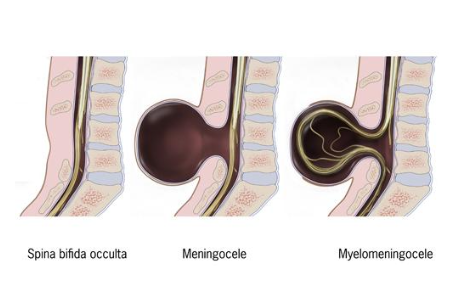
Spina bifida
Anencephaly
Normal event: Closure of the anterior neuropore
Timing: Week 4 (days 23–26) of gestation
Failure leads to: Absence of forebrain (prosencephalon) → no cerebral hemispheres
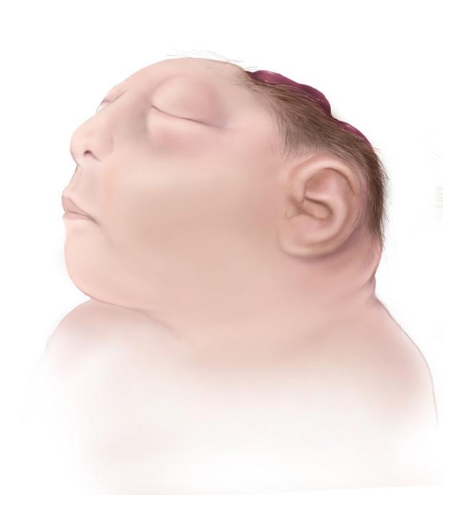
Iniencephaly
Failure of normal closure and segmentation of:
Upper neural tube
Cervical vertebrae
Occurs during weeks 3–4 of gestation
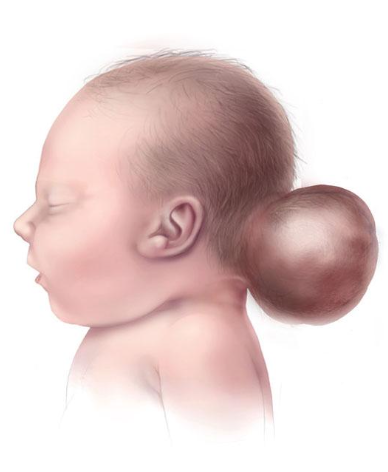
Encephalocele
Primary error: Failure of cranial neural tube closure and mesodermal skull formation
Timing: Weeks 3–4 of gestation
Result: Persistent cranial defect → protrusion of intracranial contents
Spina bifida
Normal event: Closure of the posterior neuropore
Timing: Week 4 of gestation (≈ day 26–28)
Failure leads to: Persistent opening in vertebral arches ± neural tissue exposure
Neuron function/components
Primary signaling units of nervous system (electrical and chemical signals)
Components: Cell body, dendrites (input), axon (output)
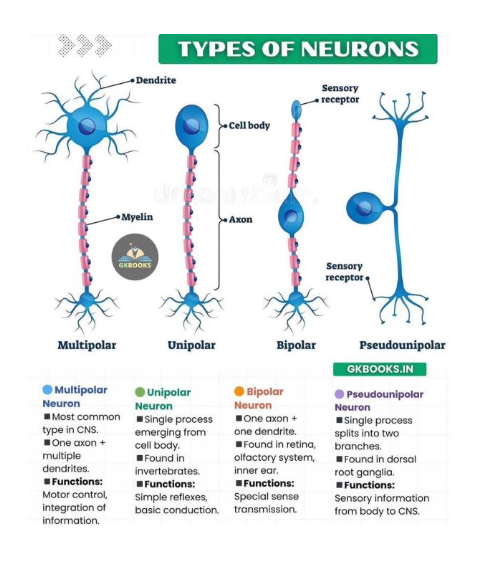
Types of neurons
Multipolar (most common)
Bipolar (vision, olfaction)
Pseudounipolar (dorsal root ganglia)
Unipolar (mostly invertebrates)
Key neurotransmitters
• Glutamate: primary excitatory CNS neurotransmitter
• GABA: primary inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter
• Acetylcholine: NMJ and autonomic nervous system
• Dopamine: motor control and reward
• Norepinephrine: arousal and autonomic regulation
Neuromodulation
How the nervous system forms, differentiates, and organizes
PT considerations for neuromuscular development
Lower extremity weakness or paralysis is level-dependent
Delayed or absent motor milestones are common
Abnormal muscle tone and impaired coordination
Early physical therapy improves functional outcomes
PT considerations for orthopedic and skin management
High risk for hip dislocation, scoliosis, and foot deformities
Impaired sensation increases risk of pressure injuries
Orthotic management is frequently required
Education on positioning and skin inspection is essential
Infant and early childhood interventions
Positioning to protect surgical site
Promote head/trunk control
Prevent contractures
Family education (handling, skin care)
Childhood and adolescence interventions
Strengthening available musculature
Orthotics (AFOs, KAFOs, RGOs)
Gait training (assistive devices)
Wheelchair mobility if needed
Scoliosis and hip surveillance
Adulthood interventions
Energy-efficient mobility
Pain management
Skin integrity and pressure relief
Community participation and fitness